无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (4): 387-394.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210354
收稿日期:2021-06-04
修回日期:2021-08-17
出版日期:2022-04-20
网络出版日期:2021-08-20
通讯作者:
赵静, 副研究员. E-mail: zhaojingmem@njtech.edu.cn作者简介:董淑蕊(1998-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: dsr@njtech.edu.cn
基金资助:
DONG Shurui( ), ZHAO Di, ZHAO Jing(
), ZHAO Di, ZHAO Jing( ), JIN Wanqin
), JIN Wanqin
Received:2021-06-04
Revised:2021-08-17
Published:2022-04-20
Online:2021-08-20
Contact:
ZHAO Jing, associate professor. E-mail: zhaojingmem@njtech.edu.cnAbout author:DONG Shurui (1988-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: dsr@njtech.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
在氧化石墨烯(GO)膜通道内引入离子化基团, 可通过静电作用吸附更多的水分子, 有望实现更高效的水分子渗透。研究采用真空抽滤方法将离子化的碱性氨基酸赖氨酸(Lys)引入GO膜内, 通过共价交联制备出 Lys(Na+)-GO复合膜。赖氨酸分子两端的氨基与GO可交联形成C-N共价键, 从而对膜结构进行调控使其更加规整有序, 并将离子化羧酸根引入氧化石墨烯通道中。相比于未离子化的赖氨酸, 离子化的赖氨酸中荷负电的羧酸根通过静电作用提高了与水分子的作用力, 增强了膜的亲水性。通过物理结构和化学结构调控的协同作用, 面向不同的水/醇分离体系, Lys(Na+)-GO复合膜的渗透通量和分离因子得到同时提升。在40 ℃下, 对质量分数90%的乙醇/水、正丁醇/水以及异丙醇/水体系进行渗透汽化测试, Lys(Na+)(10)-GO膜(抽滤溶液中Lys(Na+)与GO的质量比为10)的渗透通量分别达到882、2461和1127 g/(m2·h), 渗透侧水的质量分数分别达到95.38%、99.11%和99.42%。
中图分类号:
董淑蕊, 赵笛, 赵静, 金万勤. 离子化氨基酸对氧化石墨烯膜渗透汽化过程中水选择性渗透的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 387-394.
DONG Shurui, ZHAO Di, ZHAO Jing, JIN Wanqin. Effect of Ionized Amino Acid on the Water-selective Permeation through Graphene Oxide Membrane in Pervaporation Process[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 387-394.
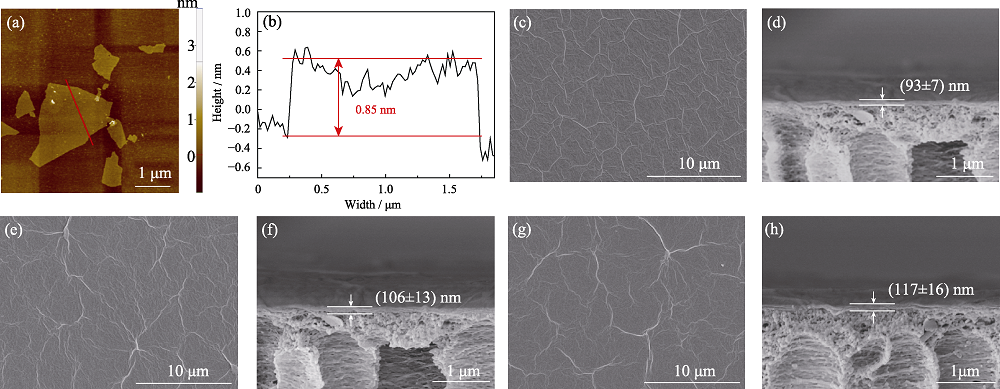
图2 GO纳米片的AFM照片(a)和高度轮廓(b); (c, d)GO纯膜, (e, f) Lys (10)-GO和(g, h) Lys(Na+)(10)-GO膜的表面和横截面的FESEM照片
Fig. 2 (a) AFM image and (b) height profile of GO nanosheet, and FESEM images of the surface and cross-section of (c, d) pristine GO, (e, f) Lys(10)-GO, and (g, h) Lys(Na+)(10)-GO membranes
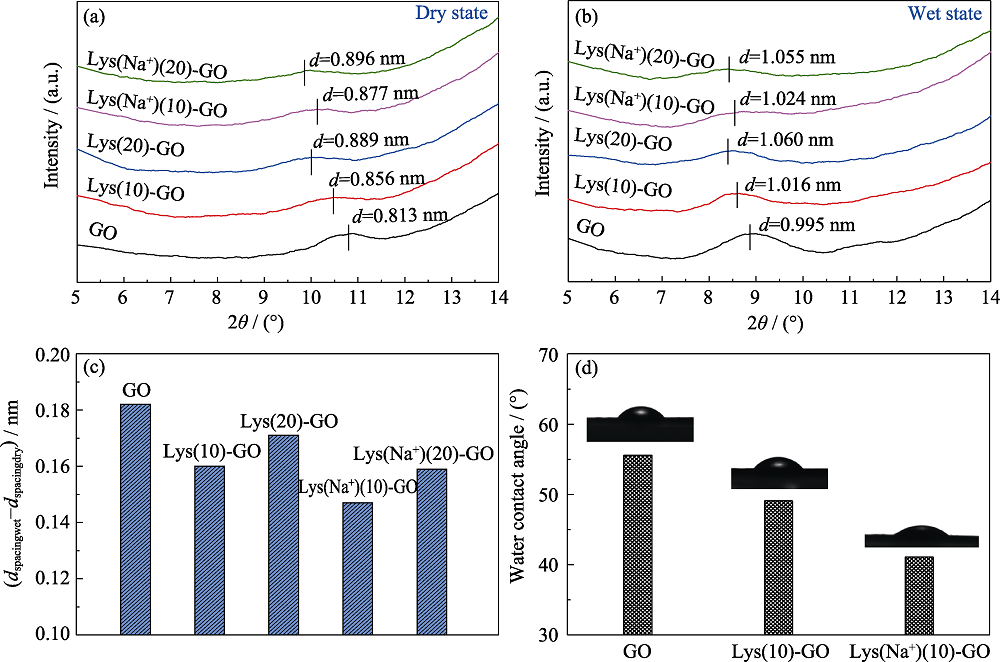
图4 (a)干燥状态和(b)湿润状态的GO、Lys(10)-GO和Lys(Na+)(10)-GO膜的XRD图谱; (c)不同膜在干态和湿态下的层间距差异; (d)GO纯膜, Lys(10)-GO和Lys(Na+)(10)-GO膜与水的接触角
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of GO, Lys(10)-GO and Lys(Na+)(10)-GO membranes in (a) dry state and (b) wet state, (c) differences in the interlayer spacing of different films in dry and wet states and (d) water contact angle of pristine GO, Lys(10)-GO and Lys(Na+)(10)-GO membranes
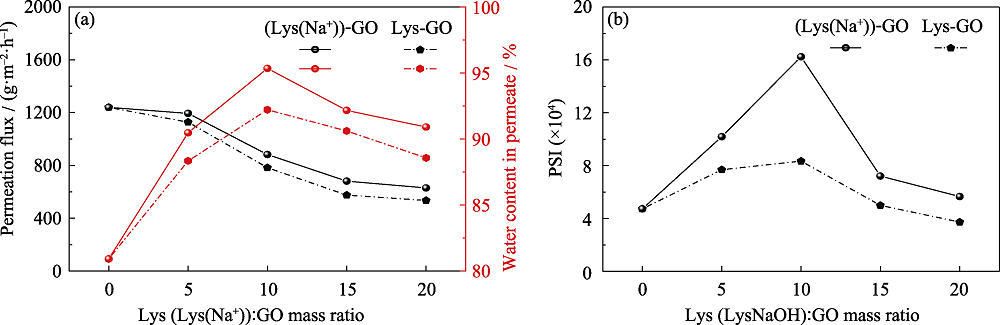
图5 具有不同Lys(Lys(Na+)):GO质量比的复合膜的(a)渗透通量、分离因子和(b)PSI
Fig. 5 (a) Permeation flux, separation factor and (b) PSI of composite membranes with different mass ratios of Lys(Lys(Na+)) to GO
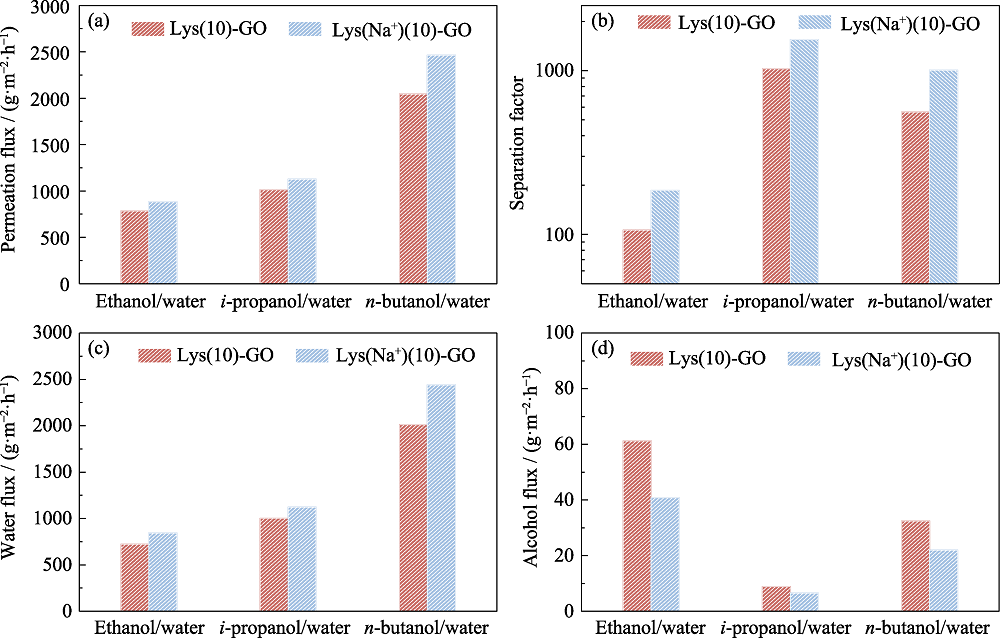
图6 Lys(10)-GO和Lys(Na+)(10)-GO膜分离不同水/醇混合物的分离性能
Fig. 6 Separation performance of Lys(10)-GO and Lys(Na+)(10)-GO membranes for separating different water/alcohol mixtures (a) Permeation flux; (b) Separation factor; (c) Water flux; (d) Alcohol flux
| Membrane | Feed solution | Temperature/℃ | Permeation flux/(g·m-2·h-1) | Separation factor | PSI (×105) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lys(Na+)(10)-GO | 90% n-butanol | 40 | 2461 | 1005 | 24.7 | This work |
| 1%IL-GO-PEBA | 98% n-butanol | 35 | 478.3 | 26.7 | 0.12 | [ |
| GO-PMDTT | 85% n-butanol | 40 | 973 | 99 | 0.95 | [ |
| PDMS-PhTMS/PVDF | 85% n-butanol | 60 | 850 | 1174 | 9.97 | [ |
| ZIF-8@PPy30/PDMS | 95% n-butanol | 40 | 564.8 | 70.2 | 0.39 | [ |
| Lys(Na+)-GO | 90% i-propanol | 40 | 1127 | 1543 | 17.4 | This work |
| GO-GTA | 85% i-propanol | 40 | 700 | 1800 | 12.6 | [ |
| PC-0 | 88% i-propanol | 40 | 844 | 711 | 5.99 | [ |
| PVA-b-NaY | 90% i-propanol | 35 | 5.12 | 2690 | 0.14 | [ |
| Lys(Na+)-GO | 90% ethanol | 40 | 882 | 186 | 1.63 | This work |
| ZIF-8@GO | 95% ethanol | 40 | 443.8 | 22.2 | 0.09 | [ |
| PVA- GO | 90% ethanol | 40 | 137 | 263 | 0.36 | [ |
| PEGDA-GO | 90% ethanol | 40 | 700 | 70 | 0.48 | [ |
| CaGO | 90% ethanol | 40 | 430 | 141 | 0.6 | [ |
| GO/ceramic | 90% ethanol | 40 | 430 | 335 | 1.43 | [ |
| AZIF-8@PDMS-7 MMM | 95% ethanol | 40 | 585.6 | 17.7 | 0.10 | [ |
表1 用于水/醇混合物渗透汽化脱水膜的性能总结
Table 1 Summary of the performance of membranes for pervaporation dehydration of water/alcohol mixtures
| Membrane | Feed solution | Temperature/℃ | Permeation flux/(g·m-2·h-1) | Separation factor | PSI (×105) | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Lys(Na+)(10)-GO | 90% n-butanol | 40 | 2461 | 1005 | 24.7 | This work |
| 1%IL-GO-PEBA | 98% n-butanol | 35 | 478.3 | 26.7 | 0.12 | [ |
| GO-PMDTT | 85% n-butanol | 40 | 973 | 99 | 0.95 | [ |
| PDMS-PhTMS/PVDF | 85% n-butanol | 60 | 850 | 1174 | 9.97 | [ |
| ZIF-8@PPy30/PDMS | 95% n-butanol | 40 | 564.8 | 70.2 | 0.39 | [ |
| Lys(Na+)-GO | 90% i-propanol | 40 | 1127 | 1543 | 17.4 | This work |
| GO-GTA | 85% i-propanol | 40 | 700 | 1800 | 12.6 | [ |
| PC-0 | 88% i-propanol | 40 | 844 | 711 | 5.99 | [ |
| PVA-b-NaY | 90% i-propanol | 35 | 5.12 | 2690 | 0.14 | [ |
| Lys(Na+)-GO | 90% ethanol | 40 | 882 | 186 | 1.63 | This work |
| ZIF-8@GO | 95% ethanol | 40 | 443.8 | 22.2 | 0.09 | [ |
| PVA- GO | 90% ethanol | 40 | 137 | 263 | 0.36 | [ |
| PEGDA-GO | 90% ethanol | 40 | 700 | 70 | 0.48 | [ |
| CaGO | 90% ethanol | 40 | 430 | 141 | 0.6 | [ |
| GO/ceramic | 90% ethanol | 40 | 430 | 335 | 1.43 | [ |
| AZIF-8@PDMS-7 MMM | 95% ethanol | 40 | 585.6 | 17.7 | 0.10 | [ |
| [1] |
ZHAO J, HE G W, LIU G H, et al. Manipulation of interactions at membrane interfaces for energy and environmental applications. Progress in Polymer Science, 2018, 80: 125-152.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
HUA D, CHUNG T S, SHI G M, FANG C. Teflon AF2400/Ultem composite hollow fiber membranes for alcohol dehydration by high-temperature vapor permeation. AIChE Journal, 2016, 62(5): 1747-1757.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
PRIHATININGTYAS I, BRUGGEN B V D. Nanocomposite pervaporation membrane for desalination. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2020, 164: 147-161.
DOI URL |
| [4] | LIANG F, LIU Q, ZHAO J, et al. Ultrafast water-selective permeation through graphene oxide membrane with water transport promoters. AIChE Journal, 2020, 66(2):e16812. |
| [5] |
DAI L, XU F, HUANG K, et al. Ultrafast water transport in two-dimensional channels enabled by spherical polyelectrolyte brushes with controllable flexibility. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2021, 60(36): 19933-19941.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
NAIR R R, WU H A, JAYARAM P N, et al. Unimpeded permeation of water through helium-leak-tight graphene-based membranes. Science, 2012, 335(6067): 442-444.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
WANG M, PAN F, YANG L, et al. Graphene oxide quantum dots incorporated nanocomposite membranes with high water flux for pervaporative dehydration. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 563: 903-913.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
SONG Y, LI R, PAN F, et al. Ultrapermeable graphene oxide membranes with tunable interlayer distances via vein-likesupramolecular dendrimers. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2019, 7(31): 18642-18652.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
DREYER D R, PARK S, BIELAWSKI C W, et al. The chemistry of graphene oxide. Chemical Society Reviews, 2010, 39(1): 228-240.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LIU L, MA Q, CAO J, et al. Recent progress of graphene oxide-based multifunctional nanomaterials for cancer treatment. Cancer Nano, 2021, 12: 18.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
SUN P, ZHU M, WANG K, et al. Selective ion penetration of graphene oxide membranes. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(1): 428-437.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
CHOWDHURY I, MANSUKHANI N D, GUINEY L M, et al. Aggregation and stability of reduced graphene oxide: complex roles of divalent cations, pH, and natural organic matter. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015, 49(18): 10886-10893.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
SUN P, ZHENG F, ZHU M, et al. Selective trans-membrane transport of alkali and alkaline earth cations through graphene oxide membranes based on cation-π interactions. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(1): 850-859.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
TANG W, LOU H, LI Y, et al. Ionic liquid modified graphene oxide-PEBA mixed matrix membrane for pervaporation of butanol aqueous solutions. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 581: 93-104.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
MANSHAD S, ISLOOR A M, NAWAWI M G M, et al. Pervaporation dehydration of bio-fuel (n-butanol) by dry thermal treatment membrane. Materials Research Express, 2020, 7(6):065001.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LEE J Y, LEE J S, LEE J. P High performance and thermally stable PDMS pervaporation membranes prepared using a phenyl-containing tri-functional crosslinker for n-butanol recovery. Separation and Purification Technology, 2020, 235: 116142.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
XU L, LI S, MAO H, et al. An advanced necklace-like metal organic framework with an ultrahighly continuous structure in the membrane for superior butanol/water separation. J. Mater. Chem. A, 2021, 9(19):11853.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
HUA D, RAI R K, ZHANG Y, et al. Aldehyde functionalized graphene oxide frameworks as robust membrane materials for pervaporative alcohol dehydration. Chemical Engineering Science, 2017, 161: 341-349.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ACHRI D, RACHIPUDI P, NAIK S, et al. Polyelectrolyte complex membranes made of chitosan-PSSAMA for pervaporation separation of industrially important azeotropic mixtures. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2019, 78: 383-395.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
KURSUN F. Application of PVA-b-NaY zeolite mixture membranes in pervaporation method. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2020, 1201: 127170.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
ZHU T, XU S, YU F, et al. ZIF-8@GO composites incorporated polydimethylsiloxane membrane with prominent separation performance for ethanol recovery. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020, 598: 117681.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHAO D, JI Y F, LIU G P, et al. Facilitated water-selective permeation via PEGylation of graphene oxide membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018, 567: 311-320
DOI URL |
| [23] |
CASTRO-MUNOZ R, BUERA-GONZALEZ J, IGLESIA, et al. Towards the dehydration of ethanol using pervaporation cross- linked poly(vinyl alcohol)/graphene oxide membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019, 582: 423-484.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
GUAN K, LIU Q, ZHOU G, et al. Cation-diffusion controlled formation of thin graphene oxide composite membranes for efficient ethanol dehydration. Science China Materials, 2019, 62(7): 925-935.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
CHENG X, CAI W, CHEN X, et al. Preparation of graphene oxide/poly(vinyl alcohol) composite membrane and pervaporation performance for ethanol dehydration. RSC Advances, 2019, 9(27): 15457-15465
DOI URL |
| [26] |
ZHU T, LE YU X, YI M, et al. Facile covalent crosslinking of zeolitic imidazolate framework/polydimethylsiloxane mixed matrix membrane for enhanced ethanol/water separation performance. ACS Sustainable Chem. Eng., 2020, 8(33): 12664-12676.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 张博,张宁,杨建华,兰建成,王金渠. 两步晶化制备高性能a&b取向T型沸石膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 939-946. |
| [2] | 朱春晖, 徐荣, 任秀秀, 左士祥, 龚耿浩, 钟璟. ZIF-8-NH2/有机硅杂化膜的制备及渗透汽化脱盐性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(11): 1239-1246. |
| [3] | 王晓磊, 张玉亭, 高冰, 张春, 顾学红. 四通道中空纤维NaA分子筛内膜的制备与表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(3): 339-344. |
| [4] | 吕尤佳, 李华征, 杨建华, 王金渠, 殷德宏, 鲁金明. 清液体系高性能T型分子筛膜的制备及表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(7): 705-710. |
| [5] | 周 亮, 杨建华, 王金渠, 鲁金明, 张 艳, 殷德宏. 蒸汽相转化涂晶法SAPO-34分子筛膜的制备及表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(3): 294-298. |
| [6] | 李良清, 张闻煦, 杨建华, 鲁金明, 殷德宏, 王金渠. 含氟体系下亲水性ZSM-5沸石分子筛膜的制备及其性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(11): 1167-1171. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||