无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (3): 277-283.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190377
所属专题: 2020年环境材料论文精选(三)有机小分子去除; 【虚拟专辑】污染物吸附水处理(2020~2021)
收稿日期:2019-07-23
修回日期:2019-09-23
出版日期:2020-03-20
网络出版日期:2019-12-04
作者简介:赵超锋(1995-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: cfzhao@ncepu.edu.cn
基金资助:
ZHAO Chaofeng1,JIN Jiaren1,HUO Yingzhong1,SUN Lu2,AI Yuejie1( )
)
Received:2019-07-23
Revised:2019-09-23
Published:2020-03-20
Online:2019-12-04
About author:ZHAO Chaofeng (1995-), male, Master candidate. E-mail:cfzhao@ncepu.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
研究采用分子动力学模拟(Molecular dynamics simulation, MD)的方法, 以苯酚、α-萘酚和4-辛基酚为代表, 研究了酚类有机污染物(Phenolic Organic Pollutants, POPs)在氧化石墨烯(Graphene Oxide, GO)上单独和竞争吸附过程。通过自由能计算得到三种POPs在GO表面的吸附能分别为: 4-辛基酚(41.34 kJ/mol)>α-萘酚(33.23 kJ/mol)>苯酚(19.31 kJ/mol)。吸附过程中的主要作用力为POPs的疏水作用, 而分子团簇、范德华相互作用、静电相互作用以及氢键等在一定程度上增加了GO对POPs的吸附能力。在混合体系中, POPs之间存在明显的竞争吸附现象, 吸附过程包含了直接吸附和形成分子团簇的间接性吸附两个过程。本研究结果为含POPs水体的治理以及GO材料的设计和筛选提供了一定的理论依据。
中图分类号:
赵超锋, 金佳人, 霍英忠, 孙陆, 艾玥洁. 氧化石墨烯吸附水体中酚类有机污染物的分子动力学模拟[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(3): 277-283.
ZHAO Chaofeng, JIN Jiaren, HUO Yingzhong, SUN Lu, AI Yuejie. Adsorption of Phenolic Organic Pollutants on Graphene Oxide: Molecular Dynamics Study[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(3): 277-283.
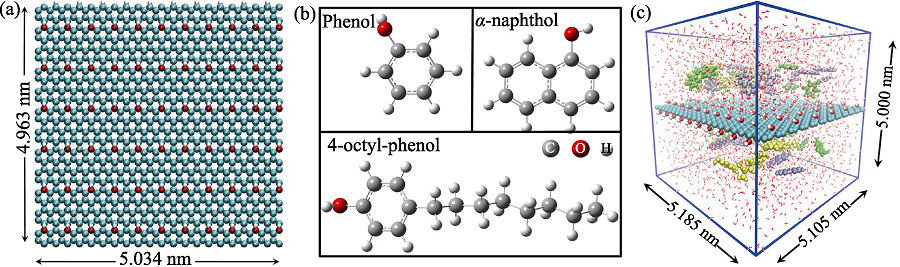
图1 MD模拟采用的(a)GO模型及其尺寸; (b)苯酚、α-萘酚和4-辛基酚的结构; (c)立方盒子的尺寸及苯酚(绿色)、α-萘酚(紫色)和4-辛基酚(黄色)在GO表面竞争吸附体系的初始结构
Fig. 1 (a) GO model, (b) structures of phenol, α-naphthol and 4-octyl-phenol molecules in MD simulations, and (c) initial configuration of phenol (green), α-naphthol (purple) and 4-octyl-phenol (yellow) molecules in the competitive system
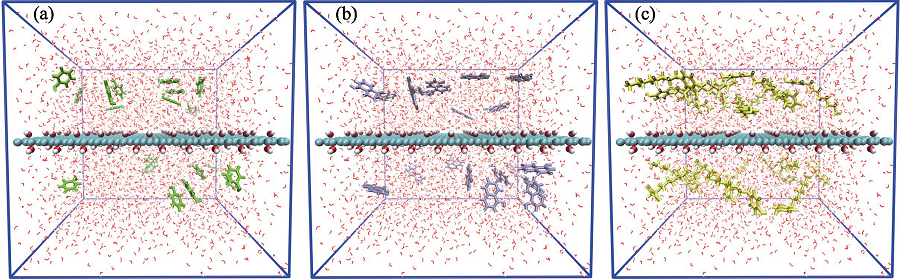
图S1 (a)苯酚、(b)α-萘酚和(c)4-辛基酚单独吸附体系的初始结构图
Fig. 2771 Initial configurations of (a) phenol, (b) α-naphthol and (c) 4-octyl-phenol molecules in the independent system
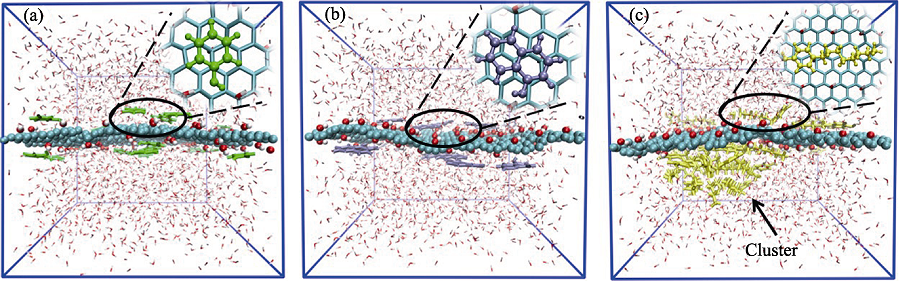
图2 (a)苯酚、(b)α-萘酚和(c)4-辛基酚在GO表面单独吸附的平衡结构
Fig. 2 Equilibrium structures of (a) phenol, (b) α-naphthol and (c) 4-octyl-phenol molecules adsorbed on GO surface
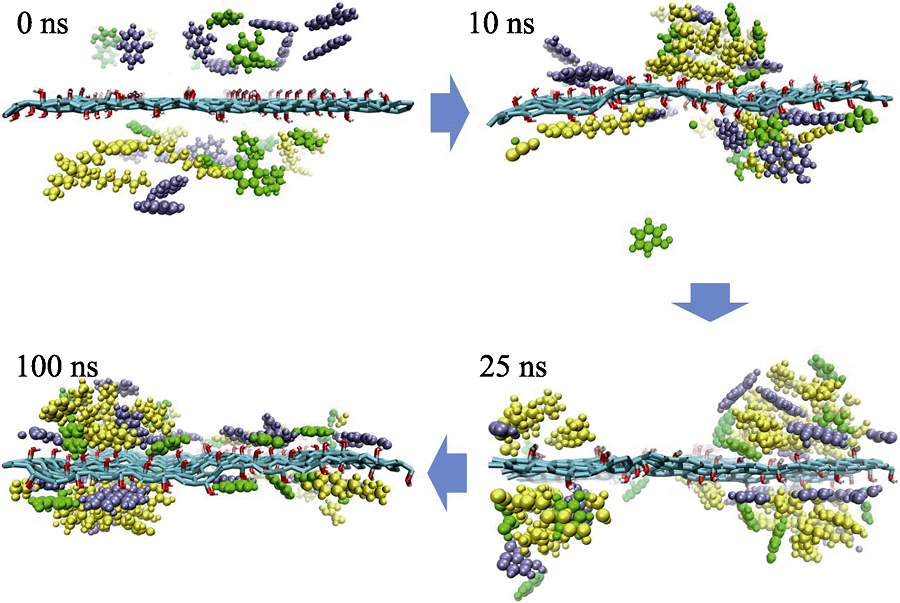
图3 竞争吸附体系中苯酚(绿色)、α-萘酚(紫色)和4-辛基酚(黄色)在GO表面不同时刻的吸附结构图
Fig. 3 Snapshots of competitive system from simulation process at different time Phenol, α-naphthol and 4-octyl-phenol molecules are shown as green, purple and yellow molecules, respectively. Water molecules are not shown to highlight the configuration
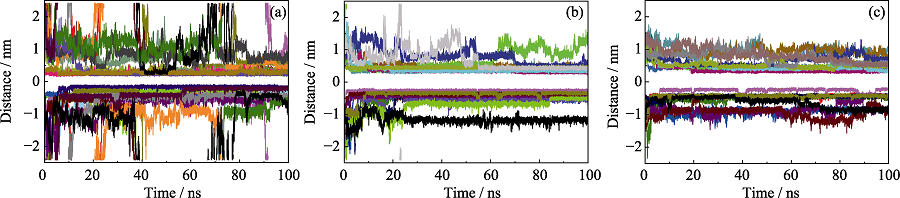
图4 竞争吸附体系中每一个(a)苯酚、(b)α-萘酚和(c)4-辛基酚分子与GO之间质心距离随时间的变化
Fig. 4 Distances of centers of mass between GO and each (a) phenol, (b) α-naphthol and (c) 4-octyl-phenol molecule, as function of time
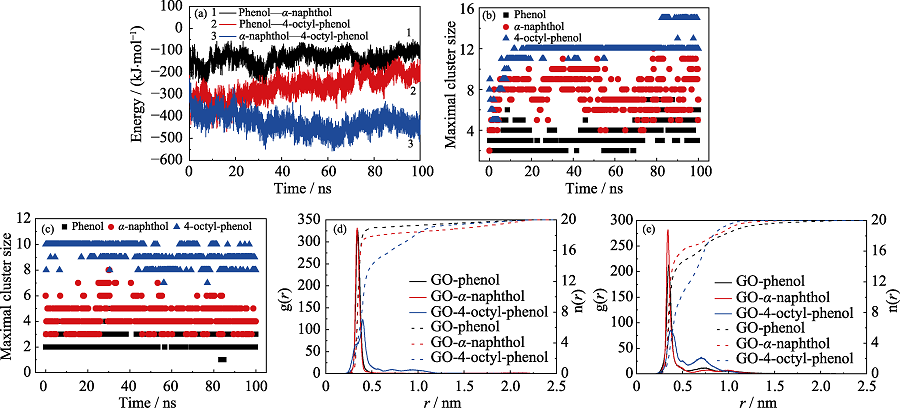
图5 (a)竞争吸附体系中三种POPs之间的相互作用能量, (b)单独和(c)竞争体系中POPs最大团簇中的分子数, (d)单独和(e)竞争体系中POPs在GO表面的径向分布函数曲线(g(r))以及半径r范围内相应的分子数目曲线(n(r))
Fig. 5 (a) Interaction energies between different POPs molecules in competitive system; The maximal cluster size of POPs in (b) independent and (c) competitive systems, respectively; The radial distribution functions (g(r)) and coordination numbers (n(r)) of POPs in (d) independent and (e) competitive systems, respectively
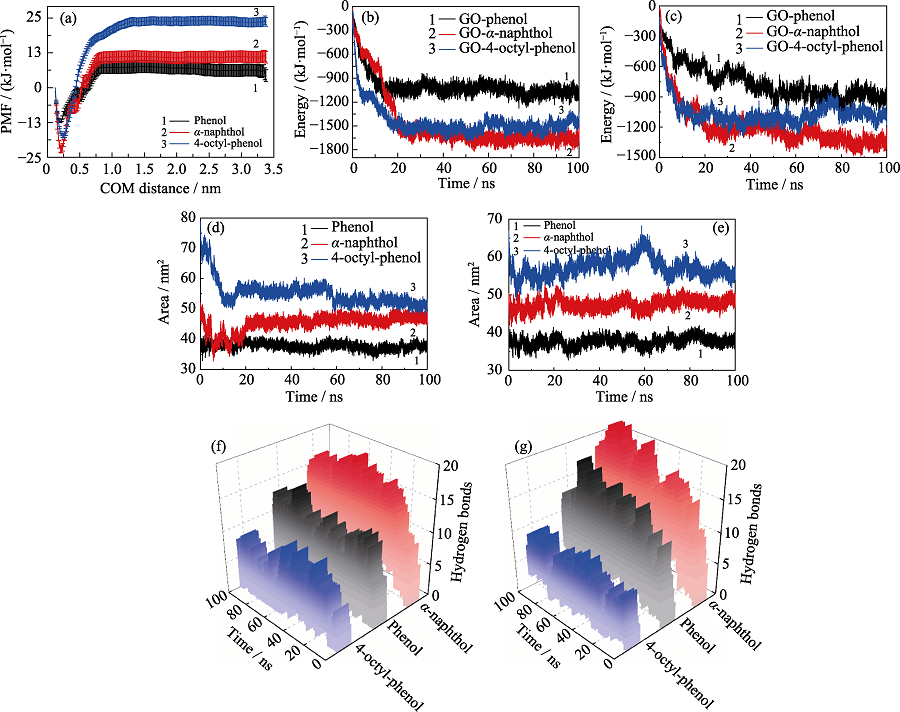
图6 (a)苯酚、α-萘酚和4-辛基酚分子的吸附自由能; GO与POPs在(b)单独和(c)竞争体系中的相互作用能量; POPs在(d)单独和(e)竞争体系中的疏水面积; GO与POPs官能团在(f)单独和(g)竞争体系中形成的氢键数目
Fig. 6 (a) Potential of mean force of POPs molecules; The interaction energies between GO and POPs molecules in (b) independent and (c) competitive systems, respectively; The hydrophobic areas of POPs molecules in (d) independent and (e) competitive systems, respectively; The hydrogen bonds between GO and POPs molecules in (f) independent and (g) competitive systems, respectively
| Time/ns | Phenol/(kJ•mol-1) | α-naphthol/(kJ•mol-1) | 4-octyl-phenol/(kJ•mol-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coulomb interaction | L-J Potential | Total | Coulomb interaction | L-J Potential | Total | Coulomb interaction | L-J Potential | Total | |
| 20 | -44.10 | -866.02 | -910.12 | -317.12 | -1172.76 | -1489.87 | -195.98 | -1311.17 | -1507.15 |
| 40 | -174.71 | -877.44 | -1052.16 | -388.46 | -1276.89 | -1665.35 | -162.60 | -1359.01 | -1521.60 |
| 60 | -124.19 | -897.25 | -1021.45 | -405.37 | -1243.64 | -1649.01 | -96.07 | -1340.12 | -1436.19 |
| 80 | -167.61 | -864.44 | -1032.05 | -358.80 | -1313.62 | -1672.42 | -125.83 | -1454.64 | -1580.47 |
| 100 | -237.23 | -880.63 | -1117.87 | -251.36 | -1338.97 | -1590.33 | -62.78 | -1344.93 | -1407.71 |
表S1 在单独吸附体系中GO与苯酚、α-萘酚、4-辛基酚分子在不同时刻的相互作用能量
Table S1 Interaction energies between GO and POPs molecules in independent system at different periods
| Time/ns | Phenol/(kJ•mol-1) | α-naphthol/(kJ•mol-1) | 4-octyl-phenol/(kJ•mol-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coulomb interaction | L-J Potential | Total | Coulomb interaction | L-J Potential | Total | Coulomb interaction | L-J Potential | Total | |
| 20 | -44.10 | -866.02 | -910.12 | -317.12 | -1172.76 | -1489.87 | -195.98 | -1311.17 | -1507.15 |
| 40 | -174.71 | -877.44 | -1052.16 | -388.46 | -1276.89 | -1665.35 | -162.60 | -1359.01 | -1521.60 |
| 60 | -124.19 | -897.25 | -1021.45 | -405.37 | -1243.64 | -1649.01 | -96.07 | -1340.12 | -1436.19 |
| 80 | -167.61 | -864.44 | -1032.05 | -358.80 | -1313.62 | -1672.42 | -125.83 | -1454.64 | -1580.47 |
| 100 | -237.23 | -880.63 | -1117.87 | -251.36 | -1338.97 | -1590.33 | -62.78 | -1344.93 | -1407.71 |
| Time/ns | Phenol/(kJ•mol-1) | α-naphthol/(kJ•mol-1) | 4-octyl-phenol/(kJ•mol-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coulomb interaction | L-J Potential | Total | Coulomb interaction | L-J Potential | Total | Coulomb interaction | L-J Potential | Total | |
| 20 | -160.11 | -448.40 | -608.51 | -235.85 | -914.54 | -1150.38 | -71.34 | -980.56 | -1051.90 |
| 40 | -240.86 | -533.62 | -774.48 | -288.30 | -960.43 | -1248.73 | -182.74 | -928.42 | -1111.16 |
| 60 | -334.12 | -573.27 | -907.39 | -354.11 | -993.34 | -1347.46 | -152.72 | -1013.83 | -1166.55 |
| 80 | -215.40 | -672.38 | -887.78 | -363.20 | -959.82 | -1323.02 | -201.10 | -912.11 | -1113.20 |
| 100 | -214.74 | -674.05 | -888.79 | -305.51 | -1069.33 | -1374.84 | -179.30 | -918.63 | -1097.92 |
表S2 在竞争吸附过程中GO与苯酚、α-萘酚、4-辛基酚分子在不同时刻的相互作用能量
Table S2 Interaction energies between GO and POPs molecules in competitive system at different periods
| Time/ns | Phenol/(kJ•mol-1) | α-naphthol/(kJ•mol-1) | 4-octyl-phenol/(kJ•mol-1) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Coulomb interaction | L-J Potential | Total | Coulomb interaction | L-J Potential | Total | Coulomb interaction | L-J Potential | Total | |
| 20 | -160.11 | -448.40 | -608.51 | -235.85 | -914.54 | -1150.38 | -71.34 | -980.56 | -1051.90 |
| 40 | -240.86 | -533.62 | -774.48 | -288.30 | -960.43 | -1248.73 | -182.74 | -928.42 | -1111.16 |
| 60 | -334.12 | -573.27 | -907.39 | -354.11 | -993.34 | -1347.46 | -152.72 | -1013.83 | -1166.55 |
| 80 | -215.40 | -672.38 | -887.78 | -363.20 | -959.82 | -1323.02 | -201.10 | -912.11 | -1113.20 |
| 100 | -214.74 | -674.05 | -888.79 | -305.51 | -1069.33 | -1374.84 | -179.30 | -918.63 | -1097.92 |
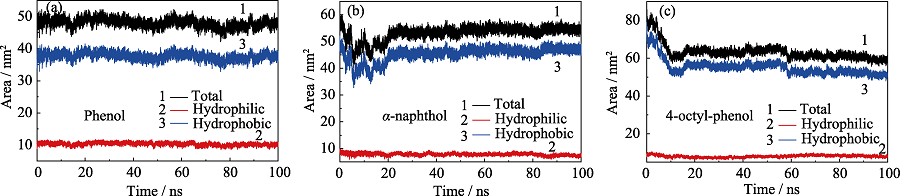
图S2 单独吸附体系中(a)苯酚、(b)α-萘酚和(c)4-辛基酚的溶剂可及表面积(solvent accessible surface area, SASA)随时间的变化
Fig. S2 SASAs of (a) phenol, (b) α-naphthol and (c) 4-octyl-phenol molecules in the independent system
| [1] | AHMARUZZAMAN M . Adsorption of phenolic compounds on low-cost adsorbents: a review. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2008,143(1/2):48-67. |
| [2] | BABICH H, DAVIS D L . Phenol: a review of environmental and health risks. Regulatory Toxicology and Pharmacology, 1981,1(1):90-109. |
| [3] | KARTHIKEYAN K G, CHOROVER JON, BORTIATYNSKI JACKIE M , et al. Interaction of 1-naphthol and its oxidation products with aluminum hydroxide. Environmental Science & Technology, 1999,33(22):4009-4015. |
| [4] | PONZO OSVALDO J, SILVIA CARBONE . Evidence of reproductive disruption associated with neuroendocrine changes induced by UV-B filters, phthalates and nonylphenol during sexual maturation in rats of both gender. Toxicology, 2013,311(1/2):41-51. |
| [5] | YU SHU-JUN, WANG XIANG-XUE, YAO WEN , et al. Macroscopic, spectroscopic, and theoretical investigation for the interaction of phenol and naphthol on reduced graphene oxide. Environmental Science & Technology, 2017,51(6):3278-3286. |
| [6] | YU SHU-JUN, WANG XIANG-XUE, AI YUE-JIE , et al. Experimental and theoretical studies on competitive adsorption of aromatic compounds on reduced graphene oxides. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016,4(15):5654-5662. |
| [7] | PAN BO, LIN DAO-HUI, MASHAYEKHI HAMID , et al. Adsorption and hysteresis of bisphenol a and 17α-ethinyl estradiol on carbon nanomaterials. Environmental Science & Technology, 2008,42(15):5480-5485. |
| [8] | RUESGAS-RAMON MARIANA, FIGUEROA-ESPINOZA MARIA CRUZ, DURAND ERWANN , Application of deep eutectic solvents (des) for phenolic compounds extraction: overview, challenges, and opportunities. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, 2017,65(18):3591-3601. |
| [9] | CIULU MARCO, CADIZ-GURREA MARIA DE LA LUZ, SEGURA-CARRETERO ANTONIO . Extraction and analysis of phenolic compounds in rice: a review. Molecules, 2018, 23(11):2890-1-20. |
| [10] | CASTRO-MUNOZ ROBERTO, YANEZ-FERNANDEZ JORGE, FILA VLASTIMIL . Phenolic compounds recovered from agro-food by-products using membrane technologies: an overview. Food Chemistry, 2016,213:753-762. |
| [11] | RAZA WASEEM, LEE JECHAN, RAZA NADEEM , et al. Removal of phenolic compounds from industrial waste water based on membrane-based technologies. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry, 2019,71:1-18. |
| [12] | ZYSZKA-HABERECHT BEATA, NIEMCZYK EMILIA, LIPOK JACEK . Metabolic relation of cyanobacteria to aromatic compounds. Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology, 2019,103(3):1167-1178. |
| [13] | SINGH PRIYARAGINI, KUMAR RAKESH . Critical review of microbial degradation of aromatic compounds and exploring potential aspects of furfuryl alcohol degradation. Journal of Polymers and the Environment, 2019,27(5):901-916. |
| [14] | LUO XU-BIAO, DENG FANG, MIN LU-JUAN , et al. Facile one-step synthesis of inorganic-framework molecularly imprinted TiO2/WO3 nanocomposite and its molecular recognitive photocatalytic degradation of target contaminant. Environmental Science & Technology, 2013,47(13):7404-7412. |
| [15] | SHAO PENG-HUI, TIAN JIA-YU, YANG FENG , et al. Identification and regulation of active sites on nanodiamonds: establishing a highly efficient catalytic system for oxidation of organic contaminants. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018,28(13):1705295. |
| [16] | BORTHAKUR PRIYAKSHREE, BORUAH PURNA K, DAS MANASH R , et al. Adsorption of 17α-ethynyl estradiol and β-estradiol on graphene oxide surface: an experimental and computational study. Journal of Molecular Liquids, 2018,269:160-168. |
| [17] | MOLLA ANIRUDDHA, LI YUAN-YUAN, MANDAL BIKASH , et al. Selective adsorption of organic dyes on graphene oxide: theoretical and experimental analysis. Applied Surface Science, 2019,464:170-177. |
| [18] | THAKUR KIRTI, KANDASUBRAMANIAN BALASUBRAMANIAN . Graphene and graphene oxide-based composites for removal of organic pollutants: a review. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data, 2019,64(3):833-867. |
| [19] | MUKHERJEE MALOSHREE, GOSWAMI SUDIPTA, BANERJEE PRIYA , et al. Ultrasonic assisted graphene oxide nanosheet for the removal of phenol containing solution. Environmental Technology & Innovation, 2019,13:398-407. |
| [20] | ZHOU QING-XIANG, WANG YU-QIN, XIAO JUN-PING , et al. Fabrication and characterisation of magnetic graphene oxide incorporated Fe3O4@polyaniline for the removal of bisphenol A, t-octyl-phenol, and alpha-naphthol from water. Scientific Reports, 2017,7(1):11316. |
| [21] | TANG HUAN, ZHAO YING, SHAN SU-JIE , et al. Theoretical insight into the adsorption of aromatic compounds on graphene oxide. Environmental Science: Nano, 2018,5(10):2357-2367. |
| [22] | ZHENG HUI-LING, GAO YANG, ZHU KAI-RUO , et al. Investigation of the adsorption mechanisms of Pb(II) and 1-naphthol by beta-cyclodextrin modified graphene oxide nanosheets from aqueous solution. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2018,530:154-162. |
| [23] | AMINPOUR MARAL, MONTEMAGNO CARLO, TUSZYNSKI JACK A . An overview of molecular modeling for drug discovery with specific illustrative examples of applications. Molecules, DOI: 10.3390/molecules24091693 |
| [24] | FENG DAI-LI, FENG YAN-HUI, QIU LIN , et al. Review on nanoporous composite phase change materials: fabrication, characterization, enhancement and molecular simulation. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews, 2019,109:578-605. |
| [25] | SPONER JIRI, BUSSI GIOVANNI, KREPL MIROSLAV , et al. RNA structural dynamics as captured by molecular simulations: a comprehensive overview. Chemical Reviews, 2018,118(8):4177-4338. |
| [26] | MA ZHAO-YANG, PATHEGAMA GAMAGE RANJITH, RATHNAWEERA THARAKA , et al. Review of application of molecular dynamic simulations in geological high-level radioactive waste disposal. Applied Clay Science, 2019,168:436-449. |
| [27] | LIU LU-MENG, LIU JUN-JIE, PEI JING-JING . Towards a better understanding of adsorption of indoor air pollutants in porous media— from mechanistic model to molecular simulation. Building Simulation, 2018,11(5):997-1010. |
| [28] | TANG HUAN, ZHAO YING, YANG XIAO-NAN , et al. Understanding the pH-dependent adsorption of ionizable compounds on graphene oxide using molecular dynamics simulations. Environmental Science: Nano, 2017,4(10):1935-1943. |
| [29] | TANG HUAN, ZHAO YING, SHAN SU-JIE , et al. Wrinkle- and edge-adsorption of aromatic compounds on graphene oxide as revealed by atomic force microscopy, molecular dynamics simulation, and density functional theory. Environmental Science & Technology, 2018,52(14):7689-7697. |
| [30] | CHEN XIAO-XIAO, CHEN BAO-LIANG . Macroscopic and spectroscopic investigations of the adsorption of nitroaromatic compounds on graphene oxide, reduced graphene oxide, and graphene nanosheets. Environmental Science & Technology, 2015,49(10):6181-6189. |
| [31] | MART NEZ JOS MARIO, MART NEZ LEANDRO . Packing optimization for automated generation of complex system's initial configurations for molecular dynamics and docking. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2003,24(7):819-825. |
| [32] | MART NEZ LEANDRO, ANDRADE RICARDO, BIRGIN ERNESTO G , et al. PACKMOL: a package for building initial configurations for molecular dynamics simulations. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2009,30(13):2157-2164. |
| [33] | BERENDSEN H J C, GRIGERA J R, STRAATSMA T P . The missing term in effective pair potentials. Journal of Physical Chemistry, 1987,91(24):6269-6271. |
| [34] | JORGENSEN WILLIAM L, MAXWELL DAVID S, TIRADO- RIVES JULIAN . Development and testing of the OPLS all-atom force field on conformational energetics and properties of organic liquids. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 1996,118(45):11225-11236. |
| [35] | WANG JUN-MEI, HOU TING-JUN . Application of molecular dynamics simulations in molecular property prediction I: density and heat of vaporization. Journal of Chemical Theory and Computation, 2011,7(7):2151-2165. |
| [36] | SUBASINGHEGE DON VISAL, DAVID ROLF, DU PU , et al. Interfacial water at graphene oxide surface: ordered or disordered? The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2019,123(7):1636-1649. |
| [37] | PRICE DANIEL J, BROOKS CHARLES L . Detailed considerations for a balanced and broadly applicable force field: a study of substituted benzenes modeled with OPLS-AA. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2005,26(14):1529-1541. |
| [38] | KAMINSKI GEORGE A . Accurate prediction of absolute acidity constants in water with a polarizable force field: substituted phenols, methanol, and imidazole. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 2005,109(12):5884-5890. |
| [39] | BERENDSEN HERMAN J C, VAN DER SPOEL DAVID, VAN DRUNEN RUDI . GROMACS: a message-passing parallel molecular dynamics implementation. Computer Physics Communications, 1995,91(1/2/3):43-56. |
| [40] | VAN DER SPOEL DAVID, LINDAHL ERIK, HESS BERK , et al. GROMACS: fast, flexible, and free. Journal of Computational Chemistry, 2005,26(16):1701-1718. |
| [41] | WANG JUN, CHEN BAO-LIANG . Adsorption and coadsorption of organic pollutants and a heavy metal by graphene oxide and reduced graphene materials. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2015,281:379-388. |
| [1] | 孙铭, 邵溥真, 孙凯, 黄建华, 张强, 修子扬, 肖海英, 武高辉. RGO/Al复合材料界面性质第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 651-659. |
| [2] | 董淑蕊, 赵笛, 赵静, 金万勤. 离子化氨基酸对氧化石墨烯膜渗透汽化过程中水选择性渗透的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 387-394. |
| [3] | 李豪, 唐志红, 卓尚军, 钱荣. 基于ZIF8/rGO的高性能NO2室温传感器[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1277-1282. |
| [4] | 张伟,高鹏,侯成义,李耀刚,张青红,王宏志. 基于ZnO复合材料的芯片式pH和温度传感器[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(4): 416-422. |
| [5] | 林启民, 崔建功, 颜鑫, 袁学光, 陈小瑜, 芦启超, 罗彦彬, 黄雪, 张霞, 任晓敏. 单点缺陷氧化石墨烯电子结构与光学特性的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(10): 1117-1122. |
| [6] | 张峰, 张凯立, 周明明, 陈超, 蔡志威, 魏国辉, 姜兴茂, 张诚, 劳伦·鲁尔曼, 吕耀康. 基于纳米银负载氧化石墨烯的新型聚乙烯复合材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 633-640. |
| [7] | 马志军, 莽昌烨, 赵海涛, 关智浩, 程亮. 石墨烯装载不同含量钴锌铁氧体及其电磁行为对比[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 407-416. |
| [8] | 王贵欣, 裴志彬, 叶长辉. 自供能柔性氧化石墨烯湿度传感器的喷墨印刷制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(1): 114-120. |
| [9] | 刘焕龙, 赵伟, 李睿哲, 黄谢意, 唐宇峰, 李冬梅, 黄富强. 还原氧化石墨烯原位包覆纳米MnTiO3颗粒的简易合成及储锂性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(9): 1022-1028. |
| [10] | 秦士林, 李继成, 李朝晖, 胡忠良, 丁燕怀, 雷钢铁, 肖启振. 基于共价键作用的四氧化三铁-还原氧化石墨烯复合材料的合成及其储锂性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(7): 741-748. |
| [11] | 阎鑫, 卢锦花, 惠小艳, 闫从祥, 高强, 孙国栋. g-C3N4/MoS2纳米片/氧化石墨烯三元复合催化剂的制备及可见光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(5): 515-520. |
| [12] | 王勇, 于云, 冯爱虎, 江峰, 胡学兵, 宋力昕. Nafion改性多级孔径石墨烯气凝胶制备与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4): 469-474. |
| [13] | 李翠霞, 金海泽, 杨志忠, 杨 轩, 董其铮, 厉婷婷. 介孔RGO/TiO2复合光催化材料的制备及光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(4): 357-364. |
| [14] | 姜文龙, 周 伟, 应纪飞, 杨铁莹, 高延敏. ZnO/GO纳米材料基热稳定钙钛矿太阳能电池[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(1): 96-100. |
| [15] | 王晓宁, 孟 虎, 马付银, 李 峥, 张 岚. 制备方法对氧化石墨烯氧化程度及对Th(IV)、U(VI)吸附的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(5): 454-460. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||