无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (8): 923-930.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190530
收稿日期:2019-10-16
修回日期:2019-12-27
出版日期:2020-08-20
网络出版日期:2020-03-03
作者简介:张东硕(1994–), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 基金资助:
ZHANG Dongshuo1,2( ),CAI Hao1,GAO Kaiyin1,MA Zichuan1,2(
),CAI Hao1,GAO Kaiyin1,MA Zichuan1,2( )
)
Received:2019-10-16
Revised:2019-12-27
Published:2020-08-20
Online:2020-03-03
Supported by:摘要:
以松木碱解液代替NaOH溶液作为锌盐沉淀剂, 采用水热法制备了Zn2SiO4-ZnO-生物炭三元复合材料(SOB-x-y, x代表松木粉的用量, y代表NaOH浓度), 通过不同手段对样品进行表征, 研究了光催化H2O2降解甲硝唑的性能。结果表明, 制备的催化剂由枣核状硅锌矿型Zn2SiO4介晶、多边形六方晶相ZnO和松木生物炭构成; 与纯六方晶相ZnO相比, 它具有更大的比表面积与孔容、更小的带隙能和更弱的荧光发射, 因而具有更好的光催化活性。Zn2SiO4-ZnO-生物炭对甲硝唑的光催化H2O2降解过程符合准一级动力学方程, 其催化活性随NaOH浓度的增大而提高, 随松木粉用量的增加先增加后减小, 以SOB-3-4的性能最优。SOB-3-4的速率常数(k)和降解率(η)随pH的降低而增大, 随H2O2浓度的升高而增大, 随催化剂用量的增加先增大后减小; 甲硝唑的降解率随其初始浓度的升高逐渐越低。当初始pH为3、催化剂用量为0.4 g/L、H2O2投加浓度为80 mmol/L及甲硝唑初始浓度为300 mg/L时, k为2.68×10 -2 min -1, 反应3 h后η达到99.70%。本研究结果对处理难降解制药废水提供了重要的实验依据。
中图分类号:
张东硕,蔡昊,高凯茵,马子川. Zn2SiO4-ZnO-生物炭复合物的制备及其可见光催化H2O2降解甲硝唑[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 923-930.
ZHANG Dongshuo,CAI Hao,GAO Kaiyin,MA Zichuan. Preparation and Visible-light Photocatalytic Degradation on Metronidazole of Zn2SiO4-ZnO-biochar Composites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(8): 923-930.

图2 光催化H2O2降解甲硝唑的动力学分析
Fig. 2 Degradation kinetics of metronidazole by H2O2 photocatalysis (a) Effect of NaOH concentration; (b) Effect of pine wood flour dosage
| Catalyst | Specific surface area/(m2?g-1) | Pore volume/ (cm3?g-1) | Pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOB-3-4 | 31.29 | 0.32 | 20.40 |
| ZnO | 24.39 | 0.24 | 19.74 |
表1 不同催化剂的比表面积、孔容及孔径
Table 1 Specific surface area, pore volume and pore size of catalysts
| Catalyst | Specific surface area/(m2?g-1) | Pore volume/ (cm3?g-1) | Pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|---|
| SOB-3-4 | 31.29 | 0.32 | 20.40 |
| ZnO | 24.39 | 0.24 | 19.74 |
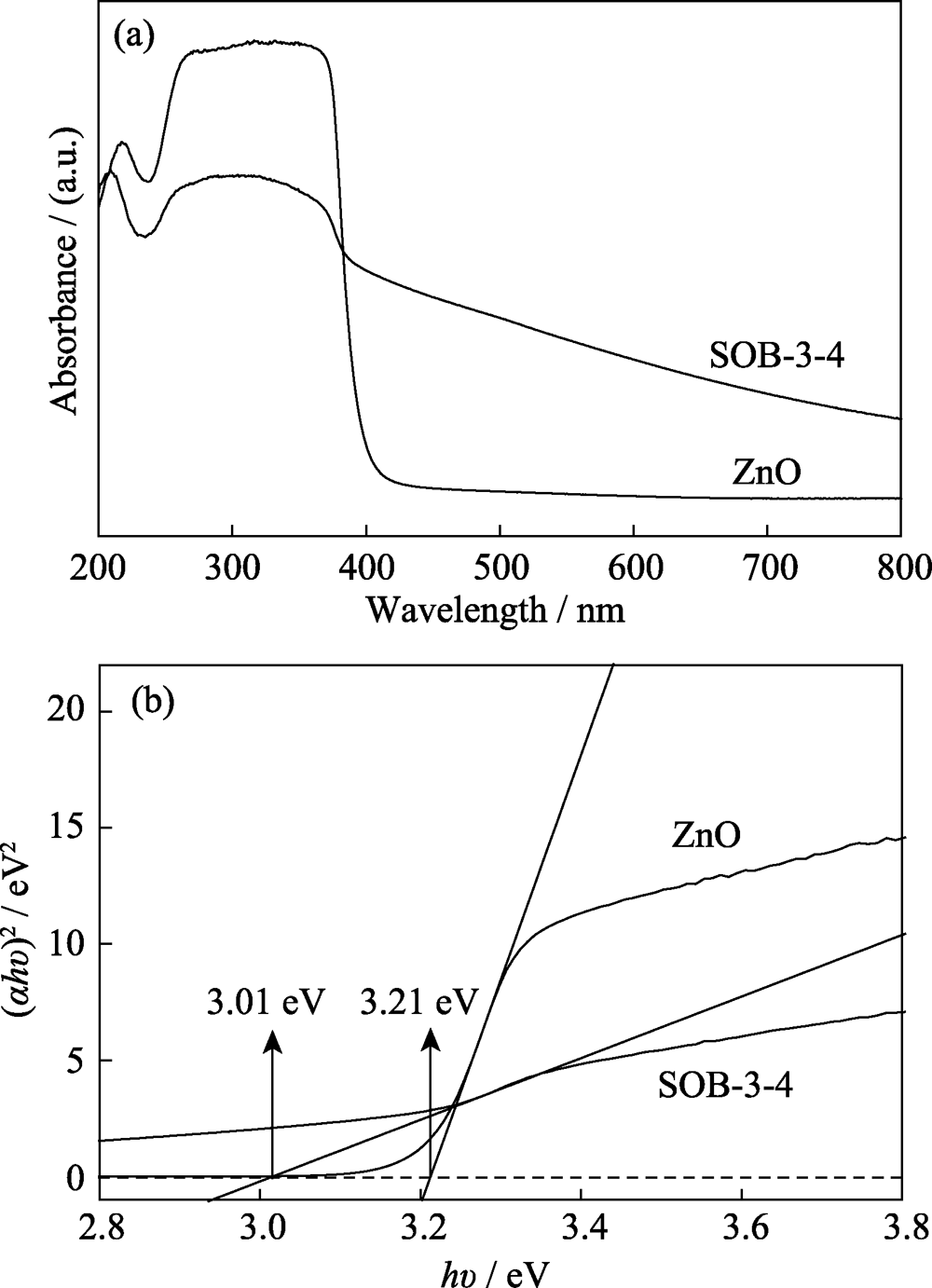
图7 SOB-3-4和ZnO的紫外-可见漫反射光谱(a)及其对应的(αhν)2与光子能量关系图(b)
Fig. 7 UV-Vis diffuse reflectance spectra of SOB-3-4 and ZnO (a), and corresponding relationship between (αhv)2 and photonic energy(b)
| [1] | YANG L L, WEI Q S, LI Z C, et al. Effects of dissolved organic matter (DOM) on photodegradation of metronidazole. Guangdong Chemical Industry, 2016,43(14):13-15. |
| [2] |
INGERSLEV F, TORÄNG L, LOKE M L, et al. Primary biodegradation of veterinary antibiotics in aerobic and anaerobic surface water simulation systems. Chemosphere, 2001,44(4):865-872.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
MÉNDEZ-DÍAZ J D, PRADOS-JOYA G, RIVERA-UTRILLA J, et al. Kinetic study of the adsorption of nitroimidazole antibiotics on activated carbons in aqueous phase. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010,345(2):481-490.
DOI URL PMID |
| [4] |
RIVERA-UTRILLA J, PRADOS-JOYA G, SÁNCHEZ-POLO M, et al. Removal of nitroimidazole antibiotics from aqueous solution by adsorption/bioadsorption on activated carbon. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2009,170(1):298-305.
DOI URL PMID |
| [5] |
FANG Z Q, QIU X Q, CHEN J H, et al. Degradation of metronidazole by nanoscale zero-valent metal prepared from steel pickling waste liquor. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2010,100(1/2):221-228.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
JOHNSON M B, MEHRVAR M. Aqueous metronidazole degradation by UV/H2O2 process in single-and multi-lamp tubular photoreactors: kinetics and reactor design. Industrial and Engineering Chemistry Research, 2008,47(17):6525-6537.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
JOSS A, ZABCZYNSKI S, GÖBEL A, et al. Biological degradation of pharmaceuticals in municipal wastewater treatment: proposing a classification scheme. Water Research, 2006,40(8):1686-1696.
DOI URL PMID |
| [8] |
CARBALLA M, OMIL F, TERNES T, et al. Fate of pharmaceutical and personal care products (PPCPs) during anaerobic digestion of sewage sludge. Water Research, 2007,41(10):2139-2150.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
HÖFL C, SIGL G, SPECHT O, et al. Oxidative degradation of aox and cod by different advanced oxidation processes: a comparative study with two samples of a pharmaceutical wastewater. Water Science and Technology, 1997,35(4):257-264.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
AMMAR H B, BRAHIM M B, ABDELHÉDI R, et al. Enhanced degradation of metronidazole by sunlight via photo-Fenton process under gradual addition of hydrogen peroxide. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2016,420:222-227.
DOI URL |
| [11] | LUO T T, WANG M, TIAN X K, et al. Safe and efficient degradation of metronidazole using highly dispersed beta-FeOOH on palygorskite as heterogeneous Fenton-like activator of hydrogen peroxide. Chemosphere, 2019,236:1-7. |
| [12] |
SHEMER H, KUNUKCU Y K, LINDEN K G. Degradation of the pharmaceutical metronidazole via UV, Fenton and photo-Fenton processes. Chemosphere, 2006,63(2):269-276.
DOI URL |
| [13] | XIONG Z H, CHEN Z X, LIU J M. Comparison of metronidazole degradation by different advanced oxidation processes in low concentration aqueous solutions. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering, 2009,3(3):465-469. |
| [14] |
WANG X Y, WANG A Q, MA J. Visible-light-driven photocatalytic removal of antibiotics by newly designed C3N4@MnFe2O4-graphene nanocomposites. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2017,336:81-92.
DOI URL PMID |
| [15] |
RAI S C, WANG K, DING Y, et al. Piezo-phototronic effect enhanced UV/visible photodetector based on fully wide band gap Type-II ZnO/ZnS core/shell nanowire array. ACS Nano, 2015,9(6):6419-6427.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
QI K Z, CHENG B, YU J G, et al. Review on the improvement of the photocatalytic and antibacterial activities of ZnO. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2017,727:792-820.
DOI URL |
| [17] | GHOLAMI P, DINPAZHOH L, KHATAEE A, et al. Sonocatalytic activity of biochar-supported ZnO nanorods in degradation of gemifloxacin: synergy study, effect of parameters and phytotoxicity evaluation. Ultrasonics - Sonochemistry, 2019,55:44-56. |
| [18] |
YANG Y, ZHUANG Y, HE Y H, et al. Fine tuning of the dimensionality of zinc silicate nanostructures and their application as highly efficient absorbents for toxic metal ions. Nano Research, 2010,3(8):581-593.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
QIAO Z, YAN T J, ZHANG X F, et al. Low-temperature hydrothermal synthesis of Zn2SiO4 nanostructures and the novel photocatalytic application in wastewater treatment. Catalysis Communications, 2018,106:78-81.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
XIE J, LI P, LI Y T, et al. Solvent-induced growth of ZnO particles at low temperature. Materials Letters, 2008,62(17/18):2814-2816.
DOI URL |
| [21] | 陈嘉川, 刘温霞, 杨桂花, 等. 造纸植物资源化学. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012: 68-71. |
| [22] | LI Y, HUA Y X, LIN Z Y. A novel process for synthesis of zinc silicate. Journal of Materials and Metallurgy, 2007,6(3):224-229. |
| [23] |
ZU L H, QIN Y, YANG J H. In situ synergistic crystallization-induced synthesis of novel Au nanostar-encrusted ZnO mesocrystals with high-quality heterojunctions for high-performance gas sensors. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015,3(19):10209-10218.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
LUDI B, NIEDERBERGER M. Zinc oxide nanoparticles: chemical mechanisms and classical and non-classical crystallization. Dalton Transactions, 2013,42(35):12554-12568.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
WANG L P, CHANG Y Z, LI A M. Hydrothermal carbonization for energy-efficient processing of sewage sludge: a review. Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019,108:423-440.
DOI URL |
| [26] | LI S J, MA Z C, WANG L, et al. Influence of MnO2 on the photocatalytic activity of P-25 TiO2 in the degradation of methyl orange. Science in China Series B:Chemistry, 2008,51(2):179-185. |
| [27] |
YU C L, YANG K, YU J C, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis and photocatalytic performance of Bi2WO6/ZnO heterojunction photocatalysts. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011,26(11):1157-1163.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
LIANG C, LIU Y, LI K, et al. Heterogeneous photo-Fenton degradation of organic pollutants with amorphous Fe-Zn-oxide/hydrochar under visible light irradiation. Separation and Purification Technology, 2017,188:105-111.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
PLGNATELLO J J. Dark and photoassisted Fe 3+-catalyzed degradation of chlorophenoxy herbicides by hydrogen peroxide . Environmental Science and Technology, 1992,26:944-951.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
DÜKKANCI M, GÜNDÜZ G, YILMAZ S, et al. Heterogeneous Fenton-like degradation of Rhodamine 6G in water using CuFeZSM-5 zeolite catalyst prepared by hydrothermal synthesis. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010,181(1/2/3):343-350.
DOI URL PMID |
| [1] | 伍林, 胡明蕾, 王丽萍, 黄少萌, 周湘远. TiHAP@g-C3N4异质结的制备及光催化降解甲基橙[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [2] | 马心全, 李喜宝, 陈智, 冯志军, 黄军同. S型异质结BiOBr/ZnMoO4的构建及光催化降解性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [3] | 陈瀚翔, 周敏, 莫曌, 宜坚坚, 李华明, 许晖. CoN/g-C3N4 0D/2D复合结构及其光催化制氢性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [4] | 薛虹云, 王聪宇, MAHMOOD Asad, 于佳君, 王焱, 谢晓峰, 孙静. 二维g-C3N4与Ag-TiO2复合光催化剂降解气态乙醛抗失活研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [5] | 洪佳辉, 马冉, 仵云超, 文涛, 艾玥洁. MOFs自牺牲模板法制备CoNx/g-C3N4纳米材料用作高效光催化还原U(VI)[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 741-749. |
| [6] | 迟聪聪, 屈盼盼, 任超男, 许馨, 白飞飞, 张丹洁. SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2核壳结构的制备及其光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [7] | 王晓俊, 许文, 刘润路, 潘辉, 朱申敏. 水凝胶负载的纳米银/氮化碳光催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [8] | 安琳, 吴淏, 韩鑫, 李耀刚, 王宏志, 张青红. 非贵金属Co5.47N/N-rGO助催化剂增强TiO2光催化制氢性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 534-540. |
| [9] | 陈士昆, 王楚楚, 陈晔, 李莉, 潘路, 文桂林. 磁性Ag2S/Ag/CoFe1.95Sm0.05O4 Z型异质结的制备及光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1329-1336. |
| [10] | 刘雪晨, 曾滴, 周沅逸, 王海鹏, 张玲, 王文中. 改性氮化碳光催化剂在生物质氧化反应中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 38-44. |
| [11] | 张弦, 张策, 姜文君, 冯德强, 姚伟. 四元BiMnVO5的合成、电子结构与可见光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| [12] | 高娃, 熊宇杰, 吴聪萍, 周勇, 邹志刚. 基于超薄纳米结构的光催化二氧化碳选择性转化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 3-14. |
| [13] | 王潇, 朱智杰, 吴之怡, 张城城, 陈志杰, 肖梦琦, 李超然, 何乐. 钴等离激元超结构粉体催化剂的制备及其光热催化应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 22-28. |
| [14] | 刘彭, 吴仕淼, 吴昀峰, 张宁. Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS光催化材料的制备及其CO2还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 15-21. |
| [15] | 王路平, 卢占会, 魏鑫, 方明, 王祥科. 改进的灰色模型在光催化数据预测中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 871-876. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||