无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (12): 1305-1315.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210157
所属专题: 【生物材料】肿瘤治疗; 【能源环境】金属有机框架材料
王玉伟1,2( ), 陈佳杰2, 田正芳3, 朱敏1(
), 陈佳杰2, 田正芳3, 朱敏1( ), 朱钰方2(
), 朱钰方2( )
)
收稿日期:2021-03-12
修回日期:2021-04-15
出版日期:2021-12-20
网络出版日期:2021-06-01
通讯作者:
朱 敏, 副教授. E-mail: mzhu@usst.edu.cn;朱钰方, 教授. E-mail: zjf2412@163.com
作者简介:王玉伟(1993-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 676627664@qq.com
基金资助:
WANG Yuwei1,2( ), CHEN Jiajie2, TIAN Zhengfang3, ZHU Min1(
), CHEN Jiajie2, TIAN Zhengfang3, ZHU Min1( ), ZHU Yufang2(
), ZHU Yufang2( )
)
Received:2021-03-12
Revised:2021-04-15
Published:2021-12-20
Online:2021-06-01
Contact:
ZHU Min, associate professor. E-mail: mzhu@usst.edu.cn;ZHU Yufang, professor. E-mail:zjf2412@163.com
About author:WANG Yuwei (1993-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: 676627664@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
金属有机框架因具有多孔结构、高比表面积、丰富的官能团和金属活性位点以及良好的生物相容性和降解性而被广泛应用于生物医学领域。本研究提出以卟啉基金属有机框架纳米颗粒(PCN-224)为载体负载高化学价态的高铁酸钾氧化剂(K2FeO4, Fe(VI)), 经牛血清蛋白(BSA)包覆表面制备多功能复合纳米颗粒(Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA), 用于肿瘤光-化学动力学联合治疗。实验结果表明, PCN-224纳米颗粒粒径约为90 nm, 而Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒粒径约为100 nm。Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒在模拟肿瘤微环境条件下能够催化H2O2反应, 产生有细胞毒性的•OH而实现化学动力学效应, 同时也能够氧化分解部分H2O2产生O2, 在660 nm激光照射下提高单线态氧(1O2)产生量, 增强光动力学效应。进一步细胞实验证实Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒具有较好的生物相容性, 能够获得增强的光-化学动力学联合治疗肿瘤效果。因此, Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒在肿瘤治疗方面具有潜在的应用前景。
中图分类号:
王玉伟, 陈佳杰, 田正芳, 朱敏, 朱钰方. 卟啉基金属有机框架负载高铁酸钾: 光-化学动力学联合治疗肿瘤性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1305-1315.
WANG Yuwei, CHEN Jiajie, TIAN Zhengfang, ZHU Min, ZHU Yufang. Potassium Ferrate-loaded Porphyrin-based (VI) Metal-organic Frameworks for Combined Photodymanic and Chemodynamic Tumor Therapy[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1305-1315.
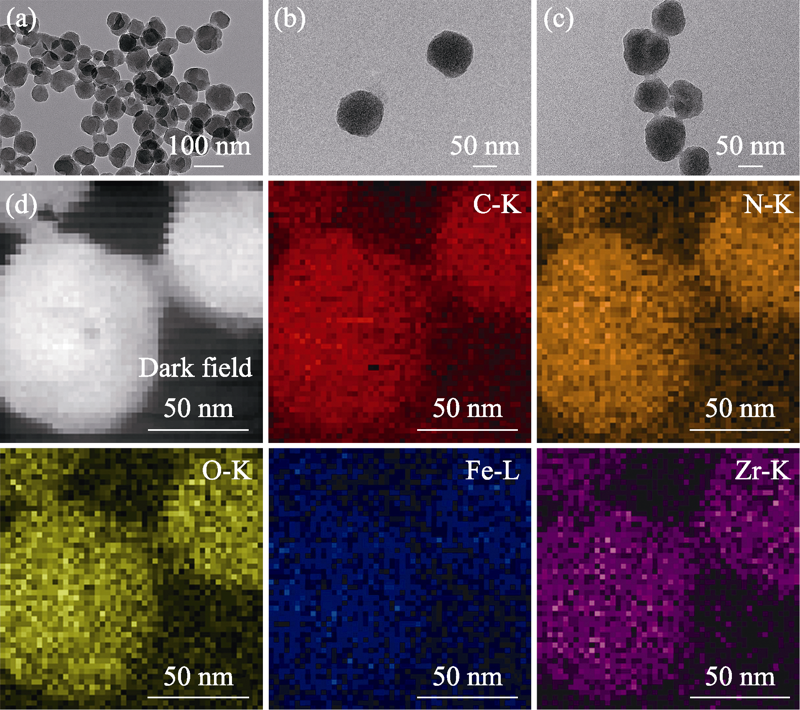
图1 (a)PCN-224、(b)Fe(VI)@PCN-224和(c)Fe(VI)@PCN @BSA纳米颗粒的TEM照片及(d)Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒的元素分布图
Fig. 1 TEM images of (a) PCN-224, (b) Fe(VI)@PCN-224 and (c) Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles, and (d) elemental mapping of Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles
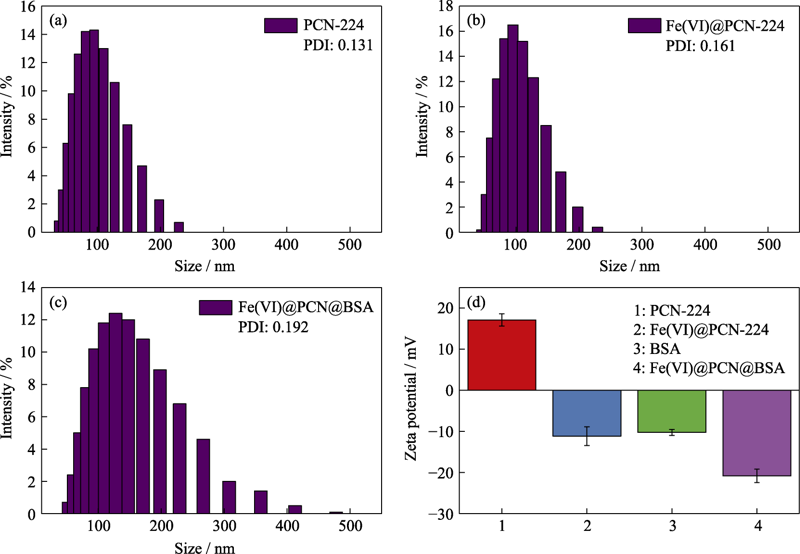
图3 (a)PCN-224、(b)Fe(VI)@PCN-224和(c)Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒的DLS粒径分布图以及(d)BSA和PCN-224、Fe(VI)@PCN-224、Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒的表面Zeta电位
Fig. 3 DLS size distributions of (a) PCN-224, (b) Fe(VI)@PCN-224 and (c) Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles, and (d) Zeta potentials of BSA, PCN-224, Fe(VI)@PCN, and Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles
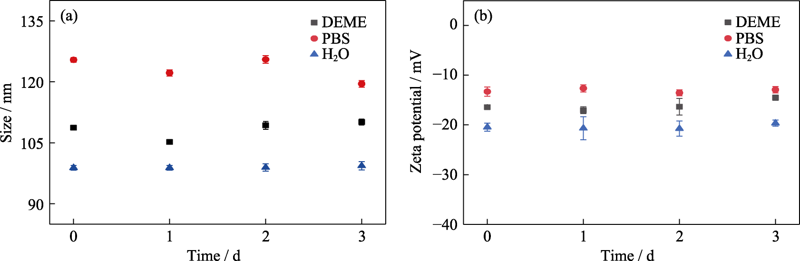
图4 Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒在H2O、PBS和DEME培养基中的(a)粒径和(b)Zeta电位的变化图
Fig. 4 Changes of (a) size and (b) Zeta potential of Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles in H2O, PBS and DEME
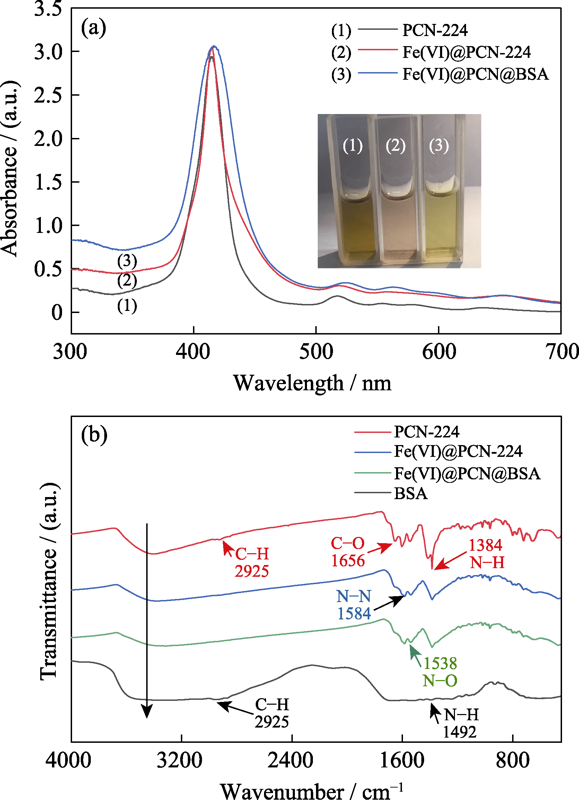
图5 (a)PCN-224、Fe(VI)@PCN-224和Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒的紫外-可见光吸收光谱图, 其中插图为纳米颗粒悬浮液的光学照片, 以及(b)BSA、PCN-224、Fe(VI)@PCN-224和Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒的傅里叶变换红外光谱图
Fig. 5 (a) UV-Vis absorption spectra of PCN-224, Fe(VI)@PCN-224, and Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA suspensions (inset is pictures of the suspensions), and (b) Fourier transform infrared spectra of BSA, PCN-224, Fe(VI)@PCN-224, and Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles
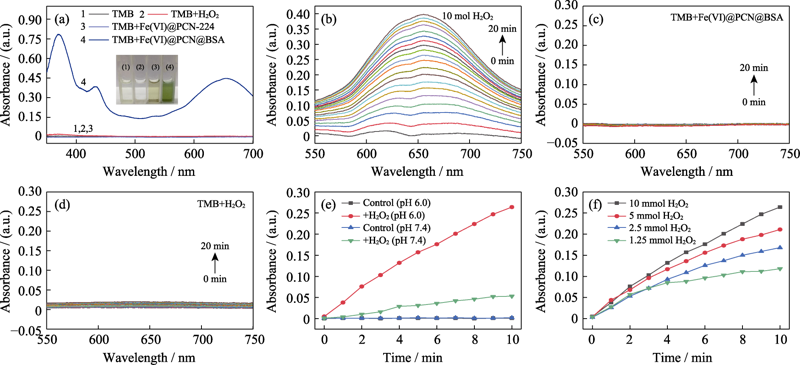
图6 Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA 纳米颗粒的化学动力学性能
Fig. 6 Chemodynamic properties of Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles (a) UV-Vis absorption spectra of TMB solutions under different conditions with inset showing photographs of TMB solutions after reaction for 10 min under different conditions; (b) Absorbance changes of TMB solutions with time after adding Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles (50 µg/mL) into TMB solutions under pH 6.0 with H2O2 (10 mmol/L); (c) Absorbance changes of TMB solutions with time after adding Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles (50 µg/mL) into TMB solutions with pH 6.0; (d) Absorbance changes of TMB solutions with time under pH 6.0 with H2O2 (10 mmol/L); (e) Curves of absorbance at 652 nm versus time for TMB solutions with Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles under acidic (pH 6.0) or neutral (pH 7.4) conditions with or without H2O2; (f) Absorbance changes at 652 nm versus time for TMB solutions under pH 6.0 with different concentrations of H2O2 after adding the same amount of Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles
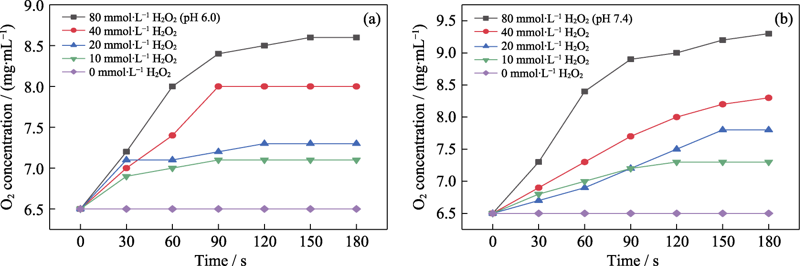
图7 (a)pH 6.0和(b)pH 7.4, 不同H2O2浓度的乙酸钠测试液中加入Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒(50 μg/mL)后的溶解氧含量变化图
Fig. 7 Changes of dissolved O2 in NaAc solutions under (a) pH 6.0 and (b) pH 7.4 with different H2O2 concentrations after the addition of Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles (50 μg/mL)
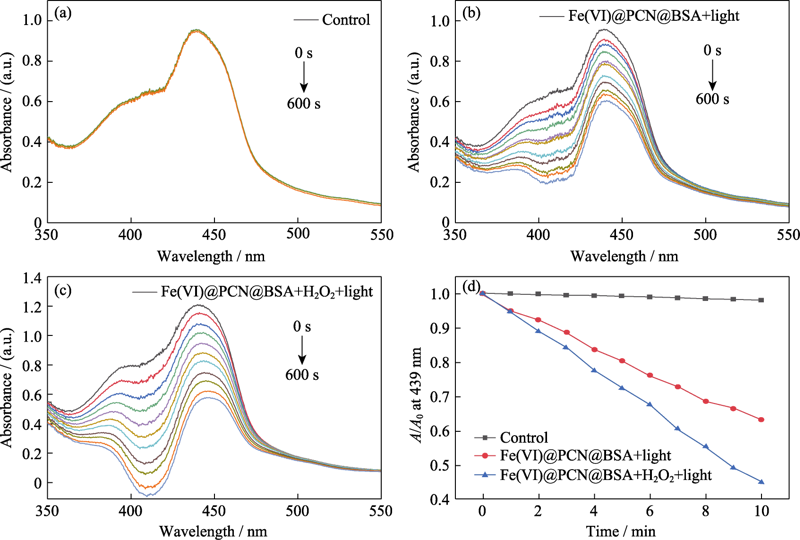
图8 (a~c)加入Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒(50 μg/mL)的DPBF溶液在不同处理条件下的紫外-可见光吸收光谱图及(d)不同组别的DPBF溶液在439 nm处的特征吸收值变化图
Fig. 8 (a-c) UV-Vis absorbance spectra of the DPBF solutions with Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles (50 μg/mL) and (d) absorbance changes of DPBF solutions at 439 nm for different groups (a) Without 660 nm laser irradiation; (b) With 660 nm laser irradiation; (c) With H2O2 (10 mmol/L) and 660 nm laser irradiation
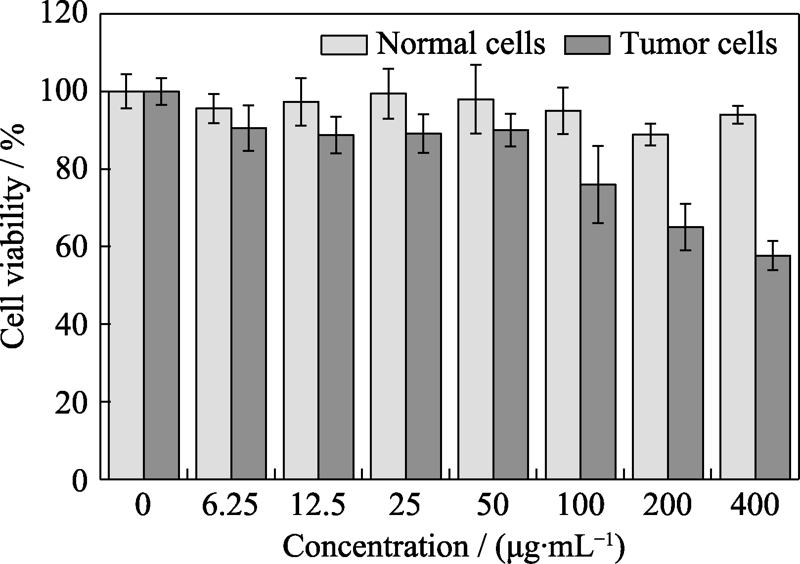
图9 不同浓度Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒对MDA-MB- 231 细胞和成纤维细胞作用24 h后的细胞存活率
Fig. 9 Cell viabilities of MDA-MB-231 cells and human dermal fibroblasts after 24 h incubation with Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles at different concentrations
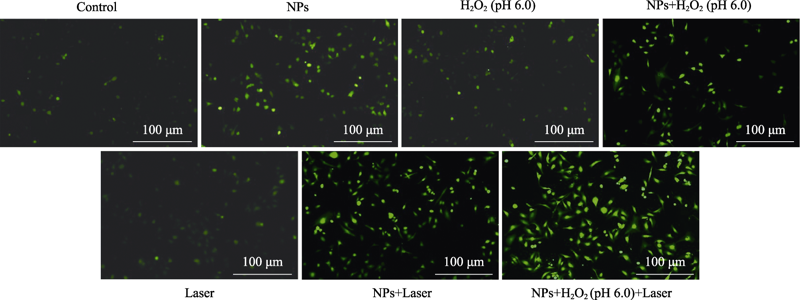
图10 不同条件处理的MDA-MB-231细胞内ROS的荧光显微照片
Fig. 10 Fluorescence images of MDA-MB-231 cells after different treatments for observing intracellular ROS Control: cells were cultured in normal medium; NPs: cells were cultured in normal medium with Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles; H2O2 (pH 6.0): cells were cultured in the medium at pH 6.0 with H2O2 (100 µmol/L); NPs+H2O2 (pH 6.0): cells were cultured in the medium at pH 6.0 with H2O2 (100 µmol/L) and Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles; Laser: 660 nm laser irradiation after cells culture in normal medium; NPs+Laser: 660 nm laser irradiation after cell culture in normal medium with Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles; NPs+H2O2 (pH 6.0)+Laser: 660 nm laser irradiation after cell culture in the medium at pH 6.0 with H2O2 (100 µmol/L) and Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles
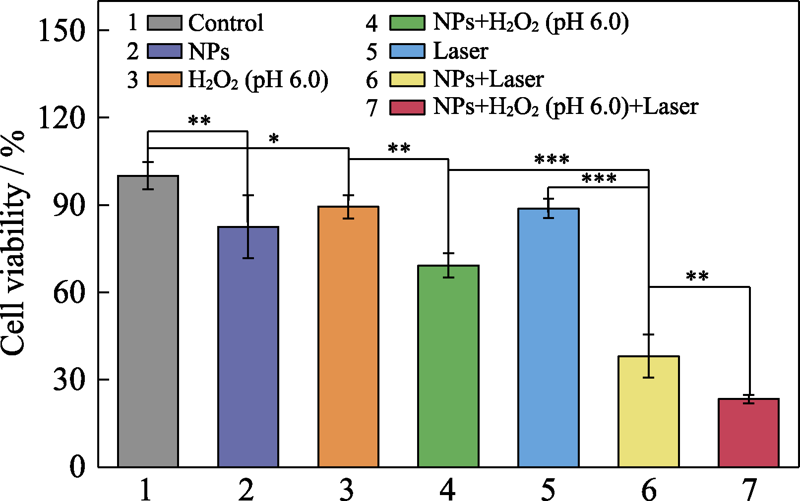
图11 Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA纳米颗粒对MDA-MB-231细胞的联合治疗评估(*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)
Fig. 11 Synergistic therapeutic effect of Fe(VI)@PCN@BSA nanoparticles on MDA-MB-231 cells (*P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001)
| [1] |
LIU CHUANG, XING JIE, AKAKURU OZIOMA UDOCHUKWU, et al. Nanozymes-engineered metal-organic frameworks for catalytic cascades-enhanced synergistic cancer therapy. Nano Letters, 2019, 19(8): 5674-5682.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
TANG ZHONGMIN, LIU YTANTAN, HE MINGYUAN, et al. Chemodynamic therapy: tumor microenvironment-mediated fenton and fenton-like reaction. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(4): 946-956.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
MIN HUAN, WANG JING, QI YINGQIU, et al. Biomimetic metal-organic framework nanoparticles for cooperative combination of antiangiogenesis and photodynamic therapy for enhanced efficacy. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(15): 1808200.
DOI URL |
| [4] | DAI XINXIN, DU TING, HAN KAI. Engineering nanoparticles for optimized photodynamic therapy. ACS Biomaterials Science & Engineering, 2019, 5(12): 6342-6354. |
| [5] |
CHANG MENGYU, WANG MAN, WANG MEIFANG, et al. A multifunctional cascade bioreactor based on hollow structured Cu2MoS4 for synergetic cancer chemo-dynamic therapy/starvation therapy/phototherapy/immunotherapy with remarkably enhanced efficacy. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(51): 1905271.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SCHUBERT JONAS, RADEKE CARMEN, FERY ANDREAS, et al. The role of pH, metal ions and their hydroxides in charge reversal of protein-coated nanoparticles. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2019, 21(21): 11011-11018.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZENG JINYUE, ZHANG MINGKANG, PENG MENGYUN, et al. Porphyrinic metal-organic frameworks coated gold nanorods as a versatile nanoplatform for combined photodynamic/photothermal/ chemotherapy of tumor. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(8): 1705451.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
CHEN JIAJIE, LIU JIAXING, HU YAPING, et al. Metal-organic framework-coated magnetite nanoparticles for synergistic magnetic hyperthermia and chemotherapy with pH-triggered drug release. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2019, 20(1): 1043-1054.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
CHEN JIAJIE, ZHU YUFANG, WU CHENGTIE, et al. Nanoplatform-based cascade engineering for cancer therapy. Chemical Society Reviews, 2020, 49(24): 9057-9094.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WANG ZHENG, ZHANG FAN, SHAO DAN, et al. Janus nanobullets combine photodynamic therapy and magnetic hyperthermia to potentiate synergetic anti-metastatic immunotherapy. Advanced Science, 2019, 6(22): 1901690.
DOI URL |
| [11] | ZHANG YA-RU, LIN RUN, LI HONG-JUN, et al. Strategies to improve tumor penetration of nano-medicines through nanoparticle design. Wiley Interdisciplinary Reviews-Nanomedicine and Nanobiotechnology, 2019, 11(1): e1519. |
| [12] |
PRASAD MINAKSHI, LAMBE UPENDRA P, BRAR BASANTI, et al. Nanotherapeutics: an insight into healthcare and multi- dimensional applications in medical sector of the modern world. Biomedicine & Pharmacotherapy, 2018, 97: 1521-1537.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LU KUANGDA, AUNG THEIET, GUO NINING, et al. Nanoscale metal-organic frameworks for therapeutic, imaging, and sensing applications. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(37): 1707634.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
MAO FANGXIN, WEN LING, SUN CAIXIA, et al. Ultrasmall biocompatible Bi2Se3 nanodots for multimodal imaging-guided synergistic radiophotothermal therapy against cancer. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(12): 11145-11155.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WU CHUANDE, ZHAO MIN. Incorporation of molecular catalysts in metal-organic frameworks for highly efficient heterogeneous catalysis. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(14): 1605446.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
CHEN JIAJIE, LIN SHIYANG, ZHAO DOUDOU, et al. Palladium nanocrystals-engineered metalorganic frameworks for enhanced tumor inhibition by synergistic hydrogen/photodynamic therapy. Advanced Functional Materials, 2020, 31(4): 2006853.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG SHUNZHI, MCGUIRK C MICHAEL, D’AQUINO ANDREA, et al. Metal-organic framework nanoparticles. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(37): 1800202.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CHEN HUANG, ZHANG LINGYU, LIU SONG, et al. Double enhanced energy storage density via polarization gradient design in ferroelectric poly(vinylidene fluoride)-based nanocomposites. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 411(18): 128585.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHANG YAN, WANG FAMING, LIU CHAOQUN, et al. Nanozymes decorated metal-organic frameworks for enhanced photodynamic therapy. ACS Nano, 2018, 12(1): 651-661.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
FU JINGKE, LI TAO, ZHU YINGCHUN, et al. Ultrasound- activated oxygen and ROS generation nanosystem systematically modulates tumor microenvironment and sensitizes sonodynamic therapy for hypoxic solid tumors. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(51): 1906195.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
NOVIKOV ALEXANDER S, KUZNETSOV MAXIM L, POMBEIRO ARMANDO J L, et al. Generation of HO• radical from hydrogen peroxide catalyzed by aqua complexes of the group III metals [M(H2O)n]3+ (M=Ga, In, Sc, Y, or La): a theoretical study. ACS Catalysis, 2013, 3(6): 1195-1208.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LIN WENXIN, GONG JIANQIU, FANG LIQUAN, et al. A photodynamic system based on endogenous bioluminescence for in vitro anticancer studies. Zeitschrift fur Anorganische und Allgemeine Chemie, 2019, 645(18/19): 1161-1164.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
PARK JIHYE, JIANG QIN, FENG DAWEI, et al. Size-controlled synthesis of porphyrinic metal-organic framework and functionalization for targeted photodynamic therapy. Journal American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(10): 3518-3525.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
ZHAO WEI, ZHAO YONGMEI, WANG QINGFU, et al. Remote light-responsive nanocarriers for controlled drug delivery: advances and perspectives. Small, 2019, 15(45): 1903060.
DOI URL |
| [25] | ElSHAMI FAWZYA I, RAMADAN ABD EL-MOTALEB M, IBRAHIM MOHAMED M, et al. Metformin containing nickel (II) complexes: synthesis, structural characterization, binding and kinetic interactions with BSA, antibacterial and in-vitro cytotoxicity studies. Applied Organometallic Chemistry, 2020, 34(3): e5437. |
| [26] |
NIU JIN, LIANG JINGJING, GAO ANG, et al. Micropore-confined amorphous SnO2 subnanoclusters as robust anode materials for Na-ion capacitors. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 7(38): 21711-21721.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZHOU BENQING, SONG JUN, WANG MENG, et al. BSA- bioinspired gold nanorods loaded with immunoadjuvant for the treatment of melanoma by combined photothermal therapy and immunotherapy. Nanoscale, 2018, 10(46): 21640-21647.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LIU WEI, WANG YONGMEI, LI YUHAO, et al. Fluorescent imaging-guided chemotherapy-and photodynamic dual therapy with nanoscale porphyrin metal-organic framework. Small, 2017, 13(17): 1603459.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SHOME ARPITA, RATHER ADIL MAJEED, MANNA UTTAM. Chemically reactive protein nanoparticles for synthesis of a durable and deformable superhydrophobic material. Nanoscale Advances, 2019, 1(5): 1746-1753.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZHANG YUAN, XING YANG, XIAN MING, et al. Folate- targeting and bovine serum albumin-gated mesoporous silica nanoparticles as a redox-responsive carrier for epirubicin release. New Journal of Chemistry, 2019, 43(6): 2694-2701.
DOI URL |
| [31] | GUO MINGZHEN, HE JIANAG, MA SHUANG, et al. Determination of Hg2+ based on the selective enhancement of peroxidase mimetic activity of hollow porous gold nanoparticles. Nano Brief Reports and Reviews, 2017, 12(4): 1750050. |
| [32] | FENG WEI, HAN XIUGUO, WANG RONGYAN, et al. Nanocatalysts-augmented and photothermal-enhanced tumor-specific sequential nanocatalytic therapy in both NIR-I and NIR-II biowindows. Advance Material, 2019, 31(5): 1805919. |
| [33] | ZHANG YONGHE, WANG BEILEI, ZHAO RUIBO, et al. Multifunctional nanoparticles as photosensitizer delivery carriers for enhanced photodynamic cancer therapy. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Application, 2020, 115: 111099. |
| [34] |
HANDE GUNDYZ, SAFACAN KONLEMEN, EENGIN U AKKAYA. Singlet oxygen probes: diversity in signal generation mechanisms yields a larger color palette. Coordination Chemistry Reviews, 2021, 429: 213641.
DOI URL |
| [35] | YIN SHENGYAN, SONG GUOSHENG, YANG YUE, et al. Persistent regulation of tumor microenvironment via circulating catalysis of MnFe2O4@metal-organic frameworks for enhanced photodynamic therapy. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019, 29(25): 2006853. |
| [36] | BAJAJ AVINASH, SAMANTA BAPPADITYA, YAN HAOHENG, et al. Stability, toxicity and differential cellular uptake of protein passivated-Fe3O4 nanoparticles. Journal of Materials Chenistry, 2009, 19(35): 6328-6331. |
| [37] |
LIN LISEN, SONG JIBIN, SONG LIANG, et al. Simultaneous fenton-like ion delivery and glutathione depletion by MnO2-based nanoagent to enhance chemodynamic therapy. Angewandte Chemie- International Edition, 2018, 57(18): 4902-4906.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
TARPEY MARGARRT M, FRIDOVICH IRWIN. Methods of detection of vascular reactive species nitric oxide, superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and peroxynitrite. Circulation Research, 2001, 89(3): 224.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
ETHIRAJAN MANIVANNAN, CHEN YIHUI, JOSHI PENNY, et al. The role of porphyrin chemistry in tumor imaging and photodynamic therapy. Chemical Society Reviews, 2011, 40(1): 340-362.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
CHEN JIAJIE, ZHU YUFANG, KASKEL STEFAN. Porphyrin- based metal-organic frameworks for biomedical applications. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition, 2020, 60(10): 5010-5035.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 张笑宇, 刘永盛, 李然, 李耀刚, 张青红, 侯成义, 李克睿, 王宏志. 基于Cu3(HHTP)2薄膜的离子液体电致变色电极[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 883-890. |
| [2] | 洪佳辉, 马冉, 仵云超, 文涛, 艾玥洁. MOFs自牺牲模板法制备CoNx/g-C3N4纳米材料用作高效光催化还原U(VI)[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 741-749. |
| [3] | 白志强, 赵璐, 白云峰, 冯锋. MXenes的制备、性质及其在肿瘤诊疗中的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 361-375. |
| [4] | 王晶, 徐守冬, 卢中华, 赵壮壮, 陈良, 张鼎, 郭春丽. 钠离子电池中空结构CoSe2/C负极材料的制备及储钠性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1344-1350. |
| [5] | 杨劢, 朱敏, 陈雨, 朱钰方. FePS3纳米片制备及其体外光热-光动力学联合治疗性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1074-1082. |
| [6] | 翟婉如,王佳惠,王茂槐,杜雪梅,魏淑贤. 金属有机框架材料中CO2/N2吸附与分离的理论研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 697-702. |
| [7] | 李国东, 姬国勋, 孙新利, 杜伟, 刘伟, 王殳凹. 层状金属有机框架材料用于水溶液中137Cs的高效去除[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(3): 367-372. |
| [8] | 曾雨淋, 陈佳杰, 田正芳, 朱敏, 朱钰方. 介孔有机硅为载体的纳米递送系统制备及其体外化疗-光热联合治疗性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(12): 1365-1372. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||