无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (11): 1154-1162.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210076
所属专题: 【能源环境】量子点
收稿日期:2021-02-05
修回日期:2021-04-13
出版日期:2021-11-20
网络出版日期:2021-04-25
通讯作者:
王晓娟, 副教授. E-mail: xwang@upc.edu.cn
作者简介:刘 彩(1996-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: liucai662@163.com
基金资助:
LIU Cai( ), LIU Fang, HUANG Fang, WANG Xiaojuan(
), LIU Fang, HUANG Fang, WANG Xiaojuan( )
)
Received:2021-02-05
Revised:2021-04-13
Published:2021-11-20
Online:2021-04-25
Contact:
WANG Xiaojuan, associate professor. E-mail: xwang@upc.edu.cn
About author:LIU Cai(1996-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: liucai662@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
光催化降解技术能够高效去除废水中的有机污染物, 具有广阔的应用前景。本研究以海藻为碳源, 采用微波水热法制备海藻基碳量子点(CDs), 并进一步合成CDs-Cu-TiO2复合材料作为可见光催化剂用于污染物降解。结果表明, 复合材料中CDs、Cu2+与TiO2紧密结合在一起, 可见光区吸收明显增强, 荧光发射效率降低。CDs与Cu2+的引入产生协同效应, 使复合材料的禁带宽度降低到2.35 eV, 并有效抑制了电子-空穴的复合。以罗丹明B为污染物模型的光催化性能实验显示, 海藻基CDs-Cu-TiO2复合材料在可见光照射下降解RhB的一级反应速率常数能够达到纯TiO2纳米颗粒的6.4倍, 150 min降解率接近100%, 是TiO2纳米颗粒的2倍。
中图分类号:
刘彩, 刘芳, 黄方, 王晓娟. 海藻基CDs-Cu-TiO2复合材料的制备及其光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1154-1162.
LIU Cai, LIU Fang, HUANG Fang, WANG Xiaojuan. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Alga-based CDs-Cu-TiO2 Composite Material[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1154-1162.

图3 样品(A)TiO2, (B)CDs, (C, D)CDs-Cu-TiO2的TEM照片; (E)CDs-Cu-TiO2的SAED图片; (F)CDs-TiO2和CDs-Cu-TiO2样品的EDS分析
Fig. 3 TEM images of (A) TiO2 , (B) CDs, (C, D) CDs-Cu-TiO2; (E) SAED image of CDs-Cu-TiO2 composite; (F) EDS patterns of CDs-TiO2 and CDs-Cu-TiO2 composite
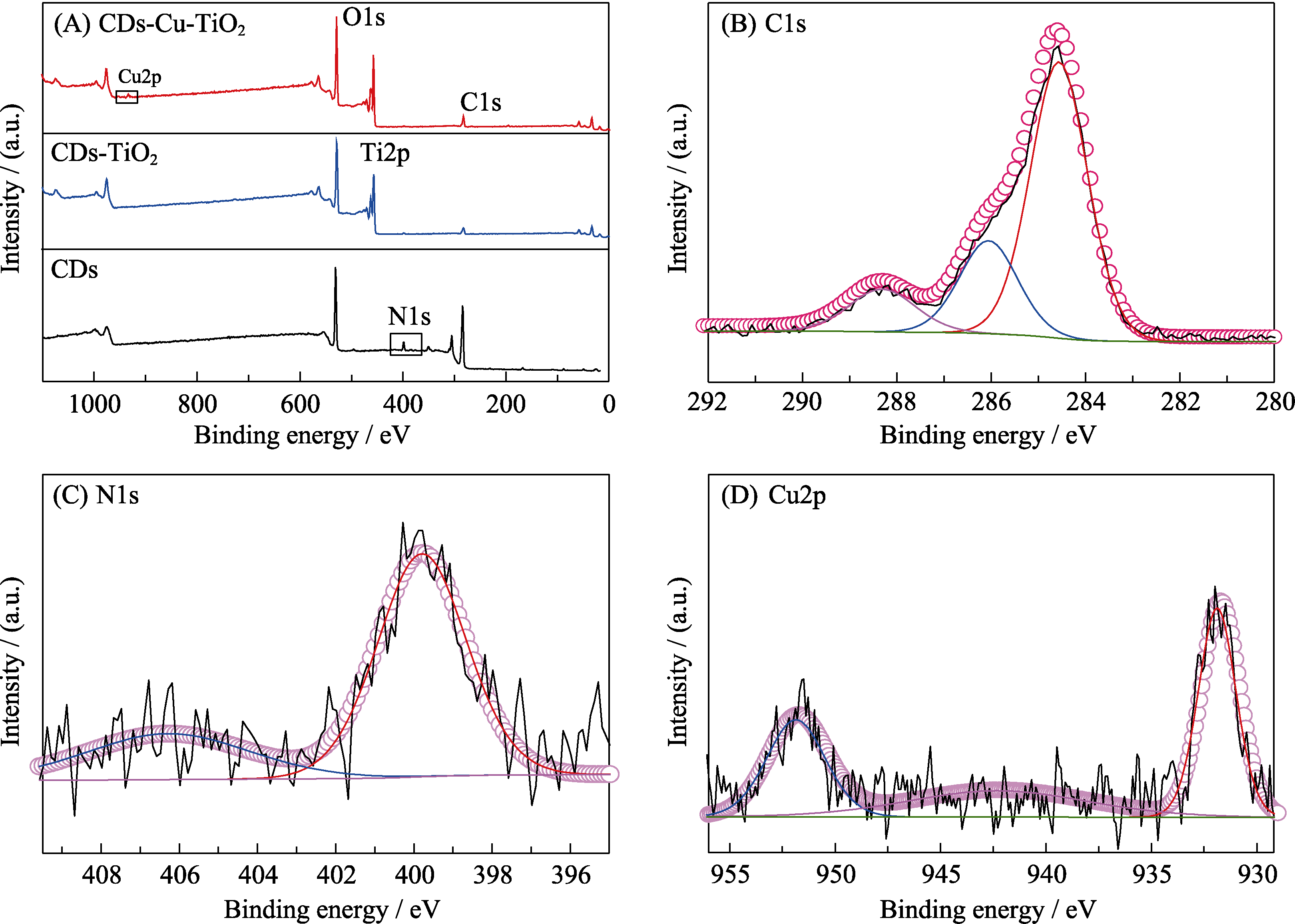
图4 (A)不同样品的XPS全谱图; CDs-Cu-TiO2的(B)C1s, (C)N1s, (D)Cu2p的高分辨分峰拟合谱
Fig. 4 (A) XPS survey spectra of different materials; XPS spectra of (B) C1s, (C) N1s, and (D) Cu2p for the CDs-Cu-TiO2 composite
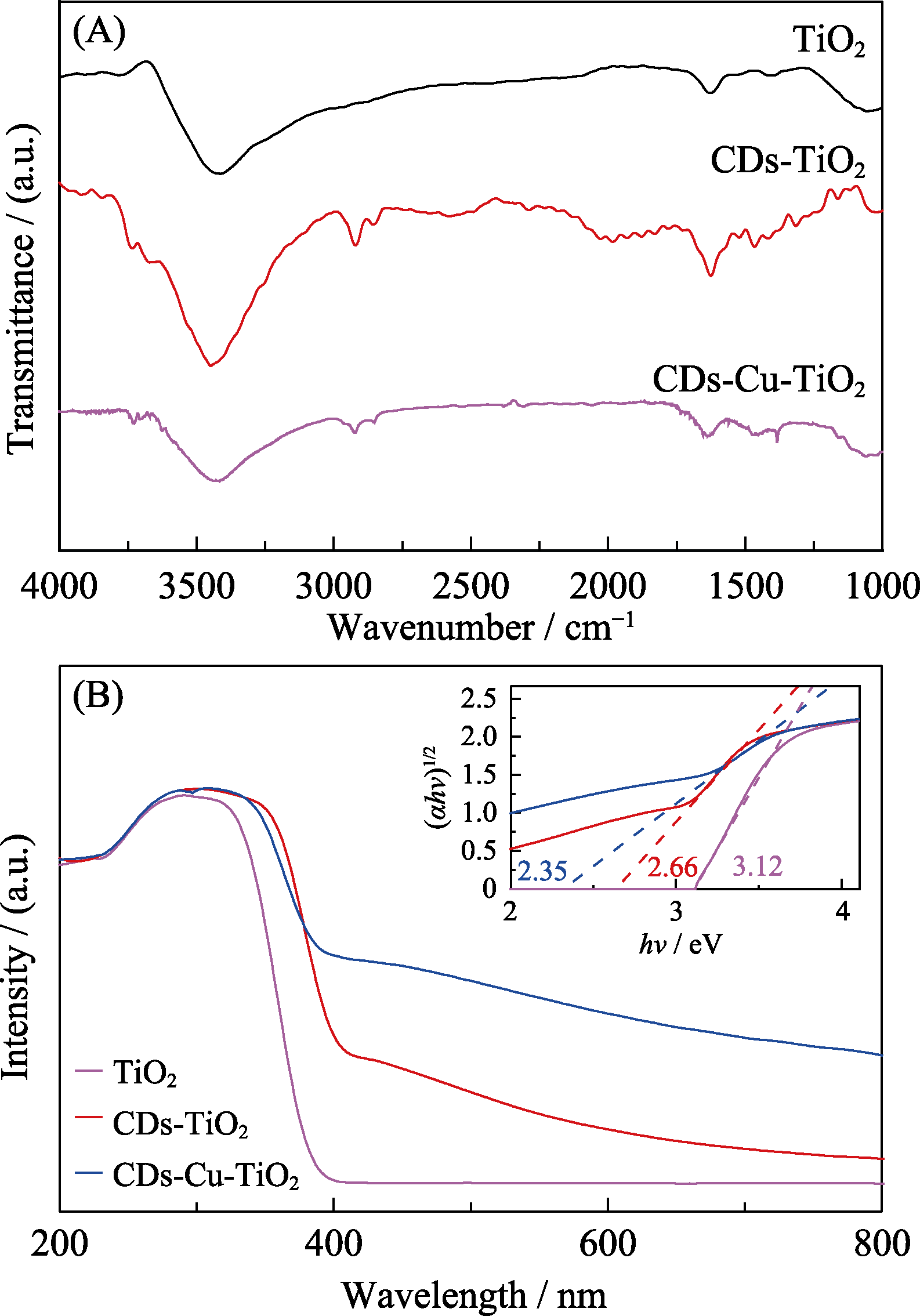
图5 复合材料的(A)红外光谱和(B)紫外-可见漫反射光谱
Fig. 5 (A)FT-IR spectra and (B) UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra of TiO2, CDs-TiO2 and CDs-Cu-TiO2 composite with inset showing the Tauc’s plots
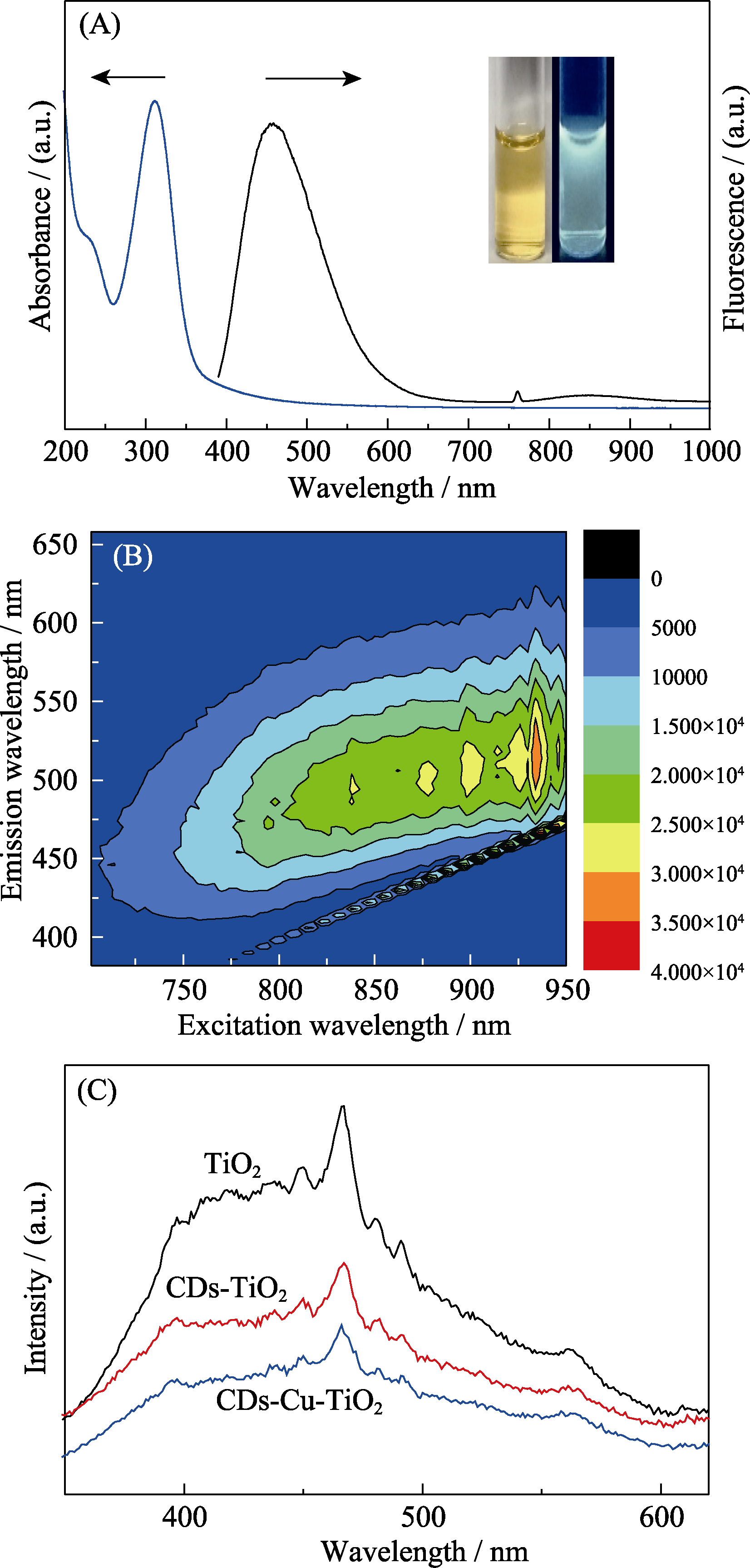
图6 (A)CDs的紫外-可见吸收光谱和荧光发射光谱(激发波长380 nm); (B)不同近红外波长激发的CDs溶液的荧光光谱; (C)TiO2, CDs-TiO2 和 CDs-Cu-TiO2 样品的荧光光谱(激发波长320 nm)
Fig. 6 (A) UV-Vis absorption spectrum and FL spectrum (λex= 380 nm) of CDs; (B) Photoluminescence emission spectra of CDs at different near infrared excitation wavelengths; (C) FL spectra (λex=320 nm) of TiO2, CDs-TiO2 and CDs-Cu-TiO2 composite
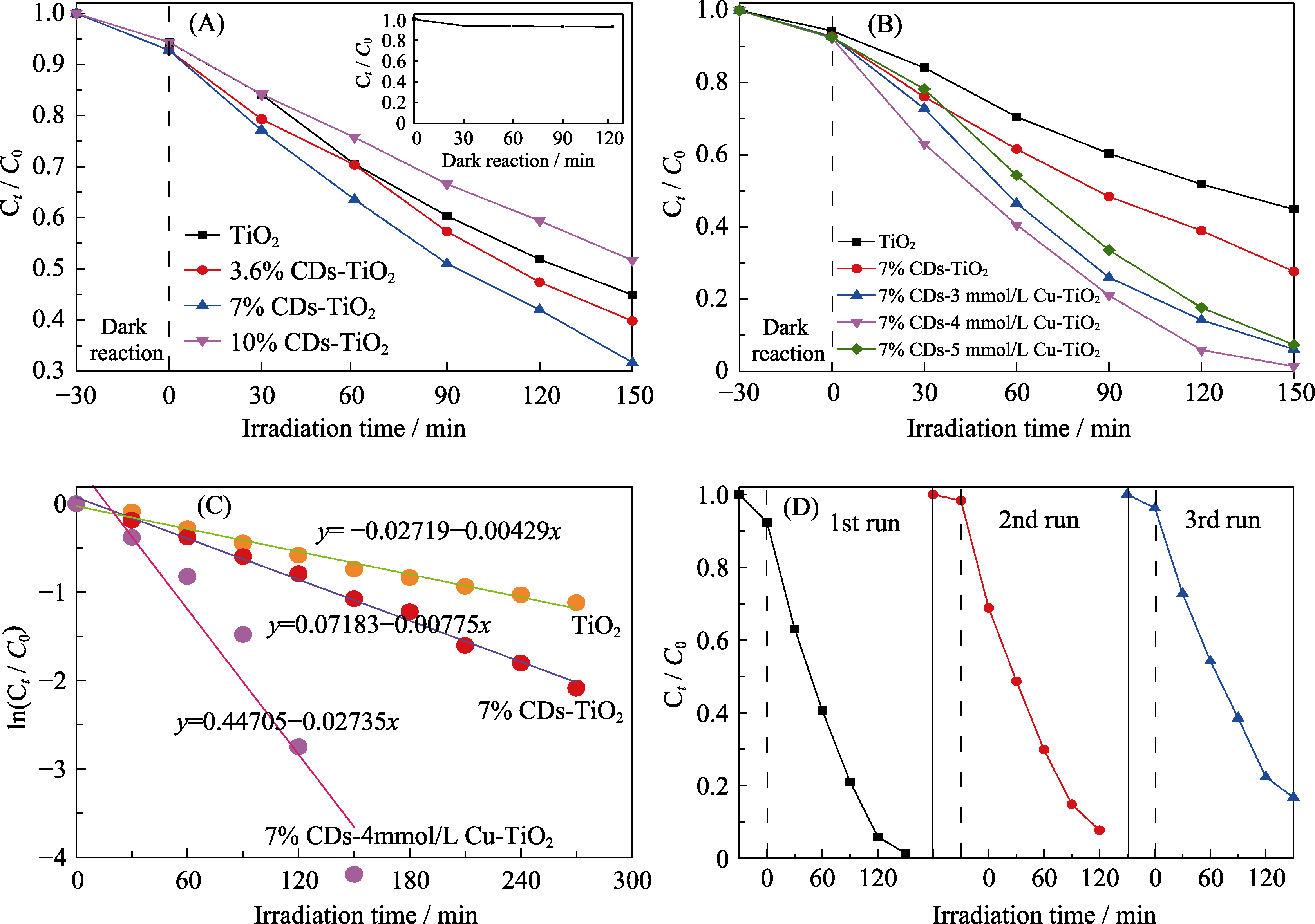
图7 (A)不同配比CDs-TiO2催化剂和(B)不同配比CDs-Cu-TiO2催化剂可见光降解RhB; (C)不同催化剂可见光下降解RhB的一级动力学分析; (D)CDs-Cu-TiO2催化降解RhB的循环实验
Fig. 7 RhB degradation under visible light irradiation using CDs-TiO2 (A) or CDs-Cu-TiO2 (B) as the photocatalyst; (C) the first order kinetics of RhB degradation in the presence of various photocatalysts; (D) recycling runs of the photocatalytic activity of CDs-Cu-TiO2 toward RhB degradation
| Atomic content of each element in CDs-Cu-TiO2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Ti2p | C1s | N1s | O1s | Cu2p |
| /% | 27.11 | 13.61 | 1.14 | 57.21 | 0.93 |
表1 CDs-Cu-TiO2中各元素的原子含量分析
Table 1 Analysis of the atomic content of each element in CDs-Cu-TiO2 composite
| Atomic content of each element in CDs-Cu-TiO2 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Element | Ti2p | C1s | N1s | O1s | Cu2p |
| /% | 27.11 | 13.61 | 1.14 | 57.21 | 0.93 |
| [1] |
ZHU Z, WU P, LIU G E, et al. Ultrahigh adsorption capacity of anionic dyes with sharp selectivity through the cationic charged hybrid nanofibrous membranes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017, 313:957-966.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
YE Y, WAN J, LI Q, et al. Catalytic oxidation of dyeing wastewater by copper oxide activating persulfate: performance, mechanism and application. International Journal of Environmental Research, 2020, 15:1-10.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
MARTINS N C T, ÂNGELO J, GIRÃO A V, et al. N-doped carbon quantum dots/TiO2 composite with improved photocatalytic activity. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2016, 193:67-74.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
SUN M, HUANG W, CHENG H, et al. Degradation of dye in wastewater by Homogeneous Fe(VI)/NaHSO3 system. Chemosphere, 2019, 228:595-601.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
BHAVIYA RAJ R, UMADEVI M, PARIMALADEVI R. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of textile dyeing wastewater under UV and visible light using ZnO/MgO nanocomposites as a novel photocatalyst. Particulate Science and Technology, 2020, 38(7):812-820.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
GARBA Z N, XIAO W, ZHOU W, et al. Process optimization and synthesis of lanthanum-cobalt perovskite type nanoparticles (LaCoO3) prepared by modified proteic method: application of response surface methodology. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2019, 36(11):1826-1838.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
CAO Z, ZHANG J, ZHANG J, et al. Degradation pathway and mechanism of reactive brilliant red X-3B in electro-assisted microbial system under anaerobic condition. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017, 329:159-165.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
QU A, XIE H, XU X, et al. High quantum yield graphene quantum dots decorated TiO2 nanotubes for enhancing photocatalytic activity. Applied Surface Science, 2016, 375:230-241.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
QIAO S, FAN B, YANG Y, et al. Copper nanoparticle/carbon quantum dots hybrid as green photocatalyst for high-efficiency oxidation of cyclohexane. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(54):43058-43064.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
HUNGE Y M, YADAV A A, LIU S, et al. Sonochemical synthesis of CZTS photocatalyst for photocatalytic degradation of phthalic acid. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2019, 56:284-289.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
HUNGE Y M, YADAV A A, KHAN S, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of bisphenol a using titanium dioxide@nanodiamond composites under UV light illumination. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2021, 582:1058-1066.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
TURKTEN N, BEKBOLET M. Photocatalytic performance of titanium dioxide and zinc oxide binary system on degradation of humic matter. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry, 2020, 401:112748.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
TEH C M, MOHAMED A R. Roles of titanium dioxide and ion-doped titanium dioxide on photocatalytic degradation of organic pollutants (phenolic compounds and dyes) in aqueous solutions: a review. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509(5):1648-1660.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
WANG J, WANG G, WEI X, et al. ZnO nanoparticles implanted in TiO2 macrochannels as an effective direct Z-scheme heterojunction photocatalyst for degradation of RhB. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 456:666-675.
DOI URL |
| [15] | WANG P L X Y, SHI Z L, LI H T. Syergistic effect of Ag and Ag2O on photocatalytic H2-evolution performance of TiO2. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(7):781-788. |
| [16] |
TEK B, YURDAKAL S, ÖZCAN L, et al. N-doped anatase/rutile photocatalysts for the synthesis of aromatic aldehydes under ultraviolet and solar irradiation. Science of Advanced Materials, 2015, 7(11):2306-2319.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
WANG X C, DENG H, JIANG Z Y, et al. Photocatalytic reduction of Re (VII) on amorphous TiO2/g-C3N4 derived from different N sources. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(12):1340-1348.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WU T, ZHU X, XING Z, et al. Greatly improving electrochemical N2 reduction over TiO2 nanoparticles by iron doping. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 58(51):18449-18453.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
PONGWAN P, WETCHAKUN K, PHANICHPHANT S, et al. Enhancement of visible-light photocatalytic activity of Cu-doped TiO2 nanoparticles. Research on Chemical Intermediates, 2016, 42(4):2815-2830.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
LIU L, GAO F, ZHAO H, et al. Tailoring Cu valence Tailoring Cu valence and oxygen vacancy in Cu/TiO2 catalysts for enhanced CO2 photoreduction efficiency. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2013, 134-135:349-358.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WANG X, SUN X, HE H, et al. A two-component active targeting theranostic agent based on graphene quantum dots. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2015, 3(17):3583-3590.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHANG Q Q, CHEN B B, ZOU H Y, et al. Inner filter with carbon quantum dots: a selective sensing platform for detection of hematin in human red cells. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2018, 100:148-154.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHANG J, LIU Q, HE H, et al. Coal tar pitch as natural carbon quantum dots decorated on TiO2 for visible light photodegradation of rhodamine B. Carbon, 2019, 152:284-294.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
WANG J, WEI J, SU S, et al. Novel fluorescence resonance energy transfer optical sensors for vitamin B12 detection using thermally reduced carbon dots. New Journal of Chemistry, 2015, 39(1):501-507.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WANG J, LI R S, ZHANG Z H, et al. Highly fluorescent carbon dots as selective and visual probes for sensing copper ions in living cells via an electron transfer process. Biosensors and Bioelectronics, 2017, 97:157-163.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
HUA J, YANG J, ZHU Y, et al. Highly fluorescent carbon quantum dots as nanoprobes for sensitive and selective determination of mercury (II) in surface waters. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2017, 187:149-155.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
GEDDA G, LEE C Y, LIN Y C, et al. Green synthesis of carbon dots from prawn shells for highly selective and sensitive detection of copper ions. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2016, 224:396-403.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
BAIG M M F, CHEN Y C. Bright carbon dots as fluorescence sensing agents for bacteria and curcumin. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2017, 501:341-349.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
JOSHI P N, MATHIAS A, MISHRA A. Synthesis of ecofriendly fluorescent carbon dots and their biomedical and environmental applications. Materials Technology, 2018, 33(10):672-680.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
SABET M, MAHDAVI K. Green synthesis of high photoluminescence nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots from grass via a simple hydrothermal method for removing organic and inorganic water pollutions. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 463:283-291.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
RAMAR V, MOOTHATTU S, BALASUBRAMANIAN K. Metal free, sunlight and white light based photocatalysis using carbon quantum dots from Citrus grandis: a green way to remove pollution. Solar Energy, 2018, 169:120-127.
DOI URL |
| [32] | FAN H, ZHANG M, BHANDARI B, et al. Food waste as a carbon source in carbon quantum dots technology and their applications in food safety detection. Trends in Food Science & Technology, 2020, 95:86-96. |
| [33] |
JIANG X, QIN D, MO G, et al. Ginkgo leaf-based synthesis of nitrogen-doped carbon quantum dots for highly sensitive detection of salazosulfapyridine in mouse plasma. Journal of Pharmaceutical and Biomedical Analysis, 2019, 164:514-519.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
SUI Y, WU L, ZHONG S, et al. Carbon quantum dots/TiO2 nanosheets with dominant (001) facets for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen evolution. Applied Surface Science, 2019, 480:810-816.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
WANG X, CHEN Q, ZHANG Z, et al. Novel enteromorpha prolifera based carbon dots: probing the radical scavenging of natural phenolic compounds. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2019, 174:161-167.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WANG F, WU Y, WANG Y, et al. Construction of novel Z-scheme nitrogen-doped carbon dots/{0 0 1} TiO2 nanosheet photocatalysts for broad-spectrum-driven diclofenac degradation: mechanism insight, products and effects of natural water matrices. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2019, 356:857-868.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
PERARASAN T, JOHN PETER I, MUTHU KUMAR A, et al. Copper doped titanium dioxide for enhancing the photovoltaic behavior in solar cell. Materials Today: Proceedings, 2019, DOI: 10.1016/j.matpr.2019.06.377.
DOI |
| [38] |
ZHANG T, LOW J, HUANG X, et al. Copper-decorated microsized nanoporous titanium dioxide photocatalysts for carbon dioxide reduction by water. ChemCatChem, 2017, 9(15):3054-3062.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
YAGHOUBI H, LI Z, CHEN Y, et al. Toward a visible light-driven photocatalyst: the effect of midgap-states-induced energy gap of undoped TiO2 nanoparticles. ACS Catalysis, 2015, 5(1):327-335.
DOI URL |
| [40] | ZHANG S, ZOU Y T, CHEN Z S, et al. Visible-light-driven activation of persulfate by RGO/g-C3N4 composites for degradation of BPA in wastewater. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3):329-336. |
| [41] |
ZHANG N, YANG M Q, TANG Z R, et al. Toward improving the graphene-semiconductor composite photoactivity via the addition of metal ions as generic interfacial mediator. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(1):623-633.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
QIAO S, FAN B, YANG Y, et al. Copper nanoparticle/carbon quantum dots hybrid as green photocatalyst for high-efficiency oxidation of cyclohexane. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(54):43058-43064.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈士昆, 王楚楚, 陈晔, 李莉, 潘路, 文桂林. 磁性Ag2S/Ag/CoFe1.95Sm0.05O4 Z型异质结的制备及光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1329-1336. |
| [2] | 蔡苗, 陈子航, 曾实, 杜江慧, 熊娟. CuS纳米片修饰Bi5O7I复合材料用于光催化还原Cr(VI)水溶液[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(6): 665-672. |
| [3] | 徐晶威,李政,王泽普,于涵,何祺,付念,丁帮福,郑树凯,闫小兵. 交错能带结构钕掺杂钒酸铋形貌与光催化性能调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 789-795. |
| [4] | 季邦, 赵文锋, 段洁利, 马立哲, 付兰慧, 杨洲. 泡沫镍网负载TiO2/WO3薄膜对乙烯的光催化降解[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 581-588. |
| [5] | 童 琴, 董亚梅, 严 良, 何丹农. 以海藻酸钠为基体的Ag/AgBr/TiO2整体式光催化剂的高效制备及其光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(6): 637-642. |
| [6] | 曲晓飞, 刘鲁英, 李雪钦, 杜芳林. Er3+掺杂TiO2空心球的制备及其光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(2): 183-188. |
| [7] | 赵昀云, 徐华蕊,朱归胜. 水热法制备海绵钛负载 TiO2 膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(2): 155-158. |
| [8] | 何 燕, 王 攀, 邓安平, 杨 静, 黄应平, 杨 勇. 反相胶束介质制备纳米CdS及可见光降解孔雀绿[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(11): 1221-1227. |
| [9] | 张耀君,张 莉. 复合材料CdS/Al-HMS的制备及可见光催化降解污染物制氢活性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(1): 66-70. |
| [10] | 周武艺,曹庆云,唐绍裘,刘英菊. 硫掺杂纳米 TiO2的掺杂机理及可见光催化活性的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(4): 776-782. |
| [11] | 侯亚奇,张弓,庄大明,吴敏生. 中频交流反应溅射TiO2薄膜制备及光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(5): 1073-1079. |
| [12] | 施利毅,李春忠,房鼎业,张剑平,朱以华,陈爱平. TiCl4-O2体系高温反应制备超细TiO2光催化材料的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 1999, 14(5): 717-725. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||