无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (12): 1297-1304.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210201
所属专题: 【虚拟专辑】生物检测与成像(2020~2021)
收稿日期:2021-03-23
修回日期:2021-05-18
出版日期:2021-12-20
网络出版日期:2021-07-12
通讯作者:
牛德超, 副教授. E-mail: dcniu@ecust.edu.cn;李永生, 教授. E-mail: ysli@ecust.edu.cn
作者简介:文子聪(1996-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: mos15915333133@163.com
基金资助:
WEN Zicong1( ), NIU Dechao1(
), NIU Dechao1( ), LI Yongsheng1,2(
), LI Yongsheng1,2( )
)
Received:2021-03-23
Revised:2021-05-18
Published:2021-12-20
Online:2021-07-12
Contact:
NIU Dechao, associate professor. E-mail: dcniu@ecust.edu.cn;LI Yongsheng, professor. E-mail: ysli@ecust.edu.cn
About author:WEN Zicong(1996-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: mos15915333133@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
本研究发展了一种简便的“原位还原”策略构建负载银簇的硅基杂化纳米颗粒(Ag@SHNPs)。首先利用两亲性嵌段共聚物PS89-b-PAA16自组装行为和3-巯基丙基三甲氧基硅烷(MPTMS)在亲水链段PAA区域的水解缩聚反应形成有机硅胶束杂化纳米结构, 再利用有机硅骨架中丰富的巯基作为还原位点, 原位将银盐转化为银簇, 最终得到负载银簇的硅基杂化纳米颗粒, 并对该杂化纳米颗粒的形貌、结构以及成分组成作了分析。通过测试材料对不同细胞系的毒性验证了其良好的生物相容性。最后以4-巯基苯甲酸(4-MBA)为探针分子, 对硅基杂化颗粒基底的表面增强拉曼散射(SERS)活性进行检测。在532 nm波长的激光激发下, 4-MBA标记的硅基杂化纳米颗粒展示出明显的拉曼信号增强特性, 增强因子约为105。因此, 该硅基杂化基底材料在SERS生物成像和高灵敏检测方面具有潜在的应用前景。
中图分类号:
文子聪, 牛德超, 李永生. 负载银簇的硅基杂化纳米颗粒制备及其SERS性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1297-1304.
WEN Zicong, NIU Dechao, LI Yongsheng. Silver Clusters-loaded Silica-based Hybrid Nanoparticles: Synthesis and SERS Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1297-1304.

图2 (a)PS89-b-PAA16胶束和对应SHNPs的水合动力学粒径分布, 以及(b)不同MPTMS用量(100、150、200 μL)下制备的SHNPs水合动力学粒径分布
Fig. 2 (a) Hydrodynamic diameter distributions of PS89-b- PAA16 micelles and SHNPs, and (b) hydrodynamic diameter distributions of SHNPs prepared with different amounts of MPTMS (100, 150, 200 μL)
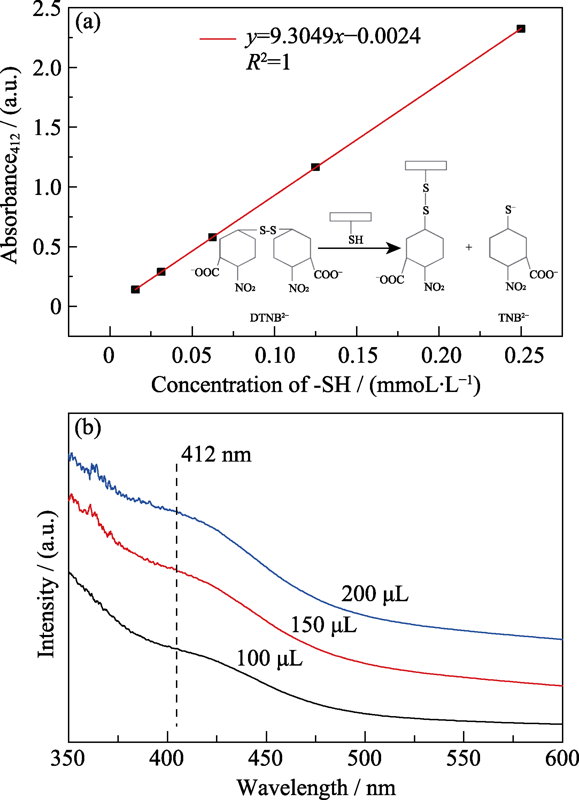
图4 (a)巯基的标准曲线(插图为Ellman试剂与巯基反应示意图)与(b)不同SHNPs与Ellman试剂反应后混合溶液的紫外-可见吸收光谱
Fig. 4 (a) Standard curve of thiol groups with inset showing the reaction between Ellman’s agent and thiol groups, and (b) UV-Vis spectra of SHNPs mixed with Ellman’s agent
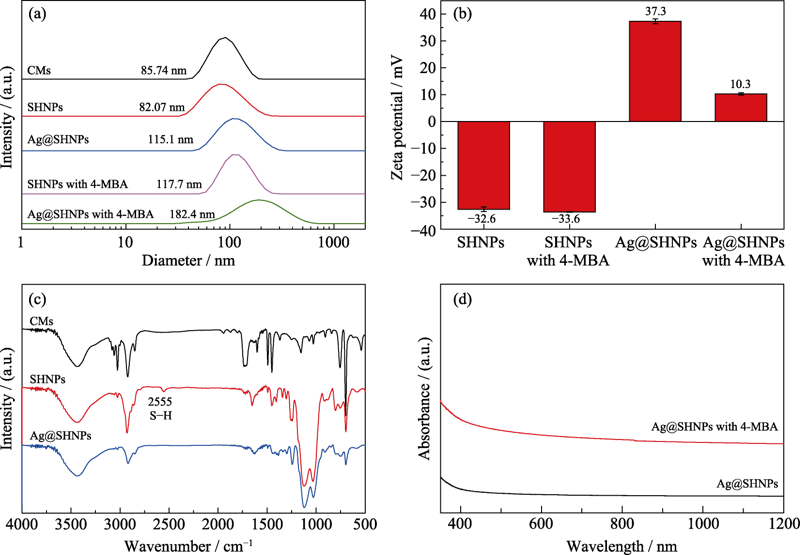
图7 SHNPs、4-MBA标记的SHNPs、Ag@SHNPs、4-MBA标记的SHNPs的(a)水合动力学粒径分布和(b)Zeta电位图, (c)CMs、SHNPs、Ag@SHNPs的FT-IR图谱, 以及(d)Ag@SHNPs、4-MBA标记的Ag@SHNPs的紫外-可见吸收光谱
Fig. 7 (a) Hydrodynamic diameter distributions and (b) histogram of Zeta potentials of SHNPs, SHNPs with 4-MBA, Ag@SHNPs, Ag@SHNPs with 4-MBA, (c) FT-IR spectra of CMs, SHNPs, Ag@SHNPs, and (d) UV-Vis spectra of Ag@SHNPs, Ag@SHNPs with 4-MBA

图9 (a)CMs、SHNPs、Ag@SHNPs在水中不同稀释倍数下的水合动力学粒径和(b)Ag@SHNPs 7 d内分散在RPMI 1640培养基和DMEM培养基中的水合动力学粒径
Fig. 9 (a) Hydrodynamic diameters of CMs, SHNPs, and Ag@SHNPs in water against dilution, and (b) hydrodynamic diameters of Ag@SHNPs dispersed in RPMI 1640 medium and DMEM medium in 7 d Colorful figures are available on website

图10 SMMC-7721细胞、NIH-3T3细胞、MEF细胞、HaCaT细胞与不同银浓度的(a)Ag@SHNPs、(b)4-MBA标记的Ag@SHNPs孵育24 h后的CCK-8细胞存活率
Fig. 10 CCK-8 cell viabilities of SMMC-7721, NIH-3T3, MEF, and HaCaT cells incubated with different Ag concentrations of (a) Ag@SHNPs and (b) Ag@SHNPs with 4-MBA for 24 h Colorful figures are available on website

图11 Ag@SHNPs、4-MBA标记的Ag@SHNPs以及纯4-MBA分子溶液在532 nm激发波长下的拉曼光谱图
Fig. 11 Raman spectra of Ag@SHNPs, Ag@SHNPs with 4-MBA and pure 4-MBA solution under 532 nm excitation
| [1] |
FLEISCHMANN M, HENDRA P J, MCQUILLAN A J. Raman spectra of pyridine adsorbed at a silver electrode. Chemical Physics Letters, 1974, 26(2): 163-166.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
STILES P L, DIERINGER J A, SHAH N C, et al. Surface- enhanced Raman spectroscopy. Annual Review of Analytical Chemistry, 2008, 1: 601-626.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LIN T, SONG Y L, LIAO J, et al. Applications of surface- enhanced Raman spectroscopy in detection fields. Nanomedicine, 2020, 15(30): 2971-2989.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHANG D, YOU H, YUAN L, et al. Hydrophobic slippery surface-based surface-enhanced Raman spectroscopy platform for ultrasensitive detection in food safety applications. Analytical Chemistry, 2019, 91(7): 4687-4695.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
GUO H, HAMLET L C, HE L, et al. A field-deployable surface-enhanced Raman scattering (SERS) method for sensitive analysis of silver nanoparticles in environmental water. Science of the Total Environment, 2019, 653: 1034-1041.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
D’ACUNTO M, CIONI P, GABELLIERI E, et al. Exploiting gold nanoparticles for diagnosis and cancer treatments. Nanotechnology, 2021, 32(19): 192001.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
HAN C, YAO Y, WANG W, et al. Rapid and sensitive detection of sodium saccharin in soft drinks by silver nanorod array SERS substrates. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2017, 251: 272-279.
DOI URL |
| [8] | WU C F, HU Q, XIAO C Y, et al. Preparation of Ag@Au core-shell nanoparticles on silicon wafer and their SERS properties. Journal of Xi’an Technological University, 2019, 39(3): 304-310. |
| [9] |
RYCENGA M, COBLEY C M, ZENG J, et al. Controlling the synthesis and assembly of silver nanostructures for plasmonic applications. Chemical Reviews, 2011, 111(6): 3669-3712.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HUSANU E, CHIAPPE C, BERNARDINI A, et al. Synthesis of colloidal Ag nanoparticles with citrate based ionic liquids as reducing and capping agents. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2018, 538: 506-512.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
SOLOVYEVA E V, UBYIVOVK E V, DENISOVA A S. Effect of diaminostilbene as a molecular linker on Ag nanoparticles: SERS study of aggregation and interparticle hot spots in various environments. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2018, 538: 542-548.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
ARAKI J, URATA T. Cellulose nanowhisker/silver nanoparticle hybrids sterically stabilized by surface poly (ethylene glycol) grafting. Langmuir, 2020, 36(36): 10868-10875.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
NIU D, LI Y, SHI J. Silica/organosilica cross-linked block copolymer micelles: a versatile theranostic platform. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017, 46(3): 569-585.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
JIA X, ZHANG Y, ZOU Y, et al. Dual intratumoral redox/enzyme- responsive NO-releasing nanomedicine for the specific, high- efficacy, and low-toxic cancer therapy. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(30): 1704490.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
NIU D, LI Y, MA Z, et al. Preparation of uniform, water-soluble, and multifunctional nanocomposites with tunable sizes. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20(5): 773-780.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LIU Y, LI Y, KANG Y, et al. Silver nanoparticle generators: silicon dioxide microspheres. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2017, 23(26): 6244-6248.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
KHOUGAZ K, ZHONG X F, EISENBERG A. Aggregation and critical micelle concentrations of polystyrene-b-poly (sodium acrylate) and polystyrene-b-poly (acrylic acid) micelles in organic media. Macromolecules, 1996, 29(11): 3937-3949.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
XIA Z, BAIRD L, ZIMMERMAN N, et al. Heavy metal ion removal by thiol functionalized aluminum oxide hydroxide nanowhiskers. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 416: 565-573.
DOI URL |
| [19] | DESAI R, MANKAD V, GUPTA S K, et al. Size distribution of silver nanoparticles: UV-visible spectroscopic assessment. Nanoscience and Nano-technology Letters, 2012, 4(1): 30-34. |
| [20] |
ZHOU Y, WANG J, YANG G, et al. Cysteine-rich protein-templated silver nanoclusters as a fluorometric probe for mercury (II) detection. Analytical Methods, 2019, 11(6): 733-738.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
LU Y, YUE Z, XIE J, et al. Micelles with ultralow critical micelle concentration as carriers for drug delivery. Nature Biomedical Engineering, 2018, 2(5): 318-325.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
MUKHERJEE S G, O’CLAONADH N, CASEY A, et al. Comparative in vitro cytotoxicity study of silver nanoparticle on two mammalian cell lines. Toxicology In Vitro, 2012, 26(2): 238-251.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
HUANG X B, WU S H, HU H C, et al. AuNanostar@4-MBA@Au core-shell nanostructure coupled with exonuclease III-assisted cycling amplification for ultrasensitive SERS detection of ochratoxin A. ACS sensors, 2020, 5(8): 2636-2643.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LE RU E C, BLACKIE E, MEYER M, et al. Surface enhanced Raman scattering enhancement factors: a comprehensive study. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2007, 111(37): 13794-13803.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
MARKINA N E, MARKIN A V, ZAKHAREVICH A M, et al. Multifunctional silver nanoparticle-doped silica for solid-phase extraction and surface-enhanced Raman scattering detection. Journal of Nanoparticle Research, 2016, 18(12): 1-9.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 李永生, 陈玲. 可控制备磁性四氧化三铁-金纳米复合颗粒及其催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(2): 221-228. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||