无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 284-292.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190371
所属专题: 2020年环境材料论文精选(二)重金属元素去除
李丽1,郭筱洁2,金阳1,陈朝贵1( ),Abdullah M Asiri3,HadiM M arwani3,赵轻舟4,盛国栋1(
),Abdullah M Asiri3,HadiM M arwani3,赵轻舟4,盛国栋1( )
)
收稿日期:2019-07-22
修回日期:2019-09-11
出版日期:2020-03-20
网络出版日期:2020-03-24
作者简介:李 丽(1995–), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 2740033871@qq.com
LI Li1,GUO Xiaojie2,JIN Yang1,CHEN Chaogui1( ),Abdullah M Asiri3,Hadi M Marwani3,ZHAO Qingzhou4,SHENG Guodong1(
),Abdullah M Asiri3,Hadi M Marwani3,ZHAO Qingzhou4,SHENG Guodong1( )
)
Received:2019-07-22
Revised:2019-09-11
Published:2020-03-20
Online:2020-03-24
About author:LI Li(1995–), male, Master candidate. E-mail: 2740033871@qq.com
Supported by:摘要:
本工作对Cd(II)在多孔六方氮化硼(p-BN)上的吸附行为和机理进行了系统而全面的研究, 考察了溶液pH、吸附剂用量、接触时间和温度等条件对于Cd(II)吸附的影响, 并采用不同手段表征了吸附前后p-BN的化学组成、形态和表面官能团的变化, 进而研究其吸附机理。研究结果显示, 在pH 7.0和313 K条件下, Cd(II)的最大吸附容量可达到184 mg·g -1, 其动力学数据与拟二级模型和颗粒内扩散模型吻合, 表明吸附主要受化学吸附控制, 限速步骤主要是分子扩散。Cd(II)在p-BN上的吸附是一个自发和吸热过程, 吸附等温线分别符合Freundlich和Langmuir模型, 说明Cd(II)通过多层和单层吸附而吸附在非均相表面上。XPS的光谱结果显示, p-BN吸附剂具有大量的B-N, B-O等结构用作键合位点, 有利于从废水中吸收Cd(II)。这些结果表明, p-BN有希望作为吸附材料用于清除水体中的Cd(II)。
中图分类号:
李丽, 郭筱洁, 金阳, 陈朝贵, Abdullah M Asiri, HadiM M arwani, 赵轻舟, 盛国栋. 氮化硼纳米片吸附Cd(II)的动力学和热力学研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(3): 284-292.
LI Li, GUO Xiaojie, JIN Yang, CHEN Chaogui, Abdullah M Asiri, Hadi M Marwani, ZHAO Qingzhou, SHENG Guodong. Distinguished Cd(II) Capture with Rapid and Superior Ability using Porous Hexagonal Boron Nitride: Kinetic and Thermodynamic Aspects[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 284-292.
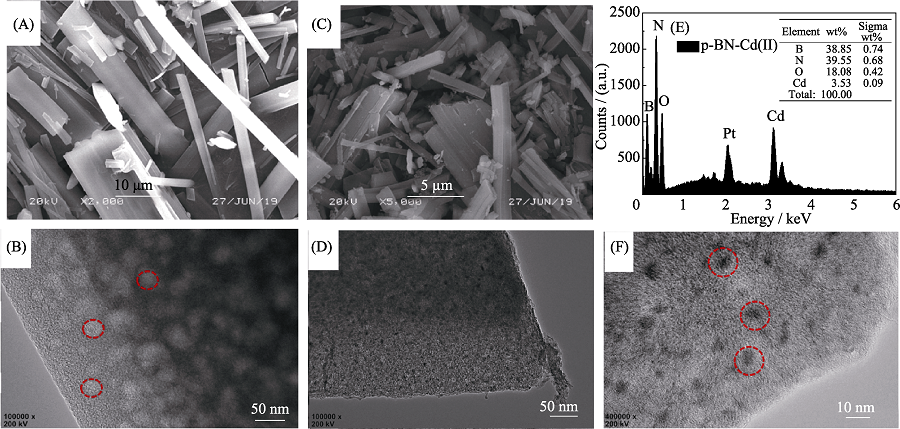
Fig. 1 (A) SEM and (B) HRTEM images of p-BN, (C) SEM and (D) HRTEM images of p-BN after adsorption, (E) EDS analysis and (F) high-magnification HRTEM image of p-BN after adsorption
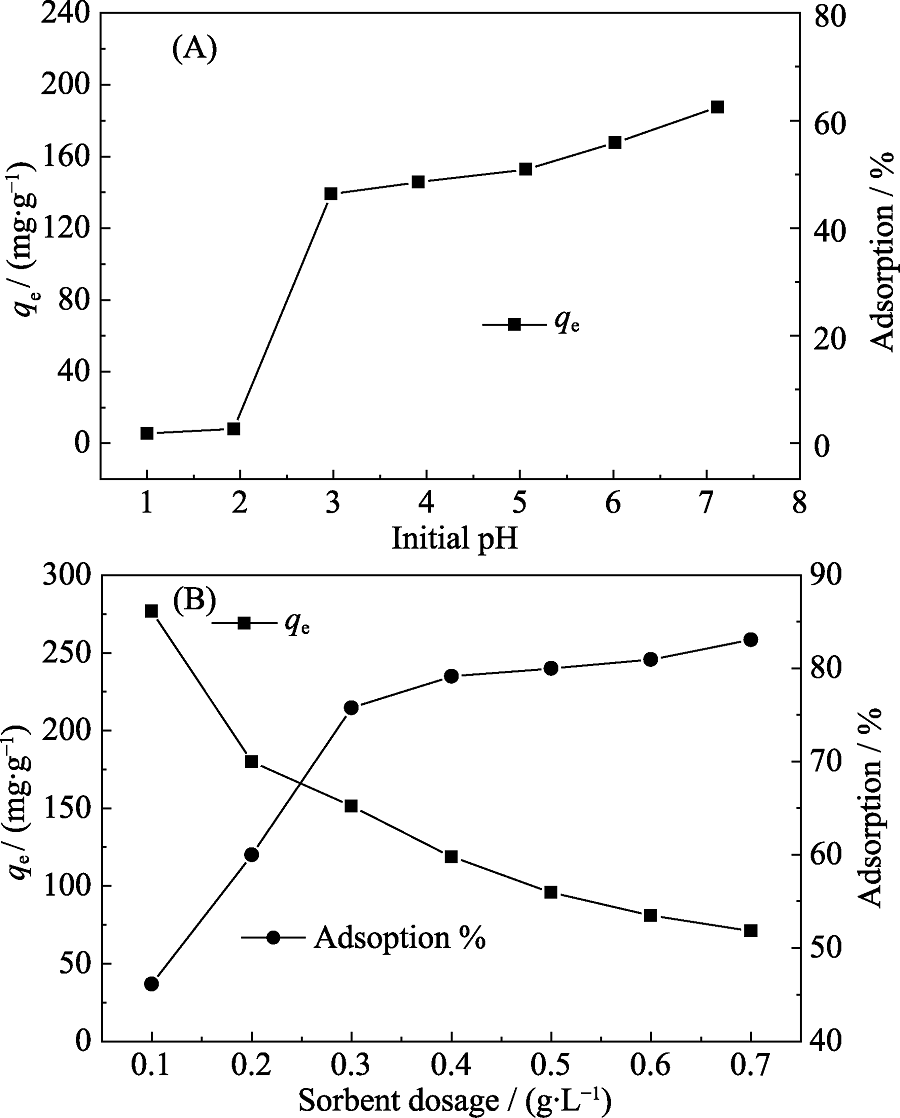
Fig. 3 (A) Effect of initial pH on Cd(II) adsorption capacity (qe) and adsorption percentage at equilibrium, and (B) effect of p-BN dosage on the adsorption capacity (qe) and adsorption percentage of Cd(II)
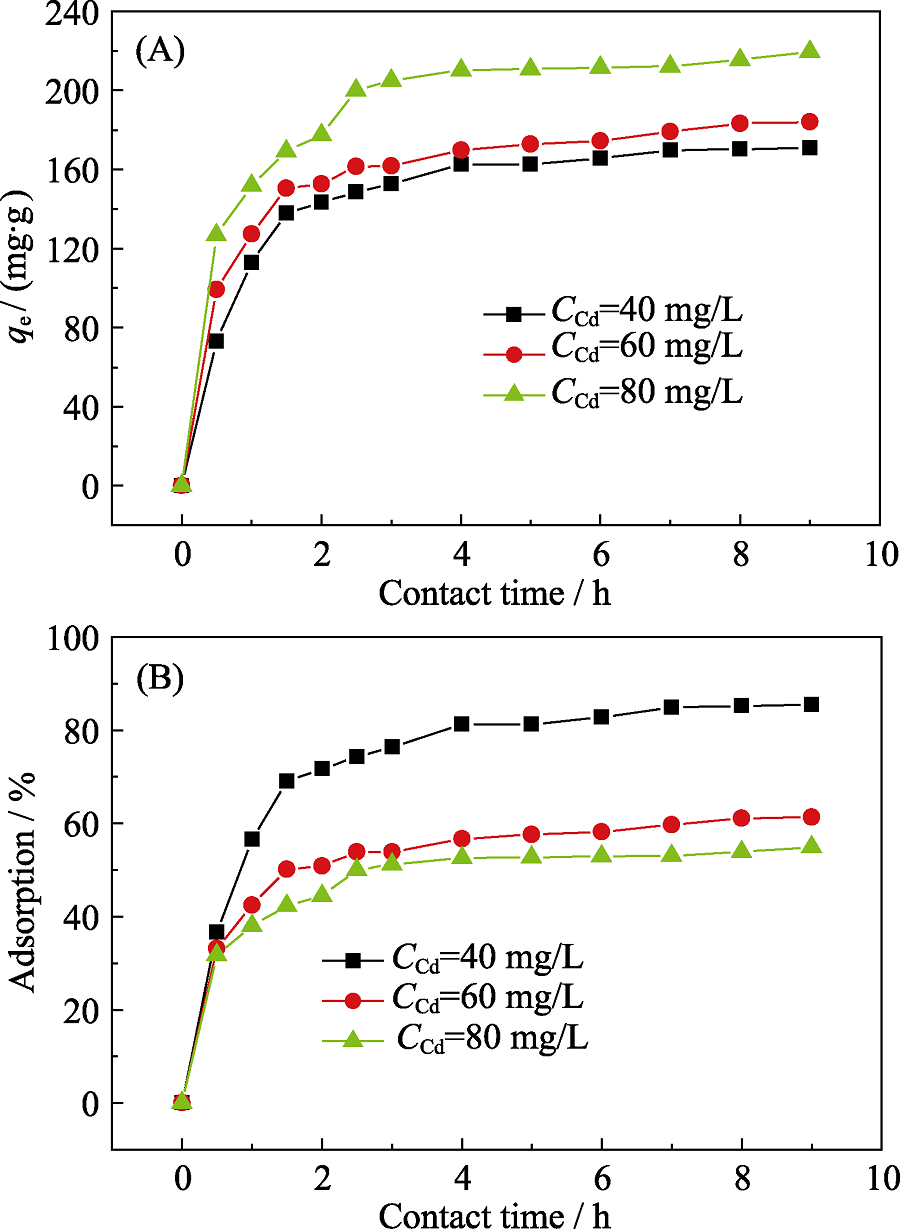
Fig. 4 (A) Adsorption capacities of Cd(II) with various contact times at different initial concentrations of Cd(II), and (B) adsorption percentages of Cd(II) on p-BN with various contact time at different initial concentrations of Cd(II)
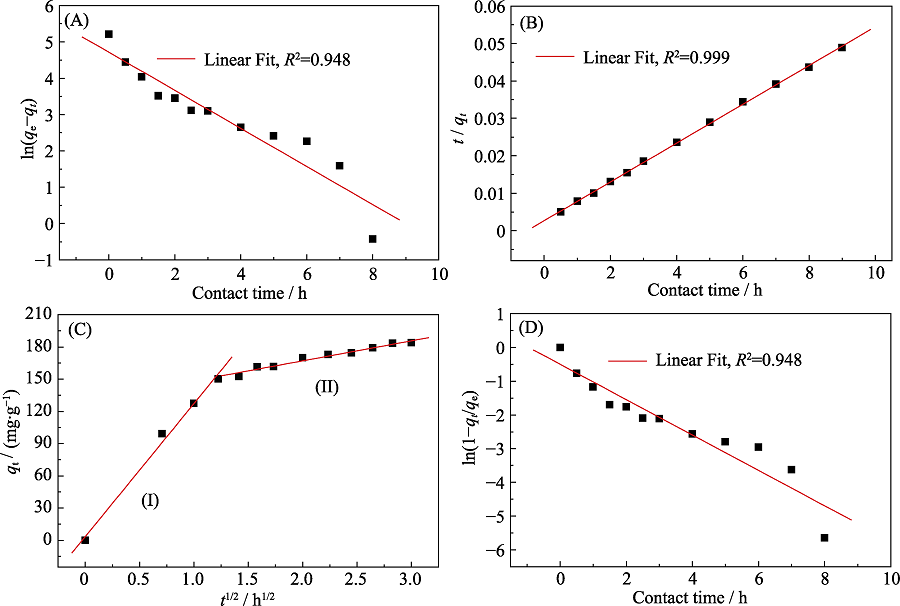
| Cd(II)/p-BN | Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | Pseudo-second-order | Intra-particle diffusion | Liquid-film diffusion | |||||
| Parameters | qe,cal=/(mg·g-1) | 111.7 | qe,cal=/(g·mg-1·h-1) | 193.1 | I | 60.2 | Kf/h-1 | 0.524 |
| K1-1 | 0.524 | K2(g·mg-1·h-1) | 1.00×10-3 | kd/(g·mg-1·h-1/2) | 49.4 | A | -0.499 | |
| R2 | 0.948 | R2 | 0.999 | R2 | 0.872 | R2 | 0.948 | |
Table S1 Adsorption kinetics models parameters
| Cd(II)/p-BN | Model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Pseudo-first-order | Pseudo-second-order | Intra-particle diffusion | Liquid-film diffusion | |||||
| Parameters | qe,cal=/(mg·g-1) | 111.7 | qe,cal=/(g·mg-1·h-1) | 193.1 | I | 60.2 | Kf/h-1 | 0.524 |
| K1-1 | 0.524 | K2(g·mg-1·h-1) | 1.00×10-3 | kd/(g·mg-1·h-1/2) | 49.4 | A | -0.499 | |
| R2 | 0.948 | R2 | 0.999 | R2 | 0.872 | R2 | 0.948 | |
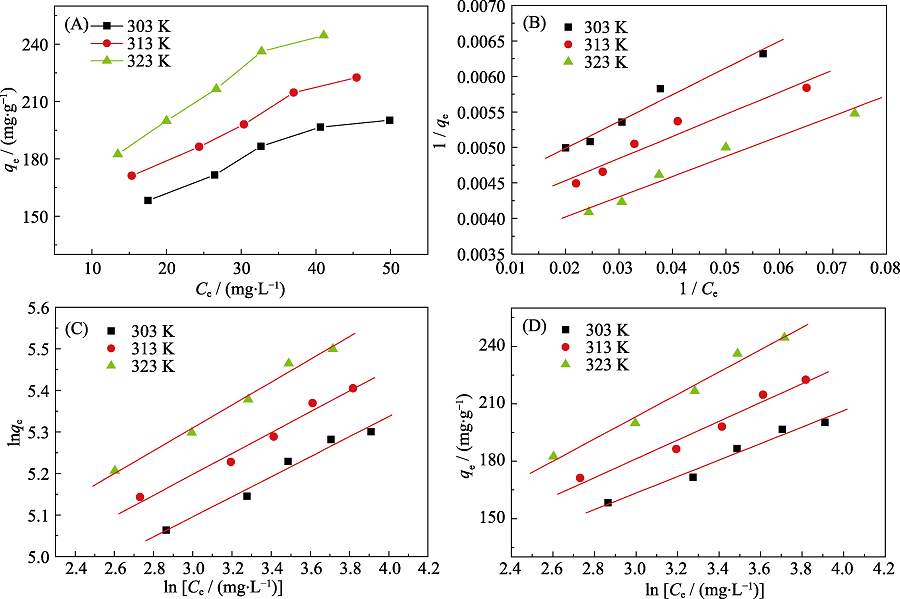
Fig. 5 (A) Adsorption isotherms of Cd(II) on p-BN at T=303, 313 and 323 K, equilibrium adsorption isotherms fitted by (B) Langmuir model, (C) Freundlich model, (D) Tempkin model Experimental conditions: Initial pH at 7.0, C0=60 mg·L-1, m=10.0 mg, V=50 mL
| Model parameter | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | Tempkin model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/(mg·g-1) | KL/(L·mg-1) | R2 | 1/n | KF | R2 | KT/(L·mg-1) | f | R2 | ||
| T/K | 303 | 236 | 0.112 | 0.984 | 0.229 | 1.27 | 0.987 | 43.1 | 2.19 | 0.987 |
| 313 | 256 | 0.126 | 0.968 | 0.225 | 1.29 | 0.989 | 49.1 | 2.00 | 0.984 | |
| 323 | 290 | 0.121 | 0.983 | 0.223 | 1.32 | 0.994 | 58.3 | 1.63 | 0.991 | |
Table 1 Adsorption isotherm models parameters of Cd(II) on p-BN
| Model parameter | Langmuir model | Freundlich model | Tempkin model | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| qm/(mg·g-1) | KL/(L·mg-1) | R2 | 1/n | KF | R2 | KT/(L·mg-1) | f | R2 | ||
| T/K | 303 | 236 | 0.112 | 0.984 | 0.229 | 1.27 | 0.987 | 43.1 | 2.19 | 0.987 |
| 313 | 256 | 0.126 | 0.968 | 0.225 | 1.29 | 0.989 | 49.1 | 2.00 | 0.984 | |
| 323 | 290 | 0.121 | 0.983 | 0.223 | 1.32 | 0.994 | 58.3 | 1.63 | 0.991 | |
| Adsorbate | C0/(mg·L-1) | ΔHθ/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔSθ/(J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔGθ/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 303 K | 313 K | 323 K | ||||
| Cd(II) | 50 | 16.51 | 72.81 | -5.55 | -6.28 | -7.01 |
| 60 | 17.58 | 73.40 | -4.66 | -5.39 | -6.13 | |
| 70 | 14.25 | 61.39 | -4.35 | -4.97 | -5.58 | |
| 80 | 16.21 | 66.54 | -3.95 | -4.62 | -5.28 | |
| 90 | 16.08 | 64.60 | -3.49 | -4.14 | -4.79 | |
Table S2 Values of thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of Cd(II) on p-BN
| Adsorbate | C0/(mg·L-1) | ΔHθ/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔSθ/(J·mol-1·K-1) | ΔGθ/(kJ·mol-1) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 303 K | 313 K | 323 K | ||||
| Cd(II) | 50 | 16.51 | 72.81 | -5.55 | -6.28 | -7.01 |
| 60 | 17.58 | 73.40 | -4.66 | -5.39 | -6.13 | |
| 70 | 14.25 | 61.39 | -4.35 | -4.97 | -5.58 | |
| 80 | 16.21 | 66.54 | -3.95 | -4.62 | -5.28 | |
| 90 | 16.08 | 64.60 | -3.49 | -4.14 | -4.79 | |
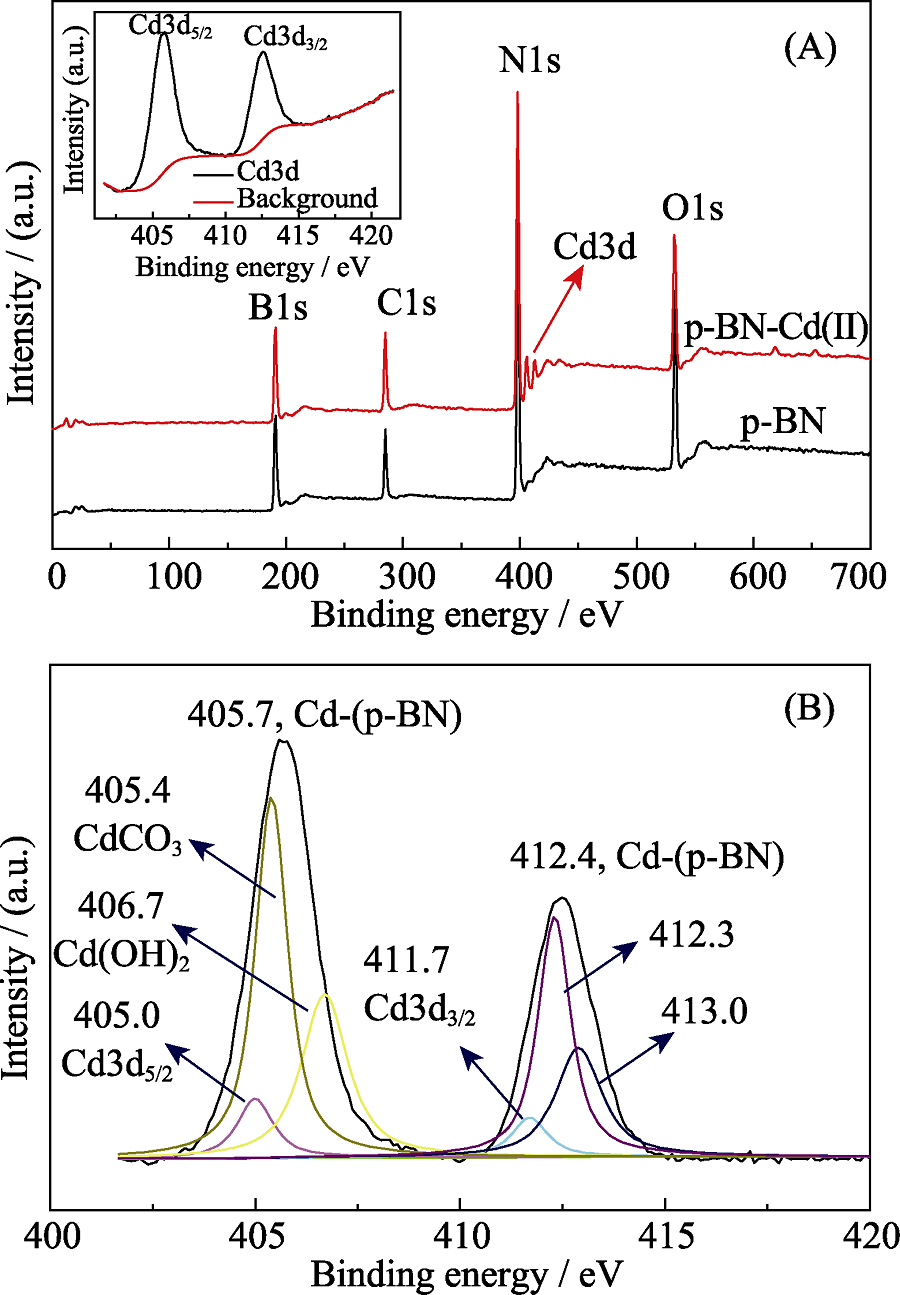
Fig. 6 (A) XPS surveys for p-BN and adsorbed p-BN(inset: high resolution Cd3d XPS spectrum and background); (B) Experimental bonding enerygy peaks of Cd(II) and the comparisons of primary peaks of Cd3d5/2 and Cd3d3/2 for free Cd(II), CdCO3, Cd(OH)2
| [1] | ZOU YI-DONG, WANG XIANG-XUE, KHAN A , et al. Environmental remediation and application of nanoscale zero-valent iron and its composites for the removal of heavy metal ions: a review. Environmental Science & Technology, 2016,50(14):7290-7304. |
| [2] | LIAO QING, PAN WANG, ZOU DONG-SHENG , et al. Using of g-C3N4 nanosheets for the highly efficient scavenging of heavy metals at environmental relevant concentrations. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018,261:32-40. |
| [3] | ZIMMERMAN J B, MIHELCIC J R, SMITH J . Global stressors on water quality and quantity. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008,42(12):4247-4254. |
| [4] | ZHAO GUI-XIA, WU XI-LIN, TAN XIAO-LI , et al. Sorption of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions: a review. The Open Colloid Science Journal, 2011,4:19-31. |
| [5] | ABBAS K, ZNAD H, AWUAL M R . A ligand anchored conjugate adsorbent for effective mercury(II) detection and removal from aqueous media. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018(334):432-443. |
| [6] | ZHANG SHOU-WEI, WANG XIANG-XUE, LI JIA-XING , et al. Efficient removal of a typical dye and Cr(VI) reduction using N-doped magnetic porous carbon. RSC Advances, 2014,4(108):63110-63117. |
| [7] | WANG ZHANG-HONG, SHEN DE-KUI, SHEN FEI , et al. Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ions (Cd2+ ) removal from aqueous solution using earthworm manure-derived carbon materials. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2017,241:612-621. |
| [8] | NADERI A, DELAVAR M A, GHORBANI Y , et al.Modification of nano-clays with ionic liquids for the removal of Cd (II) ion from aqueous phase. Appied Clay Science, 2018,158:236-245. |
| [9] | ZHOU GUANG-ZHU, WANG YUE, ZHOU RUN-SHENG , et al. Synthesis of amino-functionalized bentonite/CoFe2O4@MnO2 magnetic recoverable nanoparticles for aqueous Cd2+ removal. Science of the Total Environment, 2019,682:505-513. |
| [10] | AWUAL M R, KHRAISHEH M, ALHARTHI N H , et al. Efficient detection and adsorption of cadmium(II) ions using innovative nano-composite materials. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018,343:118-127. |
| [11] | GUPTA V K, ALI I, SALEH T A , et al. Chemical treatment technologies for waste-water recycling: an overview. RSC Advances, 2012,2(16):6380-6388. |
| [12] | MATURANA H A, PERIC I M, RIVAS B L , et al. Interaction of heavy metal ions with an ion exchange resin obtained from a natural polyelectrolyte. Polymer Bulletin, 2011,67(4):669-676. |
| [13] | MUNGRAY A A, KULKARNI S V, MUNGRAY A K . Removal of heavy metals from wastewater using micellar enhanced ultrafiltration technique: a review. Central European Journal of Chemistry, 2012,10(1):27-46. |
| [14] | KUMAR K S, DAHMS H U, WON E J , et al.Microalgae-a promising tool for heavy metal remediation. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety, 2015,113:329-352. |
| [15] | QDAIS H A, MOUSSA H . Removal of heavy metals from wastewater by membrane processes: a comparative study. Desalination, 2004,164:105-110. |
| [16] | INGLEZAKIS V J, LOIZIDOU M D . Ion exchange of some heavy metal ions from polar organic solvents into zeolite. Desalination, 2007,211:238-248. |
| [17] | MATLOCK M M, HOWERTON B S, ATWOOD D A . Chemical precipitation of heavy metals from acid mine drainage. Water Research, 2002,36:4757-4764. |
| [18] | GUPTA V K, SALEH T A . Sorption of pollutants by porous carbon, carbon nanotubes and fullerene-an overview. Environmental Science and Pollution Research, 2013,20(5):2828-2843. |
| [19] | LIAO QING, YAN SHUN-RONG, LINGHU WEN-SHENG , et al. Impact of key geochemical parameters on the highly efficient sequestration of Pb(II) and Cd(II) in water using g-C3N4 nanosheets. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018,258:40-47. |
| [20] | ZHANG HAI-FENG, DANG QI-FENG, LIU CHENG-SHENG , et al. Fabrication of methyl acrylate and tetraethylenepentamine grafted magnetic chitosan microparticles for capture of Cd(II) from aqueous solutions. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019,366:346-357. |
| [21] | CIESIELCZYK F, BARTCZAK P, JESIONOWSKI T . A comprehensive study of Cd(II) ions removal utilizing high-surface-area binary Mg-Si hybrid oxide adsorbent. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2015,12(11):3613-3626. |
| [22] | DIAZ-FLORES P E, LOPEZ-URIAS F, TERRONES M , et al. Simultaneous adsorption of Cd 2+ and phenol on modified N-doped carbon nanotubes: experimental and DFT studies. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2009,334(2):124-131. |
| [23] | HUANG JIE-YING, WU ZHEN-WEI, CHEN LI-WEI , et al. Surface complexation modeling of adsorption of Cd(II) on graphene oxides. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2015,209:753-758. |
| [24] | SHENG GUO-DONG, ALSAEDI A, SHAMMAKH W , et al. Enhanced sequestration of selenite in water by nanoscale zero valent iron immobilization on carbon nanotubes by a combined batch, XPS and XAFS investigation. Carbon, 2016,99:123-130. |
| [25] | BOPARAI H K, JOSEPH M , O’CARROLL D M, et al. Kinetics and thermodynamics of cadmium ion removal by adsorption onto nano zerovalent iron particles. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011,186(1):458-465. |
| [26] | MOSTAFA M S, BAKR A A . Adsorptive removal of Cd(II) from contaminated water via hexavalent molybdenum-containing layered double hydroxide: Ni/Mo-LDH. Energy Sources Part A-Recovery Utilization and Environmental Effects, 2019,41(18):2257-2265. |
| [27] | RAHMANIAN O, MALEKI M H, DINARI M . Ultrasonically assisted solvothermal synthesis of novel Ni/Al layered double hydroxide for capturing of Cd(II) from contaminated water. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2017,110:195-201. |
| [28] | WENG QUN-HONG, WANG XUE-BIN, WANG XI , et al. Functionalized hexagonal boron nitride nanomaterials: emerging properties and applications. Chemical Society Reviews, 2016,45(14):3989-4012. |
| [29] | YU SHU-JUN, WANG XIANG-XUE, PANG H W , et al. Boron nitride-based materials for the removal of pollutants from aqueous solutions: a review. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2018,333:343-360. |
| [30] | LI JIE, LI JING, XU WUE-WEN , et al. Porous boron nitride with high surface area: hydrogen storge and water treatment. Nanotechnology, 2013,24(15):155603. |
| [31] | XUE YAN-MING, DAI PENG-CHENG, JIANG XIANG-FEN , et al. Template-free synthesis of boron nitride foam-like porous monoliths and their high-end applications in water purification. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016,4(4):1469-1478. |
| [32] | LI JIE, JIN PENG, TANG CHENG-CHUN . Cr(III) adsorption by fluorinated activated boron nitride: a combined experimental and theoretical investigation. RSC Advances, 2014,4(29):14815-14821. |
| [33] | SONG QIAN-QIAN, FANG YI, LIU ZHEN-YA , et al. The performance of porous hexagonal BN in high adsorption capacity towards antibiotics pollutants from aqueous solution. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2017,325:71-79. |
| [34] | LI JIE, HUANG YANG, LIU ZHEN-YA , et al. Chemical activation of boron nitride fibers for improved cationic dye removal performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2015,3(15):8185-8193. |
| [35] | CHEN MING-MING, WEI DA, CHU WEI , et al. One-pot synthesis of O-doped BN nanosheets as capacitive deionization electrode for efficient removal of heavy metal ions from water. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017,5(32):17029-17039. |
| [36] | LI JIE, XIAO XING, XU XUE-WEN , et al.Activated boron nitride as an effective adsorbent for metal ions and organic pollutants. Scientific Reports, 2013,3:3208. |
| [37] | TANG CHENG-CHUN, BANDO Y, HUANG Y , et al. Synthetic routes and formation mechanisms of spherical boron nitride nanoparticles. Advanced Functional Materials, 2008,18(22):3653-3661. |
| [38] | ZHI CHUN-YI, BANDO Y, TANG CHENG-CHUN , et al. Phonon characteristics and cathodelumininescence of boron nitride nanotubes. Applied Physics Letters, 2015,86(21):213110. |
| [39] | GEORGE S . Infrared and Raman Characteristic Group Frequencies: Tables and Charts, 3rd Edition . New York: Wiley, 2001: 107-113. |
| [40] | HO YUH-SHAN, MCKAY GORDON . Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochemistry, 1999,34(5):451-465. |
| [41] | ZHANG LEI, SONG XIAO-YAN, LIU XUE-YAN , et al. Studies on the removal of tetracycline by multi-walled carbon nanotubes. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2011,178:26-33. |
| [42] | LI PING, YIN ZHOU-XIN, LIN JIAN-FENG , et al. The immobilization of U(VI) on iron oxyhydroxides under various physicochemical conditions. Environmental Science-Processes& Impacts, 2014,16(10):2278-2287. |
| [43] | Handbook of the Elements and Native Oxides, XPS International, Inc. 1999 |
| [44] | PENG DONG, JINAG WEI, LI FANG-FANG , et al. One-pot synthesis of boron carbon nitride nanosheets for facile and efficient heavy metal ions removal. ACS Sustainable Chemistry&Engineering, 2018,6(9):11685-11694. |
| [1] | 马晓森, 张丽晨, 刘砚超, 汪全华, 郑家军, 李瑞丰. 13X@SiO2合成及其甲苯吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [2] | 郭春霞, 陈伟东, 闫淑芳, 赵学平, 杨傲, 马文. 埃洛石纳米管负载锆氧化物吸附水中砷的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 529-536. |
| [3] | 王世怡, 冯爱虎, 李晓燕, 于云. Fe3O4负载Ti3C2Tx对Pb(II)的吸附性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [4] | 于业帆, 徐玲, 倪忠斌, 施冬健, 陈明清. 普鲁士蓝/生物炭材料的制备及其氨氮吸附机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 205-212. |
| [5] | 王红宁, 黄丽, 清江, 马腾洲, 黄维秋, 陈若愚. 有机-无机氧化硅空心球的合成及VOCs吸附应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [6] | 刘城, 赵倩, 牟志伟, 雷洁红, 段涛. 新型铋基SiOCNF复合膜对放射性气态碘的吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1043-1050. |
| [7] | 周帆, 毕辉, 黄富强. 用稻壳制备亚甲基蓝高吸附容量的超高比表面积活性炭[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 893-903. |
| [8] | 余祥坤, 刘坤, 李志鹏, 赵雨露, 沈锦优, 茆平, 孙爱武, 蒋金龙. 铜/凹凸棒石复合材料高效吸附放射性碘离子性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 856-864. |
| [9] | 苏莉, 杨建平, 兰悦, 王连军, 江莞. 纳米铁颗粒及其复合材料的界面设计及环境修复应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(6): 561-569. |
| [10] | 席文, 李海波. TiO2/Ti3C2Tx复合材料的制备及其杂化电容脱盐特性的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 283-291. |
| [11] | 王婷婷, 史书梅, 柳晨媛, 朱万诚, 张恒. 多级多孔硅酸镍微球的合成及其对碱性品红的高效吸附[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1330-1336. |
| [12] | 郭宇, 姜晓庆, 吴红梅, 肖昱, 仵大富, 刘鑫. 2-羟基-1-萘甲醛功能化SBA-15吸附剂的制备及其对Cr(III)的吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1163-1170. |
| [13] | 张瑞鸿, 魏鑫, 卢占会, 艾玥洁. 基于机器学习训练金属离子吸附能预测模型的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1178-1184. |
| [14] | 何俊龙, 宋二红, 王连军, 江莞. DFT方法研究一氧化氮在铬掺杂石墨烯上的吸附行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1047-1052. |
| [15] | 肖瑶, 吴中杰, 崔美, 苏荣欣, 谢连科, 黄仁亮. 生物炭-膨润土共改性及其铅离子吸附与稳定化研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1083-1090. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||