无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (8): 807-819.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200652
所属专题: 【虚拟专辑】LED发光材料
彭星淋1,2( ), 李淑星3(
), 李淑星3( ), 刘泽华4, 姚秀敏1,2, 解荣军3, 黄政仁1,2,4, 刘学建1,2(
), 刘泽华4, 姚秀敏1,2, 解荣军3, 黄政仁1,2,4, 刘学建1,2( )
)
收稿日期:2020-11-12
修回日期:2020-12-24
出版日期:2021-08-20
网络出版日期:2021-03-01
通讯作者:
刘学建, 研究员. E-mail:xjliu@mail.sic.ac.cn; 李淑星, 讲师. E-mail: lishuxing@xmu.edu.cn
作者简介:彭星淋(1995-), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: pengxinglin@student.sic.ac.cn
基金资助:
PENG Xinglin1,2( ), LI Shuxing3(
), LI Shuxing3( ), LIU Zehua4, YAO Xiumin1,2, XIE Rongjun3, HUANG Zhengren1,2,4, LIU Xuejian1,2(
), LIU Zehua4, YAO Xiumin1,2, XIE Rongjun3, HUANG Zhengren1,2,4, LIU Xuejian1,2( )
)
Received:2020-11-12
Revised:2020-12-24
Published:2021-08-20
Online:2021-03-01
Contact:
LIU Xuejian, professor. E-mail:xjliu@mail.sic.ac.cn; LI Shuxing, lecturer. E-mail: lishuxing@xmu.edu.cn
About author:PENG Xinglin(1995-), male, PhD candidate. E-mail: pengxinglin@student.sic.ac.cn
Supported by:摘要:
固态照明具有功率大、亮度高、体积小、节能环保等优点, 已成为21世纪最有前景的照明技术。作为固态照明关键材料, 荧光材料的性能直接决定固态照明器件的显色指数、流明效率和可靠性等技术参数。相较于荧光单晶、荧光玻璃、荧光薄膜及量子阱, 荧光陶瓷因具有优异的热学和光学性质及微观结构易调控等特点, 被认为是综合性能最优的大功率固态照明用荧光材料。未来, 荧光陶瓷将在汽车大灯、户外照明、激光电视、激光影院等领域得到更广泛的应用和发展, 具有广阔的市场前景。本文探讨了大功率固态照明用荧光陶瓷的设计原则, 重点介绍了目前研究相对较多的氧化物荧光陶瓷(主要指钇铝石榴石结构)和氮(氧)化物荧光陶瓷的研究进展, 最后对大功率固态照明用荧光陶瓷的未来发展方向进行了展望。
中图分类号:
彭星淋, 李淑星, 刘泽华, 姚秀敏, 解荣军, 黄政仁, 刘学建. 大功率固态照明用荧光陶瓷研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 807-819.
PENG Xinglin, LI Shuxing, LIU Zehua, YAO Xiumin, XIE Rongjun, HUANG Zhengren, LIU Xuejian. Phosphor Ceramics for High-power Solid-state Lighting[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 807-819.
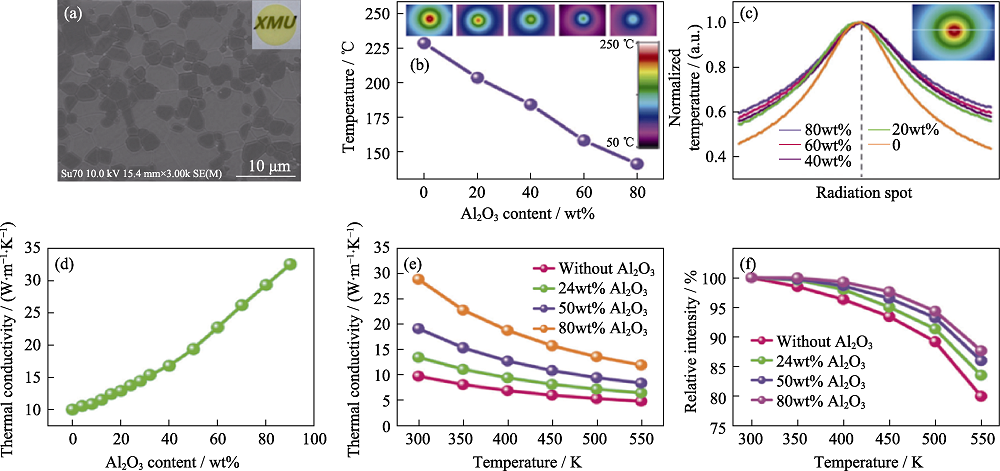
图2 Al2O3-YAG:Ce复相荧光陶瓷[11]
Fig. 2 Al2O3-YAG:Ce composite phosphor ceramics[11] (a) SEM image of the Al2O3-YAG:Ce composite ceramics; (b) Laser irradiation spot temperature of the ceramics varies with different Al2O3 contents; (c) Temperature distribution curves; (d) Thermal conductivity as a function of Al2O3 content; (e) Thermal conductivity as a function of the temperature; (f) Temperature-dependent integrated emission intensity of the composite ceramics Colorful figures are available on website
| Doped ions | Ion radius/nm | Occupied lattice | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y3+ | 0.1019 | A | [ |
| Gd3+ | 0.1053 | A | [ |
| Tb3+ | 0.104 | A | [ |
| Lu3+ | 0.0977 | A | [ |
| Mg2+ | 0.089 | A | [ |
| Sc3+ | 0.087 | A | [ |
| Al3+ | 0.0535 | B | [ |
| Sc3+ | 0.0745 | B | [ |
| Mg2+ | 0.072 | B | [ |
| Ga3+ | 0.062 | B | [ |
| Al3+ | 0.039 | C | [ |
| Si4+ | 0.026 | C | [ |
表1 石榴石体系荧光陶瓷不同格位掺杂离子及离子半径汇总表
Table 1 Doping ions and ionic radii of garnet phosphor ceramics at different lattice positions
| Doped ions | Ion radius/nm | Occupied lattice | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Y3+ | 0.1019 | A | [ |
| Gd3+ | 0.1053 | A | [ |
| Tb3+ | 0.104 | A | [ |
| Lu3+ | 0.0977 | A | [ |
| Mg2+ | 0.089 | A | [ |
| Sc3+ | 0.087 | A | [ |
| Al3+ | 0.0535 | B | [ |
| Sc3+ | 0.0745 | B | [ |
| Mg2+ | 0.072 | B | [ |
| Ga3+ | 0.062 | B | [ |
| Al3+ | 0.039 | C | [ |
| Si4+ | 0.026 | C | [ |
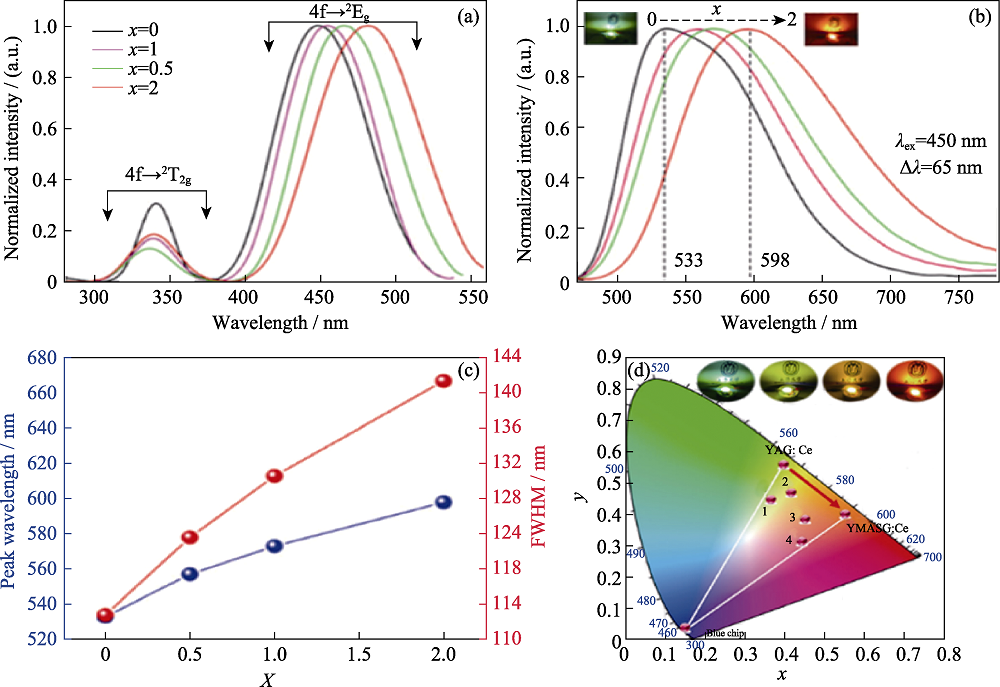
图3 YMASG:Ce荧光陶瓷[44]
Fig. 3 YMASG:Ce phosphor ceramics[44] (a) PLE spectra; (b) PL spectra; (c) Peak wavelength and FWHM; (d) Chromaticity color coordinates colorful figures are available on website
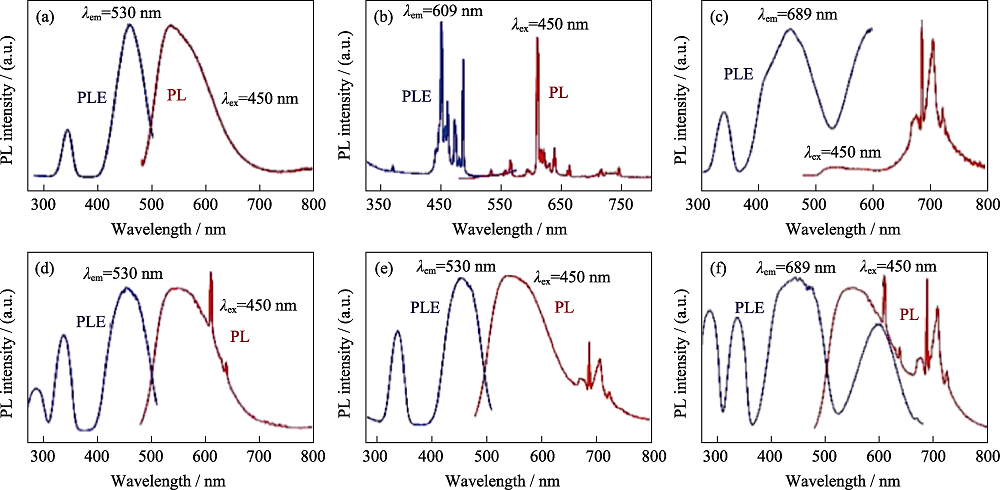
图4 YAG:Ce3+/Pr3+/Cr3+荧光陶瓷的激发和发射光谱[29]
Fig. 4 PL and PLE spectra of YAG:Ce3+/Pr3+/Cr3+phosphor ceramics[29] (a) YAG:Ce; (b) YAG:Pr; (c) YAG:Cr; (d) YAG:Ce,Pr; (e) YAG:Ce,Cr; (f) YAG:Ce,Pr,Cr
| Methods | Composition | Emission peak position/nm | CCT/K | CRI | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjust matrix chemical composition | GdYAG:Ce | 525-554 | 2968-4299 | 64.8 | [ |
| GdYAG:Ce | 528-550 | 3688-4782 | 67.1 | [ | |
| Al2O3-GdYAG:Ce | 550* | 5010 | 71.4 | [ | |
| MgAl2O4-GdYAG:Ce | 550* | 4543 | 70 | [ | |
| TbAG:Ce | 556-564 | 4000-4900 | - | [ | |
| Al2O3-TbAG:Ce | 555 | 3580 | 63 | [ | |
| TGAG:Ce | 550-570 | 3681 | 74.7 | [ | |
| GAGG:Ce | 568-574 | 3000 | 78.9 | [ | |
| GAGG:Ce | 570 | 2800 | 58.7 | [ | |
| YMASG:Ce | 537-577 | 4384 | 81 | [ | |
| YMASG:Ce | 533-598 | 2018-4516 | - | [ | |
| Al2O3-YMASG:Ce | 552-610 | 4860 | 82.5 | [ | |
| Adjust the luminescencecenter | YAG:Ce3+/Pr3+ | 535, 564, 609, 637 | - | 66.9 | [ |
| YAG:Ce3+/Cr3+ | 534, 677, 688, etc. | - | 72 | [ | |
| YAG:Ce3+/Cr3+ | 530, 690, 705 | 4329 | - | [ | |
| YAG:Ce3+/Pr3+/Cr3+ | 530, 609, 689, etc. | - | 78 | [ | |
| YAG:Ce3+/Mn2+ | 520-590 | 3870-5196 | 82.5 | [ | |
| YAG:Ce3+/Dy3+ | 496, 582, etc. | 5609 | - | [ | |
| LuAG:Dy3+ | 482, 583, 675,etc. | 3485-3619 | - | [ | |
| Composite red fluorescent material | LuAG:Ce/(Sr,Ca)AlSiN3:Eu | 515, 640 | 4450 | 94 | [ |
| LuAG:Ce/Eu-doped nitride | 565-587 | 5800 | 89.4 | [ | |
| YAG:Ce/Sr2Si5N8:Eu | 610* | 3952 | 82 | [ | |
| Al2O3-YAG:Ce/Red QD | 552, 634 | 3161-6035 | 80 | [ |
表2 石榴石型荧光陶瓷提高显色指数及降低相关色温的三种方法研究进展汇总表
Table 2 Summary of three methods for improving CRI and reducing CCT of garnet type phosphor ceramics
| Methods | Composition | Emission peak position/nm | CCT/K | CRI | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Adjust matrix chemical composition | GdYAG:Ce | 525-554 | 2968-4299 | 64.8 | [ |
| GdYAG:Ce | 528-550 | 3688-4782 | 67.1 | [ | |
| Al2O3-GdYAG:Ce | 550* | 5010 | 71.4 | [ | |
| MgAl2O4-GdYAG:Ce | 550* | 4543 | 70 | [ | |
| TbAG:Ce | 556-564 | 4000-4900 | - | [ | |
| Al2O3-TbAG:Ce | 555 | 3580 | 63 | [ | |
| TGAG:Ce | 550-570 | 3681 | 74.7 | [ | |
| GAGG:Ce | 568-574 | 3000 | 78.9 | [ | |
| GAGG:Ce | 570 | 2800 | 58.7 | [ | |
| YMASG:Ce | 537-577 | 4384 | 81 | [ | |
| YMASG:Ce | 533-598 | 2018-4516 | - | [ | |
| Al2O3-YMASG:Ce | 552-610 | 4860 | 82.5 | [ | |
| Adjust the luminescencecenter | YAG:Ce3+/Pr3+ | 535, 564, 609, 637 | - | 66.9 | [ |
| YAG:Ce3+/Cr3+ | 534, 677, 688, etc. | - | 72 | [ | |
| YAG:Ce3+/Cr3+ | 530, 690, 705 | 4329 | - | [ | |
| YAG:Ce3+/Pr3+/Cr3+ | 530, 609, 689, etc. | - | 78 | [ | |
| YAG:Ce3+/Mn2+ | 520-590 | 3870-5196 | 82.5 | [ | |
| YAG:Ce3+/Dy3+ | 496, 582, etc. | 5609 | - | [ | |
| LuAG:Dy3+ | 482, 583, 675,etc. | 3485-3619 | - | [ | |
| Composite red fluorescent material | LuAG:Ce/(Sr,Ca)AlSiN3:Eu | 515, 640 | 4450 | 94 | [ |
| LuAG:Ce/Eu-doped nitride | 565-587 | 5800 | 89.4 | [ | |
| YAG:Ce/Sr2Si5N8:Eu | 610* | 3952 | 82 | [ | |
| Al2O3-YAG:Ce/Red QD | 552, 634 | 3161-6035 | 80 | [ |
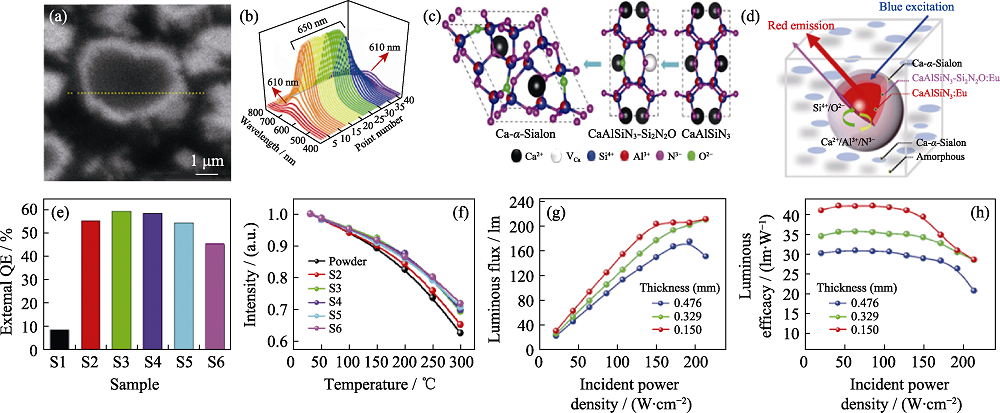
图5 CaAlSiN3:Eu2+荧光陶瓷[6, 58]
Fig. 5 CaAlSiN3:Eu2+ phosphor ceramics[6, 58] (a) Single CaAlSiN3: Eu2+ grain CL spectral line scan; (b) CL spectra; (c) Crystal structure transition; (d) Core-shell structure schematic diagram; (e) Quantum efficiency of samples; (f) Thermal stability of samples with different Si 3N4 and SiO2 contents; (g) Influence of incident power density on luminous flux; (h) Luminous efficiency of samples Colorful figures are available on website
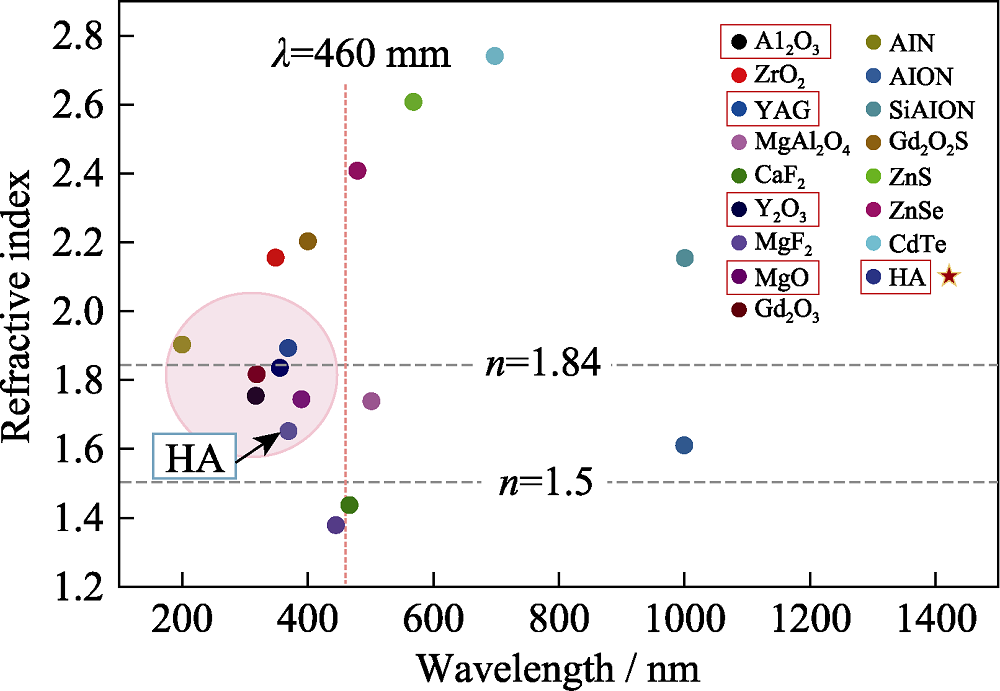
图6 常见透明陶瓷的透光区域和折射率[17]
Fig. 6 Light-transmitting area and refractive index of common transparent ceramics[17] Colorful figures are available on website
| [1] |
SCHUBERT E F, KIM J K. Solid-state light sources getting smart. Science , 2005, 308(5726):1274-1278.
DOI URL |
| [2] | WIERER J J, TSAO J Y, SIZOV D S. Comparison between blue lasers and light-emitting diodes for future solid-state lighting. Laser & Photonics Reviews , 2013, 7(6):963-993. |
| [3] | LI S, WANG L, HIROSAKI N, et al. Color conversion materials for high-brightness laser-driven solid-state lighting. Laser & Photonics Reviews , 2018, 12(12):1800173 |
| [4] |
FAN F, TURKDOGAN S, LIU Z, et al. A monolithic white laser. Nat. Nanotechnol. , 2015, 10(9):796-803.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
YAO Q, HU P, SUN P, et al. YAG:Ce3+ transparent ceramic phosphors brighten the next-generation laser-driven lighting. Adv. Mater. , 2020, 32(19):1907888.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
LI S X, TANG D M, TIAN Z F, et al. New insights into the microstructure of translucent CaAlSiN3:Eu2+ phosphor ceramics for solid-state laser lighting. Journal of Materials Chemistry C , 2017, 5(5):1042-1051.
DOI URL |
| [7] | LENEF A, KELSO J, ZHENG Y, et al. Radiance limits of ceramic phosphors under high excitation fluxes. Proceedings of SPIE , 2013, 8841:884107. |
| [8] |
XU Y R, LI S X, ZHENG P, et al. A search for extra-high brightness laser-driven color converters by investigating thermally-induced luminance saturation. Journal of Materials Chemistry C , 2019, 7(37):11449-11456.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
COZZAN C, LHEUREUX G, O'DEA N, et al. Stable, heat-conducting phosphor composites for high-power laser lighting. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces , 2018, 10(6):5673-5681.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
LI S, ZHU Q, TANG D, et al. Al2O3-YAG:Ce composite phosphor ceramic: a thermally robust and efficient color converter for solid state laser lighting. Journal of Materials Chemistry C , 2016, 4(37):8648-8654.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WANG J C, TANG X Y, ZHENG P, et al. Thermally self-managing YAG:Ce-Al2O3 color converters enabling high-brightness laser-driven solid state lighting in a transmissive configuration. Journal of Materials Chemistry C , 2019, 7(13):3901-3908.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
MA X G, LI X Y, LI J Q, et al. Pressureless glass crystallization of transparent yttrium aluminum garnet-based nanoceramics. Nature Communications , 2018, 9(1):1175.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
PARK J, KIM J, KWON H. Phosphor-aluminum composite for energy recycling with high-power white lighting. Advanced Optical Materials , 2017, 5(19):1700347.
DOI URL |
| [14] | ZHENG P, LI S, WEI R, et al. Unique design strategy for laser-driven color converters enabling superhigh-luminance and high-directionality white light. Laser & Photonics Reviews , 2019, 13(10):14930-14940. |
| [15] |
ZHANG L, SUN B, GU L, et al. Enhanced light extraction of single-surface textured YAG:Ce transparent ceramics for high power white LEDs. Applied Surface Science , 2018, 455:425-432.
DOI URL |
| [16] |
ZHANG Y, HU S, WANG Z, et al. Pore-existing Lu3Al5O12:Ce ceramic phosphor: an efficient green color converter for laser light source. Journal of Luminescence , 2018, 197:331-334.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
HUANG P, ZHOU B, ZHENG Q, et al. Nano wave plates structuring and index matching in transparent hydroxyapatite-YAG: Ce composite ceramics for high luminous efficiency white light-emitting diodes. Advanced Materials , 2019, 32(1):1905951.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
LIU X, QIAN X, ZHENG P, et al. Preparation and optical properties of MgAl2O4-Ce:GdYAG composite ceramic phosphors for white LEDs. Journal of the European Ceramic Society , 2019, 39(15):4965-4971.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
SUN B H, ZHANG L, HUANG G C, et al. Surface texture induced light extraction of novel Ce:YAG ceramic tubes for outdoor lighting. Journal of Materials Science , 2019, 54(1):159-171.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
WAGNER A, RATZKER B, KALABUKHOV S, et al. Enhanced external luminescence quantum efficiency of ceramic phosphors by surface roughening. Journal of Luminescence , 2019, 213:454-458.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
PARK H K, OH J R, DO Y R. 2D SiNx photonic crystal coated Y3Al5O12:Ce3+ ceramic plate phosphor for high-power white light-emitting diodes. Optics Express , 2011, 19(25):25593-25601.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
PARK H K, YOON S W, CHOI D Y, et al. Fabrication of wafer-scale TiO2 nanobowl arrays via a scooping transfer of polystyrene nanospheres and atomic layer deposition for their application in photonic crystals. Journal of Materials Chemistry C , 2013, 1(9):1732-1738.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
TANG Y, ZHOU S, CHEN C, et al. Composite phase ceramic phosphor of Al2O3-Ce:YAG for high efficiency light emitting. Opt. Express , 2015, 23(14):17923-17928.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
HU S, ZHANG Y, WANG Z, et al. Phase composition, microstructure and luminescent property evolutions in “light-scattering enhanced” Al 2O3-Y3Al5O12: Ce3+ ceramic phosphors. Journal of the European Ceramic Society , 2018, 38(9):3268-3278.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
CHEN J, TANG Y, YI X, et al. Fabrication of (Tb,Gd)3Al5O12:Ce3+ phosphor ceramics for warm white light-emitting diodes application. Optical Materials Express , 2019, 9(8):3333-3341.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LIU S, SUN P, LIU Y, et al. Warm white light with a high color rendering index from a single Gd3Al4GaO12:Ce3+ transparent ceramic for high-power LEDs and LDs. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces , 2018, 11(2):2130-2139.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
TIAN Y, TANG Y, YI X, et al. The analyses of structure and luminescence in (MgyY3-y)(Al5-ySiy)O12 and Y3(MgxAl5-2xSix)O12 ceramic phosphors. Journal of Alloys and Compounds , 2020, 813:152236.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
AO G, TANG Y, YI X, et al. Red emission generation in Ce3+/Mn2+ co-doping Y3Al5O12 phosphor ceramics for warm white lighting emitting diodes. Journal of Alloys and Compounds , 2019, 798:695-699.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
FENG S, QIN H, WU G, et al. Spectrum regulation of YAG:Ce transparent ceramics with Pr, Cr doping for white light emitting diodes application. Journal of the European Ceramic Society , 2017, 37(10):3403-3409.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
TANG Y, ZHOU S, YI X, et al. The characterization of Ce/Pr-doped YAG phosphor ceramic for the white LEDs. Journal of Alloys and Compounds , 2018, 745:84-89.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
TANG Y R, ZHOU S M, YI X Z, et al. The Cr-doping effect on white light emitting properties of Ce:YAG phosphor ceramics. Journal of the American Ceramic Society , 2017, 100(6):2590-2595.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
BICANIC K T, LI X Y, SABATINI R P, et al. Design of phosphor white light systems for high-power applications. ACS Photonics , 2016, 3(12):2243-2248.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
PARK H K, OH J H, KANG H, et al. Hybrid 2D photonic crystal- assisted Lu3Al5O12:Ce ceramic-plate phosphor and free-standing red film phosphor for white LEDs with high color-rendering index. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces , 2015, 7(8):4549-4559.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
PRICHA I, ROSSNER W, MOOS R, et al. Layered ceramic phosphors based on CaAlSiN3:Eu and YAG:Ce for white light- emitting diodes. Journal of the American Ceramic Society , 2016, 99(1):211-217.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
SONG Y H, HAN G S, JI E K, et al. The novel design of a remote phosphor ceramic plate for white light generation in high power LEDs. Journal of Materials Chemistry C , 2015, 3(24):6148-6152.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
LIU X, CHEN B, TU B, et al. Variation of structure and photoluminescence properties of Ce3+ doped MgAlON transparent ceramics with different doping content. Materials , 2017, 10(7):792.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
JOSHI B, LEE S W. Luminescence properties of Eu2+, Gd3+ and Pr3+ doped translucent Sialon phosphors. Journal of Rare Earths , 2015, 33(11):1142-1147.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
NISHIURA S, TANABE S, FUJIOKA K, et al. Properties of transparent Ce:YAG ceramic phosphors for white LED. Optical Materials , 2011, 33(5):688-691.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
SONG Y H, JI E K, JEONG B W, et al. High power laser-driven ceramic phosphor plate for outstanding efficient white light conversion in application of automotive lighting. Sci. Rep. , 2016, 6:31206.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
HU C, SHI Y, FENG X Q, et al. YAG:Ce/(Gd,Y)AG:Ce dual- layered composite structure ceramic phosphors designed for bright white light-emitting diodes with various CCT. Optics Express , 2015, 23(14):18243-18255.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
ANGLE J P, WANG Z J, DAMES C, et al. Comparison of two-phase thermal conductivity models with experiments on dilute ceramic composites. Journal of the American Ceramic Society , 2013, 96(9):2935-2942.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
GU C, WANG X J, XIA C, et al. A new CaF2-YAG: Ce composite phosphor ceramic for high-power and high-color-rendering WLEDs. Journal of Materials Chemistry C , 2019, 7(28):8569-8574.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
LIU Y, HU S, ZHANG Y, et al. Crystal structure evolution and luminescence property of Ce3+-doped Y2O3-Al2O3-Sc2O3 ternary ceramics. Journal of the European Ceramic Society , 2020, 40(3):840-846.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
DU Q P, FENG S W, QIN H M, et al. Massive red-shifting of Ce3+ emission by Mg2+ and Si4+ doping of YAG:Ce transparent ceramic phosphors. Journal of Materials Chemistry C , 2018, 6(45):12200-12205.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
BI J, LI JG, ZHU Q, et al. Yellow-emitting (Tb1-xCex)3Al5O12 phosphor powder and ceramic (0≤x≤0.05): phase evolution, photoluminescence, and the process of energy transfer. Ceramics International , 2017, 43(11):8163-8170.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
JI EK, SONG YH, BAK S H, et al. The design of a ceramic phosphor plate with functional materials for application in high power LEDs. Journal of Materials Chemistry C , 2015, 3(48):12390-12393.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
LIU Y, LIU S, SUN P, et al. Transparent ceramics enabling high luminous flux and efficacy for the next-generation high-power LED light. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces , 2019, 11(24):21697-21701.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
KRASNOSHCHOKA A, THORSETH A, DAM-HANSEN C, et al. Investigation of saturation effects in ceramic phosphors for laser lighting. Materials , 2017, 10(12):1407.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
XU J, HU B F, XU C, et al. A unique color converter geometry for laser-driven white lighting. Optical Materials , 2018, 86:286-290.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
YI X, ZHOU S, CHEN C, et al. Fabrication of Ce:YAG, Ce,Cr:YAG and Ce:YAG/Ce,Cr:YAG dual-layered composite phosphor ceramics for the application of white LEDs. Ceramics International , 2014, 40(5):7043-7047.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
LIU X, ZHOU H, HU Z, et al. Transparent Ce:GdYAG ceramic color converters for high-brightness white LEDs and LDs. Optical Materials , 2019, 88:97-102.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
LIU X, QIAN X, HU Z, et al. Al2O3-Ce:GdYAG composite ceramic phosphors for high-power white light-emitting-diode applications. Journal of the European Ceramic Society , 2019, 39(6):2149-2154.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
CHEN J, TANG Y, YI X, et al. Al2O3-Ce:Tb3Al5O12 composite ceramic phosphors for high efficiency warm white light illumination. Optical Materials , 2019, 97:109384.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
TIAN Y, TANG Y, YI X, et al. Study of composite Al2O3-Ce: Y3Mg1.8Al1.4Si1.8O12 ceramic phosphors. Opt. Lett. , 2019, 44(19):4845-4848.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
ZHENG R, LUO D, YUAN Y, et al. Dy3+/Ce3+ codoped YAG transparent ceramics for single-composition tunable white-light phosphor. Journal of the American Ceramic Society , 2015, 98(10):3231-3235.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
HU S, LU C H, QIN X P, et al. Color tuning of Lu3Al5O12:Dy3+ ceramic-based white light-emitting phosphorsvia Yb incorporation. Journal of the European Ceramic Society , 2017, 37(1):229-237.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
WANG L, XIE R J, SUEHIRO T, et al. Down-conversion nitride materials for solid state lighting: recent advances and perspectives. Chemical Reviews , 2018, 118(4):1951-2009.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
LI S X, ZHU Q Q, WANG L, et al. CaAlSiN3:Eu2+ translucent ceramic: a promising robust and efficient red color converter for solid state laser displays and lighting. Journal of Materials Chemistry C , 2016, 4(35):8197-8205.
DOI URL |
| [59] |
JOSHI B, HOON J S, KSHETRI Y K, et al. Transparent Sialon phosphor ceramic plates for white light emitting diodes applications. Ceramics International , 2018, 44(18):23116-23124.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
JOSHI B, KSHETRI Y K, GYAWALI G, et al. Transparent Mg-α/β-Sialon:Eu2+ ceramics as a yellow phosphor for pc-WLED. Journal of Alloys and Compounds , 2015, 631:38-45.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
LI K, WANG H, LIU X, et al. Mn2+ activated MgAlON transparent ceramic: a new green-emitting transparent ceramic phosphor for high-power white LED. Journal of the European Ceramic Society , 2017, 37(13):4229-4233.
DOI URL |
| [62] | PRICHA I, ROSSNER W, MOOS R. Pressureless sintering of luminescent CaAlSiN3:Eu ceramics. Journal of Ceramic Science and Technology , 2015, 6(1):63-67. |
| [63] |
RAUKAS M, KELSO J, ZHENG Y, et al. Ceramic phosphors for light conversion in LEDs. Ecs Journal of Solid State Science and Technology , 2013, 2(2):R3168-R3176.
DOI URL |
| [64] | WIEG A T, PENILLA E H, HARDIN C L, et al. Broadband white light emission from Ce:AlN ceramics: high thermal conductivity down-converters for LED and laser-driven solid state lighting. Appl. Materials , 2016, 4(12):126105. |
| [65] |
SCHNICK W. Shine a light with nitrides. Physica Status Solidi (RRL)-Rapid Research Letters , 2009, 3(7/8):A113-A114.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
XIE R J, HIROSAKI N, SUEHIRO T, et al. A simple, efficient synthetic route to Sr2Si5N8: Eu2+-based red phosphors for white light- emitting diodes. Chemistry of Materials , 2006, 18(23):5578-5583.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
LI S X, WANG L, TANG D M, et al. Achieving high quantum efficiency narrow-band β-Sialon:Eu2+phosphors for high-brightness LCD backlights by reducing the Eu3+ luminescence killer. Chemistry of Materials , 2018, 30(2):494-505.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
XIE R J, HIROSAKI N, MITOMO M, et al. Wavelength-tunable and thermally stable Li-α-sialon:Eu2+ oxynitride phosphors for white light-emitting diodes. Applied Physics Letters , 2006, 89(24):241103.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
ZHANG Y, LIU Y, YANG L, et al. Preparation and luminescence properties of thermally stable Mn4+ doped spinel red-emitting ceramic phosphors. Journal of Luminescence , 2020, 220:117016.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
ARREDONDO A, DESIRENA H, MORENO I, et al. Dual color tuning in Ce3+-doped oxyfluoride ceramic phosphor plate for white LED application. Journal of the American Ceramic Society , 2019, 102(3):1425-1434.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
HU S, LIU Y, ZHANG Y, et al. 3D printed ceramic phosphor and the photoluminescence property under blue laser excitation. Journal of the European Ceramic Society , 2019, 39(8):2731-2738.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 丁玲, 蒋瑞, 唐子龙, 杨运琼. MXene材料的纳米工程及其作为超级电容器电极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | 杨卓, 卢勇, 赵庆, 陈军. X射线衍射Rietveld精修及其在锂离子电池正极材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | 陈强, 白书欣, 叶益聪. 热管理用高导热碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | 林俊良, 王占杰. 铁电超晶格的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [5] | 牛嘉雪, 孙思, 柳鹏飞, 张晓东, 穆晓宇. 铜基纳米酶的特性及其生物医学应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [6] | 苑景坤, 熊书锋, 陈张伟. 聚合物前驱体转化陶瓷增材制造技术研究趋势与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [7] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [8] | 杨洋, 崔航源, 祝影, 万昌锦, 万青. 柔性神经形态晶体管研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [9] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [10] | 林思琪, 李艾燃, 付晨光, 李荣斌, 金敏. Zintl相Mg3X2(X=Sb, Bi)基晶体生长及热电性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [11] | 齐占国, 刘磊, 王守志, 王国栋, 俞娇仙, 王忠新, 段秀兰, 徐现刚, 张雷. GaN单晶的HVPE生长与掺杂进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [12] | 张超逸, 唐慧丽, 李宪珂, 王庆国, 罗平, 吴锋, 张晨波, 薛艳艳, 徐军, 韩建峰, 逯占文. 新型GaN与ZnO衬底ScAlMgO4晶体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [13] | 陈昆峰, 胡乾宇, 刘锋, 薛冬峰. 多尺度晶体材料的原位表征技术与计算模拟研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [14] | 谢兵, 蔡金峡, 王铜铜, 刘智勇, 姜胜林, 张海波. 高储能密度聚合物基多层复合电介质的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| [15] | 冯静静, 章游然, 马名生, 陆毅青, 刘志甫. 冷烧结技术的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 125-136. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||