无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (12): 1316-1324.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190903
收稿日期:2019-03-01
修回日期:2019-03-28
出版日期:2019-12-20
网络出版日期:2019-12-02
作者简介:张翊青(1995-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: zhangyq95@163.com
基金资助:
ZHANG Yi-Qing,LIU Li,ZHANG Shu-Juan,WAN Zheng-Rui,LIU Hong-Ying,ZHOU Li-Qun( )
)
Received:2019-03-01
Revised:2019-03-28
Published:2019-12-20
Online:2019-12-02
Supported by:摘要:
采用锆盐和2-氨基对苯二甲酸以溶剂热法成功制备了氨基化的金属有机骨架化合物NH2-UIO-66, 并利用浸渍还原法成功负载RuCuMo纳米粒子, 制备了RuCuMo@NH2-UIO-66催化剂。通过X射线粉末衍射仪(XRD)、透射电子显微镜(TEM)、场发射扫描电镜(SEM)等技术对NH2-UIO-66、RuCuMo@NH2-UIO-66的结构、形貌、组成和比表面积进行了表征, 并对载体、多金属负载型催化剂以及无载体的RuCuMo纳米粒子的产氢性能进行了分析。结果显示, Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66催化剂的催化活性最高, 引入Cu和Mo能显著增强Ru对氨硼烷水解产氢的催化活性。这主要归因于RuCuMo纳米粒子之间强的协同作用, RuCuMo纳米粒子与载体NH2-UIO-66间的双功能效应, 以及MOFs上氨基的锚锭作用, 可以阻止金属粒子的团聚, 促进超细粒子的形成。催化反应的活化能(Ea)为30.1 kJ?mol -1, 转化频率(TOF)为180.83 $\text{mo}{{\text{l}}_{{{\text{H}}_{2}}}}\cdot \text{mol}_{\text{Ru}}^{-1}\cdot {{\min }^{-1}}$, 非贵金属Cu和Mo的引入为催化活性的提高和工业应用提供了重要的研究价值。
中图分类号:
张翊青, 刘梨, 张淑娟, 万正睿, 刘红英, 周立群. NH2-UIO-66负载RuCuMo纳米催化剂的制备及其催化产氢[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(12): 1316-1324.
ZHANG Yi-Qing, LIU Li, ZHANG Shu-Juan, WAN Zheng-Rui, LIU Hong-Ying, ZHOU Li-Qun. Preparation and Dehydrogenation Property of NH2-UIO-66 Supported RuCuMo Nanocatalyst[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(12): 1316-1324.
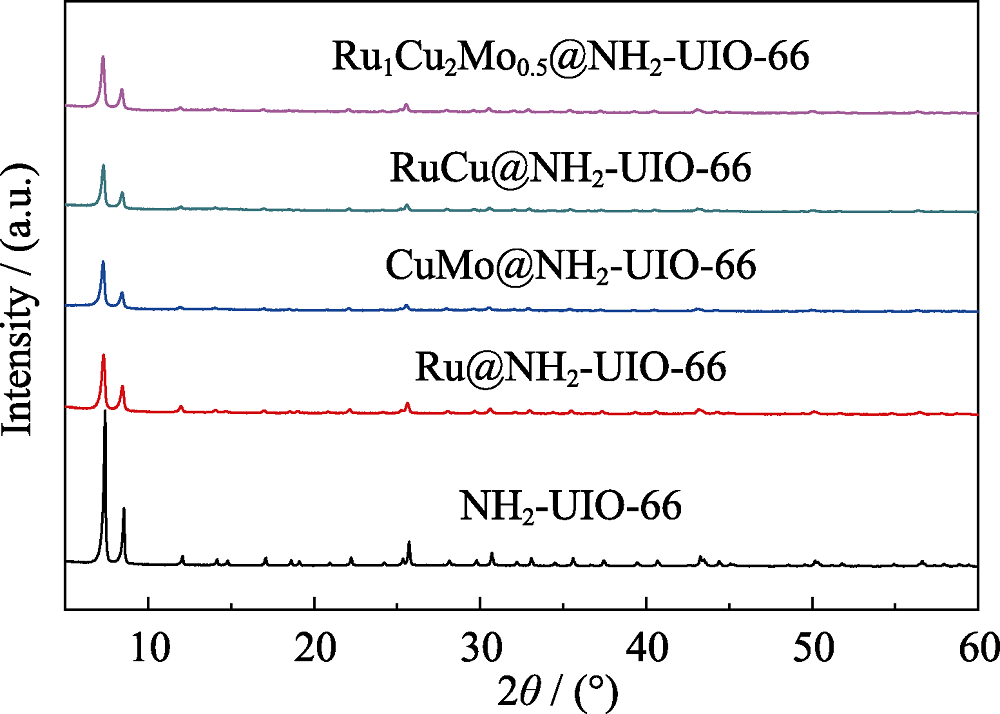
图1 NH2-UIO-66、Ru@NH2-UIO-66、CuMo@NH2-UIO-66、RuCu@NH2-UIO-66和Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66的XRD图谱
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of NH2-UIO-66, Ru@NH2-UIO-66, CuMo@NH2-UIO-66, RuCu@NH2-UIO-66 and Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66
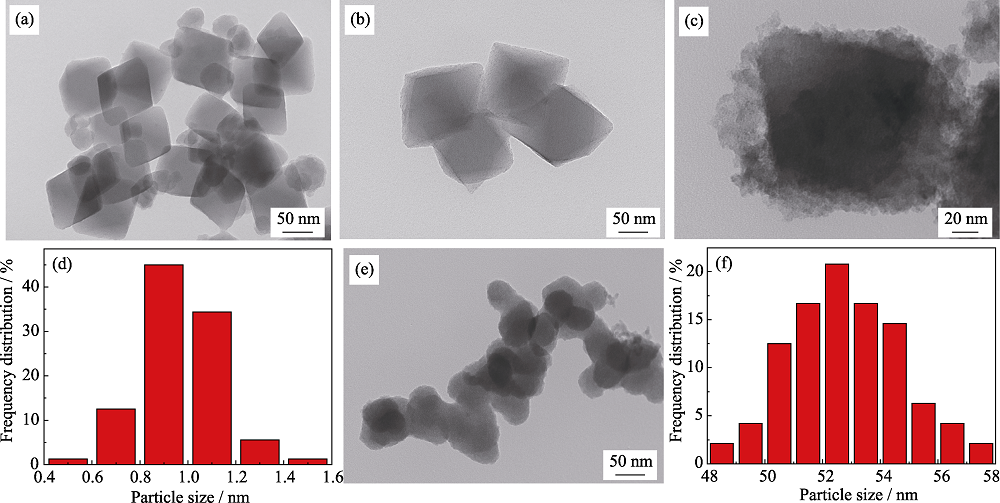
图2 (a,b) NH2-UIO-66、(c) Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66、(e) RuCuMo纳米粒子的TEM照片; (d) Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66和(f) RuCuMo纳米粒子的粒径分布图
Fig. 2 TEM images of (a, b) NH2-UIO-66, (c) Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66, (e) RuCuMo NPs, (d, f) particle size distributions of (d) Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 and (f) RuCuMo NPs
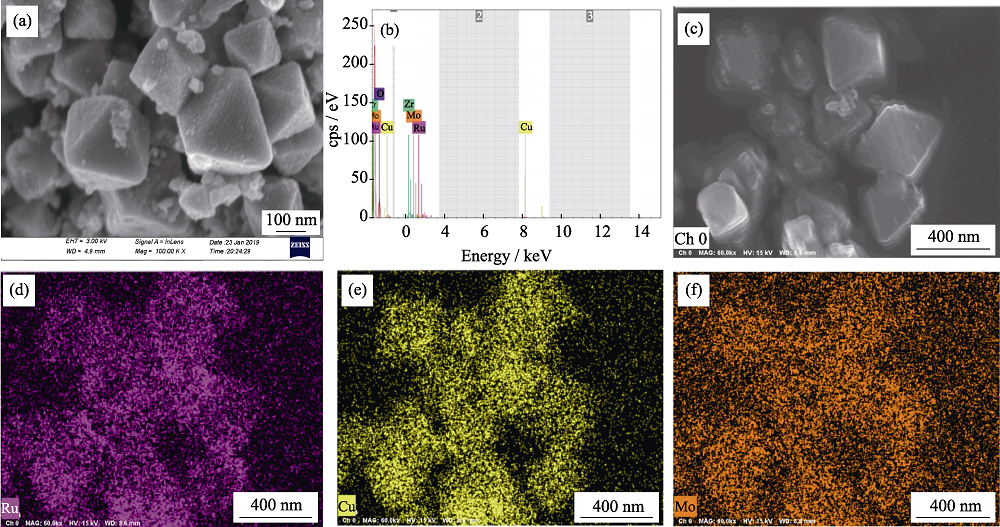
图3 (a, c) Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66的场发射扫描电镜照片, (b) EDS能谱分析和(d~f)相应的元素分布图像
Fig. 3 (a, c) FESEM image, (b) EDS analysis of Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 and (d-f) elemental mappings of Ru, Cu and Mo
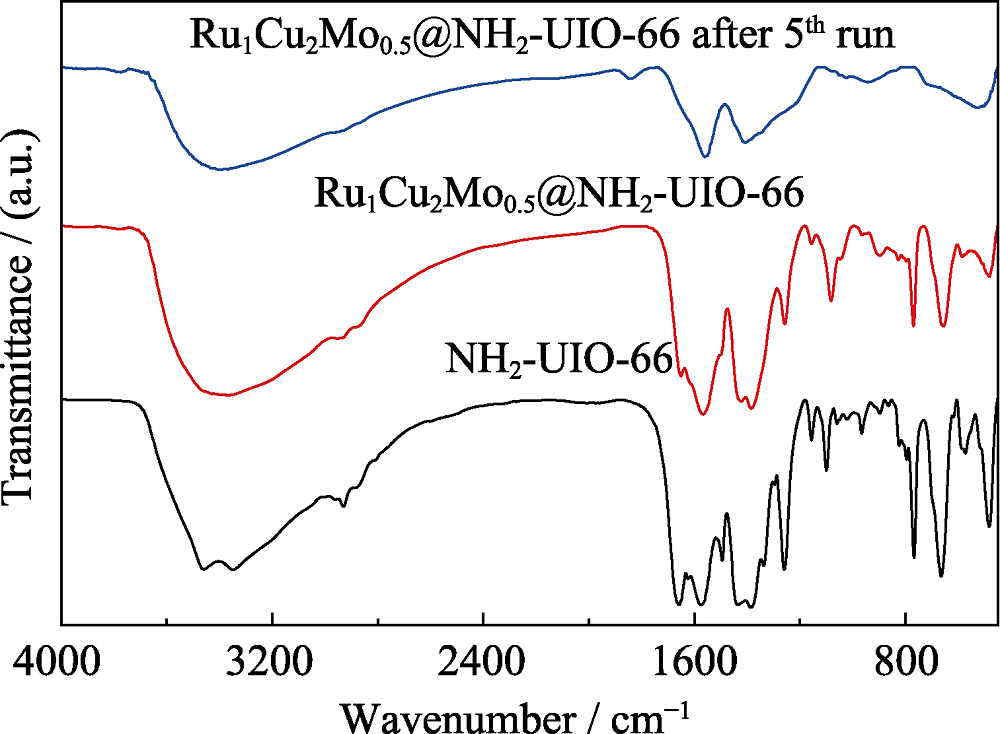
图5 NH2-UIO-66、Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66和循环5次后Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66的红外光谱图
Fig. 5 FT-IR spectra of NH2-UIO-66, Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO- 66 and Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 after 5 runs
| Catalyst | Initial ratio of Ru : Cu : Mo | Actual ratio of Ru : Cu : Mo | Actual Ru loading/wt% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru1Cu2Mo0.25@NH2-UIO-66 | 1.00 : 2.00 : 0.25 | 1.00 : 2.20 : 0.04 | 4.89 |
| Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 | 1.00 : 2.00 : 0.50 | 1.00 : 1.82 : 0.09 | 5.48 |
| Ru1Cu2Mo1.0@NH2-UIO-66 | 1.00 : 2.00 : 1.00 | 1.00 : 2.04 : 0.19 | 5.16 |
表1 ICP-AES对RuCuMo@NH2-UIO-66催化剂中的元素分析结果
Table 1 ICP-AES analyses of RuCuMo@NH2-UIO-66 catalysts with different molar ratios
| Catalyst | Initial ratio of Ru : Cu : Mo | Actual ratio of Ru : Cu : Mo | Actual Ru loading/wt% |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru1Cu2Mo0.25@NH2-UIO-66 | 1.00 : 2.00 : 0.25 | 1.00 : 2.20 : 0.04 | 4.89 |
| Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 | 1.00 : 2.00 : 0.50 | 1.00 : 1.82 : 0.09 | 5.48 |
| Ru1Cu2Mo1.0@NH2-UIO-66 | 1.00 : 2.00 : 1.00 | 1.00 : 2.04 : 0.19 | 5.16 |
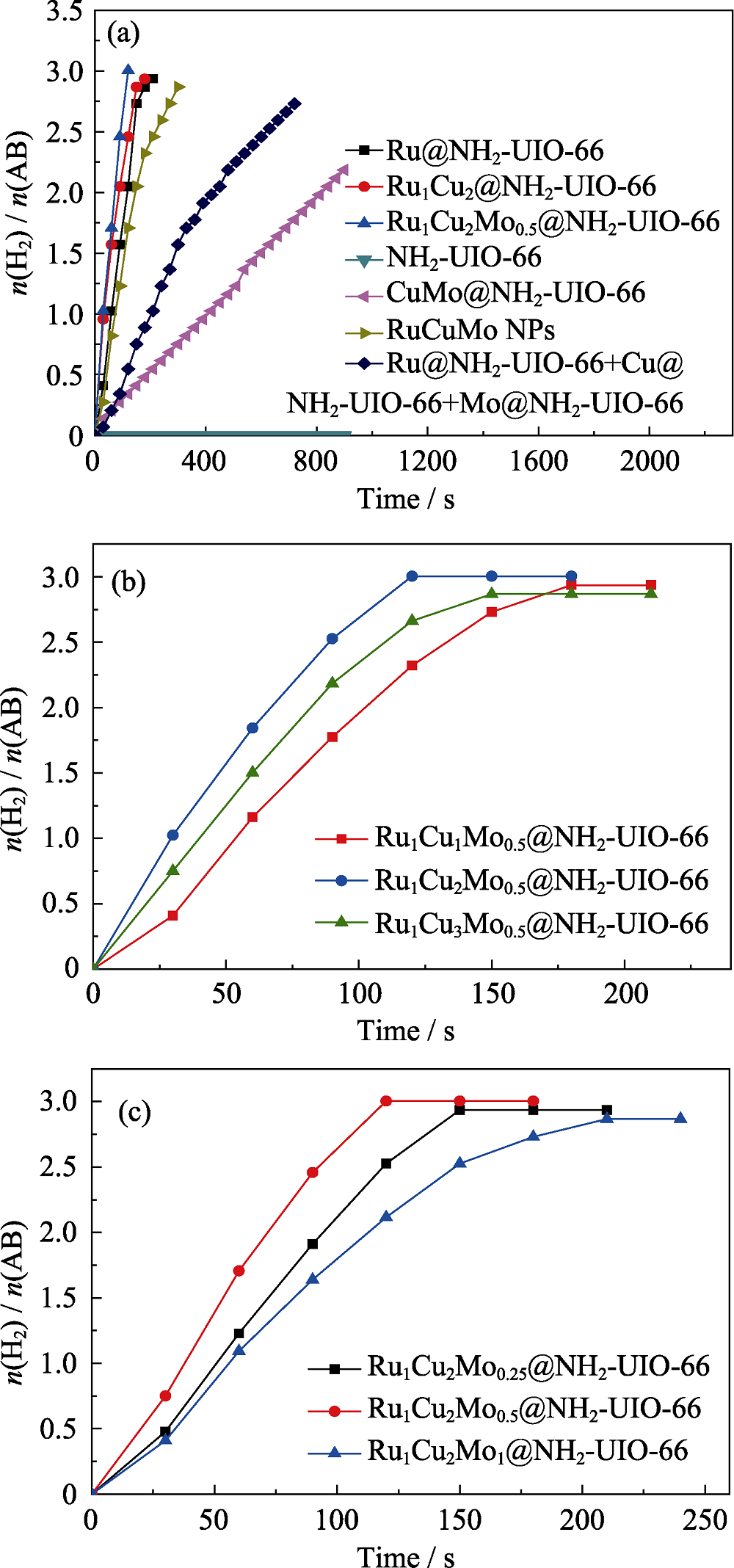
图6 (a) RuCuMo纳米粒子, Ru@NH2-UIO-66+Cu@NH2- UIO-66+Mo@NH2-UIO-66, Ru@NH2-UIO-66; Ru1Cu2@NH2-UIO-66, CuMo@NH2-UIO-66, Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO- 66, NH2-UIO-66; (b) Ru1Cux Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66和(c)Ru1Cu2 Moy@NH2-UIO-66的氨硼烷水解产氢速率曲线
Fig. 6 Plots of time vs. n(H2)/n(NH3BH3) from the hydrolysis of AB (18.5 mg): (a) RuCuMo NPs, Ru@NH2-UIO-66+Cu@NH2-UIO-66+Mo@NH2-UIO-66, Ru@NH2-UIO-66, Ru1Cu2 @NH2-UIO-66, CuMo@NH2-UIO-66, Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66, NH2-UIO-66; (b) Ru1CuxMo0.5@NH2-UIO-66, and (c) Ru1Cu2Moy@NH2-UIO-66
| Catalyst | TOF/($\text{mo}{{\text{l}}_{{{\text{H}}_{2}}}}\cdot \text{mol}_{\text{Ru}}^{-1}\cdot {{\min }^{-1}}$) | Ea/(kJ?mol-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru NPs | 26.70 | 66.50 | [34] |
| RuCu(1:1)/γ-Al2O3 | 16.40 | 52.00 | [35] |
| RuCo(1:1)/γ-Al2O3 | 32.90 | 47.00 | [35] |
| Ru(0)/TiO2 | 241.00 | 70.00 | [36] |
| RuCo@MIL-53 | 87.24 | 34.32 | [16] |
| Ru@g-C3N4 | 313.00 | 37.40 | [37] |
| RuCu/graphene | 135.00 | 30.60 | [38] |
| RuCuMo@NH2-UIO-66 | 180.83 | 30.10 | This study |
表2 不同钌基催化剂用于AB水解脱氢的催化活性
Table 2 Catalytic activities of different Ru-based catalysts used for the hydrolytic dehydrogenation of AB
| Catalyst | TOF/($\text{mo}{{\text{l}}_{{{\text{H}}_{2}}}}\cdot \text{mol}_{\text{Ru}}^{-1}\cdot {{\min }^{-1}}$) | Ea/(kJ?mol-1) | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ru NPs | 26.70 | 66.50 | [34] |
| RuCu(1:1)/γ-Al2O3 | 16.40 | 52.00 | [35] |
| RuCo(1:1)/γ-Al2O3 | 32.90 | 47.00 | [35] |
| Ru(0)/TiO2 | 241.00 | 70.00 | [36] |
| RuCo@MIL-53 | 87.24 | 34.32 | [16] |
| Ru@g-C3N4 | 313.00 | 37.40 | [37] |
| RuCu/graphene | 135.00 | 30.60 | [38] |
| RuCuMo@NH2-UIO-66 | 180.83 | 30.10 | This study |
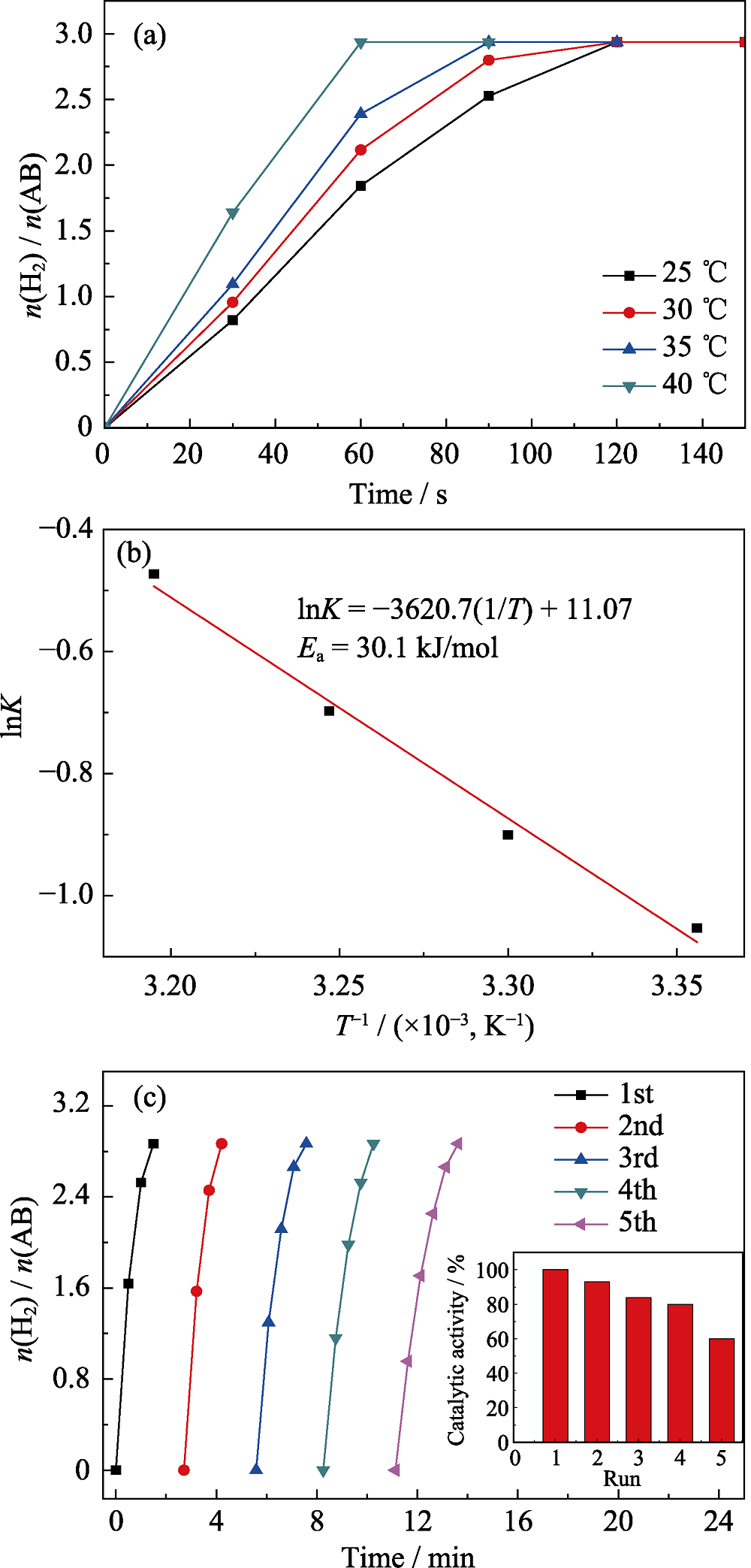
图7 温度对Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66催化水解氨硼烷的影响曲线(a)及其相应的阿伦尼乌斯图(b), Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66的5次循环稳定性图(c)
Fig. 7 Plots of time vs. n(H2)/n(NH3BH3) for the hydrolysis of AB (18.5 mg) aqueous solution catalyzed by Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 at different temperatures(a), and the corresponding Arrhenius plot (b), and reusability test for the Ru1Cu2Mo0.5@NH2-UIO-66 within five cycles(c)
| [1] | LONG J, WANG S, DING Z , et al. A mine-functionalized zirconium metal-organic framework as efficient visible-light photocatalyst for aerobic organic transformations. Chemical Communications, 2012,48(95):11656-11658. |
| [2] | GUO Z, XIAO C, MALIGALGANESH R V , et al. Pt nanoclusters confined within metal-organic framework cavities for chemoselective cinnamaldehyde hydrogenation. ACS Catalysis, 2014,4(5):1340-1348. |
| [3] | SUN D, FU Y, LIU W , et al. Studies on photocatalytic CO2 reduction over NH2-UIO-66 (Zr) and its derivatives: towards a better understanding of photocatalysis on metal-organic frameworks. Chemistry - A European Journal, 2013,19(42):14279-14285. |
| [4] | PETERSON G W, DECOSTE J B, FATOLLAHI-FARD F , et al. Engineering UiO-66-NH2 for toxic gas removal. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research, 2013,53(2):701-707. |
| [5] | XU X Y, YAN B . Eu (Ⅲ) functionalized Zr-based metal-organic framework as excellent fluorescent probe for Cd2+, detection in aqueous environment . Sensors & Actuators B Chemical, 2016,222:347-353. |
| [6] | CHANDRA M, XU Q . A high-performance hydrogen generation system: transition metal-catalyzed dissociation and hydrolysis of ammonia-borane. Journal of Power Sources, 2006,156(2):190-194. |
| [7] | FAN Y, LI X, HE X , et al. Effective hydrolysis of ammonia borane catalyzed by ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized on graphic carbon nitride. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(35):19982-19989. |
| [8] | DAI H, SU J, KAI H , et al. Pd nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as high-performance catalysts for catalytic hydrolysis of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(10):4947-4953. |
| [9] | ZHANG X B, YAN J M, HAN S , et al. Magnetically recyclable Fe@Pt core-shell nanoparticles and their use as electrocatalysts for ammonia borane oxidation: the role of crystallinity of the core. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2009,131(8):2778-2779. |
| [10] | YAN J M, ZHANG X B, SHIOYAMA H , et al. Room temperature hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane catalyzed by Co nanoparticles. Journal of Power Sources, 2010,195(4):1091-1094. |
| [11] | ZAHMAKIRAN M, DURAP F, ÖZKAR S . Zeolite confined copper (0) nanoclusters as cost-effective and reusable catalyst in hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia-borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2010,35(1):187-197. |
| [12] | YANG K, YAO Q, HUANG W , et al. Enhanced catalytic activity of NiM (M=Cr, Mo, W) nanoparticles for hydrogen evolution from ammonia borane and hydrazine borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017,42(10):6840-6850. |
| [13] | YAO Q, LU Z H, HUANG W , et al. High Pt-like activity of the Ni-Mo/graphene catalyst for hydrogen evolution from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Journal of Materials Chemical A, 2016,4(22):8579-8583. |
| [14] | ZHANG L, ZHOU L, YANG K , et al. Pd, Ni nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as high-performance catalysts for hydrogen generation from ammonia borane. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2016,677:87-95. |
| [15] | WANG Q, XU C, MING M , et al. In situ formation of AgCo stabilized on graphitic carbon nitride and concomitant hydrolysis of ammonia borane to hydrogen. Nanomaterials, 2018,8(5):280-289. |
| [16] | CHEN M, ZHOU L, LU D , et al. RuCo bimetallic alloy nanoparticles immobilized on multi-porous MIL-53 (Al) as a highly efficient catalyst for the hydrolytic reaction of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2018,43(3):1439-1450. |
| [17] | XIONG X, ZHOU L, YU G , et al. Synthesis and catalytic performance of a novel RuCuNi/CNTs nanocomposite in hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2015,40(45):15521-15528. |
| [18] | YANG K, ZHOU L, XIONG X , et al. RuCuCo nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as a novel highly efficient catalysts for the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Microporous & Mesoporous Materials, 2016,225:1-8. |
| [19] | GU Y, WU Y N, LI L , et al. Controllable modular growth of hierarchical MOF-on-MOF architectures. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2017,56(49):15658-15662. |
| [20] | YANG K, ZHOU L, YU G , et al. Ru nanoparticles supported on MIL-53 (Cr, Al) as efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016,41(15):6300-6309. |
| [21] | YURDERI M, BULUT A, ZAHMAKIRAN M , et al. Ruthenium (0) nanoparticles stabilized by metal-organic framework (ZIF-8): highly efficient catalyst for the dehydrogenation of dimethyla mine-borane and transfer hydrogenation of unsaturated hydrocarbons using dimethyla mine-borane as hydrogen source. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2014, 160-161(1):534-541. |
| [22] | CAO N, SU J, LUO W , et al. Ni-Pt nanoparticles supported on MIL-101 as highly efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from aqueous alkaline solution of hydrazine for chemical hydrogen storage. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(18):9726-9734. |
| [23] | RAKAP M . PVP-stabilized Ru-Rh nanoparticles as highly efficient catalysts for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2015,649:1025-1030. |
| [24] | CHUSUEI C C, BROOKSHIER M A, GOODMAN D W . Correlation of relative X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy shake-up intensity with CuO particle size. Langmuir, 1999,15(8):2806-2808. |
| [25] | GUCZI L, BAZIN D . Structure and selectivity of metal catalysts: revisiting bimetallic zeolite systems. Applied Catalysis A General, 1999,188(1/2):163-174. |
| [26] | GU Z, XIONG Z, REN F , et al. Flower-like PdCu catalyst with high electrocatalytic properties for ethylene glycol oxidation. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers, 2018,83:32-39. |
| [27] | WANG P, QI J, CHEN X , et al. New insights into high-valence state Mo in molybdenum carbide nanobelts for hydrogen evolution reaction. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017,42(16):10880-10890. |
| [28] | LOC LUU C, THI T V N, NGUYEN T , et al. Synthesis, characterization and adsorption ability of UiO-66-NH2. Advances in Natural Sciences Nanoscience & Nanotechnology, 2015,6(2):025004-025009. |
| [29] | LOISEAU T, SERRE C, HUGUENARD C , et al. A rationale for the large breathing of the porous aluminum terephthalate (MIL-53) upon hydration. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2004,10(6):1373-1382. |
| [30] | LI J, ZHU Q L, XU Q . Non-noble bimetallic CuCo nanoparticles encapsulated in the pores of metal-organic frameworks: synergetic catalysis in the hydrolysis of ammonia borane for hydrogen generation. Catalysis Science & Technology, 2014,5(1):525-530. |
| [31] | NING H, LU D, ZHOU L . Bimetallic RuM (M=Co, Ni) alloy NPs supported on MIL-110(Al): synergetic catalysis in hydrolytic dehydrogenation of ammonia borane. Chinese Journal of Chemical Physics, 2018,31(1):99-109. |
| [32] | WANG X, CHEN W, ZHANG L , et al. Uncoordinated a mine groups of MOFs to anchor single Ru sites as chemoselective catalysts towards the hydrogenation of quinolone. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2017,139(28):9419-9422. |
| [33] | CAO N, LIU T, SU J , et al. Ruthenium supported on MIL-101 as an efficient catalyst for hydrogen generation from hydrolysis of a mine boranes. New Journal of Chemistry, 2014,38(9):4032. |
| [34] | ZHOU Q, YANG H, XU C . Nanoporous Ru as highly efficient catalyst for hydrolysis of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2016,41(30):12714-12721. |
| [35] | RACHIERO G, DEMIRCI U, MIELE P . Bimetallic RuCo and RuCu catalysts supported on γ-Al2O3. A comparative study of their activity in hydrolysis of ammonia-borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2011,36(12):7051-7065. |
| [36] | AKBAYRAK S, TANYILDIZI S, MORKAN I , et al. Ruthenium (0) nanoparticles supported on nanotitania as highly active and reusable catalyst in hydrogen generation from the hydrolysis of ammonia borane. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(18):9628-9637. |
| [37] | YAN R, LI X, HE X , et al. Effective hydrolysis of ammonia borane catalyzed by ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized on graphic carbon nitride. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2014,39(35):19982-19989. |
| [38] | CAO N, HU K, LUO W , et al. RuCu nanoparticles supported on graphene: a highly efficient catalyst for hydrolysis of ammonia borane. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014,590:241-246. |
| [1] | 张翊青,张淑娟,万正睿,莫晗,王念贵,周立群. RuFe纳米粒子修饰片状BiVO4协同催化氨硼烷水解产氢[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 809-816. |
| [2] | 柯剑煌, 谢凯, 韩喻, 孙巍巍, 罗世强, 刘锦锋. 基于不同共溶剂体系对于高电压正极材料LiCoPO4的形貌控制[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 618-624. |
| [3] | 隋丽丽,王润,赵丹,申书昌,孙立,徐英明,程晓丽,霍丽华. 多级结构α-MoO3空心微球的构筑及其对有机染料的吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(2): 193-200. |
| [4] | 武萱蓉, 杨巧珍, 赵永祥, 路艳罗. ZnS微球的水热/溶剂热法合成及其光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(5): 473-478. |
| [5] | 李 斌, 李英莲, 莫淑一, 陈明光, 王东生, 龙 飞. In2Se3/CuSe核壳结构微纳粉的合成及其喷涂热处理制备CuInSe2薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(10): 1135-1140. |
| [6] | 卢 青, 华罗光, 陈亦琳, 高碧芬, 林碧洲. 氧缺陷Bi2WO6-x可见光催化剂的制备和性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(4): 413-419. |
| [7] | 周 超, 冯 清, 高延敏. 溶剂热法制备Cu2ZnSnS4粉末及其表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(5): 487-492. |
| [8] | 李跃军, 曹铁平, 邵长路, 王长华. γ-Bi2O3/TiO2复合纤维的制备及光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(7): 687-692. |
| [9] | 朱振峰, 王小枫, 刘 辉, 刘佃光. 准单分散SnO2微球的微波溶剂热合成[J]. 无机材料学报, 2012, 27(3): 311-316. |
| [10] | 李天保, 梁 建, 许并社, 王 进. 硼酸镁一维纳米材料的制备和表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(9): 947-951. |
| [11] | 朱孔军, 苏礼奎, 季宏丽, 裘进浩, 柏 林, 柳泽河道, 梶芳浩二. 水热-溶剂热法合成(K, Na)NbO3无铅压电陶瓷及其性能测试[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(11): 1159-1163. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||