无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (11): 1178-1184.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200748
收稿日期:2020-12-31
修回日期:2021-04-15
出版日期:2021-11-20
网络出版日期:2021-06-01
通讯作者:
艾玥洁, 副教授. E-mail: aiyuejie@ncepu.edu.cn
作者简介:张瑞鸿(1996-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: zhangruihong@ncepu.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHANG Ruihong1( ), WEI Xin2, LU Zhanhui1, AI Yuejie3(
), WEI Xin2, LU Zhanhui1, AI Yuejie3( )
)
Received:2020-12-31
Revised:2021-04-15
Published:2021-11-20
Online:2021-06-01
Contact:
AI Yuejie, associate professor. E-mail: aiyuejie@ncepu.edu.cn
About author:ZHANG Ruihong(1996-), femal, Master candidate. E-mail: zhangruihong@ncepu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
本研究通过密度泛函理论对氧化石墨烯和金属离子的吸附行为进行理论模拟。基于机器学习方法训练预测模型的过程中, 缺失值采用推荐系统中广泛使用的奇异值分解方法处理, 并用梯度提升机解释了影响吸附能的重要因素。结果发现吸附体系中存在九种特征可为吸附能提供90%的累积重要性, 分别为离子半径、零点振动能量、密立根电荷、沸点、偶极矩、原子量、摩尔定容热容、自旋多重度和键长。定量评估了六种回归方法的预测精度, 包括支持向量回归、岭回归、随机森林、极端随机森林、极端梯度提升和轻梯度提升机。结果表明, 机器学习方法可提供足够的吸附能预测准确性, 其中极端随机森林方法表现出最优的预测性能, 均方误差仅为0.075。该模型用于香兰素吸附金属离子的测试, 验证了基于机器学习训练金属离子吸附能预测模型的可行性, 但仍需进一步提高其泛化能力。本研究基于机器学习预测吸附能, 简化预测过程、节省计算时间, 可为吸附去除金属离子的理论和实验研究提供参考。
中图分类号:
张瑞鸿, 魏鑫, 卢占会, 艾玥洁. 基于机器学习训练金属离子吸附能预测模型的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1178-1184.
ZHANG Ruihong, WEI Xin, LU Zhanhui, AI Yuejie. Training Model for Predicting Adsorption Energy of Metal Ions Based on Machine Learning[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1178-1184.
| No. | Feature descriptor | No. | Feature descriptor | No. | Feature descriptor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Charge | 8 | Ionic radius | 15 | CV (Cal/mol-K) |
| 2 | Spin | 9 | Melting point | 16 | S(Cal/mol-K) |
| 3 | Atomic radius | 10 | Boiling point | 17 | Zero-point vibrational energy/(kCal·mol-1) |
| 4 | Atomic number | 11 | First ionization energy | 18 | Molecular mass |
| 5 | Atomic weight | 12 | Electronegativity | 19 | Mulliken charges |
| 6 | Density/(g·cm-3) | 13 | M-O (bond length) | 20 | APT charges |
| 7 | Atomic volume | 14 | E(Thermal)/(kCal·mol-1) | 21 | Dipole moment/D |
表1 基于DFT计算得到的21个特征描述符
Table 1 21 feature descriptors calculated based on DFT
| No. | Feature descriptor | No. | Feature descriptor | No. | Feature descriptor |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Charge | 8 | Ionic radius | 15 | CV (Cal/mol-K) |
| 2 | Spin | 9 | Melting point | 16 | S(Cal/mol-K) |
| 3 | Atomic radius | 10 | Boiling point | 17 | Zero-point vibrational energy/(kCal·mol-1) |
| 4 | Atomic number | 11 | First ionization energy | 18 | Molecular mass |
| 5 | Atomic weight | 12 | Electronegativity | 19 | Mulliken charges |
| 6 | Density/(g·cm-3) | 13 | M-O (bond length) | 20 | APT charges |
| 7 | Atomic volume | 14 | E(Thermal)/(kCal·mol-1) | 21 | Dipole moment/D |
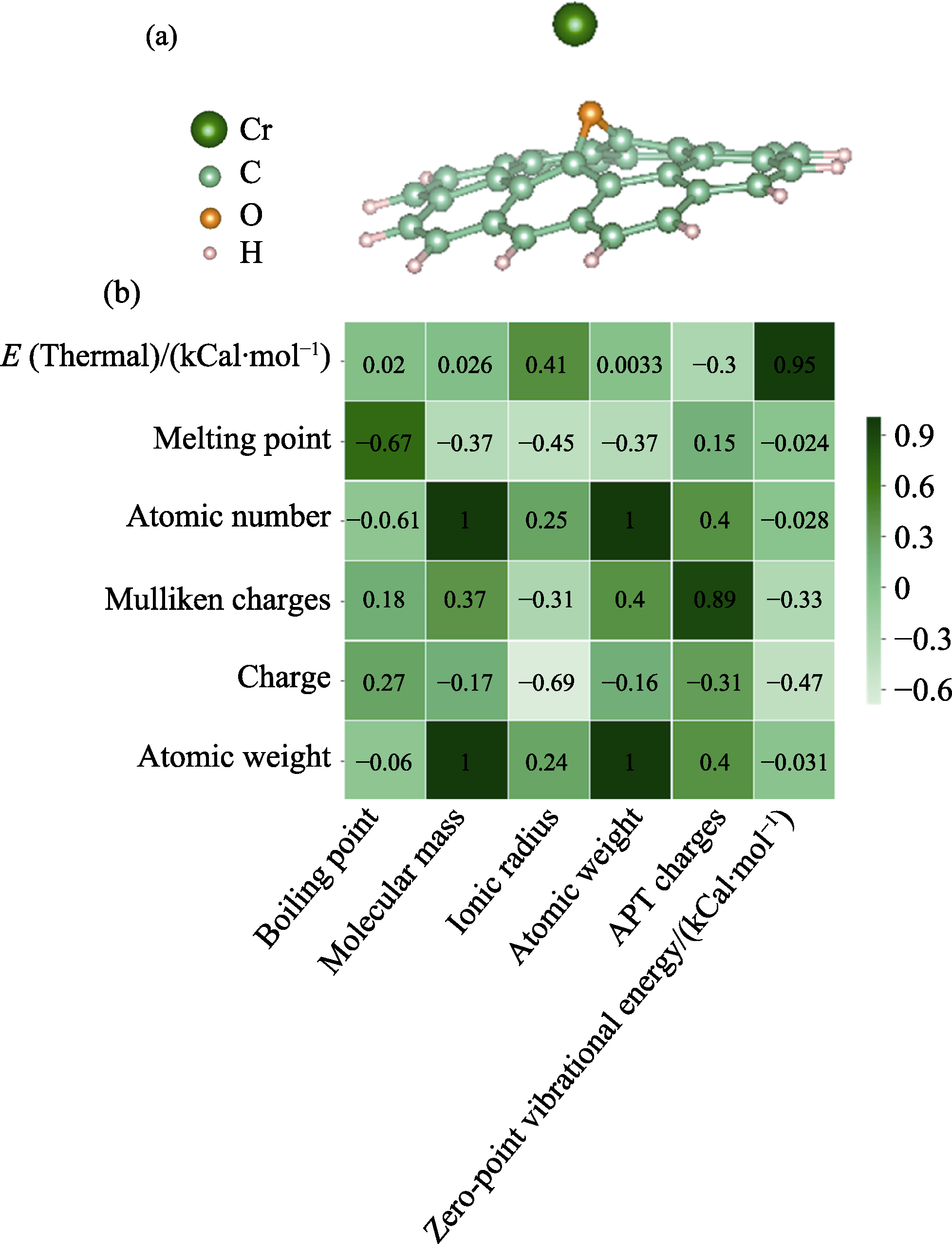
图1 (a)相关系数>0.6的特征间相关性热力图和(b)GO吸附Cr3+的吸附结构示例
Fig. 1 (a) Thermal map of correlation between features with correlation coefficient>0.6, and (b) example of adsorption structure of GO adsorbing Cr3+ Note: 1 Cal=4.104 J
| Category | Method | Optimal hyperparameters |
|---|---|---|
| Kernel | Support vector regression (SVR) | C = 2, kernel=“ rbf ” |
| Ridge regression | Alpha = 30 | |
| Random forest | Random forest (RF) | n_estimators = 31, max_depth = 6, max_features = 2 |
| Extremely randomized trees (ERT) | n_estimators = 31, max_depth = 7, random_state = 1 | |
| Boosting | Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) | n_estimators = 31, max_depth = 2, min_child_weight = 13, learning_rate =.32 |
| Light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM) | n_estimators =17, objective = ‘regression’, num_leaves = 31, learning_ rate = 0.32 |
表2 六种机器学习方法的最优超参数
Table 2 Optimal hyperparameters of six machine learning methods
| Category | Method | Optimal hyperparameters |
|---|---|---|
| Kernel | Support vector regression (SVR) | C = 2, kernel=“ rbf ” |
| Ridge regression | Alpha = 30 | |
| Random forest | Random forest (RF) | n_estimators = 31, max_depth = 6, max_features = 2 |
| Extremely randomized trees (ERT) | n_estimators = 31, max_depth = 7, random_state = 1 | |
| Boosting | Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost) | n_estimators = 31, max_depth = 2, min_child_weight = 13, learning_rate =.32 |
| Light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM) | n_estimators =17, objective = ‘regression’, num_leaves = 31, learning_ rate = 0.32 |
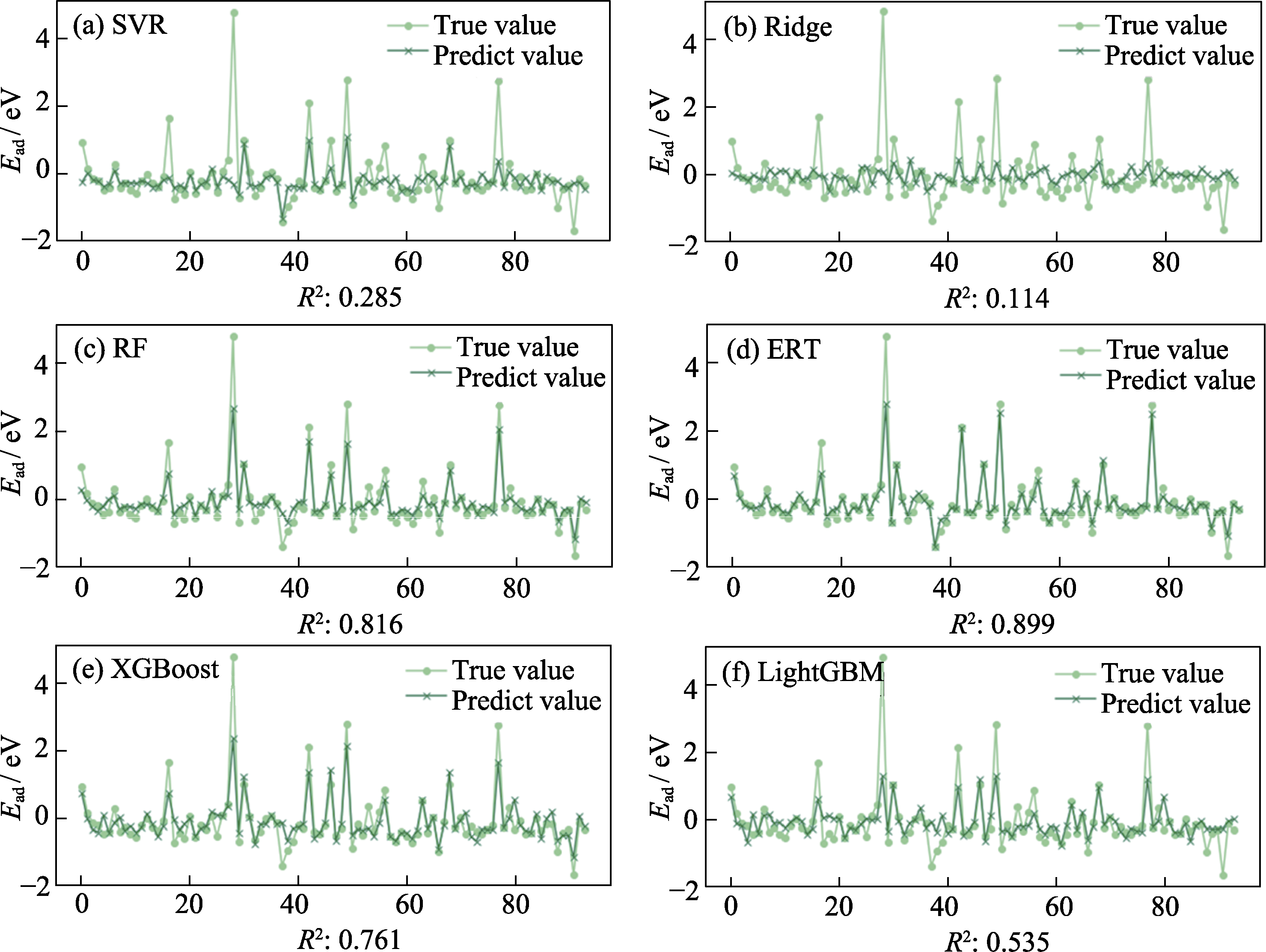
图3 6种机器学习方法的模型拟合效果及评分
Fig. 3 Fitting effect diagram and score of six machine learning methods. (a) Support vector regression (SVR); (b) Ridge regression (Ridge); (c) Random forest (RF); (d) Extremely randomized trees (ERT); (e) Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost); (f) Light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM)
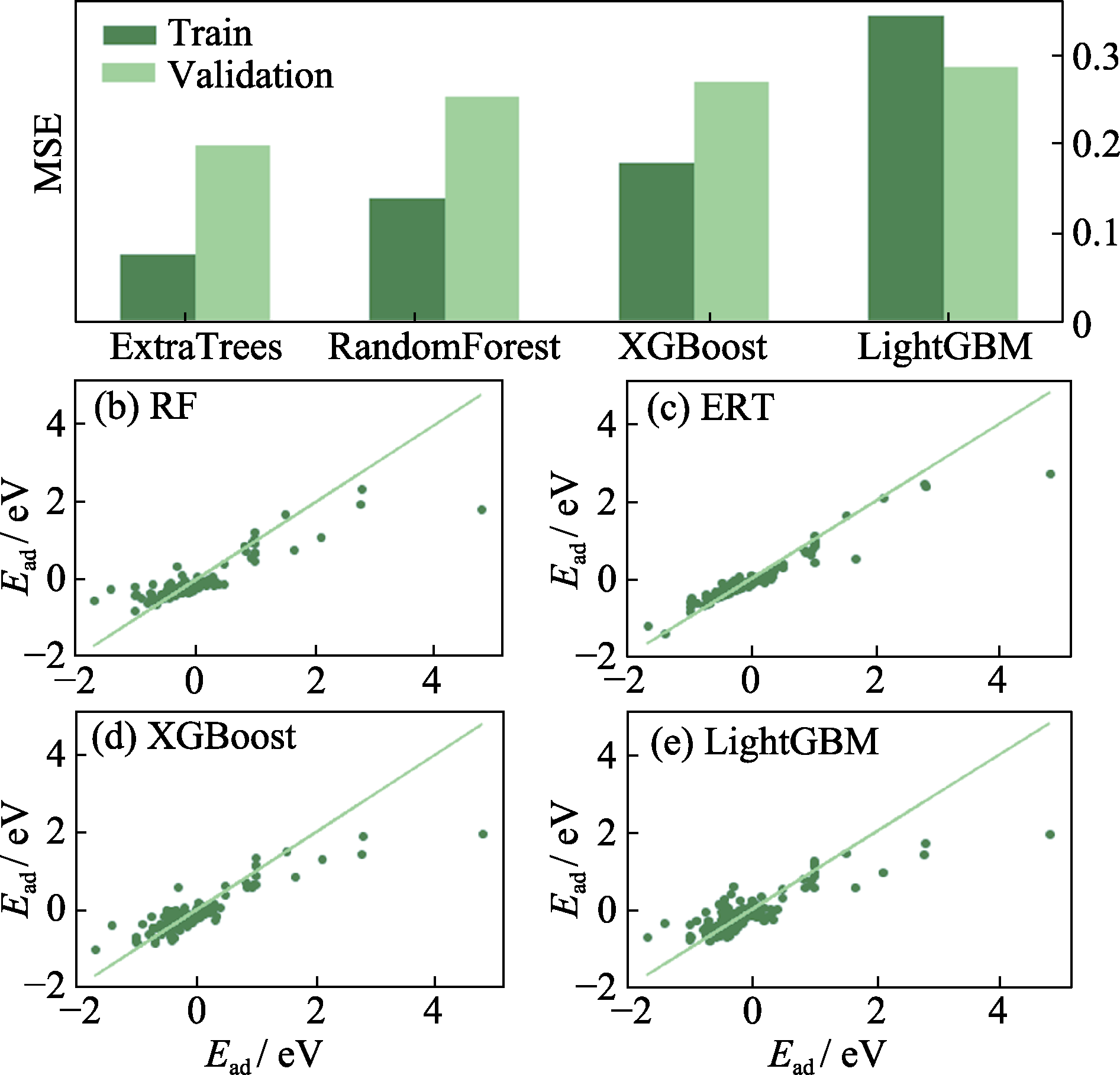
图4 (a)四种集成方法的MSE; (b~e)四种集成方法真实值和预测值的相关图
Fig. 4 (a) Mean square error (MSE) of the four ensemble methods, and (b-e) correlation graphs of the true and predicted values of the four ensemble methods (b) Random forest (RF); (c) Extremely randomized trees (ERT); (d) Extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost); (e) Light gradient boosting machine (LightGBM)
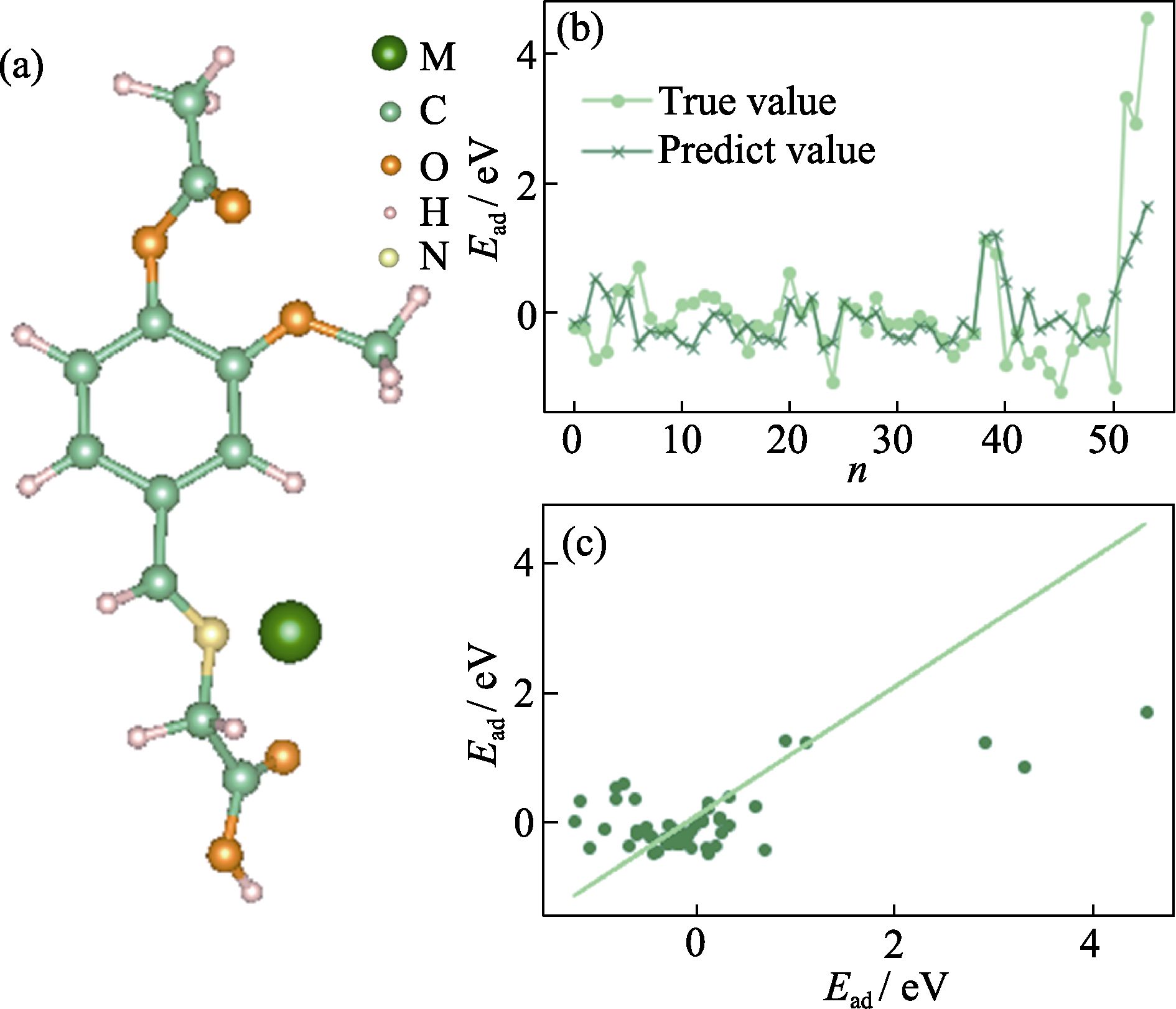
图5 (a)香兰素单体吸附金属离子的结构示例图; (b)ERT用于VMA-Mn+吸附能的拟合效果图; (c)ERT用于VMA-Mn+吸附能的相关图
Fig. 5 (a) Example of the structure of vanillin monomer adsorbing metal ions; (b) Fitting effect graph of Extremely Randomized Trees (ERT) for VMA-Mn+ adsorption energy; (c) Correlation diagram of ERT for VMA-Mn+ adsorption energy
| [1] |
PENG W J, LI H Q, LIU Y Y, et al. A review on heavy metalions adsorption from water by graphene oxide and its composites. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017, 230:496-504.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
AHMAD S Z N, SALLEH W N W, ISMAIL A F, et al. Adsorptive removal of heavy metal ions using graphene-based nanomaterials: toxicity, roles of functional groups and mechanisms. Chemosphere, 2020, 248:126008.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
LIU Y, ZHAO C F, ZHANG A R, et al. Theoretical study on the removal of uranyl by nitrogen, phosphorus and sulfur doped graphene materials. Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2019, 49(1):91-102.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
PENG X J, WANG Y F. Efficient stochastic simulation algorithm for chemically reacting systems based on support vector regression. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2009, 22(5):502-510.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
CAI C, LI L, DENG X, et al. Machine learning and high- throughput computational screening of metal-organic framework for separation of methane/ethane/propane. Acta Chimica Sinica, 2020, 78(5):427.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ORUPATTUR N V, MUSHRIF S H, PRASAD V. Catalytic materials and chemistry development using a synergistic combination of machine learning and ab initio methods. Computational Materials Science, 2020, 174:109497-16.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LI X, XI L L, YANG J. First principles high-throughput research on thermoelectric materials: a review. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3):236-246.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
MENG Y, WANG X, YANG J, et al. Research on machine learning based model for predicting the impact status of laminated glass. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1):61-68.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
FENG C, SHARMAN E, YE S, et al. A neural network protocol for predicting molecular bond energy. Sci. China Chem., 2019, 62(12):1698-1703.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LU S, ZHOU Q, OUYANG Y, et al. Accelerated discovery of stable lead-free hybrid organic-inorganic perovskites via machine learning. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1):3405.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
TEHRANI A M, OLIYNYK A O, PARRY M, et al. Machine learning directed search for ultraincompressible, superhard materials. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(31):9844-9853.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KANG Y, LI L, LI B. Recent progress on discovery and properties prediction of energy materials: simple machine learning meets complex quantum chemistry. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2020, 54:72-88.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
BROCKHERDE F, VOGT L, LI L, et al. By-passing the Kohn-Sham equations with machine learning. Nature Communications, 2017, 8(1):872.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
XIAO Y, MIARA L J, WANG Y, et al. Computational screening of cathode coatings for solid-state batteries. Joule, 2019, 3(5):1252-1275.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
PANAPITIYA G, AVENDANO-FRANCO G, REN P, et al. Machine learning prediction of CO adsorption in thiolated, Ag alloyed Au nanoclusters. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2018, 140(50):17508-17514.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
PARDAKHTI M, MOHARRERI E, WANIK D, et al. Machine learning using combined structural and chemical descriptors for prediction of methane adsorption performance of metal organic frameworks (MOFs). ACS Combinatorial Science, 2017, 19(10):640-645.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
SI Y, SAMULSKIE T. Synthesis of water soluble graphene. Nano Letters, 2008, 8(6):1679-1682.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CHEN D, FENG H, LI J. Graphene oxide: preparation, functionalization, and electrochemical applications. Chemical Reviews, 2012, 112(11):6027-6053.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SHENG Z H, SHAO L, CHEN J J, et al. Catalyst free synthesis of nitrogen-doped graphene via thermal annealing graphite oxide with melamine and its excellent electrocatalysis. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(6):4350-4358.
DOI URL |
| [20] | MAURIZIO C, VICENZO B, MICHAEL A R. A direct procedure for the evaluation of solvent effects in MC-SCF calculations. Journal of Chemical Physics, 1999, 111(12):5295-5302. |
| [21] | BRAND M. Incremental Singular Value Decomposition of Uncertain Data with Missing Values. Computer Vision-ECCV 2002, Berlin, Heidelberg, 2002: 707-720. |
| [22] | NEELAKANTAN A, VILNIS L, LEQ V, et al. Adding gradiant noise improves learning for very deep networks. arXiv: Machine Learning, 2015, 1511:06807. |
| [23] | 迪安J A, 魏俊发. 兰氏化学手册, 2版. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003: 1-1579. |
| [24] |
FRIEDMAN J H, JAO S. Greedy function approximation: a gradient boosting machine. Annals of Statistics, 2001, 29(5):1189-1232.
DOI URL |
| [25] | LIASHCHYNSKYI P, LIASHCHYNSKYI P. Grid search, random search, genetic algorithm: a big comparison for NAS. arXiv: Learning, 2019, 1912:06059. |
| [26] | MARTENS H A, DARDENNE P J, CSYSTEMS I L. Validation and verification of regression in small data sets. ChemomERTics & Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 1998, 44(1/2):99-121. |
| [27] |
FRIEDMAN J H. Stochastic gradient boosting. Computational Statistics & Data Analysis, 2002, 38(4):367-378.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
SMOLA A J, SCHOLKOPF B. A tutorial on support vector regression. Statistics and Computing, 2004, 14(3):199-222.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
RUPP M. Machine learning for quantum mechanics in a nutshell. International Journal of Quantum Chemistry, 2015, 115(16):1058-1073.
DOI URL |
| [30] | SVETNIK V. Random forest: a classification and regression tool for compound classification and QSAR modeling. Journal of Chemical Information and Modeling, 2003, 43(6):1947-1958. |
| [31] | GEURTS P, ERNST D, WEHENKEL L. Extremely randomized trees. Machine Learning, 2006, 63(1):3-42. |
| [32] | DRUCKER H. Improving regressors using boosting techniques. Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc, 1997: 107-115. |
| [33] | FRANLLIN J. The elements of statistical learning: data mining, inference, and prediction. The Mathematical Intelligencer, 2005, 27(2):83-85. |
| [34] | SANTOS R I H, REIS D T, PEREIRA D H. A DFT based analysis of adsorption of Cd2+, Cr3+, Cu2+, Hg2+, Pb2+, and Zn2+, on vanillin monomer: a study of the removal of metalions from effluents. Journal of Molecular Modeling, 2019, 25(9):267. |
| [1] | 王世怡, 冯爱虎, 李晓燕, 于云. Fe3O4负载Ti3C2Tx对Pb(II)的吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [2] | 江依义, 沈旻, 宋半夏, 李南, 丁祥欢, 郭乐毅, 马国强. 双功能电解液添加剂对锂离子电池高温高电压性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 710-716. |
| [3] | 王鹏, 靳遵龙, 陈宁光, 刘勇豪. Mo掺杂α-MnO2电催化析氧反应的理论研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 541-546. |
| [4] | 曹志军, 李在均. 钌-生物质碳人工酶的制备及在比色检测杀虫剂毒死蜱残留中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 554-560. |
| [5] | 施思齐, 孙拾雨, 马舒畅, 邹欣欣, 钱权, 刘悦. 融合材料领域知识的数据准确性检测方法[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1311-1320. |
| [6] | 焦志翔, 贾帆豪, 王永晨, 陈建国, 任伟, 程晋荣. 基于机器学习的BiFeO3-PbTiO3-BaTiO3固溶体居里温度预测[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1321-1328. |
| [7] | 李友兵, 秦彦卿, 陈科, 陈露, 张霄, 丁浩明, 李勉, 张一鸣, 都时禹, 柴之芳, 黄庆. 熔盐法合成纳米层状Sc2SnC MAX相[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 773-778. |
| [8] | 何俊龙, 宋二红, 王连军, 江莞. DFT方法研究一氧化氮在铬掺杂石墨烯上的吸附行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1047-1052. |
| [9] | 孟嫣然, 王星尔, 杨健, 徐涵, 岳峰. 基于机器学习算法的夹层玻璃冲击破坏预测模型研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(1): 61-68. |
| [10] | 李一敏,王成乐,李娟. 磷钼酸盐中金属离子对聚丙烯阻燃效率的提升[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(9): 1029-1033. |
| [11] | 王祥学, 李星, 王佳琦, 朱洪涛. 氮化碳基纳米复合材料在重金属去除方面研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(3): 260-270. |
| [12] | 周子航, 王群, 葛翔, 李朝阳. 掺锶羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒的合成、表征及模拟研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(11): 1283-1289. |
| [13] | 齐欣欣, 宋广平, 尹维龙, 王明福, 赫晓东, 郑永挺, 王荣国, 柏跃磊. 新型三元层状硼化物Cr4AlB4的物相稳定性和力学行为分析[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 53-60. |
| [14] | 南 辉, 王文利, 韩建华, 尹学文, 周 宇, 赵晓冲, 林 红. 基于FeI2/Ni2+溶液还原制备低成本的高导电性及催化性 纸张石墨[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(9): 997-1003. |
| [15] | 王军凯, 张远卓, 李俊怡, 张海军, 李发亮, 韩 磊, 宋述鹏. 微波加热催化反应低温制备β-SiC粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(7): 725-730. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||