无机材料学报 ›› 2022, Vol. 37 ›› Issue (1): 79-85.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210212
所属专题: 【信息功能】电介质材料
收稿日期:2021-03-29
修回日期:2021-04-20
出版日期:2022-01-20
网络出版日期:2021-07-20
通讯作者:
张媛媛, 副教授. E-mail: yyzhang@ee.ecnu.edu.cn
作者简介:李 胜(1996-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 51181213007@stu.ecnu.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Sheng( ), SONG Guoqiang, ZHANG Yuanyuan(
), SONG Guoqiang, ZHANG Yuanyuan( ), TANG Xiaodong
), TANG Xiaodong
Received:2021-03-29
Revised:2021-04-20
Published:2022-01-20
Online:2021-07-20
Contact:
ZHANG Yuanyuan, associate professor. E-mail: yyzhang@ee.ecnu.edu.cn
About author:LI Sheng (1996-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 51181213007@stu.ecnu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
多铁材料在新型器件领域的应用非常广泛, 其研究已成为当今材料研究领域的热点之一。钛酸钡(BaTiO3, BTO)在室温下具有较强的铁电性、高介电常数和电光特性等丰富的物理性能, 吸引了科研人员对其进行多铁化的研究。本工作通过固相烧结法制备BTO和BaTi0.94(TM1/2Nb1/2)0.06O3(TM = Mn/Ni/Co)陶瓷, 系统研究了B位共掺杂对陶瓷的生长特性与电学、磁学和光学方面的影响。实验结果表明: 掺杂有效抑制了六方相的产生, 样品晶体结构由四方相向立方相转变, 不同元素离子半径的差异使得相变的程度有所不同。通过拉曼散射发现BTO基陶瓷四方相的特征峰变弱, 进一步证明了共掺杂导致四方相减少。介电温谱表明BaTi0.94(TM1/2Nb1/2)0.06O3的居里温度(TC)也较BTO有大幅度降低, 同时样品的铁电性虽然也明显削弱, 但是还保持有较好的铁电性, 这些都和晶体结构的相变程度密切相关。磁性测试结果表明: 在三组共掺组分中, Ni-Nb共掺杂具有最好的室温铁磁性, 铁磁性的形成机制可以通过F中心交换(F-center exchange, FCE)理论来解释。与BTO相比, BaTi0.94(TM1/2Nb1/2)0.06O3的带隙明显减小, 这主要是因为掺杂产生杂质能级使带隙减小, 与能带理论吻合。上述结果表明: 通过B位共掺杂可以获得室温下铁电性与铁磁性共存的BTO基多铁陶瓷, 有望在多铁性功能器件中获得更广泛的应用。
中图分类号:
李胜, 宋国强, 张媛媛, 唐晓东. BTO基多铁陶瓷的制备及物理性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 79-85.
LI Sheng, SONG Guoqiang, ZHANG Yuanyuan, TANG Xiaodong. Preparation and Physical Property of BTO-based Multiferroic Ceramics[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 79-85.
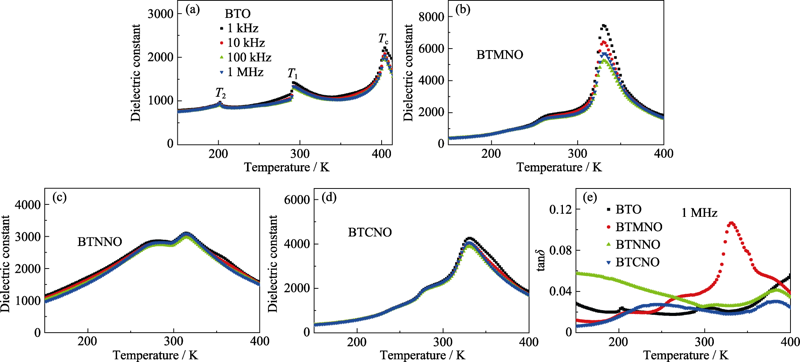
图3 在1 kHz~1 MHz频率范围BTO系列陶瓷的介电常数(a~d)和损耗与温度的关系(e)
Fig. 3 Temperature dependence of dielectric constant (a-d) and loss (e) of BTO series ceramics in the frequency range from 1 kHz to 1 MHz
| Sample | EC/(kV·cm-1) | Pr/(μC·cm-2) | Ps/(μC·cm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BTO | 4.3 | 13.24 | 28.7 |
| BTMNO | 1.22 | 5.85 | 19.1 |
| BTNNO | 0.67 | 0.55 | 15.5 |
| BTCNO | 1.85 | 6.02 | 19.9 |
表1 电滞回线中各物理参数
Table 1 Physical parameters in the electric hysteresis loop
| Sample | EC/(kV·cm-1) | Pr/(μC·cm-2) | Ps/(μC·cm-2) |
|---|---|---|---|
| BTO | 4.3 | 13.24 | 28.7 |
| BTMNO | 1.22 | 5.85 | 19.1 |
| BTNNO | 0.67 | 0.55 | 15.5 |
| BTCNO | 1.85 | 6.02 | 19.9 |
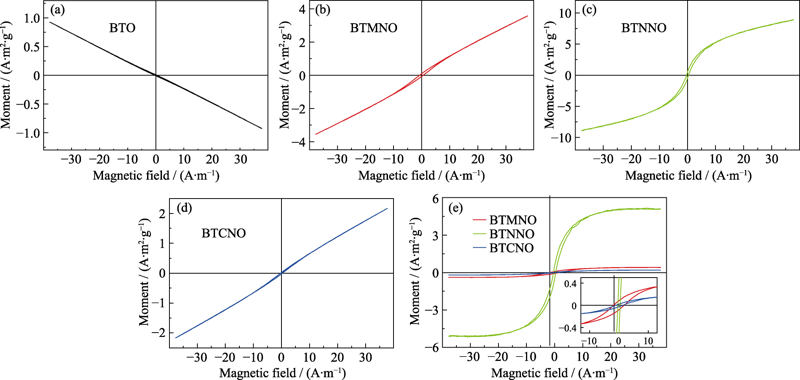
图5 300 K下, BTO系列陶瓷磁化曲线(a-d)和去除顺磁部分后的磁化曲线(e)
Fig. 5 Isothermal magnetization of BTO series ceramics at 300 K (a-d) and isothermal magnetization loops after subtracting the paramagnetic contributions of samples (e) Colourful figures are available on website
| [1] |
DONG S, LIU J M, CHEONG S W, et al. Multiferroic materials and magnetoelectric physics: symmetry, entanglement, excitation, and topology. Advances in Physics, 2015, 64(5/6):519-626.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
EERENSTEIN W, MATHUR N D, SCOTT J F. Multiferroic and magnetoelectric materials. Nature, 2006, 442(7104):759-765.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
KIMURA T, GOTO T, SHINTANI H, et al. Magnetic control of ferroelectric polarization. Nature, 2003, 426(6962):55-58.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CORASANITI M, BARONE P, NUCARA A, et al. Electronic bands and optical conductivity of the Dzyaloshinsky-Moriya multiferroic Ba2CuGe2O7. Physical Review B, 2017, 96(8):085115.
DOI URL |
| [5] | CHEN L, JIA Y, ZHAO J, et al. Strong piezoelectric-catalysis in barium titanate/carbon hybrid nanocomposites for dye wastewater decomposition. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2021, 586:758-765. |
| [6] |
XU X, WU Z, XIAO L, et al. Strong pieo-electro-chemical effect of piezoelectric BaTiO3 nanofibers for vibration-catalysis. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 762:915-921.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
XIA Y, JIA Y, QIAN W, et al. Pyroelectrically induced pyro- electro-chemical catalytic activity of BaTiO3 nanofibers under room-temperature cold-hot cycle excitations. Metals, 2017, 7(4):122.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
WANG K F, LIU J M, REN Z F. Multiferroicity: the coupling between magnetic and polarization orders. Advances in Physics, 2009, 58(4):321-448.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
BENEDEK N A, FENNIE C J. Why are there so few perovskite ferroelectrics? The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2013, 117(26):13339-13349.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HILL N A. Why are there so few magnetic ferroelectrics? The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2000, 104(29):6694-6709.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HIROYUKI N, KATAYAMA-YOSHIDA H. Theoretical prediction of magnetic properties of Ba(Ti1-xMx)O3 (M=Sc,V,Cr,Mn,Fe,Co, Ni,Cu). Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2001, 40(Part 2, 12B):L1355-L1358.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SONG C, WANG C, LIU X, et al. Room temperature ferromagnetism in cobalt-doped LiNbO3 single crystalline films. Crystal Growth & Design, 2009, 9(2):1235-1239.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
REN Z, XU G, WEI X, et al. Room-temperature ferromagnetism in Fe-doped PbTiO3 nanocrystals. Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 91(6):063106.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
KUMAR M, YADAV K L. Observation of room temperature magnetoelectric coupling in a Ni substituted Pb1-xNixTiO3 system. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 102(7):076107.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
DANG N V, THE-LONG P, THANH T D, et al. Structural phase separation and optical and magnetic properties of BaTi1-xMnxO3 multiferroics. Journal of Applied Physics, 2012, 111(11):113913.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZHOU L, ZHANG Y, LI S, et al. Fe doping effect on the structural, ferroelectric and magnetic properties of polycrystalline BaTi1-xFexO3 ceramics. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2020, 31(17):14487-14493.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
RUBAVATHI P E, VENKIDU L, BABU M V G, et al. Structure, morphology and magnetodielectric investigations of BaTi1-xFexO3-δ ceramics. Journal of Materials Science-Materials in Electronics, 2019, 30(6):5706-5717.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
RANI A, KOLTE J, VADLA S S, et al. Structural, electrical, magnetic and magnetoelectric properties of Fe doped BaTiO3 ceramics. Ceramics International, 2016, 42(7):8010-8016.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
GHEORGHIU F, CIOMAGA C E, SIMENAS M, et al. Preparation and functional characterization of magnetoelectric Ba(Ti1-xFex)O3-x/2 ceramics. Application for a miniaturized resonator antenna. Ceramics International, 2018, 44(17):20862-20870.
DOI URL |
| [20] | PHAN T L, THANG P D, HO T A, et al. et al. Local geometric and electronic structures and origin of magnetism in Co-doped BaTiO3 multiferroics. Journal of Applied Physics, 2015, 117(17): 17D904. |
| [21] |
PHONG P T, HUY B T, LEE Y I, et al. Polymorphs and dielectric properties of BaTi1-xNixO3. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 583:237-243.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
DAS S, GHARA S, MAHADEVAN P, et al. Designing a lower band gap bulk ferroelectric material with a sizable polarization at room temperature. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(5):1176-1182.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHENG D, DENG H, SI S, et al. Modified structural, optical, magnetic and ferroelectric properties in (1-x)BaTiO3- xBaCo0.5Nb0.5O3-δ ceramics. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(5):6073-6078.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
N V, DUNG N T, PHONG P T, et al. Effect of Fe3+ substitution on structural, optical and magnetic properties of barium titanate ceramics. Physica B: Condensed Matter, 2015, 457:103-107.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
ZHENG D, DENG H, PAN Y, et al. Modified multiferroic properties in narrow bandgap (1-x)BaTiO3-xBaNb1/3Cr2/3O3-δ ceramics. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(17):26823-26828.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
DAS S K, MISHRA R N, ROUL B K. Magnetic and ferroelectric properties of Ni doped BaTiO3. Solid State Communications, 2014, 191:19-24.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
VENKATESWARAN U D, NAIK V M, NAIK R. High-pressure Raman studies of polycrystalline BaTiO3. Physical Review B, 1998, 58(21):14256-14260.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ROBINS L H, KAISER D L, ROTTER L D, et al. Investigation of the structure of barium titanate thin films by Raman spectroscopy. Journal of Applied Physics, 1994, 76(11):7487-7498.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
POKORNÝ J, PASHA U M, BEN L, et al. Use of Raman spectroscopy to determine the site occupancy of dopants in BaTiO3. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 109(11):114110.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZAYTSEVA I V, PUGACHEV A M, OKOTRUB K A, et al. Residual mechanical stresses in pressure treated BaTiO3 powder. Ceramics International, 2019, 45(9):12455-12460.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
SHUAI Y, ZHOU S, BÜRGER D, et al. Decisive role of oxygen vacancy in ferroelectric versus ferromagnetic Mn-doped BaTiO3 thin films. Journal of Applied Physics, 2011, 109(8):084105.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
COEY J M D, VENKATESAN M, FITZGERALD C B. Donor impurity band exchange in dilute ferromagnetic oxides. Nature Materials, 2005, 4(2):173-179.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
COEY J M D, DOUVALIS A P, FITZGERALD C B, et al. Ferromagnetism in Fe-doped SnO2 thin films. Applied Physics Letters, 2004, 84(8):1332-1334.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
MOSTARI M S, HAQUE M J, RAHMAN ANKUR S, et al. Effect of mono-dopants (Mg2+) and co-dopants (Mg2+, Zr4+) on the dielectric, ferroelectric and optical properties of BaTiO3 ceramics. Materials Research Express, 2020, 7(6):066302.
DOI URL |
| [35] | WENG B, XIAO Z, MENG W, et al. Bandgap engineering of barium bismuth niobate double perovskite for photoelectronchemical water oxidation. Advanced Energy Materals, 2017, 7(9):1602260. |
| [36] |
YANG F, YANG L, AI C, et al. Tailoring bandgap of perovskite BaTiO3 by transition metals Co-doping for visible-light photoelectrical applications: a first-principles study. Nanomaterials, 2018, 8(7):455.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
YIN J, ZOU Z, YE J. A novel series of the new visible-light- driven photocatalysts MCo1/3Nb2/3O3 (M=Ca, Sr, and Ba) with special electronic structures. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2003, 107(21):4936-4941.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 孔国强, 冷明哲, 周战荣, 夏池, 沈晓芳. Sb掺杂O3型Na0.9Ni0.5Mn0.3Ti0.2O2钠离子电池正极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 656-662. |
| [2] | 林俊良, 王占杰. 铁电超晶格的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [3] | 杨颖康, 邵怡晴, 李柏良, 吕志伟, 王路路, 王亮君, 曹逊, 吴宇宁, 黄荣, 杨长. Cl掺杂对CuI薄膜发光性能增强研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 687-692. |
| [4] | 李悦, 张旭良, 景芳丽, 胡章贵, 吴以成. 铈掺杂硼酸钙镧晶体的生长与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 583-588. |
| [5] | 齐占国, 刘磊, 王守志, 王国栋, 俞娇仙, 王忠新, 段秀兰, 徐现刚, 张雷. GaN单晶的HVPE生长与掺杂进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [6] | 王志强, 吴济安, 陈昆峰, 薛冬峰. 大尺寸Er,Yb:YAG单晶的生长及其性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 329-334. |
| [7] | 陆晨辉, 葛万银, 宋盼盼, 张盼锋, 徐美美, 张伟. 用于白光LED稀土Eu掺杂SiAlON基荧光粉的发光性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 97-104. |
| [8] | 王洋, 范广新, 刘培, 尹金佩, 刘宝忠, 朱林剑, 罗成果. 钾离子掺杂提高锂离子电池正极锰酸锂性能的微观机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1023-1029. |
| [9] | 柳琪, 朱璨, 谢贵震, 王俊, 张东明, 邵刚勤. Ce掺杂SrMgF4超结构多晶体的吸收/光致发光光谱[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 897-902. |
| [10] | 邹顺, 何夕云, 曾霞, 仇萍荪, 凌亮, 孙大志. 掺铋钇铁石榴石磁光陶瓷的热压烧结及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 773-779. |
| [11] | 魏子钦, 夏翔, 李勤, 李国荣, 常江. 钛酸钡/硅酸钙复合生物活性压电陶瓷的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 617-622. |
| [12] | 焦博新, 刘兴翀, 全子威, 彭永姗, 周若男, 李海敏. L-精氨酸掺杂钙钛矿太阳电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 669-675. |
| [13] | 王新健, 朱逸璇, 张鹏, 杨文龙, 王挺, 郇宇. (Ba0.85Ca0.15)(Ti0.9Zr0.1-xSnx)O3无铅压电陶瓷的相结构与压电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 513-519. |
| [14] | 安琳, 吴淏, 韩鑫, 李耀刚, 王宏志, 张青红. 非贵金属Co5.47N/N-rGO助催化剂增强TiO2光催化制氢性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 534-540. |
| [15] | 李高然, 李红阳, 曾海波. 硼基材料在锂硫电池中的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 152-162. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||