无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (8): 847-855.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200639
张维维1( ), 陆晨1, 应国兵1, 张建峰1(
), 陆晨1, 应国兵1, 张建峰1( ), 江莞2
), 江莞2
收稿日期:2020-11-09
修回日期:2020-12-09
出版日期:2021-08-20
网络出版日期:2020-12-30
通讯作者:
张建峰, 教授. E-mail: jfzhang_sic@163.com
作者简介:张维维(1996-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: zwwbob@163.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Weiwei1( ), LU Chen1, YING Guobing1, ZHANG Jianfeng1(
), LU Chen1, YING Guobing1, ZHANG Jianfeng1( ), JIANG Wan2
), JIANG Wan2
Received:2020-11-09
Revised:2020-12-09
Published:2021-08-20
Online:2020-12-30
Contact:
ZHANG Jianfeng, professor. E-mail: jfzhang_sic@163.com
About author:ZHANG Weiwei(1996-), female, Master candidate. E-mail: zwwbob@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
在覆铜板绝缘层基体中添加导热陶瓷填料是提高其导热性能的一种有效方法。AlN是一种导热率高、绝缘性好的陶瓷填料, 但其易水解的性质限制了实际应用。此外, 相比于陶瓷填料-树脂基体复合材料体系, 有关填料填充型覆铜板产品性能的系统研究较少。本研究通过对AlN进行磷酸酸洗, 获得了抗水解性能优异的pAlN, 进一步研究了不同pAlN粒径和填充量对覆铜板导热性、剥离强度、介电性能和其他性能的影响。为了获得更有效的填料分布网络, 采取了不同粒径pAlN级配填充策略, 探究了多种级配方案对覆铜板性能的影响, 获得了最优级配和综合性能优异的覆铜板。在最优级配为pAlN-50 μm60%-5 μm5%时, 覆铜板绝缘层的热导率增大至0.757 W/(m·K), 相比纯树脂覆铜板提高160%, 具有优异的力学性能(剥离强度为1.012 N/mm, 弯曲强度为335 MPa)和介电性能(介电常数为4.499, 介电损耗为6.668×10-3), 同时吸水率低至0.53%。同时探讨了AlN填料在覆铜板应用中存在的问题和解决方法, 系统研究了不同填充方案对覆铜板绝缘层性能的影响, 对其实际应用具有指导意义。
中图分类号:
张维维, 陆晨, 应国兵, 张建峰, 江莞. AlN表面处理及级配填充对覆铜板绝缘层性能的影响规律与机制研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 847-855.
ZHANG Weiwei, LU Chen, YING Guobing, ZHANG Jianfeng, JIANG Wan. Effect and Mechanism of the Surface Treatment and Gradation Filling of AlN on the Performance of Insulation Layer of Copper Clad Laminate[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(8): 847-855.
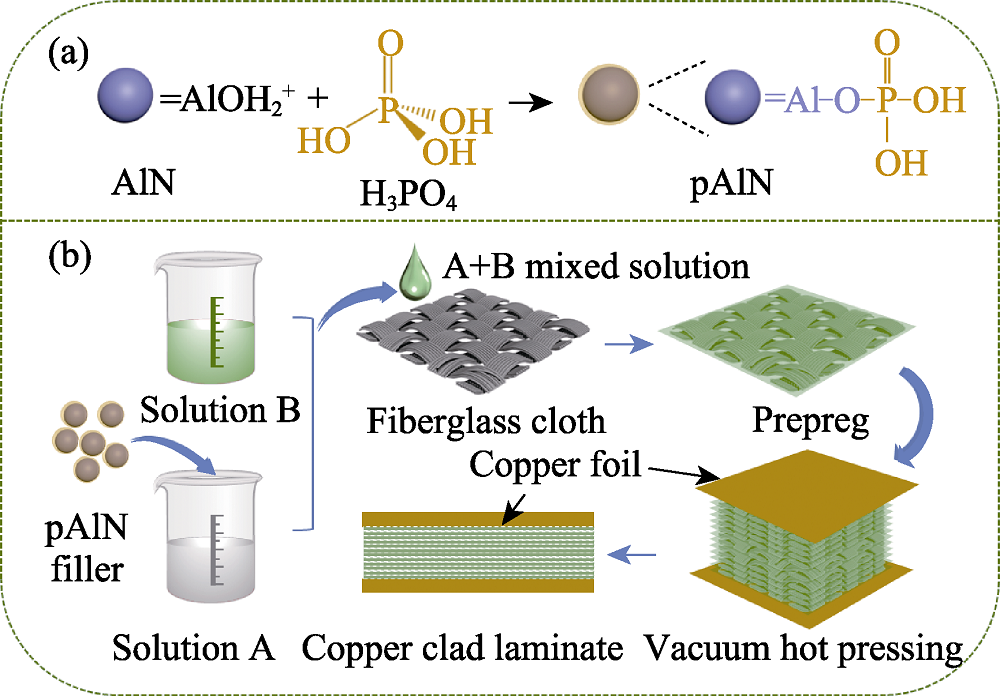
图1 (a)磷酸抗水解机理和(b)覆铜板制备流程示意图
Fig. 1 Schematic diagrams of (a) the anti-hydrolysis mechanism of phosphoric acid on AlN and (b) the preparation process of CCL
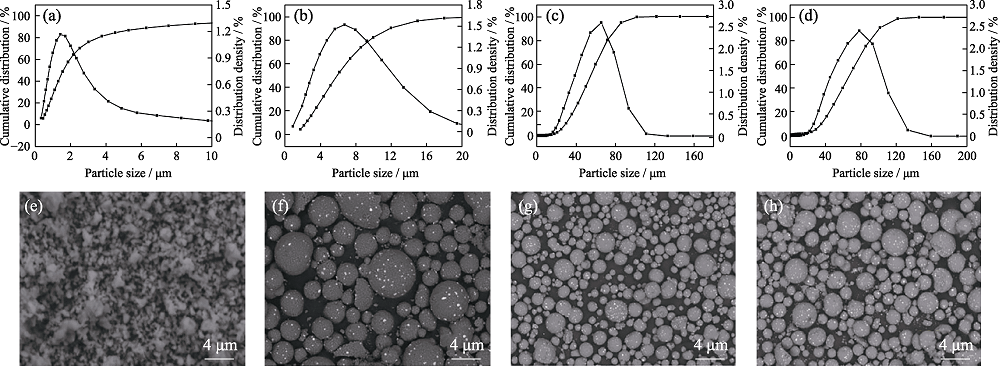
图2 AlN的(a~d)粒径分布曲线及(e~h)SEM照片
Fig. 2 (a-d) Particle size distribution curves and (e-h) SEM images of AlN with different particle sizes (a) 1 μm AlN; (b) 5 μm AlN; (c) 50 μm AlN; (d) 80 μm AlN; (e-h) SEM images of the AlN corresponding to (a-d)
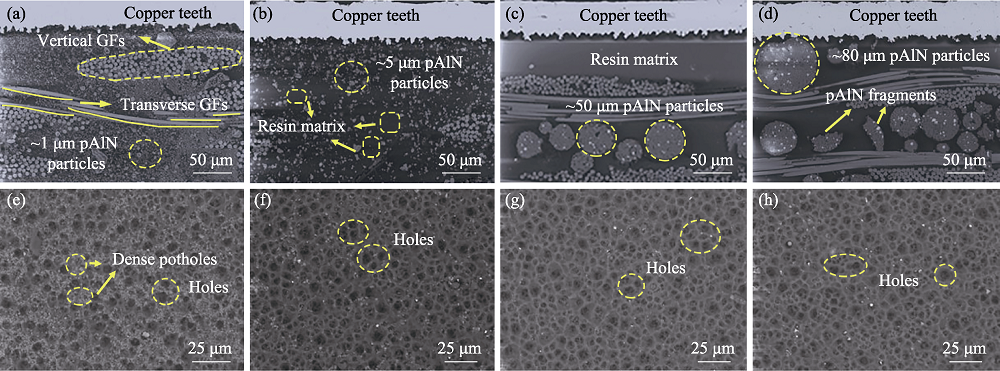
图4 相同比例, 不同粒径pAlN填充的覆铜板的(a~d)截面和(e~h)表面的SEM照片
Fig. 4 SEM images of (a-d) cross-sections and (e-h) surfaces of CCLs filled with pAlN of same filling ratio but different sizes (a) pAlN-1 μm; (b) pAlN-5 μm; (c) pAlN-50 μm; (d) pAlN-80 μm; (e-h) SEM images corresponding to the surfaces of (a-d) CCLs
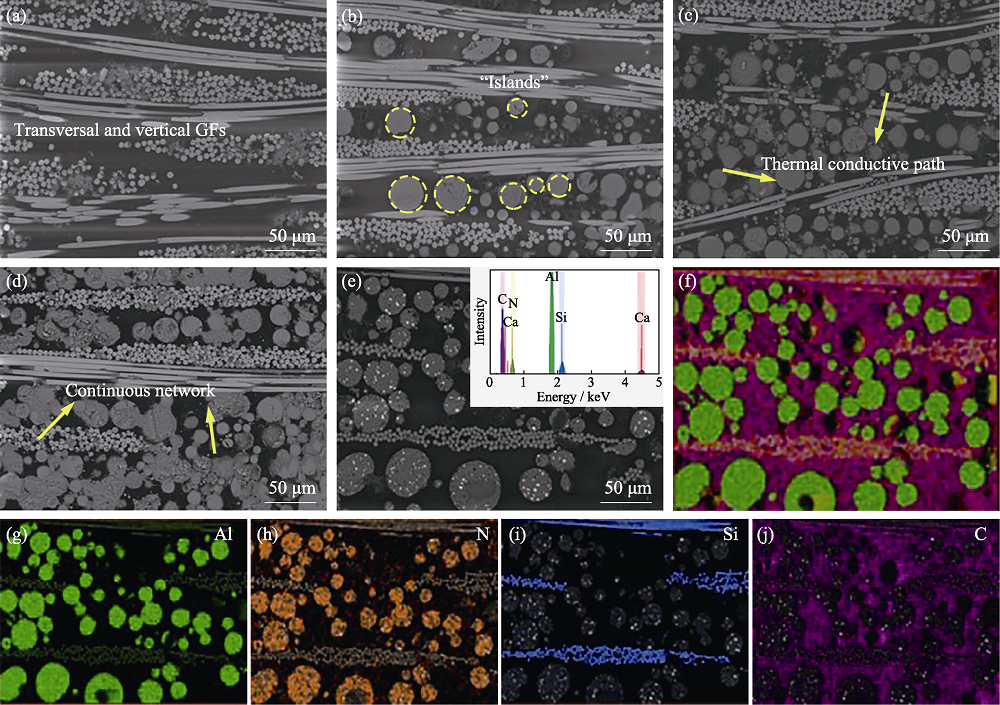
图5 填充不同比例pAlN覆铜板的截面SEM照片((a)无填料, (b)pAlN-50 μm-20%, (c) pAlN-50 μm-60%, (d) pAlN-50 μm60%-5 μm5%))、(e)EDS扫描选区(插图为元素分布)、(f)全元素扫描图和(g~j)分别对应 Al、N、Si、C元素分布
Fig. 5 SEM images of the cross-section of CCLs with different filling ratios of pAlN((a) no filler; (b) pAlN-50 μm-20%; (c) pAlN-50 μm-60%; (d) pAlN-50 μm60%-5 μm5%); (e) EDS scan selection area with the inset showing the element distribution; (f) the full element scan image; (g-j) corresponding element distributions of Al, N, Si, C

图6 不同填充方式覆铜板的导热机理示意图
Fig. 6 Heat conduction mechanism diagram of CCLs under different filling schemes (a) Without filler; (b) With single-size filler; (c) With graded filler
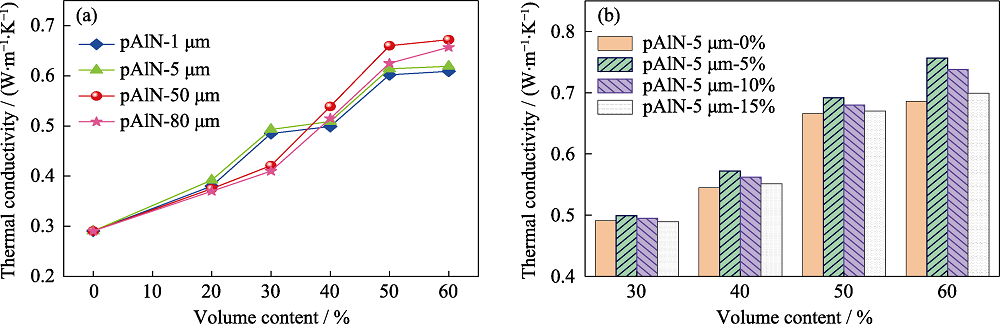
图7 (a)不同粒径、不同填充量的pAlN和(b)级配填充(pAlN-50 μm x%-5 μm y%, x=0~60, y=0~15, 下同)对覆铜板导热性能的影响
Fig. 7 (a) Effects of pAlN with different sizes, different filling amounts and (b) gradation filling (pAlN-50 μm x%-5 μm y%, x=0-60, y=0-15, same below) on the thermal conductivity of CCLs
| Treatment | Thermal conductivity/ (W·m-1·K-1) | Peel strength/ (N·mm-1) | Dielectric constant | Dielectric loss/×10-3 | Bending strength/MPa | Water absorption/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without fillers | 0.291 | 0.949 | 3.90 | 5.41 | 220 | 0.40 |
| AlN-1 μm60% | 0.390 | 0.380 | 5.10 | 9.10 | 208 | 0.76 |
| pAlN-1 μm60% | 0.610 | 0.980 | 4.55 | 9.04 | 282 | 0.47 |
表1 AlN磷酸抗水解处理对覆铜板的性能影响
Table 1 Effect of phosphoric acid treatment of AlN on the performance of CCLs
| Treatment | Thermal conductivity/ (W·m-1·K-1) | Peel strength/ (N·mm-1) | Dielectric constant | Dielectric loss/×10-3 | Bending strength/MPa | Water absorption/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without fillers | 0.291 | 0.949 | 3.90 | 5.41 | 220 | 0.40 |
| AlN-1 μm60% | 0.390 | 0.380 | 5.10 | 9.10 | 208 | 0.76 |
| pAlN-1 μm60% | 0.610 | 0.980 | 4.55 | 9.04 | 282 | 0.47 |
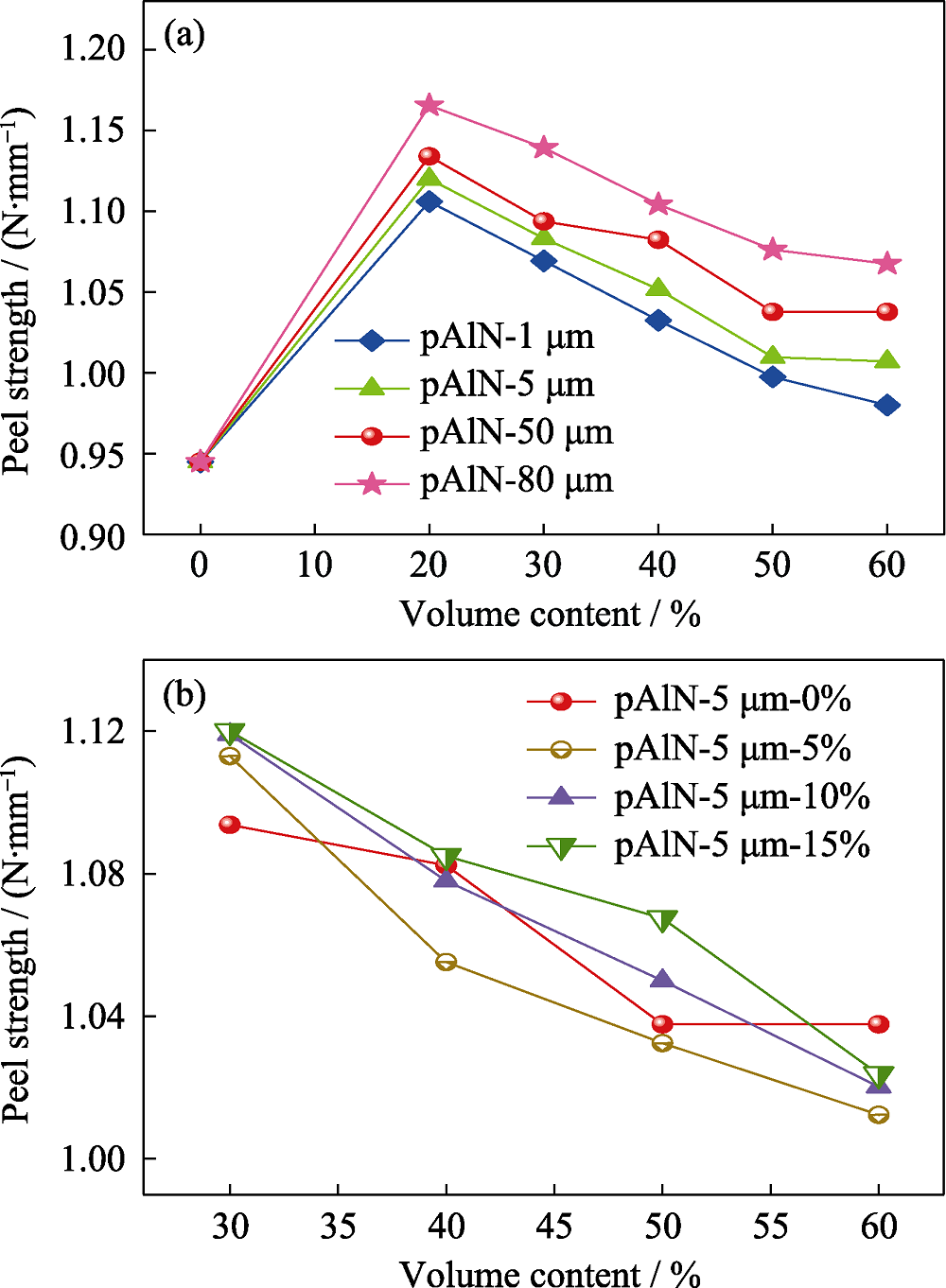
图8 (a)不同粒径及不同填充量的pAlN和(b)级配填充对覆铜板剥离强度的影响
Fig. 8 (a) Effects of pAlN with different sizes, different filling amounts and (b) gradation filling on the peel strength of CCLs
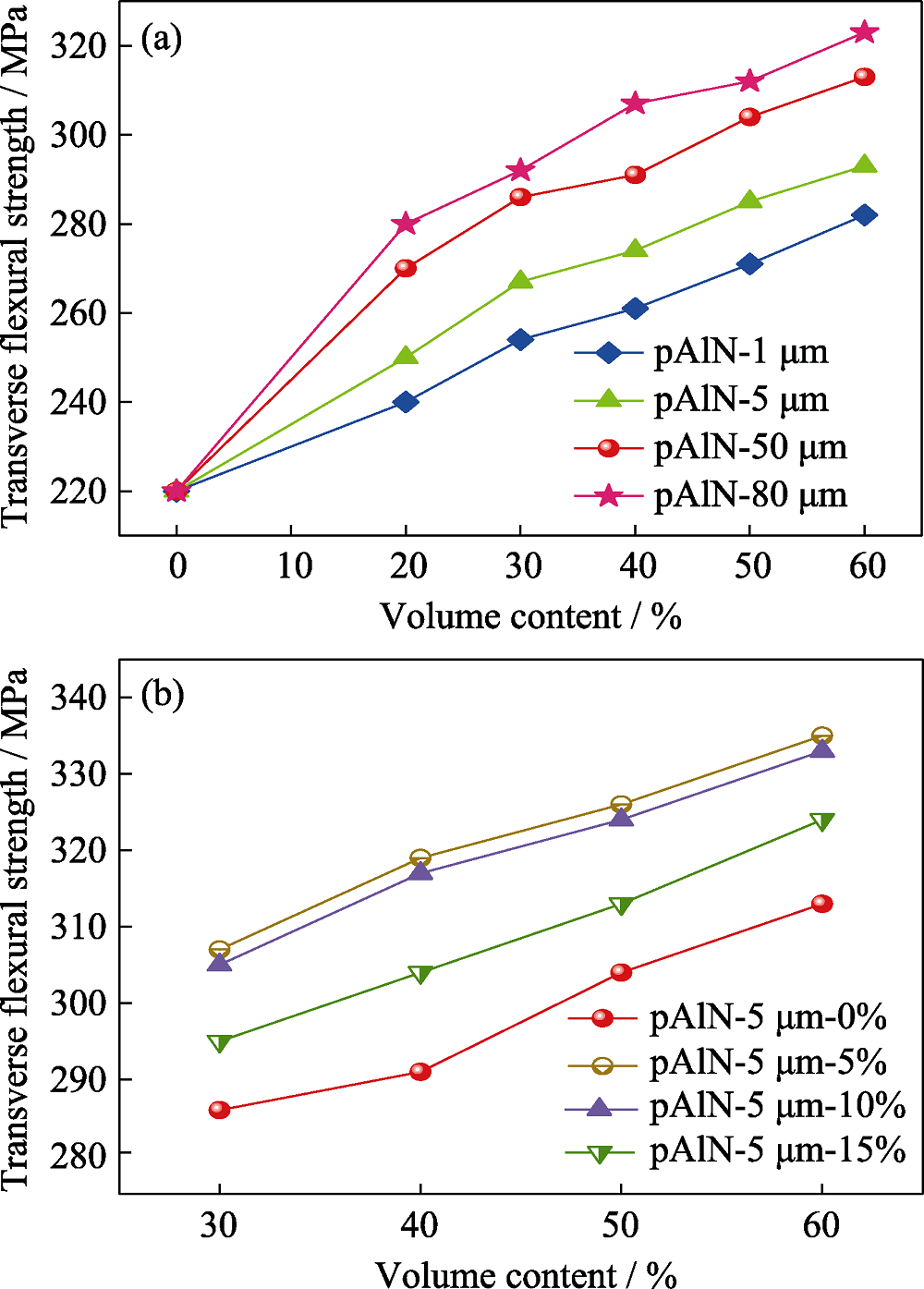
图9 (a)不同粒径及不同填充量的pAlN和(b)级配填充对覆铜板弯曲强度的影响
Fig. 9 (a) Effects of pAlN with different sizes, different filling amounts and (b) gradation filling on the bending strength of CCLs
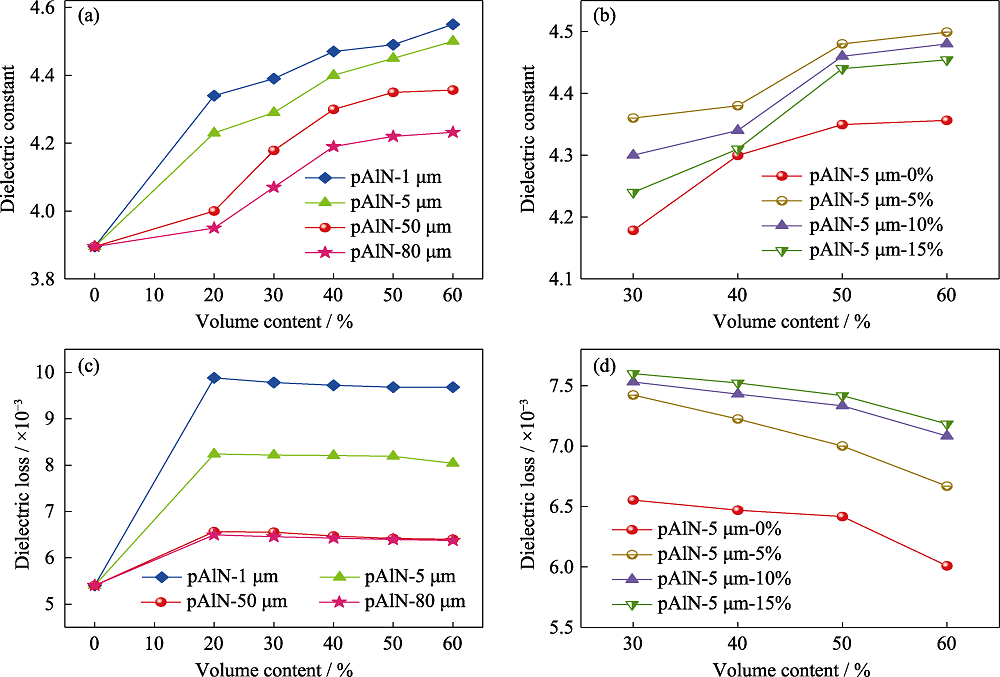
图10 不同粒径及不同填充量的pAlN对覆铜板介电常数(a)和介电损耗(b)的影响; 级配填充对覆铜板介电常数(c)和介电损耗(d)的影响
Fig. 10 Effect of pAlN with different size and filling amount on the dielectric constant (a) and dielectric loss (b) of the CCLs; Influence of gradation filling on the dielectric constant (c) and dielectric loss (d) of corresponding CCLs
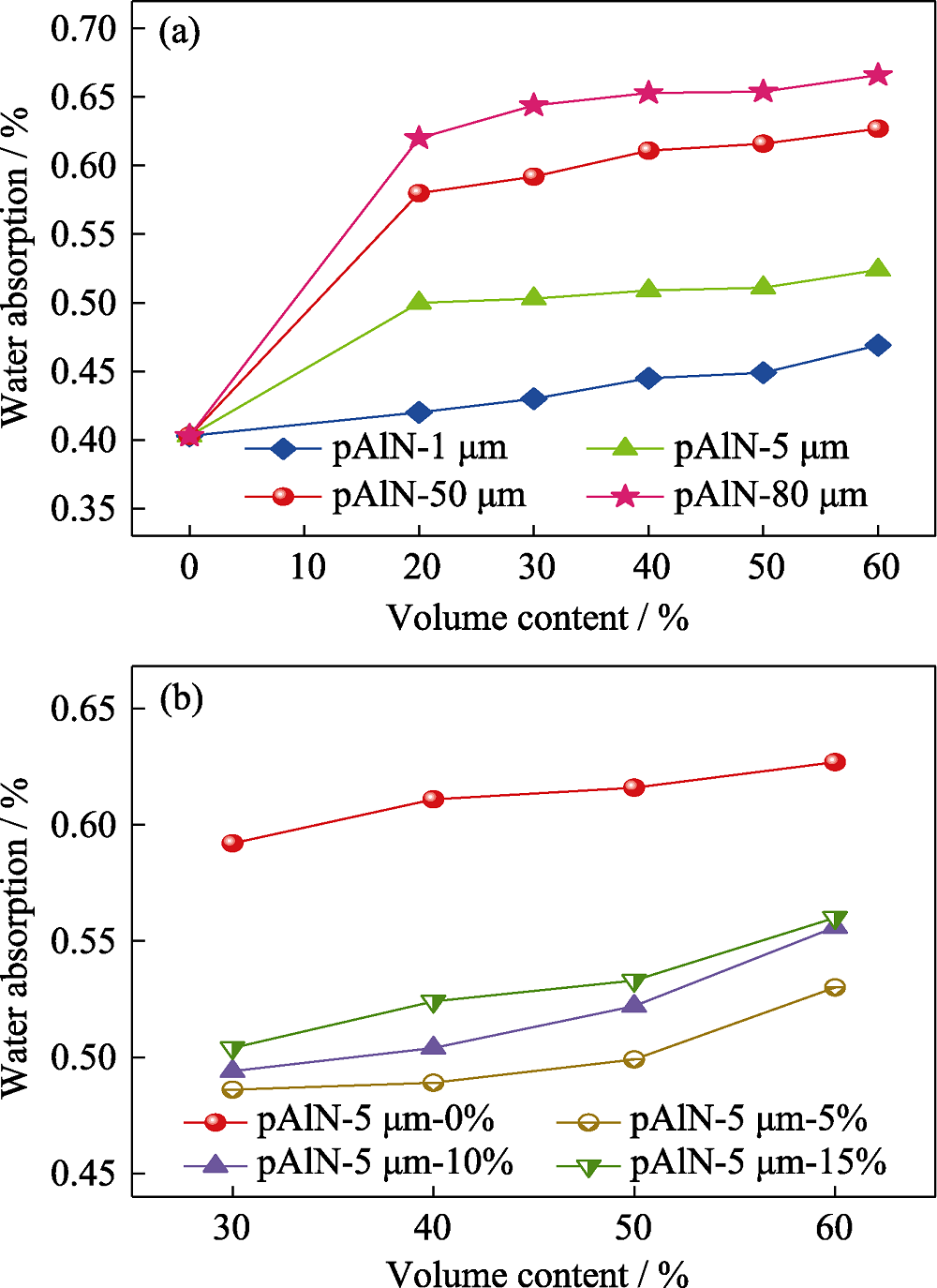
图11 不同粒径、不同填充量的pAlN (a)和级配填充(b)对覆铜板吸水率的影响
Fig. 11 (a) Effect of pAlN with different size and different filling amount and (b) gradation filling on the water absorption of CCLs
| [1] |
WANG C, WEN N, ZHOU G Y, et al. Incorporation of Tin on copper clad laminate to increase the interface adhesion for signal loss reduction of high-frequency PCB lamination. Applied Surface Science , 2017, 422:738-744.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
GUO J M, WANG H, ZHANG C X, et al. MPPE/SEBS composites with low dielectric Loss for high-frequency copper clad laminates applications. Polymers , 2020, 12(9):1875.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
OUYANG Y, DING F, BAI L Y, et al. Design of network Al2O3 spheres for significantly enhanced thermal conductivity of polymer composites. Composites Part A , 2020, 128:105673.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
GOLDIN N, DODIUK H, LEWITUS D. Enhanced thermal conductivity of photopolymerizable composites using surface modified hexagonal boron nitride fillers. Composites Science and Technology , 2017, 152(10):36-45.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
REN L L, ZENG X L, SUN R, et al. Spray-assisted assembled spherical boron nitride as fillers for polymers with enhanced thermally conductivity. Chemical Engineering Journal , 2019, 370:166-175.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
ZHANG L, ZHANG J, YUE Z X, et al. Thermally stable polymer-ceramic composites for microwave antenna applications. Journal of Advanced Ceramics , 2016, 5(4):269-276.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
PONRAJ B, BHIMIREDDI R, VARMA K B R. Effect of nano- and micron-sized K0.5Na0.5NbO3 fillers on the dielectric and piezoelectric properties of PVDF composites. Journal of Advanced Ceramics , 2016, 5(4):308-320.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
MENTLíK V, MICHAL O. Influence of SiO2 nanoparticles and nanofibrous filler on the dielectric properties of epoxy-based composites. Materials Letters , 2018, 223:41-44.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
OUYANG Y, LI X F, DING F, et al. Simultaneously enhance thermal conductive property and mechanical properties of silicon rubber composites by introducing ultrafine Al2O3 nanospheres prepared via thermal plasma. Composites Science and Technology , 2020, 190:108019.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
GUERRA V, WAN C Y, MCNALLY T. Thermal conductivity of 2D nano-structured boron nitride (BN) and its composites with polymers. Progress in Materials Science , 2019, 100:170-186.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
GUO Y Q, LYU Z Y, YANG X T, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivities and decreased thermal resistances of functionalized boron nitride/polyimide composites. Composites Part B , 2019, 164:732-739.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
LULE Z, KIM J. Thermally conductive and highly rigid polylactic acid (PLA) hybrid composite filled with surface treated alumina/ nano-sized aluminum nitride. Composites Part A , 2019, 124:105506.
DOI URL |
| [13] | YANG Y, GAO J M, LEI T, et al. Thermal conductivity and mechanical properties of polyimide composites with mixed fillers of BN flakes and SiC@SiO2 whiskers. Polymer Engineering & Science , 2020, 60(5):1044-1053. |
| [14] |
KIM C Y, LINH DANG T M, ZHANG Y M, et al. The alignment of AlN platelets in polymer matrix and its anisotropic thermal properties. Journal of Materiomics , 2019, 5(4):679-687.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
WU G L, WANG Y Q, WANG K K, et al. The effect of modified AlN on the thermal conductivity, mechanical and thermal properties of AlN/polystyrene composites. RSC Advances , 2016, 6(104):102542-102548.
DOI URL |
| [16] | HE D P, GAO H, ZHANG J J, et al. Simulation and experimental verification of thermal property for aluminum nitrides and copper clad laminates under space thermal environment. Journal of Inorganic Materials , 2019, 34(9):947-952. |
| [17] |
KOCJAN A. The hydrolysis of AlN powder - a powerful tool in advanced materials engineering. The Chemical Record , 2018, 18(7/8):1232-1246.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
TANG L, HE M K, NA X Y, et al. Functionalized glass fibers cloth/spherical BN fillers/epoxy laminated composites with excellent thermal conductivities and electrical insulation properties. Composites Communications , 2019, 16:5-10.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
GANESH I, OLHERO S M, FERREIRA J. Phosphoric acid treated AlN powder for aqueous processing of net-shape dense AlN and β-SiAlON parts. Advances in Applied Ceramics , 2009, 108(2):111-117.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
HU L H, WANG Y K, WANG S C. Aluminum nitride surface functionalized by polymer derived silicon oxycarbonitride ceramic for anti-hydrolysis. Journal of Alloys and Compounds , 2019, 772:828-833.
DOI URL |
| [21] | ZHANG W W, LU C, GE M N, et al. Surface modified and gradation-mixed Al2O3 as an effective filler for the polyphenylene oxide (PPO) insulative layer in copper clad laminates. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics , 2020 |
| [22] |
KUMAR R S, HAREESH U N, RAMAVATH P, et al. Hydrolysis control of alumina and AlN mixture for aqueous colloidal processing of aluminum oxynitride. Ceramics International , 2011, 37(7):2583-2590.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ZHANG J, QI S H. Mechanical, thermal and dielectric properties of aluminum nitride/epoxy resin composites. Journal of Elastomers and Plastics , 2015, 47(5):431-438.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
CHANG H C, LIN H T, LIN C H, et al. Facile preparation of a phosphinated bisphenol and its low water-absorption epoxy resins for halogen-free copper clad laminates. Polymer Degradation and Stability , 2013, 98(1):102-108.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LI A, ZHANG C, ZHANG Y F. Thermal conductivity of graphene-polymer composites: mechanisms, properties, and applications. Polymers , 2017, 9(437):1-17.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
GU J W, GUO Y Q, YANG X T, et al. Synergistic improvement of thermal conductivities of polyphenylene sulfide composites filled with boron nitride hybrid fillers. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing , 2017, 95:267-273.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
WANG W Q, MEYER J, ZENG Q X, et al. Adhesion characteristics of aromatic thermosetting copolyester and glass fiber laminates with copper foils for improved circuit boards. Polymers for Advanced Technologies , 2016, 27(12):1577-1585.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
JIN H Y, WANG W, GAO J Q, et al. Study of machinable AlN/BN ceramic composites. Materials Letters , 2006, 60(2):190-193.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
BIAN W C, YAO T, CHEN M, et al. The synergistic effects of the micro-BN and nano-Al2O3 in micro-nano composites on enhancing the thermal conductivity for insulating epoxy resin. Composites Science and Technology , 2018, 168:420-428.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
TANG D H, SU J Q, KONG M Q, et al. Preparation and properties of epoxy/BN highly thermal conductive composites reinforced with SiC whisker. Polymer Composites , 2015, 37(9):2611-2621.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
GAO R, GU A J, LIANG G Z, et al. Properties and origins of high-performance poly(phenylene oxide)/cyanate ester resins for high-frequency copper-clad laminates. Journal of Applied Polymer Science , 2011, 121(3):1675-1684.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 牟庭海, 许文涛, 凌军荣, 董天文, 秦梓轩, 周有福. 微波烧结制备ZrO2-AlN复合陶瓷的微观结构与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1231-1236. |
| [2] | 何端鹏,高鸿,张静静,吴杰,刘泊天,王向轲. 氮化铝覆铜板在空间热场下热学性能的模拟仿真及实验验证[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 947-952. |
| [3] | 茅茜茜, 徐勇刚, 毛小建, 张海龙, 李军, 王士维. 碳热还原氮化法结合泡沫前驱体制备超细氮化铝粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(10): 1123-1127. |
| [4] | 何永钦, 李晓云, 张景贤, 李晓光. 原位裂解碳对氮化铝基微波衰减陶瓷性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4): 421-426. |
| [5] | 王华杰, 刘学超, 孔海宽, 忻 隽, 高 攀, 卓世异, 施尔畏. 物理气相输运法生长AlN六方微晶柱[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(2): 215-218. |
| [6] | 茅茜茜, 李 军, 张海龙, 徐勇刚, 王士维. 泡沫前驱体碳热还原氮化法合成氮化铝粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(10): 1115-1120. |
| [7] | 黄林芸, 李晨辉, 柯文明, 史玉升, 贺智勇, 张启富. 稀土氧化物对SPS烧结AlN陶瓷电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(3): 267-271. |
| [8] | 彭 榕, 周和平, 宁晓山, 徐伟. 铝和氮化铝陶瓷结合强度与机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2011, 26(3): 249-253. |
| [9] | 薛剑峰,李 军,周国红,张海龙,王士维. 电泳沉积制备氮化铝陶瓷的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(6): 1151-1154. |
| [10] | 肖 劲,周 峰,陈燕彬. 微波碳热还原法制备氮化铝粉末的工艺研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(4): 755-758. |
| [11] | 李鹏亮,周敬恩,席生岐. 高能球磨制备立方AlN及其高温相变[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(4): 821-827. |
| [12] | 傅仁利,陈克新,周和平,费雷拉J.M.F. 规则结晶形态氮化铝颗粒的自蔓延高温合成[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(6): 1402-1406. |
| [13] | 段成军^{1,2,王群^1,王从曾^1,高帆^1,赵景泰^2. 空心阴极等离子烧结AlN陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(5): 1011-1017. |
| [14] | 李建强,潘伟,陈健,房明浩,潘紫霄. 利用熔盐热析出反应法对AlN陶瓷表面金属化研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(5): 1086-1090. |
| [15] | 许小红,武海顺,马文瑾,段静芳,李佐宜. 氮化铝薄膜织构的极图法研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(2): 490-494. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||