无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (6): 579-591.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200555
所属专题: 【虚拟专辑】分离膜,复相陶瓷(2020~2021)
李子宜1( ), 章佳佳1, 邹小勤2, 左家玉1, 李俊1, 刘应书1(
), 章佳佳1, 邹小勤2, 左家玉1, 李俊1, 刘应书1( ), 裴有康3,4
), 裴有康3,4
收稿日期:2020-09-22
修回日期:2020-10-27
出版日期:2021-06-20
网络出版日期:2020-12-10
通讯作者:
刘应书, 教授. E-mail: ysliu@ustb.edu.cn
作者简介:李子宜(1990-), 男, 副教授. E-mail: ziyili@ustb.edu.cn
基金资助:
LI Ziyi1( ), ZHANG Jiajia1, ZOU Xiaoqin2, ZUO Jiayu1, LI Jun1, LIU Yingshu1(
), ZHANG Jiajia1, ZOU Xiaoqin2, ZUO Jiayu1, LI Jun1, LIU Yingshu1( ), PUI David Youhong3,4
), PUI David Youhong3,4
Received:2020-09-22
Revised:2020-10-27
Published:2021-06-20
Online:2020-12-10
Contact:
LIU Yingshu, professor. E-mail: ysliu@ustb.edu.cn
About author:LI Ziyi(1990-), male, associate professor. E-mail: ziyili@ustb.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
菱沸石(Chabazite, CHA)分子筛膜因其八元环小孔(0.38 nm)三维孔道结构、可调的表面特性、较高的材料稳定性与制备可重复性, 使其在轻质气体分离方面具有优异性能, 近年来逐渐成为分子筛膜研究热点之一。本综述介绍了两种CHA分子筛膜(SAPO-34膜、SSZ-13膜)的基本特性, 对比了CHA分子筛膜的合成方法(原位合成法、二次生长法、微波加热法)优缺点及其应用现状, 并重点针对主流的二次生长法制备SSZ-13膜与SAPO-34膜过程中关键条件对薄膜质量的影响规律进行了详细阐述, 包括铺种条件(载体种类、晶种类别、铺种方式), 水热合成条件(晶化时间、晶化温度、含水量、硅铝比、模板剂、阳离子种类)与煅烧方式(常规煅烧、分段煅烧、快速热处理), 经细化分析总结出上述两种膜的优选合成条件; 并进一步汇总了CHA分子筛膜表面化学调控(硅铝比调控、阳离子交换、杂原子替换、氨基功能化、表面修饰)对气体分离增强的策略, 总结了CHA分子筛膜在各种气体体系中的分离特点与单组分气体渗透特性。最后, 对CHA分子筛膜今后的发展和应用前景进行了展望。
中图分类号:
李子宜, 章佳佳, 邹小勤, 左家玉, 李俊, 刘应书, 裴有康. 菱沸石分子筛膜的合成调控与气体分离研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(6): 579-591.
LI Ziyi, ZHANG Jiajia, ZOU Xiaoqin, ZUO Jiayu, LI Jun, LIU Yingshu, PUI David Youhong. Synthesis and Gas Separation of Chabazite Zeolite Membranes[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 579-591.
| Method | Advantage | Disadvantage | Status of use |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-situ synthesis | ① Simple production equipment ② Easy to use | ① Low success rate ② Long synthesis time ③ Difficult to control | Less research, basically used for the synthesis of SAPO-34 membrane |
| Secondary growth | ① Simple production equipment ② High success rate ③ Short synthesis time | ① Tedious steps | More research, conducive to large-scale mass production |
| Microwave heating | ① High success rate ② Short synthesis time | ① Tedious steps ② High equipment cost ③ High energy consumption | New method, still in basic research stage |
表1 CHA分子筛膜合成方法对比
Table 1 Comparison of CHA zeolite membrane synthesis methods
| Method | Advantage | Disadvantage | Status of use |
|---|---|---|---|
| In-situ synthesis | ① Simple production equipment ② Easy to use | ① Low success rate ② Long synthesis time ③ Difficult to control | Less research, basically used for the synthesis of SAPO-34 membrane |
| Secondary growth | ① Simple production equipment ② High success rate ③ Short synthesis time | ① Tedious steps | More research, conducive to large-scale mass production |
| Microwave heating | ① High success rate ② Short synthesis time | ① Tedious steps ② High equipment cost ③ High energy consumption | New method, still in basic research stage |
| Influencing factors | SSZ-13 | SAPO-34 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seed conditions | Support | α-Al2O3, mullite | α-Al2O3 |
| Seed crystal | Ball milled nano seeds | Flake nano seeds | |
| Seeding method | Dip coating | Wipe, electrophoretic deposition | |
| Hydrothermal synthesis conditions | Formula (structure directing agent, Si/Al, water content, cationic species) | Non-pure silica: 1SiO2 : (5-100)Al2O3 : (0.1-0.2)NaOH : (0-0.06)KOH(Oriented growth regulation) : (0.05-0.6)TMAdaOH : (0-0.05)TEAOH : (40-120)H2O Pure silica : 1SiO2 : (0.5-1.4)TMAdaOH : (0.5-1.4)HF : (3-6)H2O | 1Al2O3 : (1-2)P2O5 : (0.3-0.6)SiO2 : (1-4)TEAOH : (0-1.6)DPA : (55-400)H2O |
| Temperature | 160-170 ℃ | 180-230 ℃ | |
| Time | 24-72 h | 6-30 h | |
| Calcination conditions | Conventional calcination | 400-550 ℃ (6-12 h), temperature rise and fall rate (0.2-1) ℃/min | 400-480 ℃ (4-10 h), temperature rise and fall rate (0.5- 2) ℃/min |
| Rapid heat treatment | 700-1000 ℃ (0.5-2 min)+conventional calcination | 700 ℃ (1-5 min)+ conventional calcination | |
表2 SSZ-13膜和SAPO-34膜二次合成优选条件汇总表
Table 2 Summary table of preferred conditions for secondary synthesis of SSZ-13 membrane and SAPO-34 membrane
| Influencing factors | SSZ-13 | SAPO-34 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Seed conditions | Support | α-Al2O3, mullite | α-Al2O3 |
| Seed crystal | Ball milled nano seeds | Flake nano seeds | |
| Seeding method | Dip coating | Wipe, electrophoretic deposition | |
| Hydrothermal synthesis conditions | Formula (structure directing agent, Si/Al, water content, cationic species) | Non-pure silica: 1SiO2 : (5-100)Al2O3 : (0.1-0.2)NaOH : (0-0.06)KOH(Oriented growth regulation) : (0.05-0.6)TMAdaOH : (0-0.05)TEAOH : (40-120)H2O Pure silica : 1SiO2 : (0.5-1.4)TMAdaOH : (0.5-1.4)HF : (3-6)H2O | 1Al2O3 : (1-2)P2O5 : (0.3-0.6)SiO2 : (1-4)TEAOH : (0-1.6)DPA : (55-400)H2O |
| Temperature | 160-170 ℃ | 180-230 ℃ | |
| Time | 24-72 h | 6-30 h | |
| Calcination conditions | Conventional calcination | 400-550 ℃ (6-12 h), temperature rise and fall rate (0.2-1) ℃/min | 400-480 ℃ (4-10 h), temperature rise and fall rate (0.5- 2) ℃/min |
| Rapid heat treatment | 700-1000 ℃ (0.5-2 min)+conventional calcination | 700 ℃ (1-5 min)+ conventional calcination | |
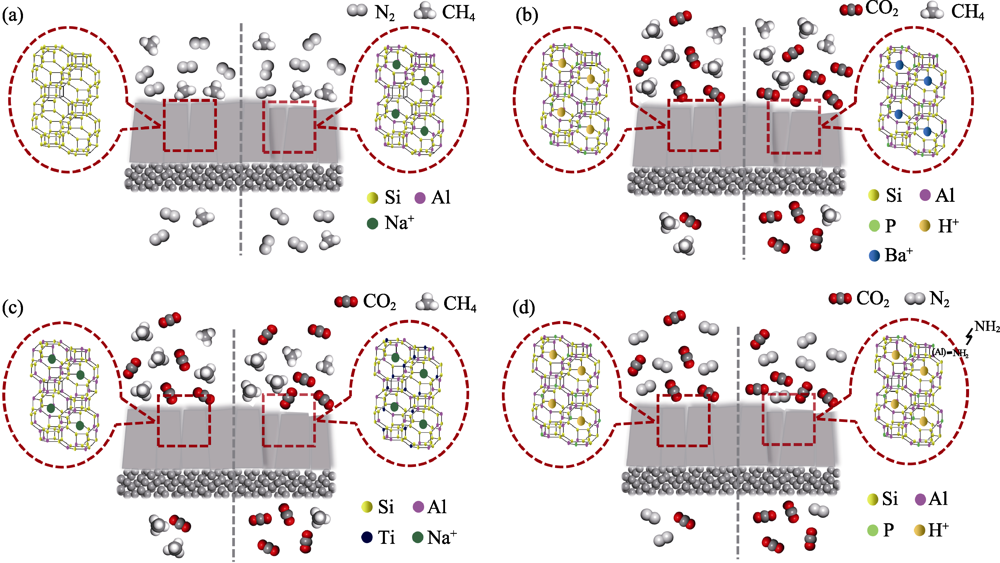
图4 CHA分子筛膜表面化学调控前(左)和后(右)的气体分离机制示意图[24,36,49,83,87]
Fig. 4 Schematic diagram of gas separation mechanisms on CHA zeolite membrane before (left) and after (right) the modulation of membrane surface chemistry[24,36,49,83,87] (a) Si/Al regulation; (b) Cation exchange; (c) Heteroatom replacement; (d) Amino functionalization
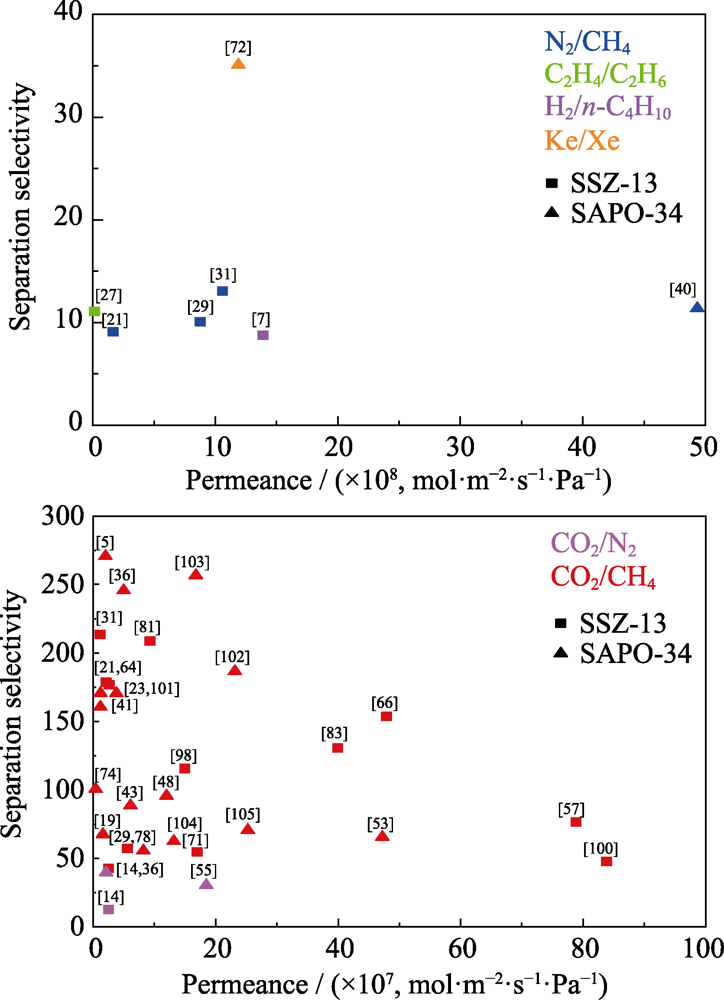
图5 CHA分子筛膜对不同气体体系的分离性能
Fig. 5 Separation performances of different gas mixtures on CHA zeolite membranes Temperature range: -25-80 ℃; Pressure range: 0.05-0.9 MPa
| Serial number | Ref. | Thickness/μm | Temperature/℃ | Pressure/MPa | Gas separation, X/Y | X permeance/ (×10-8, mol·m-2·s-1·Pa-1) | Separation selectivity, X/Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kalipcilar[ | 10-40 | 25 | - | H2/n-C4H10 | 14 | 8.7 |
| 2 | Zheng[ | 10 | 30 | 0.2 | C2H4/C2H6 | 0.29 | 11 |
| 3 | Feng[ | 4.3 | 20 | 0.138 | Kr/Xe | 12 | 35 |
| 4 | Yang[ | 3.7 | 22 | - | H2/C3H8 | 8.4 | 810 |
表3 CHA分子筛膜对H2、烃类气体、稀有气体的分离性能
Table 3 Separation performances of H2, hydrocarbon and noble gases on CHA zeolite membranes
| Serial number | Ref. | Thickness/μm | Temperature/℃ | Pressure/MPa | Gas separation, X/Y | X permeance/ (×10-8, mol·m-2·s-1·Pa-1) | Separation selectivity, X/Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kalipcilar[ | 10-40 | 25 | - | H2/n-C4H10 | 14 | 8.7 |
| 2 | Zheng[ | 10 | 30 | 0.2 | C2H4/C2H6 | 0.29 | 11 |
| 3 | Feng[ | 4.3 | 20 | 0.138 | Kr/Xe | 12 | 35 |
| 4 | Yang[ | 3.7 | 22 | - | H2/C3H8 | 8.4 | 810 |
| Serial number | Ref. | Thickness/μm | Temperature/℃ | Pressure/MPa | Gas separation, X/Y | X permeance/ (×10-7, mol·m-2·s-1·Pa-1) | Separation selectivity, X/Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kosinov[ | 4-6 | 20 | 0.6 | CO2/CH4 | 2.5 | 42 |
| 20 | 0.6 | CO2/N2 | 2.5 | 12 | |||
| 2 | Wu[ | 6-8 | 20 | 0.27 | CO2/CH4 | 2.1 | 178 |
| 20 | 0.27 | N2/CH4 | 0.18 | 9 | |||
| 3 | Song[ | 6 | 25 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 5.6 | 56.5 |
| 25 | 0.2 | N2/CH4 | 0.89 | 10 | |||
| 4 | Li[ | 2 | 25 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 1.16 | 213 |
| 25 | 0.2 | N2/CH4 | 1.07 | 13 | |||
| 5 | Yu[ | 1.5 | -24 | 0.9 | CO2/CH4 | 79 | 76 |
| 6 | Karakiliç[ | 2-4 | 22 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 2.6 | 176 |
| 7 | Qiu[ | 0.44 | 20 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 48 | 153 |
| 8 | Kida[ | - | 40 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 17 | 54 |
| 40 | 0.1 | H2/CH4 | 11 | 34 | |||
| 9 | Tang[ | 10 | 20 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 9.3 | 208 |
| 10 | Kida[ | 5 | 25 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 40 | 130 |
| 11 | Imasaka[ | 3 | 40 | 0.3 | CO2/CH4 | 15 | 115 |
| 12 | Maghsoudi[ | 20 | 30 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 0.34 | 21.6 |
| 13 | Yu[ | 1.3 | 3 | 0.9 | CO2/CH4 | 84 | 47 |
| 14 | Li[ | 5 | 80 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 2.0 | 270 |
| 15 | Li[ | - | 24 | 0.138 | CO2/CH4 | 1.6 | 67 |
| 16 | Carreon[ | - | 22 | 0.138 | CO2/CH4 | 3.8 | 170 |
| 17 | Venna[ | - | 22 | 0.138 | CO2/CH4 | 5.0 | 245 |
| 22 | 0.138 | CO2/N2 | 2.1 | 39 | |||
| 18 | Huang[ | 2 | 22 | 0.074 | N2/CH4 | 4.93 | 11.3 |
| 19 | Chen[ | 2-3 | 25 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 1.18 | 160 |
| 20 | Chang[ | - | - | 4 | CO2/CH4 | 6.1 | 88 |
| 21 | Liu[ | 3 | 30 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 12 | 95 |
| 22 | Rehman[ | - | 80 | 0.4 | CO2/CH4 | 47.3 | 65 |
| 23 | Liu[ | 7-15 | 25 | 0.1 | CO2/N2 | 18.5 | 29.8 |
| 24 | Li[ | 4-6 | 22 | 7 | CO2/CH4 | 0.4 | 100 |
| 25 | Zhang[ | - | 20 | 4.6 | CO2/CH4 | 8.2 | 55 |
| 26 | Noble[ | - | 22 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 1.2 | 170 |
| 27 | Shi[ | 2-4 | 22 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 23.2 | 186 |
| 28 | Shi[ | 4-5 | 22 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 16.8 | 256 |
| 29 | Li[ | 3 | - | 4 | CO2/CH4 | 13.2 | 62 |
| 30 | Bai[ | 0.8 | - | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 25.3 | 70 |
表4 CHA分子筛膜对CO2/CH4、CO2/N2、N2/CH4、H2/CH4分离性能
Table 4 Separation performances of CO2/CH4, CO2/N2, N2/CH4, H2/CH4 on CHA zeolite membranes
| Serial number | Ref. | Thickness/μm | Temperature/℃ | Pressure/MPa | Gas separation, X/Y | X permeance/ (×10-7, mol·m-2·s-1·Pa-1) | Separation selectivity, X/Y |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Kosinov[ | 4-6 | 20 | 0.6 | CO2/CH4 | 2.5 | 42 |
| 20 | 0.6 | CO2/N2 | 2.5 | 12 | |||
| 2 | Wu[ | 6-8 | 20 | 0.27 | CO2/CH4 | 2.1 | 178 |
| 20 | 0.27 | N2/CH4 | 0.18 | 9 | |||
| 3 | Song[ | 6 | 25 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 5.6 | 56.5 |
| 25 | 0.2 | N2/CH4 | 0.89 | 10 | |||
| 4 | Li[ | 2 | 25 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 1.16 | 213 |
| 25 | 0.2 | N2/CH4 | 1.07 | 13 | |||
| 5 | Yu[ | 1.5 | -24 | 0.9 | CO2/CH4 | 79 | 76 |
| 6 | Karakiliç[ | 2-4 | 22 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 2.6 | 176 |
| 7 | Qiu[ | 0.44 | 20 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 48 | 153 |
| 8 | Kida[ | - | 40 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 17 | 54 |
| 40 | 0.1 | H2/CH4 | 11 | 34 | |||
| 9 | Tang[ | 10 | 20 | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 9.3 | 208 |
| 10 | Kida[ | 5 | 25 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 40 | 130 |
| 11 | Imasaka[ | 3 | 40 | 0.3 | CO2/CH4 | 15 | 115 |
| 12 | Maghsoudi[ | 20 | 30 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 0.34 | 21.6 |
| 13 | Yu[ | 1.3 | 3 | 0.9 | CO2/CH4 | 84 | 47 |
| 14 | Li[ | 5 | 80 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 2.0 | 270 |
| 15 | Li[ | - | 24 | 0.138 | CO2/CH4 | 1.6 | 67 |
| 16 | Carreon[ | - | 22 | 0.138 | CO2/CH4 | 3.8 | 170 |
| 17 | Venna[ | - | 22 | 0.138 | CO2/CH4 | 5.0 | 245 |
| 22 | 0.138 | CO2/N2 | 2.1 | 39 | |||
| 18 | Huang[ | 2 | 22 | 0.074 | N2/CH4 | 4.93 | 11.3 |
| 19 | Chen[ | 2-3 | 25 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 1.18 | 160 |
| 20 | Chang[ | - | - | 4 | CO2/CH4 | 6.1 | 88 |
| 21 | Liu[ | 3 | 30 | 0.1 | CO2/CH4 | 12 | 95 |
| 22 | Rehman[ | - | 80 | 0.4 | CO2/CH4 | 47.3 | 65 |
| 23 | Liu[ | 7-15 | 25 | 0.1 | CO2/N2 | 18.5 | 29.8 |
| 24 | Li[ | 4-6 | 22 | 7 | CO2/CH4 | 0.4 | 100 |
| 25 | Zhang[ | - | 20 | 4.6 | CO2/CH4 | 8.2 | 55 |
| 26 | Noble[ | - | 22 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 1.2 | 170 |
| 27 | Shi[ | 2-4 | 22 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 23.2 | 186 |
| 28 | Shi[ | 4-5 | 22 | 0.14 | CO2/CH4 | 16.8 | 256 |
| 29 | Li[ | 3 | - | 4 | CO2/CH4 | 13.2 | 62 |
| 30 | Bai[ | 0.8 | - | 0.2 | CO2/CH4 | 25.3 | 70 |
| [1] |
LI S, CARREON M A, ZHANG Y, et al. Scale-up of SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010,352(1/2):7-13.
DOI URL |
| [2] | NAIR S, LAI Z, NIKOLAKIS V, et al. Separation of close- boiling hydrocarbon mixtures by MFI and FAU membranes made by secondary growth. Microporous & Mesoporous Materials, 2001,48(1):219-228. |
| [3] |
GU X H, DONG J H, NENOFF T M, et al. Synthesis of defect-free FAU-type zeolite membranes and separation for dry and moist CO2/N2 mixtures. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2005,44(4):937-944.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ZHU W, GORA L, VAN DEN BERG A W C, et al. Water vapour separation from permanent gases by a zeolite-4A membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2005,253(1/2):57-66.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LI S, MARTINEK J G, FALCONER J L, et al. High-pressure CO2/CH4 separation using SAPO-34 membranes. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2005,44(9):3220-3228.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
MA L, CHENG Y, CAVATAIO G, et al. Characterization of commercial Cu-SSZ-13 and Cu-SAPO-34 catalysts with hydrothermal treatment for NH3-SCR of NOx in diesel exhaust. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013,225(3):323-330.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
KALIPCILAR H, BOWEN T C, NOBLE R D, et al. Synthesis and separation performance of SSZ-13 zeolite membranes on tubular supports. Chemistry of Materials, 2002,14(8):3458-3464.
DOI URL |
| [8] | ZHANG L X, JIA M D, MIN E. Synthesis of SAPO-34/ceramic composite membranes. Studies in Surface Science and Catalysis, 1997,105(11):2211-2216. |
| [9] |
YAN N, XU H, ZHANG W, et al. Probing locations of organic structure-directing agents (OSDAs) and host-guest interactions in CHA-type SAPO-34/44. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018,264:55-59.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
YU M, NOBLE R D, FALCONER J L. Zeolite membranes: microstructure characterization and permeation mechanisms. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2011,44(11):1196-1206.
DOI URL |
| [11] | WANG JIN-QU, YANG JIAN-HUA, LI HUA-ZHENG, et al. Research progress of zeolite molecular sieve membrane. Membrane Science and Technology, 2014,34(3):1-7, 42. |
| [12] |
CARO J, NOACK M. Zeolite membranes-recent developments and progress. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2008,115(3):215-233.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
BOWEN T C, NOBLE R D, FALCONER J L. Fundamentals and applications of pervaporation through zeolite membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2004,245(1/2):1-33.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
KOSINOV N, AUFFRET C, GVCVCYENER C, et al. High flux high-silica SSZ-13 membrane for CO2 separation. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014,2(32):13083-13092.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
TOTH A J, SZILAGYI B, HAAZ E, et al. Enhanced separation of maximum boiling azeotropic mixtures with extractive heterogeneous-azeotropic distillation. Chemical Engineering Research and Design, 2019,147:55-62.
DOI URL |
| [16] | CLET G, GORA L, NISHIYAMA N, et al. An alternative synthesis method for zeolite Y membranes. Chemical Communications, 2001,1:41-42. |
| [17] |
JIANG H, ZHANG B, LIN Y S, et al. Synthesis of zeolite membranes. Chinese Science Bulletin, 2004,49(24):2547-2554.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
HONG M, LI S, FUNKE H F, et al. Ion-exchanged SAPO-34 membranes for light gas separations. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2007,106(1/2/3):140-146.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LI S, FALCONER J L, NOBLE R D. SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2004,241(1):121-135.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
SAPATSIS M, LOVALLO M, OKUBO T, et al. Characterization of zeolite L nanoclusters. Chemistry of Materials, 1995,7(9):1734-1741.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
WU T, DIAZ M C, ZHENG Y, et al. Influence of propane on CO2/CH4 and N2/CH4 separations in CHA zeolite membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015,473:201-209.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
CHISHOLM N O, FUNKE H H, NOBLE R D, et al. Carbon dioxide/alkane separations in a SSZ-13 membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018,568:17-21.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
CARREON M A, LI S, FALCONER J L, et al. SAPO-34 seeds and membranes prepared using multiple structure directing agents. Advanced Materials, 2008,20(4):729-732.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
KOSINOV N, AUFFRET C, BORGHUIS G J, et al. Influence of the Si/Al ratio on the separation properties of SSZ-13 zeolite membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015,484:140-145.
DOI URL |
| [25] | LEE M, HONG S, KIM D, et al. Chabazite-type zeolite membranes for effective CO2 separation: the role of hydrophobicity and defect structure. Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019,11(4):3946-3960. |
| [26] |
HONG S, KIM D, JEONG Y, et al. Healing of microdefects in SSZ-13 membranes via filling with dye molecules and its effect on dry and wet CO2 separations. Chemistry of Materials, 2018,30(10):3346-3358.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
ZHENG Y, HU N, WANG H, et al. Preparation of steam-stable high-silica CHA (SSZ-13) membranes for CO2/CH4 and C2H4/C2H6 separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2015,475:303-310.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZHOU R, WANG H, WANG B, et al. Defect-patching of zeolite membranes by surface modification using siloxane polymers for CO2 separation. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2015,54(30):7516-7523.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
SONG S, GAO F, ZHANG Y, et al. Preparation of SSZ-13 membranes with enhanced fluxes using asymmetric alumina supports for N2/CH4 and CO2/CH4 separations. Separation and Purification Technology, 2019,209:946-954.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
WANG B, ZHENG Y, ZHANG J, et al. Separation of light gas mixtures using zeolite SSZ-13 membranes. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019,275:191-199.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
LI X, WANG Y, WU T, et al. High-performance SSZ-13 membranes prepared using ball-milled nanosized seeds for carbon dioxide and nitrogen separations from methane. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2020,28(5):1285-1292.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
LIANG L, ZHU M, CHEN L, et al. Single gas permeance performance of high silica SSZ-13 zeolite membranes. Membranes, 2018,8(3):43.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
JIANG J, WANG X, ZHANG Y, et al. Fabrication of pure-phase CHA zeolite membranes with ball-milled seeds at low K + concentration. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials , 2015,215:98-108.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
JIANG J, PENG L, WANG X, et al. Effect of Si/Al ratio in the framework on the pervaporation properties of hollow fiber CHA zeolite membranes. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019,273:196-202.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
WU T, LUCERO J, CRAWFORD J M, et al. SAPO-34 membranes for xenon capture from air. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019,573:288-292.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
VENNA S R, CARREON M A. Amino-functionalized SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 and CO2/N2 separation. Langmuir, 2011,27(6):2888-2894.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZONG Z, CARREON M A. Thin SAPO-34 membranes synthesized in stainless steel autoclaves for N2/CH4 separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017,524:117-123.
DOI URL |
| [38] | FUNKE H H, TOKAY B, ZHOU R, et al. Spatially resolved gas permeation through SAPO-34 membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012,409:212-221. |
| [39] | PING E W, ZHOU R, FUNKE H H, et al. Seeded-gel synthesis of SAPO-34 single channel and monolith membranes, for CO2/CH4 separations. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012,415:770-775. |
| [40] |
HUANG Y, WANG L, SONG Z, et al. Growth of high-quality, thickness-reduced zeolite membranes towards N2/CH4 separation using high-aspect-ratio seeds. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2015,54(37):10843-10847.
DOI URL |
| [41] | CHEN Y, ZHANG Y, ZHANG C, et al. Fabrication of high-flux SAPO-34 membrane on α-Al2O3 four-channel hollow fibers for CO2 capture from CH4. Journal of CO2 Utilization, 2017,18:30-40. |
| [42] |
WANG M, LI M, CHANG N, et al. Vapor separation of methanol-dimethyl carbonate mixture on SAPO-34 zeolite membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018,565:311-321.
DOI URL |
| [43] |
CHANG N, TANG H, BAI L, et al. Optimized rapid thermal processing for the template removal of SAPO-34 zeolite membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2018,552:13-21.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
LIGHTFOOT P, WOODCOCK D A, MAPLE M J, et al. The widespread occurrence of negative thermal expansion in zeolites. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2001,11(1):212-216.
DOI URL |
| [45] | SATO K, SUGIMOTO K, SHIMOTSUMA N, et al. Development of practically available up-scaled high-silica CHA-type zeolite membranes for industrial purpose in dehydration of N-methyl pyrrolidone solution. Journal of Membrane Science, 2012,409:82-95. |
| [46] |
BRAUN I, SCHULZ EKLOFF G, WOHRLE D, et al. Synthesis of AlPO4-5 in a microwave-heated, continuous-flow, high- pressure tube reactor. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 1998,23(1/2):79-81.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
HU N, LI Y, ZHONG S, et al. Microwave synthesis of zeolite CHA (chabazite) membranes with high pervaporation performance in absence of organic structure directing agents. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016,228:22-29.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
LIU X, DU S, ZHANG B. The seeded growth of dense and thin SAPO-34 membranes on porous α-Al2O3 substrates under microwave irradiation. Materials Letters, 2013,91:195-197.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
CHEW T L, AHMAD A L, BHATIA S. Ba-SAPO-34 membrane synthesized from microwave heating and its performance for CO2/CH4 gas separation. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011,171(3):1053-1059.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
AKHTAR F, OJUVA A, WIRAWAN S K, et al. Hierarchically porous binder-free silicalite-1 discs: a novel support for all- zeolite membranes. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011,21(24):8822-8828.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
HE Y, CUI X, LIU X, et al. Preparation of self-supporting NaA zeolite membranes using geopolymers. Journal of Membrane Science, 2013,447:66-72.
DOI URL |
| [52] | STOEGER J A, CHOI J, TSAPATSIS M. Rapid thermal processing and separation performance of columnar MFI membranes on porous stainless steel tubes. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011,4(9):3479-3486. |
| [53] |
REHMAN R U, SONG Q, PENG L, et al. Hydrophobic modification of SAPO-34 membranes for improvement of stability under wet condition. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering, 2019,27(10):2397-2406.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
MU Y, CHEN H, XIANG H, et al. Defects-healing of SAPO-34 membrane by post-synthesis modification using organosilica for selective CO2 separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019,575:80-88.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
LIU B, TANG C, LI X, et al. High-performance SAPO-34 membranes for CO2 separations from simulated flue gas. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020,292:109712.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
KOSINOV N, AUFFRET C, SRITAPHI V G P, et al. Influence of support morphology on the detemplation and permeation of ZSM-5 and SSZ-13 zeolite membranes. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2014,197:268-277.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
YU L, HOLMGREN A, HEDLUND J. A novel method for fabrication of high-flux zeolite membranes on supports with arbitrary geometry. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019,7(17):10325-10330.
DOI URL |
| [58] |
CARREON M A, LI S, FALCONER J L, et al. Alumina- supported SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2008,130(16):5412-5413.
DOI URL |
| [59] | LIU J Q, LUO Y B, LI M G, et al. Synthesis of nanosized SSZ-13 zeolite and performance of its mixed matrix membrane for CO2/CH4 separation. China Petroleum Processing & Petrochemical Technology, 2019,21(2):19-26. |
| [60] |
TAKATA T, TSUNOJI N, TAKAMITSU Y, et al. Nanosized CHA zeolites with high thermal and hydrothermal stability derived from the hydrothermal conversion of FAU zeolite. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016,225:524-533.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
NAJAFI N, ASKARI S, HALLADJ R. Hydrothermal synthesis of nanosized SAPO-34 molecular sieves by different combinations of multi templates. Powder Technology, 2014,254:324-330.
DOI URL |
| [62] |
YANG H, LIU X, LU G, et al. Synthesis of SAPO-34 nanoplates via hydrothermal method. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016,225:144-153.
DOI URL |
| [63] |
SUN Q, WANG N, GUO G, et al. Ultrafast synthesis of nano- sized zeolite SAPO-34 with excellent MTO catalytic performance. Chemical Communications, 2015,51(91):16397-16400.
DOI URL |
| [64] |
KARAKILIÇ P, WANG X, KAPTEIJN F, et al. Defect-free high-silica CHA zeolite membranes with high selectivity for light gas separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019,586:34-43.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
JABBARI Z, FATEMI S, DAVOODPOUR M. Comparative study of seeding methods; dip-coating, rubbing and EPD, in SAPO-34 thin film fabrication. Advanced Powder Technology, 2014,25(1):321-330.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
HENGE Q, ZHANG Y, KONG L, et al. High performance SSZ-13 membranes prepared at low temperature. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020,603:118023.
DOI URL |
| [67] |
WHITE J C, DUTTA P K, SHQAU K, et al. Synthesis of ultrathin zeolite Y membranes and their application for separation of carbon dioxide and nitrogen gases. Langmuir, 2010,26(12):10287-10293.
DOI URL |
| [68] |
BOHSTRÖM Z, ARSTAD B, LILLERUD K P. Preparation of high silica chabazite with controllable particle size. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2014,195:294-302.
DOI URL |
| [69] |
VAN HEYDEN H, MINTOVA S, BEIN T. Nanosized SAPO-34 synthesized from colloidal solutions. Chemistry of Materials, 2008,20(9):2956-2963.
DOI URL |
| [70] |
MIYAMOTO M, NAKATANI T, FUJIOKA Y, et al. Verified synthesis of pure silica CHA-type zeolite in fluoride media. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2015,206:67-74.
DOI URL |
| [71] |
KIDA K, MAETA Y, YOGO K. Preparation and gas permeation properties on pure silica CHA-type zeolite membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017,522:363-370.
DOI URL |
| [72] |
FENG X, ZONG Z, ELSAIDIl S K, et al. Kr/Xe separation over a chabazite zeolite membrane. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016,138(31):9791-9794.
DOI URL |
| [73] |
CARREON M A. Molecular sieve membranes for N2/CH4 separation. Journal of Materials Research, 2018,33(1):32-43.
DOI URL |
| [74] |
LI S, FALCONER J L, NOBLE R D. SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 separations: effect of Si/Al ratio. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2008,110(2/3):310-317.
DOI URL |
| [75] |
KIM S J, LIU Y, MOORE J S, et al. Thin hydrogen-selective SAPO-34 zeolite membranes for enhanced conversion and selectivity in propane dehydrogenation membrane reactors. Chemistry of Materials, 2016,28(12):4397-4402.
DOI URL |
| [76] |
RIVERA RAMOS M E, RUIZ MERCADO G J, HERNANDEZ MALDONADO A J. Separation of CO2 from light gas mixtures using ion-exchanged silicoaluminophosphate nanoporous sorbents. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008,47(15):5602-5610.
DOI URL |
| [77] |
AVILA A M, FUNKE H H, ZHANG Y, et al. Concentration polarization in SAPO-34 membranes at high pressures. Journal of Membrane Science, 2009,335(1/2):32-36.
DOI URL |
| [78] |
ZHANG Y, TOKAY B, FUNKE H H, et al. Template removal from SAPO-34 crystals and membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2010,363(1/2):29-35.
DOI URL |
| [79] |
PENG C, LIU Z, HOORIMOTO A, et al. Preparation of nanosized SSZ-13 zeolite with enhanced hydrothermal stability by a two-stage synthetic method. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2018,255:192-199.
DOI URL |
| [80] |
KIM J, JANG E, HONG S, et al. Microstructural control of a SSZ-13 zeolite film via rapid thermal processing. Journal of Membrane Science, 2019,591:117342.
DOI URL |
| [81] |
TANG H, BAI L, WANG M, et al. Fast synthesis of thin high silica SSZ-13 zeolite membrane using oil-bath heating. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2019,44(41):23107-23119.
DOI URL |
| [82] |
YANG S, KWON Y H, KOH D Y, et al. Highly selective SSZ-13 zeolite hollow fiber membranes by ultraviolet activation at near-ambient temperature. ChemNanoMat, 2019,5(1):61-67.
DOI URL |
| [83] |
KIDA K, MAETA Y, YOGO K. Pure silica CHA-type zeolite membranes for dry and humidified CO2/CH4 mixtures separation. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018,197:116-121.
DOI URL |
| [84] |
LEE M, JEONG Y, HONG S, et al. High performance CO2-perm-selective SSZ-13 membranes: elucidation of the link between membrane material and module properties. Journal of Membrane Science, 2020,611:118390.
DOI URL |
| [85] |
DJIEUGOUE M A, PRAKASH A M, KEVAN L. Catalytic study of methanol-to-olefins conversion in four small-pore silicoaluminophosphate molecular sieves: influence of the structural type, nickel incorporation, nickel location, and nickel concentration. Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2000,104(27):6452-6461.
DOI URL |
| [86] |
CHEN X, GUO J, FU Z, et al. Characterization and catalytic behaviors of methylamine modified FAU zeolites. Journal of Porous Materials, 2013,20(5):1271-1281.
DOI URL |
| [87] |
IMASAKA, ISHII H, HAYASHI J, et al. Synthesis of CHA-type titanosilicate zeolites using titanium oxide as Ti source and evaluation of their physicochemical properties. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2019,273:243-248.
DOI URL |
| [88] |
ARAKI S, ISHII H, IMASAKA S, et al. Synthesis and gas permeation properties of chabazite-type titanosilicate membranes synthesized using nano-sized seed crystals. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2020,292:109798.
DOI URL |
| [89] | SERGEI A ZUBKOV, LEONID M KUSTOV, VADIM B KAZANSKY, et al. Investigation of hydroxyl groups in crystalline silicoaluminophosphate SAPO-34 by diffuse reflectance infrared spectroscopy. Journal of the Chemical Society, 1991,87:897. |
| [90] |
HUANG J, ZOU J, HO W S W. Carbon dioxide capture using a CO-selective facilitated transport membrane. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008,47(4):1261-1267.
DOI URL |
| [91] |
ZOU J, HO W S W. CO2-selective polymeric membranes containing amines in crosslinked poly(vinyl alcohol). Journal of Membrane Science, 2006,286(1/2):310-321.
DOI URL |
| [92] | TEE Y H, ZOU J, HO W S W. CO2-selective membranes containing dimethylglycine mobile carriers and polyethylenimine fixed carrier. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2006,37(1):37-47. |
| [93] |
SINGH Z V, COWAN M G, MCDANEL W M, et al. Determination and optimization of factors affecting CO2/CH4 separation performance in poly(ionic liquid)-ionic liquid-zeolite mixed-matrix membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016,509:149-155.
DOI URL |
| [94] |
BARA J E, CAMPER D E, GIN D L, et al. Room-temperature ionic liquids and composite materials: platform technologies for CO2 capture. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2010,43(1):152-159.
DOI URL |
| [95] |
LIU B, ZHOU R, BU N, et al. Room-temperature ionic liquids modified zeolite SSZ-13 membranes for CO2/CH4 separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2017,524:12-19.
DOI URL |
| [96] |
CHEN K J, MADDEN D G, PHAM T, et al. Tuning pore size in square-lattice coordination networks for size-selective sieving of CO2. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2016,55(35):10268-10272.
DOI URL |
| [97] |
SINGH Z V, COWAN M G, MCDANEL W M, et al. Determination and optimization of factors affecting CO2/CH4 separation performance in poly (ionic liquid)-ionic liquid-zeolite mixed-matrix membranes. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016,509:149-155.
DOI URL |
| [98] |
IMASAKA S, ITAKURA M, YANO K, et al. Rapid preparation of high-silica CHA-type zeolite membranes and their separation properties. Separation and Purification Technology, 2018,199:298-303.
DOI URL |
| [99] |
MAGHSOUDI H, SOLTANIEH M. Simultaneous separation of H2S and CO2 from CH4 by a high silica CHA-type zeolite membrane. Journal of Membrane Science, 2014,470:159-165.
DOI URL |
| [100] |
YU L, HOLMGREN A, ZHOU M, et al. Highly permeable CHA membranes prepared by fluoride synthesis for efficient CO2/CH4 separation. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2018,6(16):6847-6853.
DOI URL |
| [101] |
LI S, FALCONER J L, NOBLE R D. Improved SAPO-34 membranes for CO2/CH4 separations. Advanced Materials, 2006,18(19):2601-2603.
DOI URL |
| [102] |
SHI H. Synthesis of SAPO-34 zeolite membranes with the aid of crystal growth inhibitors for CO2-CH4 separation. New Journal of Chemistry, 2014,38(11):5276-5278.
DOI URL |
| [103] |
SHI H. Organic template-free synthesis of SAPO-34 molecular sieve membranes for CO2-CH4 separation. RSC Advances, 2015,5(48):38330-38333.
DOI URL |
| [104] |
LI M, ZHANG J, LIU X, et al. Synthesis of high performance SAPO-34 zeolite membrane by a novel two-step hydrothermal synthesis+dry gel conversion method. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016,225:261-271.
DOI URL |
| [105] |
BAI L, CHANG N, LI M, et al. Ultrafast synthesis of thin SAPO-34 zeolite membrane by oil-bath heating. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2017,241:392-399.
DOI URL |
| [106] |
KOSINOV N, GASCON J, KAPTEIJN F, et al. Recent developments in zeolite membranes for gas separation. Journal of Membrane Science, 2016,499:65-79.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 丁玲, 蒋瑞, 唐子龙, 杨运琼. MXene材料的纳米工程及其作为超级电容器电极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | 杨卓, 卢勇, 赵庆, 陈军. X射线衍射Rietveld精修及其在锂离子电池正极材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | 陈强, 白书欣, 叶益聪. 热管理用高导热碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | 林俊良, 王占杰. 铁电超晶格的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [5] | 牛嘉雪, 孙思, 柳鹏飞, 张晓东, 穆晓宇. 铜基纳米酶的特性及其生物医学应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [6] | 苑景坤, 熊书锋, 陈张伟. 聚合物前驱体转化陶瓷增材制造技术研究趋势与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [7] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [8] | 杨洋, 崔航源, 祝影, 万昌锦, 万青. 柔性神经形态晶体管研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [9] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [10] | 陈昆峰, 胡乾宇, 刘锋, 薛冬峰. 多尺度晶体材料的原位表征技术与计算模拟研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [11] | 张超逸, 唐慧丽, 李宪珂, 王庆国, 罗平, 吴锋, 张晨波, 薛艳艳, 徐军, 韩建峰, 逯占文. 新型GaN与ZnO衬底ScAlMgO4晶体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [12] | 齐占国, 刘磊, 王守志, 王国栋, 俞娇仙, 王忠新, 段秀兰, 徐现刚, 张雷. GaN单晶的HVPE生长与掺杂进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [13] | 林思琪, 李艾燃, 付晨光, 李荣斌, 金敏. Zintl相Mg3X2(X=Sb, Bi)基晶体生长及热电性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [14] | 刘岩, 张珂颖, 李天宇, 周菠, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 陶瓷材料电场辅助连接技术研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 113-124. |
| [15] | 谢兵, 蔡金峡, 王铜铜, 刘智勇, 姜胜林, 张海波. 高储能密度聚合物基多层复合电介质的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||