无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (7): 779-784.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200540
• 研究快报 • 上一篇
王慧1,2( ), 张淑娟1,3, 陈亭伟1, 张传林1, 罗豪甦2, 郑仁奎1(
), 张淑娟1,3, 陈亭伟1, 张传林1, 罗豪甦2, 郑仁奎1( )
)
收稿日期:2020-09-15
修回日期:2020-10-11
出版日期:2021-07-20
网络出版日期:2020-12-01
通讯作者:
郑仁奎, 教授. E-mail:zrk@ustc.edu
作者简介:王慧(1994-), 女, 博士研究生. E-mail:AliceWang9494@163.com
WANG Hui1,2( ), ZHANG Shujuan1,3, CHEN Tingwei1, ZHANG Chuanlin1, LUO Haosu2, ZHENG Renkui1(
), ZHANG Shujuan1,3, CHEN Tingwei1, ZHANG Chuanlin1, LUO Haosu2, ZHENG Renkui1( )
)
Received:2020-09-15
Revised:2020-10-11
Published:2021-07-20
Online:2020-12-01
Contact:
ZHENG Renkui, professor. E-mail:zrk@ustc.edu
About author:WANG Hui(1994-), female, PhD candidate. E-mail:AliceWang9494@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
PdSe2薄膜主要通过机械剥离法和气相沉积法制得, 本研究采用一种简单有效的可在SiO2/Si衬底上制备PdSe2薄膜的方法。通过高真空磁控溅射技术在SiO2/Si衬底上沉积一层Pd金属薄膜, 将Pd金属薄膜与Se粉封在高真空的石英管中并在一定的温度下进行硒化, 获得PdSe2薄膜。根据截面高分辨透射电镜(HRTEM)照片可知PdSe2薄膜的平均厚度约为30 nm。进一步研究硒化温度对PdSe2薄膜电输运性能的影响, 当硒化温度为300 ℃时, 所制得的PdSe2薄膜的体空穴浓度约为1×1018 cm-3, 具有最大的室温迁移率和室温磁阻, 分别为48.5 cm2·V-1·s-1和12%(B=9 T)。值得注意的是, 本实验中通过真空硒化法获得的薄膜空穴迁移率大于通过机械剥离法制得的p型PdSe2薄膜。随着硒化温度从300 ℃逐渐升高, 由于Se元素容易挥发, Pd薄膜的硒化程度逐渐减小, 导致薄膜硒含量、迁移率和磁电阻降低。本研究表明:真空硒化法是一种简单有效地制备PdSe2薄膜的方法, 在贵金属硫族化合物的大面积制备及多功能电子器件的设计中具有潜在的应用价值。
中图分类号:
王慧, 张淑娟, 陈亭伟, 张传林, 罗豪甦, 郑仁奎. PdSe2半导体薄膜的真空硒化法制备研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 779-784.
WANG Hui, ZHANG Shujuan, CHEN Tingwei, ZHANG Chuanlin, LUO Haosu, ZHENG Renkui. Electronic Property of PdSe2 Thin Films Fabricated by Post-selenization of Pd Films[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 779-784.
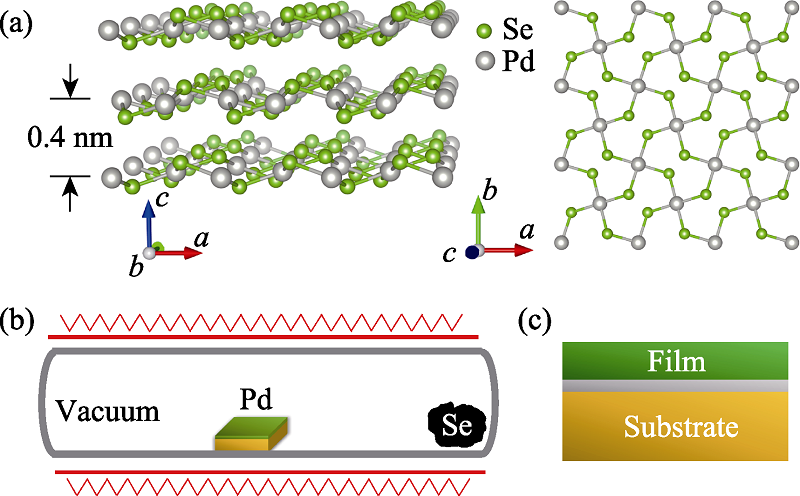
Fig. 1 Side and top view of the crystal structure of PdSe2 thin films (a), schematic illustration for the growth of PdSe2 films on SiO2/Si substrates by post-selenization of a Pd layer in an evacuated quartz ampule (b), and structure diagram of the PdSe2/SiO2/Si structure (c)

Fig. 2 Photograph of an as-synthesized 5 mm×5 mm PdSe2 thin film (a), and top-view micrographs of the films selenized at 200 (b), 250 (c), 300 (d), 450 (e), and 600 ℃ (f), respectively
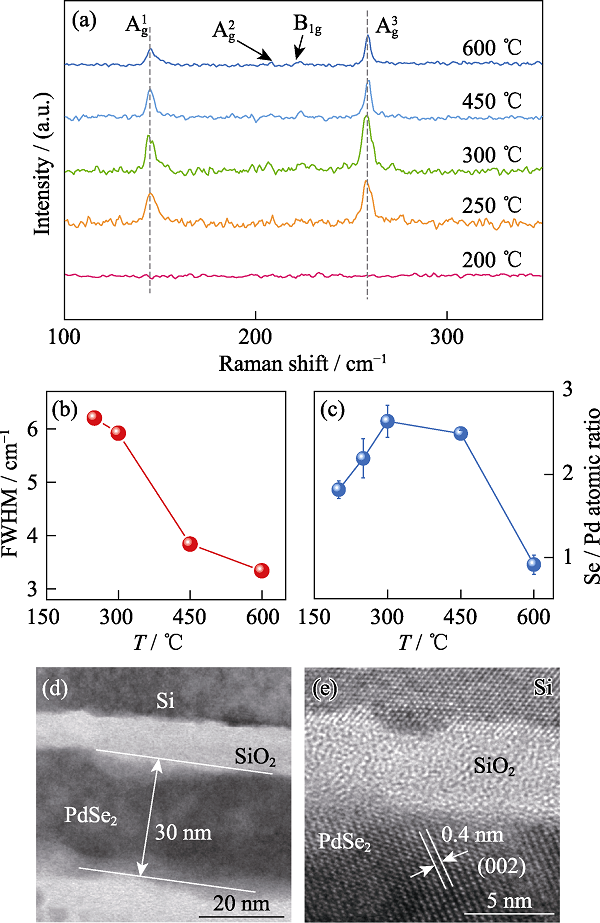
Fig. 3 Raman spectra (a), FWHM of the Ag3 peaks (b) and Se/Pd atomic ratios (c) of the PdSe2 thin films selenized at different temperatures, cross-sectional HRTEM images for a film selenized at 300 ℃(d-e)
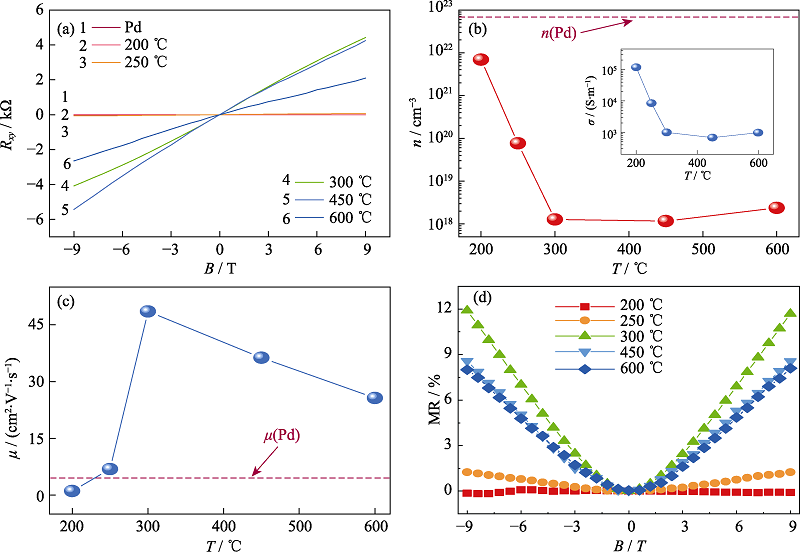
Fig. 4 Hall resistivity (a), carrier concentration (b), carrier mobility (c), and MR (d) of PdSe2 thin films fabricated at different selenization temperatures Inset in (b) is conductivities of different PdSe2 thin films. Dashed lines in (b, c) represent the carrier density and mobility of the Pd layer
| Method | Mobility/(cm2·V-1·s-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Exfoliation | 20.0 | [13] |
| Exfoliation | 14.0 | [18] |
| Exfoliation | 0.9 | [35] |
| Exfoliation | 1.8 | [36] |
| Vacuum selenization | 48.5 | This work |
Table 1 Comparison of the hole carrier mobility of our p-type PdSe2 with other thin films
| Method | Mobility/(cm2·V-1·s-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|
| Exfoliation | 20.0 | [13] |
| Exfoliation | 14.0 | [18] |
| Exfoliation | 0.9 | [35] |
| Exfoliation | 1.8 | [36] |
| Vacuum selenization | 48.5 | This work |
| [1] |
JARIWALA D, SANGWAN V K, LAUHON L J, et al. Emerging device applications for semiconducting two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. ACS Nano, 2014,8(2):1102-1120.
DOI URL |
| [2] |
BUTLER S Z, HOLLEN S M, CAO L, et al. Progress, challenges, and opportunities in two-dimensional materials beyond graphene. ACS Nano, 2013,7(4):2898-2926.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
WANG Q H, KALANTAR-ZADEH K, KIS A, et al. Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nature Nanotechnology, 2012,7:699-712.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
ALI M N, XIONG J, FLYNN S, et al. Large, non-saturating magnetoresistance in WTe2. Nature, 2014,514:205-208.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
SHI W, YE J, ZHANG Y, et al. Superconductivity series in transition metal dichalcogenides by ionic gating. Scientific Reports, 2015,5:12534.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
NETO A H C. Charge density wave, superconductivity, and anomalous metallic behavior in 2D transition metal dichalcogenides. Physical Review Letters, 2001,86(19):4382-4385.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
PODZOROV V, GERSHENSON M E, KLOC C, et al. High- mobility field-effect transistors based on transition metal dichalcogenides. Applied Physics Letters, 2004,84(17):3301.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
RADISAVLJEVIC B, KIS A. Mobility engineering and a metal-insulator transition in monolayer MoS2. Nature Materials, 2013,12:815-823.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
TONGAY S, ZHOU J, ATACA C, et al. Broad-range modulation of light emission in two-dimensional semiconductors by molecular physisorption gating. Nano Letters, 2013,13(6):2831-2836.
DOI URL |
| [10] | TAN S, YIN S, OUYANG G. Size effect on the interface modulation of interlayer and auger recombination rates in MoS2/WSe2 van der Waals heterostructures. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020,35(6):682-688. |
| [11] |
KO C, LEE Y, CHEN Y, et al. Ferroelectrically gated atomically thin transition-metal dichalcogenides as nonvolatile memory. Advanced Materials, 2016,28(15):2923-2930.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SOULARD C, ROCQUEFELTE X, PETIT E, et al. Experimental and theoretical investigation on the relative stability of the PdSe2- and pyrite-type structures of PdSe2. Inorganic Chemistry, 2004,43(6):1943-1949.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
OYEDELE A D, YANG S, LIANG L B, et al. PdSe2: pentagonal two-dimensional layers with high air stability for electronics. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017,139(40):14090-14097.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
XIA F, WANG H, JIA Y. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nature Communications, 2014,5:4458.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
PHANEUF-L'HEUREUX A L, FAVRON A, GERMAIN J F, et al. Polarization-resolved Raman study of bulk-like and Davydov- induced vibrational modes of exfoliated black phosphorus. Nano Letters, 2016,16:7761-7767.
DOI URL |
| [16] | ZHANG S, ZHOU J, WANG Q, et al. Penta-graphene: a new carbon allotrope. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, 2015,112(8):2372-2377. |
| [17] |
MA Y, KOU L, LI X, et al. Room temperature quantum spin Hall states in two-dimensional crystals composed of pentagonal rings and their quantum wells. NPG Asia Materials, 2016,8:e264.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
CHOW W L, YU P, LIU F A, et al. High mobility 2D palladium diselenide field-effect transistors with tunable ambipolar characteristics. Advanced Materials, 2017,29(21):1602969.
DOI URL |
| [19] | LIANG Q J, WANG Q X, ZHANG Q, et al. High-performance, room temperature, ultra-broadband photodetectors based on air-stable PdSe2. Advanced Materials, 2019,31(24):1807609. |
| [20] |
SUN J F, SHI H L, SIEGRIST T, et al. Electronic, transport, and optical properties of bulk and mono-layer PdSe2. Applied Physics Letters, 2015,107(15):153902.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
AHMAD S. Strain dependent tuning electronic properties of noble metal dichalcogenides PdX2 (X=S, Se) mono-layer. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2017,198:162-166.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
LEI W, ZHANG S, HEYMANN G, et al. A new 2D high-pressure phase of PdSe2 with high-mobility transport anisotropy for photovoltaic applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2019,7:2096-105.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
ELGHAZALI M A, NAUMOV P G, MIRHOSSEINI H, et al. Pressure-induced superconductivity up to 13.1 K in the pyrite phase of palladium diselenide PdSe2. Physical Review B, 2017,96(6):060509.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
GAO Y Z, LIU X F, HU W, et al. Tunable n-type and p-type doping of two-dimensional layered PdSe2 via organic molecular adsorption. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2020,22(23):12973-12979.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
LI E, WANG D F, FAN P, et al. Construction of bilayer PdSe2 on epitaxial graphene. Nano Research, 2018,11(11):5858-5865.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
JUNG Y, SHEN J, LIU Y H, et al. Metal seed layer thickness- induced transition from vertical to horizontal growth of MoS2 and WS2. Nano Letters, 2014,14(12):6842-6849.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
KONG D S, WANG H T, CHA J J, et al. Synthesis of MoS2 and MoSe2 films with vertically aligned layers. Nano Letters, 2013,13(3):1341-1347.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZENG L H, WU D, LIN S H, et al. Controlled synthesis of 2D palladium diselenide for sensitive photodetector applications. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019,29(1):1806878.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
LUO L B, WANG D, XIE C, et al. PdSe2 multilayer on germanium nanocones array with light trapping effect for sensitive infrared photodetector and image sensing application. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019,29(22):1900849.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
ZENG L H, CHEN Q M, ZHANG Z X, et al. Multilayered PdSe2/perovskite Schottky junction for fast, self-powered, polarization-sensitive, broadband photodetectors, and image sensor application. Advanced Science, 2019,6:1901134.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
LI X Y, ZHANG S H, GUO Y G, et al. Physical properties and photovoltaic application of semiconducting Pd2Se3 monolayer. Nanomaterials, 2018,8(10):832.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
PURETZKY A A, OYEDELE A D, XIAO K, et al. Anomalous interlayer vibrations in strongly coupled layered PdSe2. 2D Materials. 2018,5:035016.
DOI URL |
| [33] |
LAKSHMIKUMAR S T, RASTOGI A C. Selenization of Cu and in thin films for the preparation of selenide photo-absorber layers in solar cells using Se vapour source. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 1994,32:7-19.
DOI URL |
| [34] |
LE P H, LIAO C N, LUO C W, et al. Thermoelectric properties of bismuth-selenide films with controlled morphology and texture grown using pulsed laser deposition. Applied Surface Science, 2013,285(Part B):657-663.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
BARTOLOMEO A D, PELELLA A, LIU X W, et al. Pressure- tunable ambipolar conduction and hysteresis in thin palladium diselenide field effect transistors. Advanced Functional Materials, 2019,29(29):1902483.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
ZHONG J H, YU J, CAO L K, et al. High-performance polarization-sensitive photodetector based on a few-layered PdSe2 nanosheet. Nano Research, 2020,13(6):1780-1786.
DOI URL |
| [37] |
ZHANG Y W, NING H L, LI Y N, et al. Negative to positive crossover of the magnetoresistance in layered WS2. Applied Physics Letters, 2016,108:153114.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 姜红梅, 赵文雅, 付瑞净, 肖冠军. 魔力尺寸硒化镉纳米晶的压力稳定性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 502-506. |
| [2] | 李鹏, 聂晓蕾, 田烨, 方文兵, 魏平, 朱婉婷, 孙志刚, 张清杰, 赵文俞. Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3/环氧树脂柔性复合热电厚膜的制备及其面内制冷性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 679-684. |
| [3] | 刘旸, 于姗, 郑凯文, 陈维维, 董兴安, 董帆, 周莹. N-Bi2O2CO3/CdSe量子点光催化氧化NO及原位红外光谱研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 425-432. |
| [4] | 骆军, 何世洋, 李志立, 李永博, 王风, 张继业. 热电材料高通量实验制备与表征方法[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(3): 247-259. |
| [5] | 敖伟栋, 刘妍, 马青山, 刘欢, 周斌, 郑霄家, 于东麒, 张文华. 垂直排列ReS2(1-x)Se2x合金纳米片的控制合成及带隙调控[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(10): 1083-1088. |
| [6] | 田 力, 张晓勇, 毛启楠, 李学耕, 于平荣, 王 东. 真空快速退火对CIGS太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(1): 35-40. |
| [7] | 张克智, 陶加华, 刘俊峰, 何 俊, 董宇晨, 孙 琳, 杨平雄, 褚君浩. 简单的溶胶–凝胶法制备致密的铜锌锡硫硒薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(7): 781-784. |
| [8] | 王文静, 袁慧敏, 萧淑琴. 不同退火过程对FeZrBCu软磁合金薄膜巨磁阻抗效应的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(7): 721-724. |
| [9] | 应祥岳,聂秋华,戴世勋,徐铁峰,金珍娟. 声子模式与电子-声子结合强度对Dy3+掺杂硒化物玻璃荧光效率的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(6): 1125-1130. |
| [10] | 刘长友,介万奇. ZnSe单晶CVT法生长与系统优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(4): 855-859. |
| [11] | 王娜,苏慧兰,董群,张荻,赖奕坚. 室温生物诱导合成硒化铅纳米半导体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(2): 209-212. |
| [12] | 夏明哲,李东升,杨德仁,阙端麟. 聚苯乙烯微球表面合成CdSe纳米晶[J]. 无机材料学报, 2005, 20(6): 1306-1310. |
| [13] | 张振华,彭景翠,陈小华. 碳纳米管电磁量子性质的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(2): 257-267. |
| [14] | 李砯,侯乙东,李旦振,张安,付贤智. 纳米Fe3O4磁性粒子的制备及物性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2003, 18(4): 929-932. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||