无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 471-478.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200584
所属专题: 电致变色材料与器件; 【虚拟专辑】电致变色与热致变色材料; 电致变色专栏2021
• 专栏:电致变色材料与器件(特邀编辑:王金敏,刁训刚) • 上一篇 下一篇
王天悦1,2( ), 王梦颖1(
), 王梦颖1( ), 黄庆姣3, 杨佳明3, 王顺花2, 刁训刚1(
), 黄庆姣3, 杨佳明3, 王顺花2, 刁训刚1( )
)
收稿日期:2020-10-14
修回日期:2020-11-25
出版日期:2021-05-20
网络出版日期:2021-04-19
通讯作者:
王梦颖, 博士. E-mail:mercy@buaa.edu.cn; 刁训刚, 教授. E-mail: diaoxg@buaa.edu.cn
作者简介:王天悦(1994-), 男, 硕士. E-mail:Oceanwty@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Tianyue1,2( ), WANG Mengying1(
), WANG Mengying1( ), HUANG Qingjiao3, YANG Jiaming3, WANG Shunhua2, DIAO Xungang1(
), HUANG Qingjiao3, YANG Jiaming3, WANG Shunhua2, DIAO Xungang1( )
)
Received:2020-10-14
Revised:2020-11-25
Published:2021-05-20
Online:2021-04-19
Contact:
WANG Mengying, PhD. E-mail: mercy@buaa.edu.cn; DIAO Xungang, professor. E-mail: diaoxg@buaa.edu.cn
About author:WANG Tianyue(1994-), male, master. E-mail:Oceanwty@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
从可见光到近红外波段透过率可调制的电致变色材料, 对于智能窗及其热管理方面的应用来说极具吸引力。钛酸锂是一种有潜力的电致变色阴极材料, 但对其在智能窗领域的应用前景还缺乏相关的数据支持。本工作采用溶胶-凝胶旋涂法制备透过率高、结晶性好的钛酸锂(Li4Ti5O12)薄膜, 通过联用电化学工作站和紫外-可见分光光度计原位表征了其电致变色性能。实验发现所有Li4Ti5O12薄膜对扫描速率等测试条件十分敏感, 且有优异的双波段调制性能。此外, Li4Ti5O12薄膜厚度对材料的初始态透过率、调制幅度、响应时间、电压窗口和循环耐久性均有显著影响。其中450 nm厚的Li4Ti5O12着色/褪色响应时间分别为19.1和8.9 s, 透过率调制在可见光区(550 nm处)为45%, 经过20000 s连续循环, 性能未发生明显衰退。Li4Ti5O12薄膜在近红外波段(1000 nm处)的透过率调制高达80%, 表现出优秀的节能潜力。本研究成功组装了由灰色至蓝色、循环性能良好的全固态无机电致变色器件: Glass/FTO/Li4Ti5O12/LiNbO3/NiOx/ITO, 证明钛酸锂作为电致变色智能窗材料有潜力走向普及应用。
中图分类号:
王天悦, 王梦颖, 黄庆姣, 杨佳明, 王顺花, 刁训刚. 溶胶-凝胶旋涂法制备电致变色智能窗用钛酸锂薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 471-478.
WANG Tianyue, WANG Mengying, HUANG Qingjiao, YANG Jiaming, WANG Shunhua, DIAO Xungang. Preparation of Lithium Titanate Thin Film for Electrochromic Smart Window by Sol-Gel Spin Coating Method[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 471-478.
| Target | Power source | Pressure/ Pa | Atmosphere (Ar : O2) | Power/ W | Time/ min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiNbO3 | RF | 0.8 | 95 : 5 | 300 | 120 |
| Ni | DC | 1.5 | 94 : 6 | 200 | 25 |
| ITO | DC | 0.3 | 78.4 : 21.6 | 200 | 20 |
表1 全固态无机器件Glass/FTO/Li4Ti5O12/LiNbO3/NiOx/ITO的制备参数
Table 1 Preparation parameters of all-solid-state inorganic devices Glass/FTO/Li4Ti5O12/LiNbO3/NiOx/ITO
| Target | Power source | Pressure/ Pa | Atmosphere (Ar : O2) | Power/ W | Time/ min |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LiNbO3 | RF | 0.8 | 95 : 5 | 300 | 120 |
| Ni | DC | 1.5 | 94 : 6 | 200 | 25 |
| ITO | DC | 0.3 | 78.4 : 21.6 | 200 | 20 |
| Sample | Lattice constant/nm | Interplanar spacing/nm | Average crystallite size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| LTO-1 | 0.834463 | 0.48055 | 14.9 |
| LTO-2 | 0.834586 | 0.48055 | 16.2 |
| LTO-3 | 0.834554 | 0.48068 | 15.8 |
| LTO-4 | 0.834637 | 0.48055 | 18.5 |
| LTO-5 | 0.834687 | 0.48055 | 19.4 |
表2 不同厚度Li4Ti5O12薄膜的晶格常数、晶面间距和晶粒尺寸
Table 2 Lattice constant, interplanar spacing and grain size of Li4Ti5O12 thin films with different thicknesses
| Sample | Lattice constant/nm | Interplanar spacing/nm | Average crystallite size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| LTO-1 | 0.834463 | 0.48055 | 14.9 |
| LTO-2 | 0.834586 | 0.48055 | 16.2 |
| LTO-3 | 0.834554 | 0.48068 | 15.8 |
| LTO-4 | 0.834637 | 0.48055 | 18.5 |
| LTO-5 | 0.834687 | 0.48055 | 19.4 |
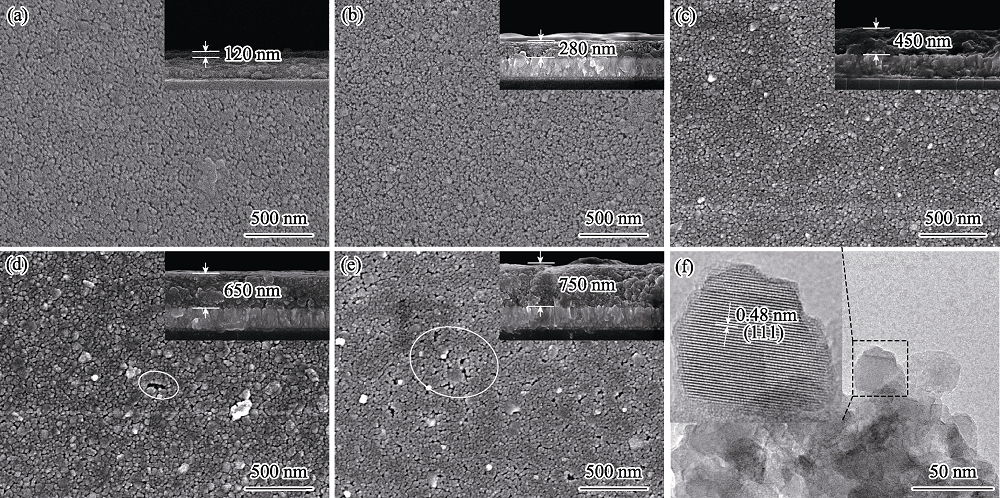
图2 不同厚度Li4Ti5O12薄膜的SEM表/截面(a~e)和TEM照片(f)
Fig. 2 SEM surface images (a-e) with insets showing cross-sectional structures and TEM image (f) of Li4Ti5O12 thin films with different thicknesses
| Sample | Tb/% | Tc/% | ΔT/% | tc/s | tb/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTO-1 | 91.84 | 72.7 | 19.14 | 26.3 | 3.6 |
| LTO-2 | 90.07 | 64.35 | 25.72 | 20.5 | 4.5 |
| LTO-3 | 88.04 | 37.28 | 50.76 | 19.1 | 8.9 |
| LTO-4 | 87.4 | 34.35 | 53.05 | 21.8 | 7.6 |
| LTO-5 | 75.12 | 26.19 | 48.93 | 28.6 | 12.0 |
表3 不同厚度Li4Ti5O12薄膜的透过率和着褪色时间
Table 3 Transmittance and response time of Li4Ti5O12 thin films with different thicknesses
| Sample | Tb/% | Tc/% | ΔT/% | tc/s | tb/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| LTO-1 | 91.84 | 72.7 | 19.14 | 26.3 | 3.6 |
| LTO-2 | 90.07 | 64.35 | 25.72 | 20.5 | 4.5 |
| LTO-3 | 88.04 | 37.28 | 50.76 | 19.1 | 8.9 |
| LTO-4 | 87.4 | 34.35 | 53.05 | 21.8 | 7.6 |
| LTO-5 | 75.12 | 26.19 | 48.93 | 28.6 | 12.0 |

图4 LTO-3在不同扫描速率下的CV曲线(a)和原位透过率光谱图(b), 适压范围的变扫速CV曲线(c)和原位透过率光谱图(d)
Fig. 4 CV curves under limited voltage condition (a), in-situ transmittance spectra (b) and CV curves under reasonable voltage condition (c), and in-situ transmittance spectra (d) of LTO-3 at various scan rates

图5 不同厚度Li4Ti5O12薄膜100圈内的CV曲线(a~e)和20000 s内的原位透过率光谱(f~j)
Fig. 5 CV curves (a-e) within 100 cycles and in-situ transmittance spectra (f-j) within 20000 s of Li4Ti5O12 thin films with different thicknesses
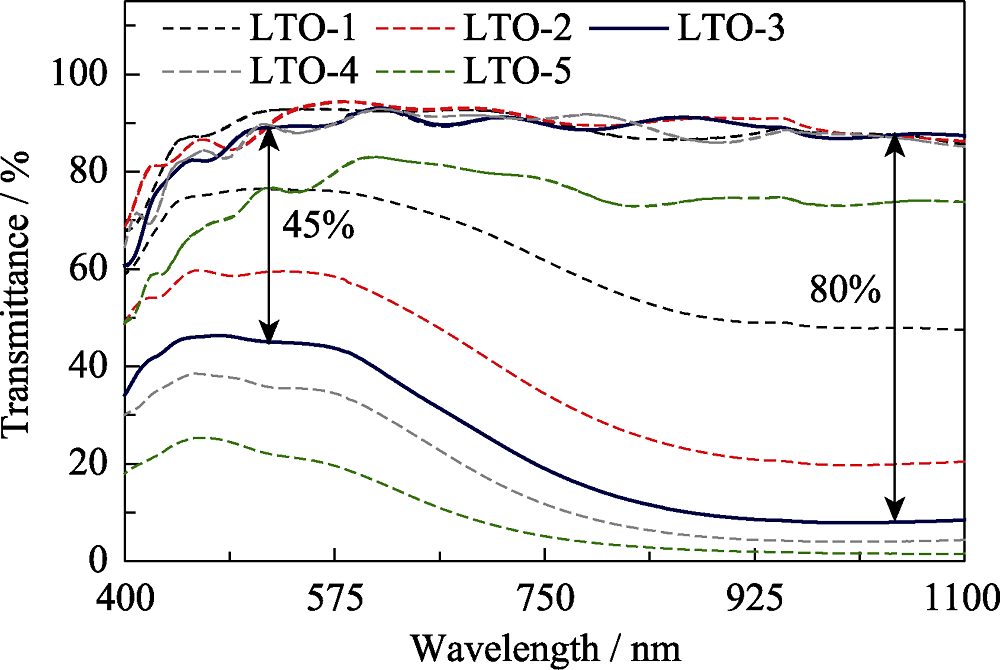
图6 不同厚度的Li4Ti5O12薄膜在400~1100 nm波段的着/褪色透过率光谱
Fig. 6 Colored and bleached transmittance spectra of Li4Ti5O12 films with different thicknesses in the wavelength 400-1100 nm

图7 全固态无机器件Glass/FTO/Li4Ti5O12/LiNbO3/NiOx/ITO的结构示意图
Fig. 7 Schematic diagram of the structure of the all-solid- state inorganic device Glass/FTO/Li4Ti5O12/LiNbO3/NiOx/ITO

图8 Glass/FTO/Li4Ti5O12/LiNbO3/NiOx/ITO全固态无机器件的电致变色性能
Fig. 8 Electrochromic performance of all-solid-state inorganic Glass/FTO/Li4Ti5O12/LiNbO3/NiOx/ITO devices (a) In-situ transmittance spectrum; (b) STEP curves; (c) Transmittance spectrum in the wavelength of 400-1100 nm; (d) Li4Ti5O12 colored and bleached photographs
| [1] |
DEB S K. A novel electrophotographic system. Applied Optics, 1969,8(Suppl 1):192-195.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
LAMPERT C M. Electrochromic materials and devices energy- efficient windows. Solar Energy Materials, 1984,11(1/2):1-27.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
BAETENS R, JELLE B P, GUSTAVSEN A. Properties, requirements and possibilities of smart windows for dynamic daylight and solar energy control in buildings: a state-of-the-art review. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2010,94(2):87-105.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
CAI G, WANG J, LEE P S. Next-generation multifunctional electrochromic devices. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2016,49(8):1469-1476.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] | WANG Z, WANG X, CONG S, et al. Fusing electrochromic technology with other advanced technologies: a new roadmap for future development. Materials Science & Engineering R-Reports, 2020,140:100524. |
| [6] | GRANQVIST C G. Electrochromic tungsten oxide films: review of progress 1993-1998. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2000,60(3):201-262. |
| [7] | ZHENG H, OU J Z, STRANO M S, et al. Nanostructured tungsten oxide-properties, synthesis, and applications. Advanced Functional Materials, 2011,21(12):2175-2196. |
| [8] | MEHMOOD A, LONG X, HAIDRY A A, et al. Trends in sputter deposited tungsten oxide structures for electrochromic applications: a review. Ceramics International, 2020,46(15):23295-23313. |
| [9] |
MA D, WANG J. Inorganic electrochromic materials based on tungsten oxide and nickel oxide nanostructures. Science China- Chemistry, 2017,60(1):54-62.
DOI URL |
| [10] | MA D, LI T, XU Z, et al. Electrochromic devices based on tungsten oxide films with honeycomb-like nanostructures and nanoribbons array. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2018,177:51-56. |
| [11] | PATIL P S, KADAM L D. Preparation and characterization of spray pyrolyzed nickel oxide (NiO) thin films. Applied Surface Science, 2002,199(1-4):211-221. |
| [12] |
XIA X H, TU J P, ZHANG J, et al. Electrochromic properties of porous NiO thin films prepared by a chemical bath deposition. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2008,92(6):628-633.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
LUO Z, LIU L, YANG X, et al. Revealing the charge storage mechanism of nickel oxide electrochromic supercapacitors. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020,12(35):39098-39107.
URL PMID |
| [14] | LI X, CHU J, CHENG Y, et al. Novel prussian blue@carbon-dots hybrid thin film: the impact of carbon-dots on material structure and electrochromic performance. Electrochimica Acta, 2020,355:136659. |
| [15] | CHOI D, SON M, IM T, et al. Crack-free fabrication of prussian blue-based blending film for the dramatic enhancement of dual electrochromic device. Ceramics International, 2020,46(13):21008-21013. |
| [16] | QIAN J, MA D, XU Z, et al. Electrochromic properties of hydrothermally grown Prussian blue film and device. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2018,177:9-14. |
| [17] |
KOBAYASHI T, YONEYAMA H, TAMURA H. Polyaniline film-coated electrodes as electrochromic display devices. Journal of Electroanalytical Chemistry, 1984,161(2):419-423.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
WANG Y, JIANG H, ZHENG R, et al. A flexible, electrochromic, rechargeable Zn-ion battery based on actiniae-like self-doped polyaniline cathode. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2020,8(25):12799-12809.
DOI URL |
| [19] | KORENT A, SODERZNIK K Z, STURM S, et al. A correlative study of polyaniline electropolymerization and its electrochromic behavior. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2020,167(10):106504. |
| [20] | PRAKASH A S, MANIKANDAN P, RAMESHA K, et al. Solution-combustion synthesized nanocrystalline Li4Ti5O12 as high-rate performance Li-ion battery anode. Chemistry of Materials, 2010,22(9):2857-2863. |
| [21] | YI T F, JIANG L J, SHU J, et al. Recent development and application of Li4Ti5O12 as anode material of lithium ion battery. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2010,71(9):1236-1242. |
| [22] |
ZHAO L, HU Y S, LI H, et al. Porous Li4Ti5O12 coated with N-doped carbon from ionic liquids for Li-ion batteries. Advanced Materials, 2011,23(11):1385-1388.
DOI URL PMID |
| [23] | JUNG H G, MYUNG S T, YOON C S, et al. Microscale spherical carbon-coated Li4Ti5O12 as ultra high power anode material for lithium batteries. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011,4(4):1345-1351. |
| [24] | SHI X, YU S, DENG T, et al. Unlock the potential of Li4Ti5O12 for high-voltage/long-cycling-life and high-safety batteries: dual-ion architecture superior to lithium-ion storage. Journal of Energy Chemistry, 2020,44:13-18. |
| [25] |
YU X, WANG R, HE Y, et al. Electrochromic behavior of transparent Li4Ti5O12/FTO electrode. Electrochemical and Solid State Letters, 2010,13(8):J99-J101.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
GUO Z F, PAN K, WANG X J. Electrochromic & magnetic properties of electrode materials for lithium ion batteries. Chinese Physics B, 2016,25(1):17801.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ROEDER M, BELEKE A B, GUNTOW U, et al. Li4Ti5O12 and LiMn2O4 thin-film electrodes on transparent conducting oxides for all-solid-state and electrochromic applications. Journal of Power Sources, 2016,301:35-40.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
MANDAL J, DU S, DONTIGNY M, et al. Li4Ti5O12: a visible-to- infrared broadband electrochromic material for optical and thermal management. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018,28:1802180.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
LI M, GOULD T, SU Z, et al. Electrochromic properties of Li4Ti5O12: from visible to infrared spectrum. Applied Physics Letters, 2019,115(7):073902.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
JOSHI Y, SAKSENA A, HADJIXENOPHONTOS E, et al. Electrochromic behavior and phase transformation in Li4+xTi5O12 upon lithium-ion deintercalation/intercalation. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020,12(9):10616-10625.
DOI URL PMID |
| [31] |
MOSA J, VELEZ J F, LORITE I, et al. Film-shaped Sol-Gel Li4Ti5O12 electrode for lithium-ion microbatteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2012,205:491-494.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
MOSA J, VÉLEZ J F, REINOSA J J. et al. Li4Ti5O12 thin-film electrodes by Sol-Gel for lithium-ion microbatteries. Journal of Power Sources, 2013,244:482-487.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
MOSA J, APARICIO M, TADANAGA K, et al. Li4Ti5O12 thin-film electrodes by in-situ synthesis of lithium alkoxide for Li-ion microbatteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2014,149:293-299.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
ANH V, QIAN Y, STEIN A. Porous electrode materials for lithium-ion batteries-how to prepare them and what makes them special. Advanced Energy Materials, 2012,2(9):1056-1085.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
XIE Z, LIU Q, ZHANG Q, et al. Fast-switching quasi-solid state electrochromic full device based on mesoporous WO3 and NiO thin films Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2019,200:110017.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WANG M, LIU Q, DONG G, et al. Influence of thickness on the structure, electrical, optical and electrochromic properties of AZO thin films and their inorganic all-solid-state devices. Electrochimica Acta, 2017,258:1336-1347.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
SUTHAR D, CHASTA G, HIMANSHU , et al. Impact of different annealing conditions on physical properties of ZnSe thin films for ecofriendly buffer layer applications. Materials Research Bulletin, 2020,132:110982.
DOI URL |
| [38] |
BATHE S R, ILLA M S, NARAYAN R, et al. Electrochromism in polymer-electrolyte-enabled nanostructured WO3: active layer thickness and morphology on device performance ChemNanoMat, 2018,4(2):203-212.
DOI URL |
| [39] |
SENGUPTA S S, PARK S M, PAYNE D A, et al. Origins and evolution of stress development in Sol-Gel derived thin layers and multideposited coatings of lead titanate. Journal of Applied Physics, 1998,83(4):2291-2296.
DOI URL |
| [40] |
KRAJEWSKI M, HAMANKIEWICZ B, CZERWIŃSKI A. Voltammetric and impedance characterization of Li4Ti5O12/n-Ag composite for lithium-ion batteries. Electrochimica Acta, 2016,219:277-283.
DOI URL |
| [41] |
QIN M, HAO Z, LI Y, et al. Preparation of ternary phase Li4Ti5O12/anatase/rutile nanocomposites with defects and their enhanced capability for lithium ion storage. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018,769:463-470.
DOI URL |
| [42] |
WEN R T, GRANQVIST C G, NIKLASSON G A. Eliminating degradation and uncovering ion-trapping dynamics in electrochromic WO3 thin films. Nature Materials, 2015,14(10):996-1001.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 张家强, 邹馨蕾, 王能泽, 贾春阳. 两步电沉积法制备Zn-Fe PBA薄膜及其在电致变色器件中的性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 961-968. |
| [2] | 张笑宇, 刘永盛, 李然, 李耀刚, 张青红, 侯成义, 李克睿, 王宏志. 基于Cu3(HHTP)2薄膜的离子液体电致变色电极[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 883-890. |
| [3] | 黄郅航, 滕官宏伟, 铁鹏, 范德松. 钙钛矿陶瓷薄膜的电致变色特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 611-616. |
| [4] | 武琦, 丛杉, 赵志刚. 多彩氧化钨薄膜的红外电致变色性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 485-491. |
| [5] | 贾汉祥, 邵泽伟, 黄爱彬, 金平实, 曹逊. 光学设计用于全固态电致变色器件的高溅射效率三明治结构电解质[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 479-484. |
| [6] | 王金敏, 后丽君, 马董云. 氧化钼电致变色材料与器件[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 461-470. |
| [7] | 张翔, 李文杰, 王乐滨, 陈曦, 赵九蓬, 李垚. 无机电致变色材料反射特性研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 451-460. |
| [8] | 钟晓岚, 刘雪晴, 刁训刚. 基于氧化钨和氧化镍的电致变色器件研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 128-139. |
| [9] | 方华靖, 赵泽天, 武文婷, 汪宏. 柔性电致变色器件研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 140-151. |
| [10] | 周开岭, 汪浩, 张倩倩, 刘晶冰, 严辉. WO3电致变色薄膜离子传输动力过程及其循环稳定性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 152-160. |
| [11] | 赵起, 乔科, 姚勇吉, 陈长, 陈东初, 高彦峰. 基于高电导率的疏水气相SiO2复合凝胶电解质的高性能电致变色器件[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 161-167. |
| [12] | 范宏伟, 李克睿, 侯成义, 张青红, 李耀刚, 王宏志. 多功能电致变色器件:从多器件到单器件集成[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 115-127. |
| [13] | 贾汉祥, 曹逊, 金平实. 无机全固态电致变色材料与器件研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 511-524. |
| [14] | 陈钧,马培华,张诚,劳伦·鲁尔曼,吕耀康. 新型多功能无机/有机复合薄膜的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 217-223. |
| [15] | 王金敏, 于红玉, 马董云. 纳米二氧化锰的制备及其应用研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(12): 1307-1314. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||