无机材料学报 ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (5): 521-526.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200389
朱治昱1,2( ), 焦艳1,2, 邵冲云1, 何冬兵1(
), 焦艳1,2, 邵冲云1, 何冬兵1( ), 胡丽丽1(
), 胡丽丽1( )
)
收稿日期:2020-07-10
修回日期:2020-10-15
出版日期:2021-05-20
网络出版日期:2021-04-19
通讯作者:
何冬兵, 副研究员. E-mail: hdb798123@163.com;胡丽丽, 研究员. E-mail: hulili@siom.ac.cnhulili@siom.ac.cn
作者简介:朱治昱(1996-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail:zhuzhiyu2019@gmail.com
ZHU Zhiyu1,2( ), JIAO Yan1,2, SHAO Chongyun1, HE Dongbing1(
), JIAO Yan1,2, SHAO Chongyun1, HE Dongbing1( ), HU Lili1(
), HU Lili1( )
)
Received:2020-07-10
Revised:2020-10-15
Published:2021-05-20
Online:2021-04-19
Contact:
HE Dongbing, associate professor. E-mail: hdb798123@163.com;HU Lili, professor. E-mail: hulili@siom.ac.cn
About author:ZHU Zhiyu(1996-), male, Master candidate. E-mail:zhuzhiyu2019@gmail.com
摘要:
对光热折变(Photo-thermal-refractive, PTR)玻璃在总剂量分别为0.35、1、10及100 kGy的γ射线下辐照, 并进行热退火处理, 采用吸收光谱、光致发光光谱及EPR电子顺磁共振谱研究了光热折变玻璃在γ射线辐照下的辐照机理。研究结果表明, γ辐照后的PTR玻璃在可见波段的吸收主要由银原子Ag0、银分子簇Ag2、银分子簇Ag3、银纳米颗粒Agm0及非桥氧空穴中心HC1及HC2引起; 在不同剂量γ射线辐照下, 玻璃基质中的变价离子(Ag+、Ce3+)价态先发生变化, 同时玻璃基质中的非桥氧键发生电离, 形成了非桥氧空穴型缺陷中心HC1、HC2。进一步增加辐照剂量, 产生了银的分子簇Ag2和Ag3; 同时玻璃基质中非桥氧空穴中心HC2的浓度增大, 导致在639 nm附近的吸收增强。分别在不同温度下对辐照后的PTR玻璃进行相同时间的热处理及在低于Tg(玻璃转变温度)的温度下进行不同时间的热处理, 观察到250 ℃退火后PTR玻璃中HC1及HC2缺陷中心发生漂白; 并在430 ℃退火后出现了银纳米颗粒的吸收峰, 该吸收峰随退火时间的延长发生了红移及展宽。
中图分类号:
朱治昱, 焦艳, 邵冲云, 何冬兵, 胡丽丽. γ辐照及热退火对光热折变玻璃光学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 521-526.
ZHU Zhiyu, JIAO Yan, SHAO Chongyun, HE Dongbing, HU Lili. Effects of γ-Irradiation and Thermal Annealing on Photo-thermal-refractive Glass[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 521-526.
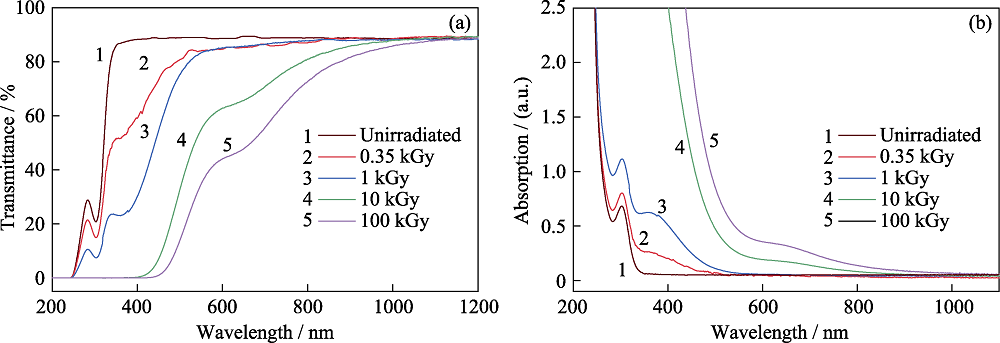
图2 未辐照及0.35、1、10和100 kGy γ射线辐照后PTR玻璃的透过谱图(a)和吸收谱图(b) (厚度2 mm)
Fig. 2 (a) Transmission spectra and (b) absorbance spectra of unirradiated PTR glass and PTR glass irradiated with 0.35, 1, 10, and 100 kGy γ-ray
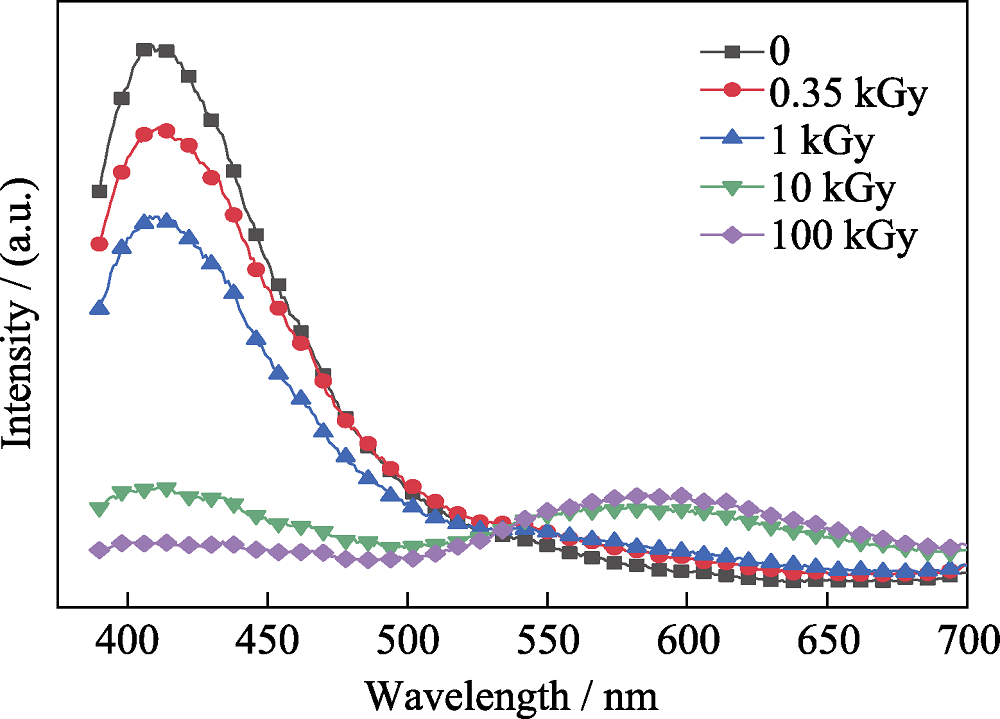
图3 未辐照及0.35、1、10和100 kGy γ射线辐照后PTR玻璃的光致发光光谱(激发波长为340 nm)
Fig. 3 Emission spectra of PTR glass before and after being irradiated by 0.35, 1, 10, and 100 kGy γ-ray (Excitation wavelength: 340 nm)
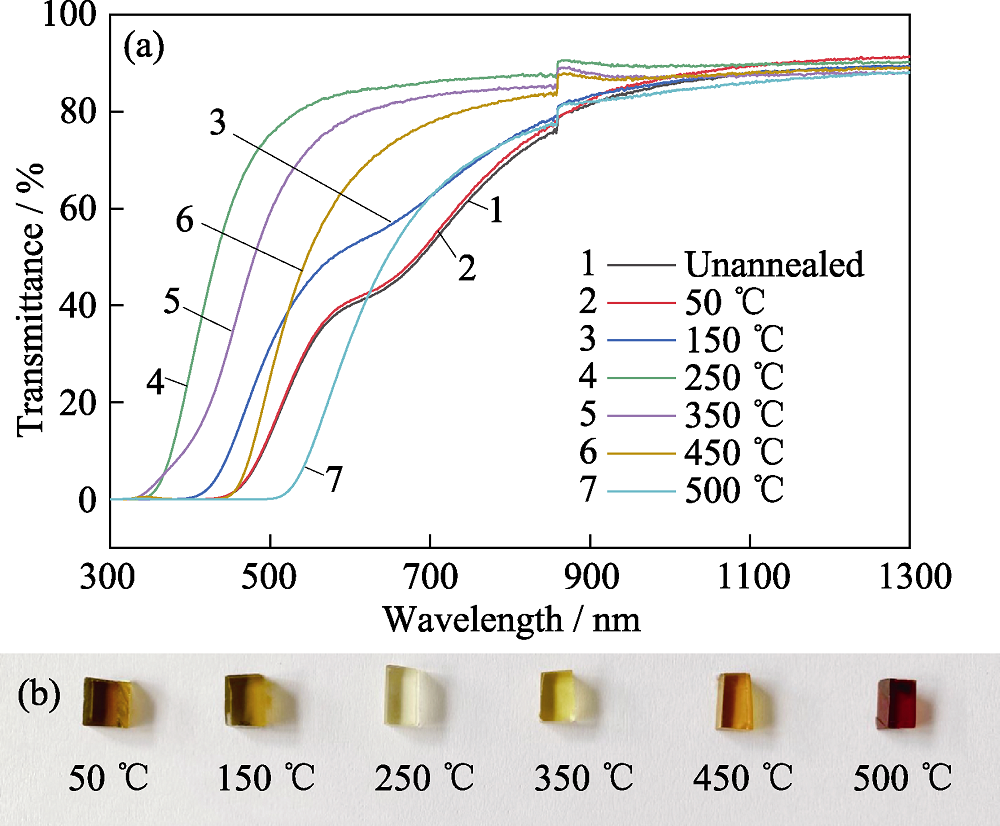
图5 在不同温度下, 对100 kGy γ射线辐照后的PTR玻璃进行30 min热处理后的透过光谱(a)和实物照片(b)
Fig. 5 (a) Transmission spectra and (b) photos of PTR glass irradiated with 100 kGy γ-ray and thermal treatment at different temperatures for 30 min
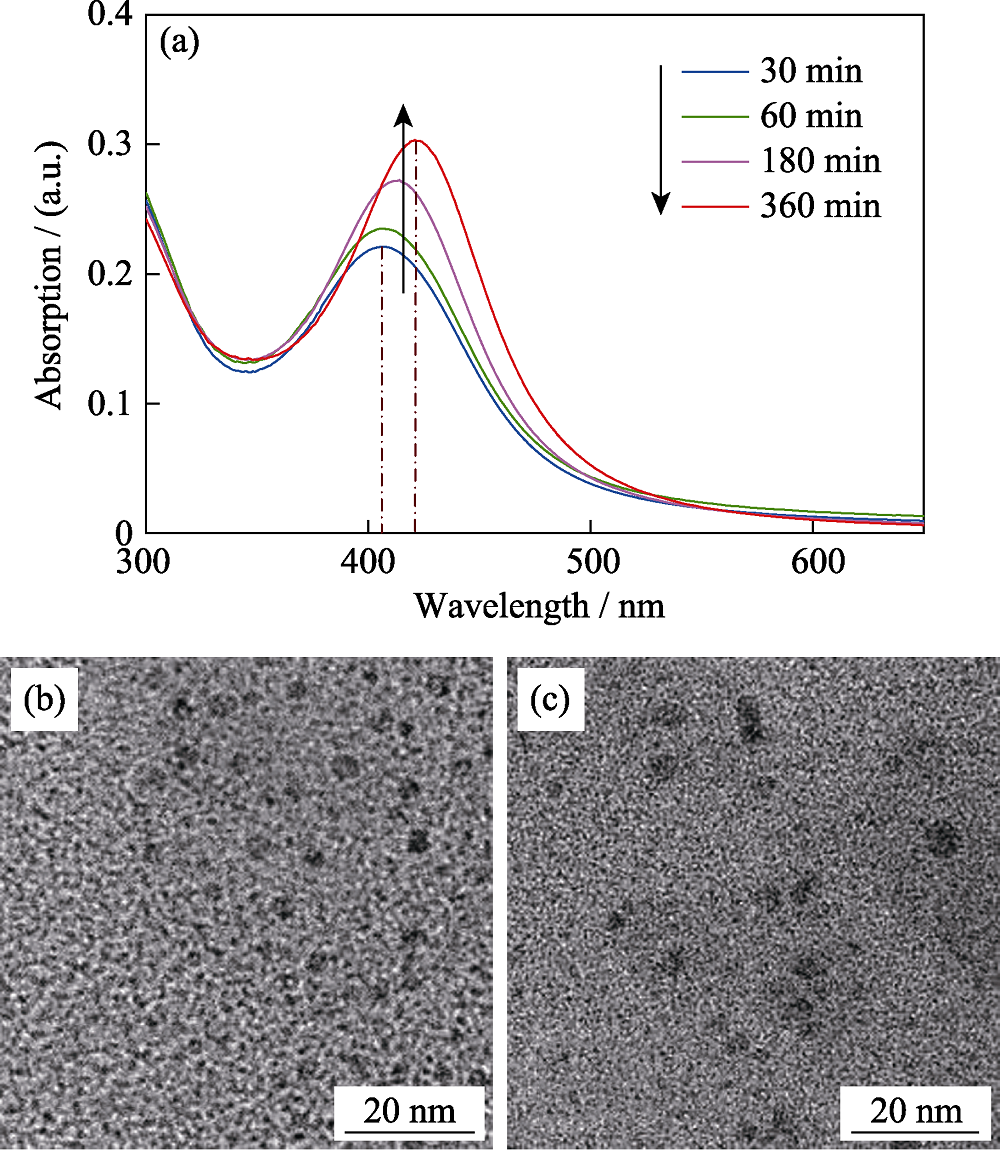
图6 在430 ℃下对100 kGy γ射线辐照后的PTR玻璃进行不同时间热处理后的吸收谱(a), 30 min (b)和120 min (c)和热处理后的TEM照片
Fig. 6 Absorbance spectra of PTR glass after 100 kGy γ-irradiation and thermal treatment at 430 ℃ for different time (a), TEM images of PTR glass after 100 kGy γ-irradiation and thermal treatment at 430 ℃ for 30 min (b) and 180 min (c)
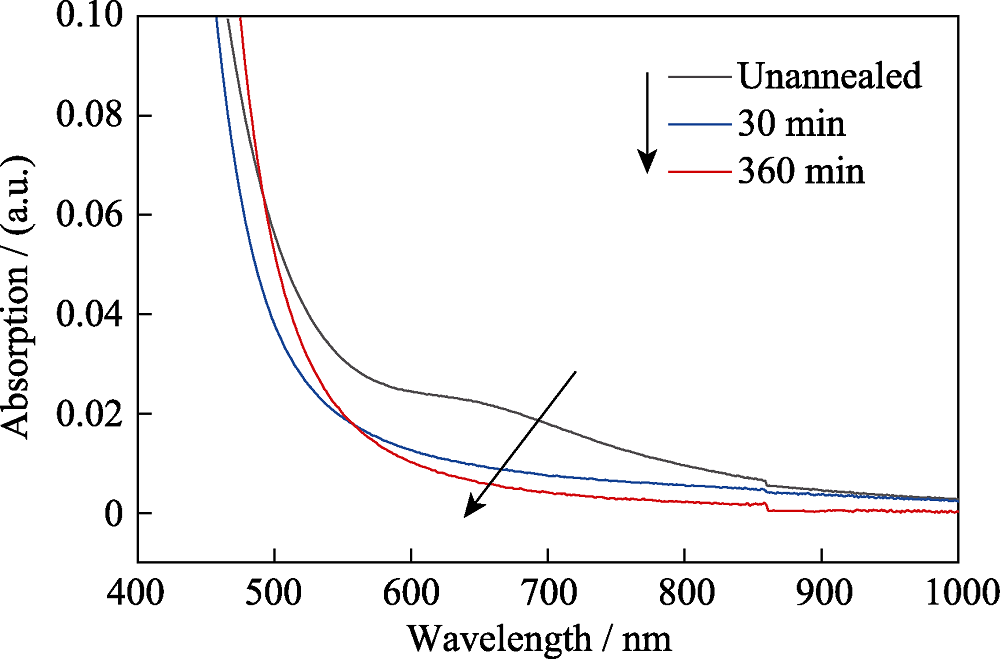
图7 经100 kGy γ射线辐照, 并于430 ℃进行30、360 min热处理前后PTR玻璃的光学吸收谱
Fig. 7 Absorption spectra of 100 kGy γ-ray irradiated PTR glass before and after thermal treatment at 430 ℃ for 30 min and 360 min
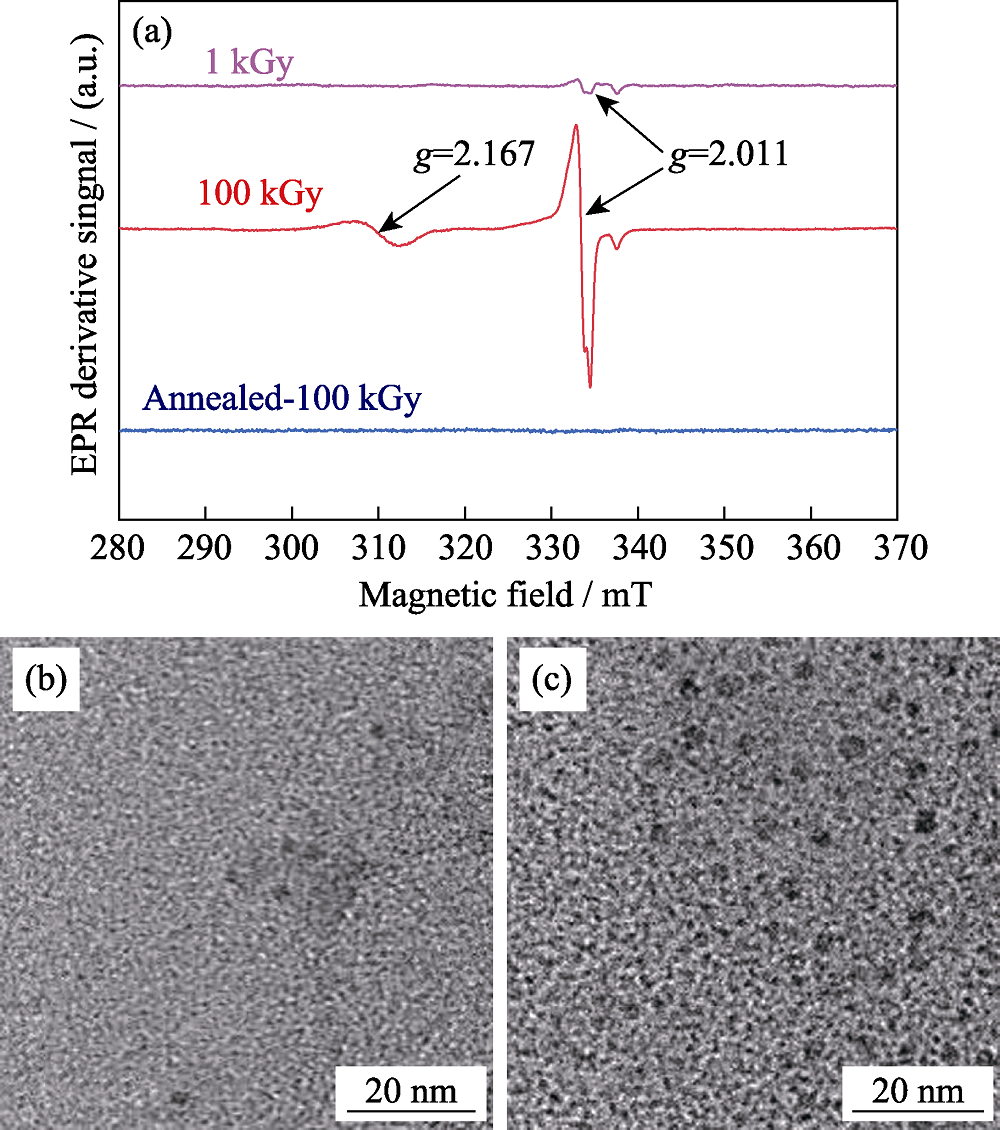
图8 经1、100kGy γ射线辐照及100 kGy γ射线辐照并于430 ℃退火120 min的PTR玻璃的EPR谱(a)以及1 kGy(b)和100 kGy(c) γ射线辐照后的TEM照片
Fig. 8 EPR spectra of PTR glass irradiated with 1, 100 kGy γ-ray, and 100 kGy γ-irradiation and thermal treatment at 430 ℃ for 120 min (a), TEM images of PTR glass after 1 kGy (b) and 100 kGy (c) γ-irradiation
| [1] | NIKONOROV N, ASEEV V, DUBROVIN V, et al. Design and Fabrication of Optical Devices Based on New Polyfunctional Photo-thermo-refractive Glasses. 4th International Conference on Photonics. Optics and Laser Technology. IEEE, 2016: 20-27. |
| [2] | LUMEAU J, ZANOTTO E D. A review of the photo-thermal mechanism and crystallization of photo-thermo-refractive (PTR) glass. International Materials Reviews, 2016,62(6):348-366. |
| [3] |
LUMEAU J, GLEBOVA L, GLEBOV L B. Near-IR absorption in high-purity photothermorefractive glass and holographic optical elements: measurement and application for high-energy lasers. Applied Optics, 2011,50(30):5905-5911.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] | YANG Z N, WANG H Y, LU Q S, et al. An 80-W laser diode array with 0.1 nm linewidth for rubidium vapor laser pumping. Chinese Physics Letters, 2011, 28(10): 104202-1-3. |
| [5] | XING H, DEJIANG C, SIBO W, et al. Single-frequency Nd: YVO4 laser based on reflective bragg grating combined with fabry-perot etalon. Acta Optica Sinica, 2019, 39(5): 05140021- 1-6. |
| [6] | SERGE I, MAXIM S, DARYA K, et al. Blue shift of the plasmon resonance in fluoride photo-thermo-refractive glass. Optical Materials Express, 2018,8(9):2734-2742. |
| [7] | SIDOROV A I, NIKONOROV N V, IGNATIEV A I, et al. The effect of UV irradiation and thermal treatments on structural properties of silver-containing photo-thermo-refractive glasses: studies by Raman spectroscopy. Optical Materials, 2019,98:109422. |
| [8] |
FU X J, SONG L X, LI J C. Coloration of Ce-doped multicomponent silicate glasses by electron irradiation. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014,29(10):1018-1022.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
DUBROVIN V D, IGNATIEV A I, NIKONOROV N V, et al. Luminescence of silver molecular clusters in photo-thermo- refractive glasses. Optical Materials, 2014,36(4):753-759.
DOI URL |
| [10] | SALH R. Defect Related Luminescence in Silicon Dioxide Network: A Review. Rijeka: InTech, 2011: 135-172 |
| [11] | ZATSEPIN A F, GUSEVA V B, VAZHENIN V A, et al. Paramagnetic defects in gamma-irradiated Na/K-silicate glasses. Physics of the Solid State, 2012,54(9):1776-1784. |
| [12] | LAMAESTRE R E D, BEA H, BERNAS H, et al. Irradiation- induced Ag nanocluster nucleation in silicate glasses: analogy with photography. Physical review B, Condensed Matter and Materials Physics, 2007,76(20):205431. |
| [13] | TSAI H S, CHAO D S, WU Y H, et al. Spectroscopic investigation of gamma radiation-induced coloration in silicate glass for nuclear applications. Journal of Nuclear Materials, 2014,453(1/2/3):233-238. |
| [14] | NIKONOROV N V, SIDOROV A I, TSEKHOMSKII V A. Silver nanoparticles in oxide glasses: technologies and properties. In-Tech, 2010,177(10):177-200. |
| [15] | KREIBIG U. Small silver particles in photosensitive glass: their nucleation and growth. Applied Physics, 1976,10(3):255-264. |
| [16] | ORESHKINA K V, DUBROVIN V D, IGNAT’EV A I, et al. The effect of silver on the optical, spectral-luminescent, and crystallization properties of bromide photo-thermo-refractive glasses. Optics & Spectroscopy, 2017,123(4):590-596. |
| [17] | LUMEAU J, GLEBOVA L, GLEBOV L B. Absorption and scattering in photo-thermo-refractive glass induced by UV- exposure and thermal development. Optical Materials, 2014,36(3):621-627. |
| [18] | MARTINA STOICA, MICHAEL KRACKER. CHRISTIAN RÜSSEL. Photoinduced formation of silver nanoparticles in a new Na2O/K2O/CaO/CaF2/Al2O3/ZnO/SiO2 photo thermal refractive glass: evidence of Ag-AgBr core shell structures. Opt. Mater. Express, 2017,7(12):4427-4434. |
| [19] | NACHAROV A P, NIKONOROV N V, SIDOROV A I, et al. Influence of ultraviolet irradiation and heat treatment on the morphology of silver nanoparticles in photothermorefractive glasses. Glass Physics and Chemistry, 2008,34(6):693-699. |
| [20] | DUBROVIN V D, IGNATIEV A I, NEVEDOMSKII V M, et al. The influence of synthesis conditions and ultraviolet irradiation on the morphology and concentration of silver nanocrystals in photothermo-refractive glasses. Glass Technology European Journal of Glass Science & Technology Part A, 2014. 55(6):191-195. |
| [21] | NIKONOROV N V, SAVIN A A, TSEKHOMSKII V A. Influence of ionizing radiation on the spectral properties of photo-thermo- refractive glass containing silver nanoparticles. Glass Physics & Chemistry, 2013,39(3):261-265. |
| [22] | CLAUDIO J M, GONZALEI J P D, LIMA J F, et al. Electron paramagnetic resonance (EPR) studies on the photo-thermo ionization process of photo-thermo-refractive glasses. Journal of Non Crystalline Solids, 2016,452:320-324. |
| [23] |
SIMO A, POLTE J, PFANDER N, et al. Formation mechanism of silver nanoparticles stabilized in glassy matrices. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012,134(45):18824-18833.
URL PMID |
| [1] | 顾薛苏, 殷杰, 王康龙, 崔崇, 梅辉, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 颗粒级配对黏结剂喷射打印碳化硅陶瓷性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 216-. |
| [2] | 陈雨, 林埔安, 蔡冰, 张文华. 钙钛矿太阳能电池无机空穴传输材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 105-. |
| [3] | 田煜彬, 田超凡, 李森, 赵永鑫, 邢涛, 李智, 陈萧如, 向帅蓉, 代鹏程. 高导电性生物质碳布的制备及其燃料电池气体扩散层性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 127-. |
| [4] | 江润璐, 吴鑫, 郭昊骋, 郑琦, 王连军, 江莞. UiO-67基导电复合材料的制备及其热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 197-. |
| [5] | 李海燕, 旷峰华, 吴昊龙, 刘小根, 包亦望, 万德田. 残余拉应力的温度依赖性及其对裂纹扩展行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 214-. |
| [6] | 方万丽, 沈黎丽, 李海燕, 陈薪羽, 陈宗琦, 寿春晖, 赵斌, 杨松旺. NiOx介孔层的成膜过程对碳电极钙钛矿太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 2-. |
| [7] | 丁统顺, 丰平, 孙学文, 单沪生, 李琪, 宋健. Fmoc-FF-OH钝化钙钛矿薄膜及其太阳能电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 50-. |
| [8] | 徐昊, 钱伟, 花银群, 叶云霞, 戴峰泽, 蔡杰. 皮秒激光加工的微织构对碳化硅润湿性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 73-. |
| [9] | 邱海洋, 苗广潭, 李辉, 栾奇, 刘国侠, 单福凯. 等离子体处理对突触晶体管长程塑性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 406-412. |
| [10] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [11] | 杨洋, 崔航源, 祝影, 万昌锦, 万青. 柔性神经形态晶体管研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [12] | 吴俊林, 丁继扬, 黄新友, 朱丹阳, 黄东, 代正发, 杨文钦, 蒋兴奋, 周健荣, 孙志嘉, 李江. Gd2O2S:Tb闪烁陶瓷的制备与结构: 水浴合成中H2SO4/Gd2O3摩尔比的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 452-460. |
| [13] | 陈鑫力, 李岩, 王伟胜, 石智文, 竺立强. 明胶/羧化壳聚糖栅控氧化物神经形态晶体管[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 421-428. |
| [14] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [15] | 方仁瑞, 任宽, 郭泽钰, 徐晗, 张握瑜, 王菲, 张培文, 李悦, 尚大山. 基于氧化物基电解质栅控晶体管突触的关联学习[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 399-405. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||