无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (12): 1256-1262.DOI: 10.15541/jim20210043
收稿日期:2021-01-25
修回日期:2021-03-03
出版日期:2021-12-20
网络出版日期:2021-04-05
通讯作者:
潘再法, 副教授. E-mail: panzaifa@zjut.edu.cn
作者简介:张 聪(1996-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 1765521429@qq.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Cong( ), LI Yurou, SHAO Kang, LIN Jing, WANG Kai, PAN Zaifa(
), LI Yurou, SHAO Kang, LIN Jing, WANG Kai, PAN Zaifa( )
)
Received:2021-01-25
Revised:2021-03-03
Published:2021-12-20
Online:2021-04-05
Contact:
PAN Zaifa, associate professor. E-mail: panzaifa@zjut.edu.cn
About author:ZHANG Cong(1996-), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 1765521429@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
发光防伪具有可视性强、设计简便的特点, 是众多防伪技术中常用的方法。传统防伪材料存在发光颜色单一、防伪图案和颜色静态的缺点, 易于模仿, 亟需开发可实现动态、可靠防伪性能的发光材料。本工作采用水热法制备了铬掺杂镓锗酸锌多色长余辉材料, 并对其余辉性能和动态防伪应用进行研究。实验结果表明: 通过改变镓锗比, 可以调节蓝绿光和红光区的发射强度, 实现发光颜色的可调。该系列样品在波长为254和365 nm的紫外光激发下分别呈现白色和红色, 发光颜色具有多模态发光特征。此外该系列样品具有多色的余辉发光, 不同颜色的衰减速率不同, 可以实现余辉颜色随时间发生动态变化的效果。据此设计成的防伪图案, 发光颜色在时间维度上具有动态变化特性, 可显著提高防伪安全性, 表明所制备的铬掺杂镓锗酸锌多色长余辉材料在动态防伪领域有重要的应用前景。
中图分类号:
张聪, 李雨柔, 邵康, 林静, 王锴, 潘再法. 多色长余辉材料的发光性质及动态防伪应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1256-1262.
ZHANG Cong, LI Yurou, SHAO Kang, LIN Jing, WANG Kai, PAN Zaifa. Luminescence Property of the Multicolor Persistent Luminescence Materials for Dynamic Anti-counterfeiting Applications[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(12): 1256-1262.
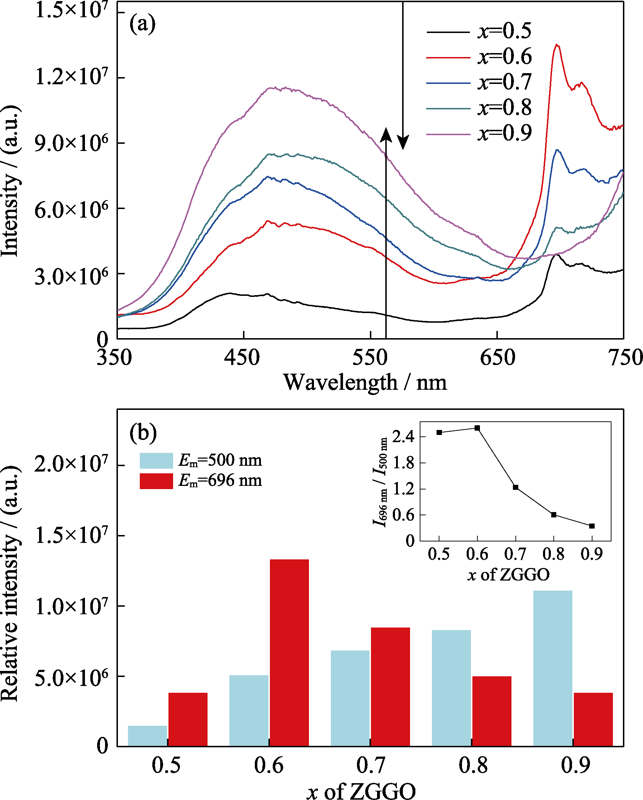
图3 ZGGO : Cr系列样品在273 nm激发下的发射谱(a), ZGGO : Cr系列样品在蓝绿光和近红外光区域的发光强度的对比图(b), 插图是I696 nm/I500 nm随x变化的曲线
Fig. 3 Normalized emission spectra of ZGGO : Cr series samples under 273 nm excitation (a), and comparison of luminescence intensity of ZGGO : Cr series samples in blue-green and NIR region (b) The inset in (b) shows the I696 nm/I500 nm changing with x
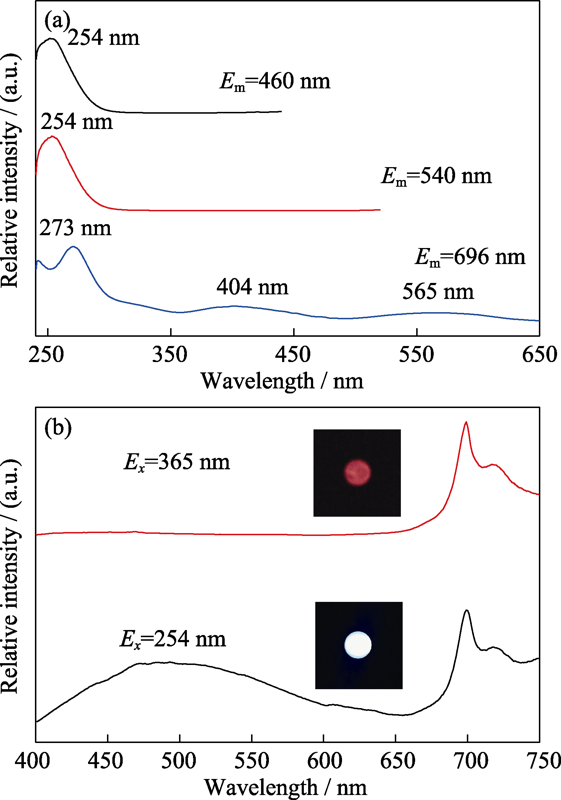
图4 x=0.7时ZGGO : Cr的激发光谱(a), x=0.7时ZGGO : Cr在254和365 nm激发下的发射光谱和发光照片(b)
Fig. 4 Normalized excitation spectra of ZGGO : Cr (x=0.7) (a), and emission spectra of ZGGO : Cr (x=0.7) under 254 nm and 365 nm excitation (b) Insets in (b) show the photographic images of the sample under 254 and 365 nm irradiation
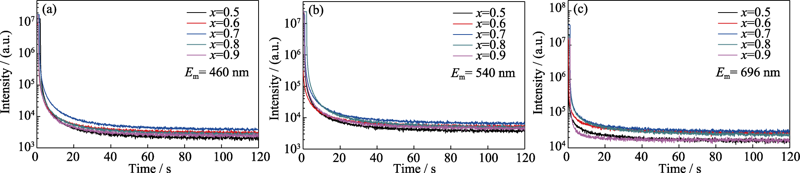
图5 ZGGO : Cr系列样品的余辉衰减曲线(预先用氙灯充能5 min)
Fig. 5 Persistent luminescence decay curves of ZGGO : Cr with Xenon lamp pre-charged for 5 min (a) 460 nm; (b) 540 nm; (c) 696 nm Colourful figures are available on website
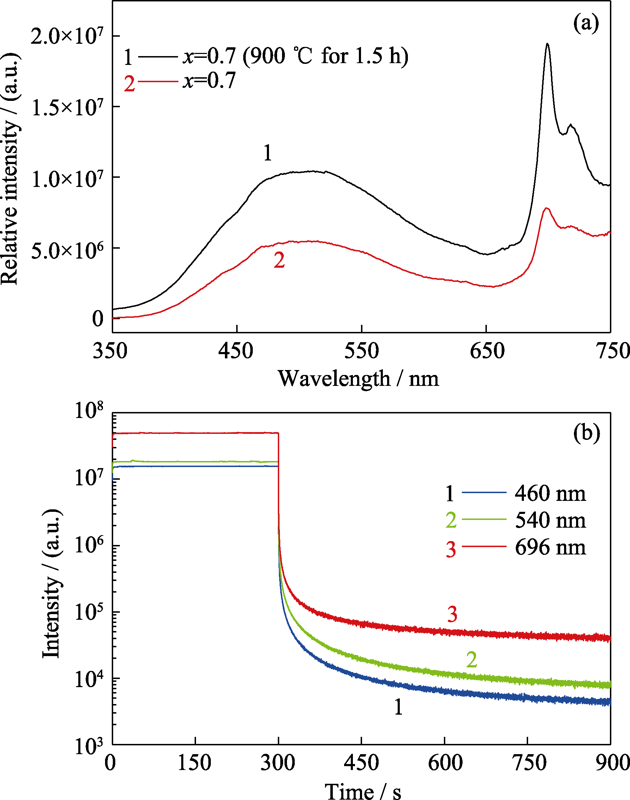
图6 ZGGO : Cr(x=0.7)样品高温处理前后的发射谱图(a)和900 ℃煅烧1.5 h后的余辉衰减曲线(氙灯预先照射5 min)(b)
Fig. 6 Emission spectra of ZGGO : Cr (x=0.7) samples before and after high temperature treatment (a) and persistent luminescence decay curves of ZGGO : Cr after high temperature treatment with Xenon lamp pre-charged for 5 min (b)
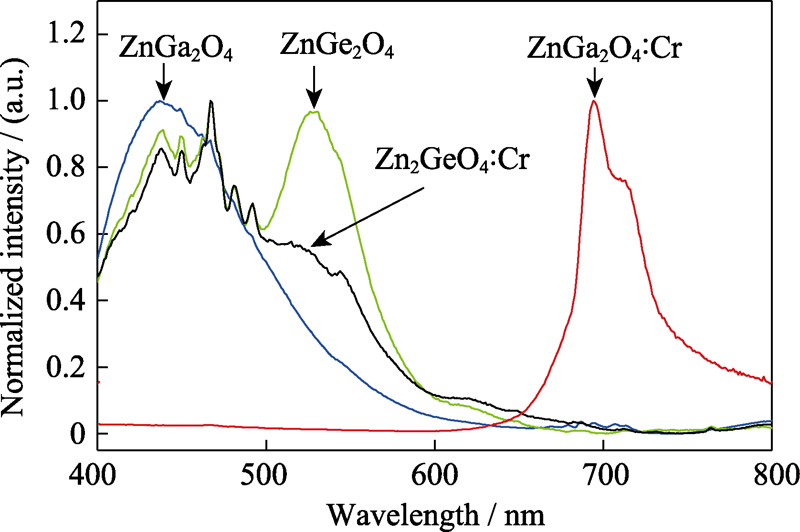
图7 Zn2GaO4, Zn2GeO4, Zn2GeO4 : Cr3+和Zn2GaO4 : Cr3+的发射光谱(λex=254 nm)
Fig. 7 Normalized emission spectra of Zn2GaO4, Zn2GeO4, Zn2GeO4 : Cr3+, and Zn2GaO4 : Cr3+ (λex=254 nm)

图8 防伪图案制作原理(a), 发光图案在254 nm紫外灯和不同衰减时间下的照片(b), 发光图案在365 nm紫外灯和不同衰减时间下的照片(c)
Fig. 8 Manufacturing principle of anti-counterfeiting pattern (a), images of the luminescent pattern under 254 nm UV lamp and different decay time (b), and images of the luminescent pattern under 365 nm UV lamp and different decay time (c)
| [1] |
ARPPE R, SØRENSEN T J. Physical unclonable functions generated through chemical methods for anti-counterfeiting. Nature Reviews Chemistry, 2017, 1(4): 0031.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LIM K T P, LIU H, LIU Y, et al. Holographic colour prints for enhanced optical security by combined phase and amplitude control. Nature Communications, 2019, 10(1): 25-32.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
ZHU S, MENG Q, WANG L, et al. Highly photoluminescent carbon dots for multicolor patterning, sensors, and bioimaging. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2013, 52(14): 3953-3957.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHOU W, ZHUANG J, LI W, et al. Towards efficient dual-emissive carbon dots through sulfur and nitrogen co-doped. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(32): 8014-8021.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
WANG L, TAN W H. Multicolor FRET silica nanoparticles by single wavelength excitation. Nano Letters, 2006, 6(1): 84-88.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
KRUTZIK P, NOLAN G. Fluorescent cell barcoding in flow cytometry allows high-throughput drug screening and signaling profiling. Nature Methods, 2006, 3: 361-368.
DOI URL |
| [7] | ZHOU B, HUANG J, YAN L, et al. Probing energy migration through precise control of interfacial energy transfer in nanostructure. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31: 1806308. |
| [8] |
YAO W, TIAN Q, TIAN B, et al. Dual upconversion nanophotoswitch for security encoding. Science China Materials, 2019, 62(3): 368-378.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
ZHAO S, WANG Z, MA Z, et al. Achieving multimodal emission in Zn4B6O13 : Tb3+, Yb3+ for information encryption and anti- counterfeiting. Inorganic Chemistry, 2020, 59(21): 15681-15689.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
WANG J, MA Q, ZHENG W, et al. One-dimensional luminous nanorods featuring tunable persistent luminescence for autofluorescence-free biosensing. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(8): 8185-8191.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GU L, SHI H, GU M, et al. Dynamic ultralong organic phosphorescence by photoactivation. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2018, 57(28): 8425-8431.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
KALININ Y V, PANDEY S, HONG J, et al. A chemical display: generating animations by controlled diffusion from porous voxels. Advanced Functional Materials, 2015, 25(26): 3998-4004.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
ZHANG Y, HUANG R, LI H, et al. Triple-mode emissions with invisible near-infrared after-glow from Cr3+-doped zinc aluminum germanium nanoparticles for advanced anti-counterfeiting applications. Small, 2020, 16(35): 2003121.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
GANGWAR A K, KANIKA K, KEDAWAT G, et al. Single excitable dual emissive novel luminescent pigment to generate advanced security features for anti-counterfeiting applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019, 7(44): 13867-13877.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
PAN Z, LU Y, LIU F. Sunlight-activated long-persistent luminescence in the near-infrared from Cr3+-doped zinc gallogermanates. Nature Materials, 2012, 11(1): 58-63.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
LI J Y, YAN X P. Synthesis of functionalized triple-doped zinc gallogermanate nanoparticles with superlong near-infrared persistent luminescence for long-term orally administrated bioimaging. Nanoscale, 2016, 8: 14965-14970.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
LI L, PAN F, TANNER P A, et al. Tunable dual visible and near- infrared persistent luminescence in doped zinc gallogermanate nanoparticles for simultaneous photosensitization and bioimaging. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2020, 3(2): 1961-1971.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
BAI Q, LI P, WANG Z, et al. Inducing tunable host luminescence in Zn2GeO4 tetrahedral materials via doping Cr3+. Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2018, 199: 179-188.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
ZHOU Z H, ZHENG W, KONG J T, et al. Rechargeable and LED- activated ZnGa2O4 : Cr3+ near-infrared persistent luminescence nanoprobes for background-free biodetection. Nanoscale, 2017, 9: 6846-6853.
DOI URL |
| [20] | WANG K, YAN L P, SHAO K, et al. Near-infrared afterglow enhancement and trap distribution analysis of silicon-chromium co-doped persistent luminescence materials Zn1+xGa2-2xSixO4:Cr3+. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 983-990. |
| [21] |
LI Y, GECEVICIUS M, QIU J R. Long persistent phosphors-from fundamentals to applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016, 45(8): 2090-2136.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
ZHANG Y, WU Z, GENG D, et al. Full color emission in ZnGa2O4: simultaneous control of the spherical morphology, luminescent, and electric properties via hydrothermal approach. Advanced Functional Materials, 2014, 24(42): 6581-6593.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
LIU Z, JING X, WANG L. Luminescence of native defects in Zn2GeO4. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2007, 154(6): H500-H506.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
CHI F F, WEI X T, JIANG B, et al. Luminescence properties and the thermal quenching mechanism of Mn2+ doped Zn2GeO4 long persistent phosphors. Dalton Transactions, 2018, 47(4): 1303-1311.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
HE H, ZHANG Y, PAN Q, et al. Controllable synthesis of Zn2GeO4 : Eu nanocrystals with multi-color emission for white light-emitting diodes. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2015, 3(21): 5419-5429.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 王锴, 严丽萍, 邵康, 张聪, 潘再法. 硅铬共掺杂尖晶石长余辉材料Zn1+xGa2-2xSixO4:Cr3+中近红外余辉的增强及陷阱分布分析[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 983-990. |
| [2] | 阿不都卡德尔·阿不都克尤木, 艾力江·吐尔地, 热娜古丽·阿不都热合曼, 马木提江·吐尔逊, 努尔比亚·努尔买提. Dy, Cr共掺杂ZnGa2O4长余辉纳米粒子的制备及发光性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(12): 1363-1369. |
| [3] | 沈冬冬, 季振国. 电子束还原SrAl2O4: (Eu2+, Dy3+)长余辉材料的力致发光研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(1): 93-96. |
| [4] | 邱 涛, 季振国, 孔 哲, 李红霞, 张尔攀. 长余辉夜光材料Sr4Al14O25:(Eu,Dy)的制备及性能优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(12): 1341-1344. |
| [5] | 栾 林,郭崇峰,黄德修. 锶铝比例对铝酸锶长余辉发光材料性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(1): 53-56. |
| [6] | 洪樟连,张朋越,黄秋平,樊先平,王民权. Y2O2S:0.03Eu,0.03Ti的长余辉特性及Ti向Eu3+的余辉传能机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(2): 329-334. |
| [7] | 毛大立,赵莉,常程康,费琴,姜岭. 纳米 Sr2MgSi2O7: Eu2+, Dy3+的长余辉发光行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2005, 20(1): 220-224. |
| [8] | 施朝淑,戚泽明. 长余辉(寿命)发光材料研究的最新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(5): 961-969. |
| [9] | 袁双龙,杨云霞,徐志珍,方斌. 掺杂对Y2O2S:Eu长余辉特性的影响及长余辉发光机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(3): 523-528. |
| [10] | 姜岭,常程康,毛大立. 长余辉发光材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(2): 268-274. |
| [11] | 林元华,南策文,张中太,王雨田. 热释发光-正电子湮灭法研究SrAl2O4基磷光体长余辉发光机制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(1): 201-206. |
| [12] | 耿杰,吴召平,陈玮,罗澜. SrAl2O4:Eu2+,Dy3+发光粉体的长余辉特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(2): 480-484. |
| [13] | 赵淑金,林元华,张中太,南策文. Eu2+离子在Sr2Al6O11基磷光体中发光行为的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(1): 225-228. |
| [14] | 林元华,陈清明,张中太,唐子龙. 烧成条件对长余辉蓄光玻璃光学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2000, 15(6): 982-986. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||