无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (1): 46-52.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190242
所属专题: MAX相和MXene材料; 结构陶瓷论文精选(2020); 【虚拟专辑】层状MAX,MXene及其他二维材料
汪丹丹1,田无边1( ),丁健翔2,马爱斌3,张培根1,何炜1,孙正明1(
),丁健翔2,马爱斌3,张培根1,何炜1,孙正明1( )
)
收稿日期:2019-05-23
修回日期:2019-06-24
出版日期:2020-01-20
网络出版日期:2019-09-12
作者简介:汪丹丹(1990-), 女, 博士研究生. E-mail:ddwang1111@163.com
基金资助:
WANG Dan-Dan1,TIAN Wu-Bian1( ),DING Jian-Xiang2,MA Ai-Bin3,ZHANG Pei-Gen1,HE Wei1,SUN Zheng-Ming1(
),DING Jian-Xiang2,MA Ai-Bin3,ZHANG Pei-Gen1,HE Wei1,SUN Zheng-Ming1( )
)
Received:2019-05-23
Revised:2019-06-24
Published:2020-01-20
Online:2019-09-12
About author:WANG Dan-Dan(1990-), female, PhD candidate. E-mail:ddwang1111@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
采用等通道转角挤压(Equal Channel Angular Pressing, ECAP)并结合热处理制备了Ag/Ti3AlC2复合材料。通过XRD、SEM分析物相和形貌, 探讨了不同热处理条件下Ag/Ti3AlC2材料的电阻率和力学性能。结果表明: 采用ECAP可以明显致密化Ag/Ti3AlC2疏松坯体, 且在ECAP的剪切作用下, 层片状Ti3AlC2颗粒沿基面分层并按一定方向排列。Ti3AlC2的定向排列使材料性能呈现各向异性: 垂直于Ti3AlC2排列方向时, Ag/Ti3AlC2材料的电阻率和压缩强度更高。后续热处理提升了Ag/Ti3AlC2的电阻率和压缩强度, 并发现在800 ℃时增幅显著。这主要归因于Ag与Ti3AlC2在高温下明显增强的界面反应。本研究表明采用ECAP方法可以在致密化Ag/MAX复合材料的同时调控其显微组织, 而结合热处理可以进一步调控界面反应并优化材料性能。
中图分类号:
汪丹丹, 田无边, 丁健翔, 马爱斌, 张培根, 何炜, 孙正明. 等通道转角挤压制备Ag/Ti3AlC2复合材料及其热处理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(1): 46-52.
WANG Dan-Dan, TIAN Wu-Bian, DING Jian-Xiang, MA Ai-Bin, ZHANG Pei-Gen, HE Wei, SUN Zheng-Ming. Ag/Ti3AlC2 Composites Prepared by Equal Channel Angular Pressing Followed by Heat Treatment[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 46-52.
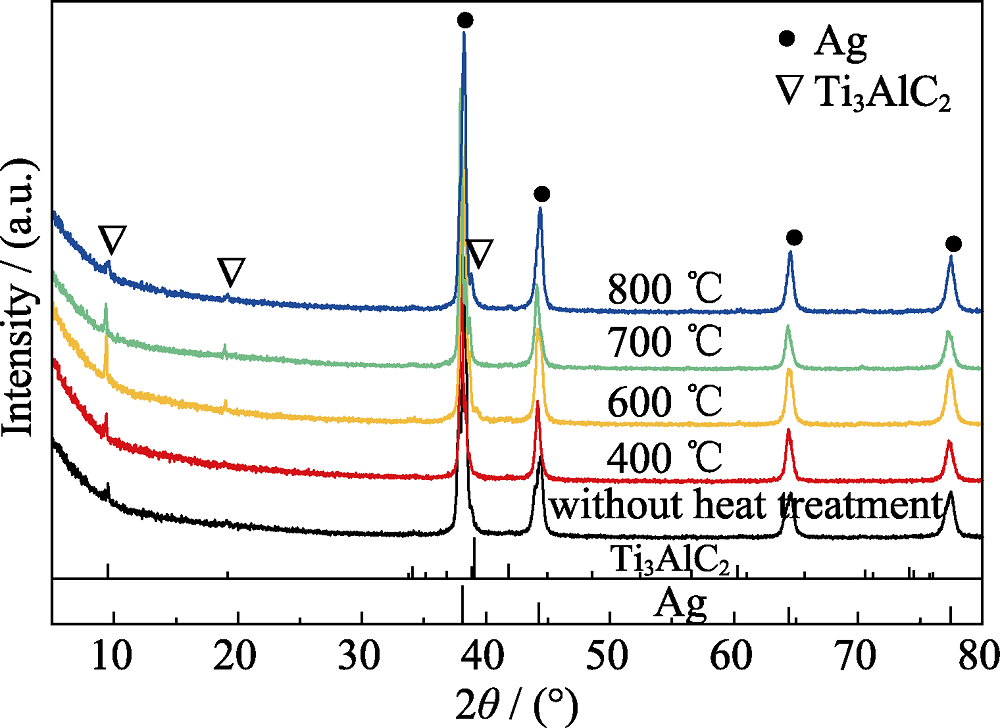
图3 Ag/Ti3AlC2 ECAP后未热处理和400、600、700及800 ℃热处理的XRD图谱
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of ECAPed Ag/Ti3AlC2 samples without and with heat treatment at 400, 600, 700, 800 ℃
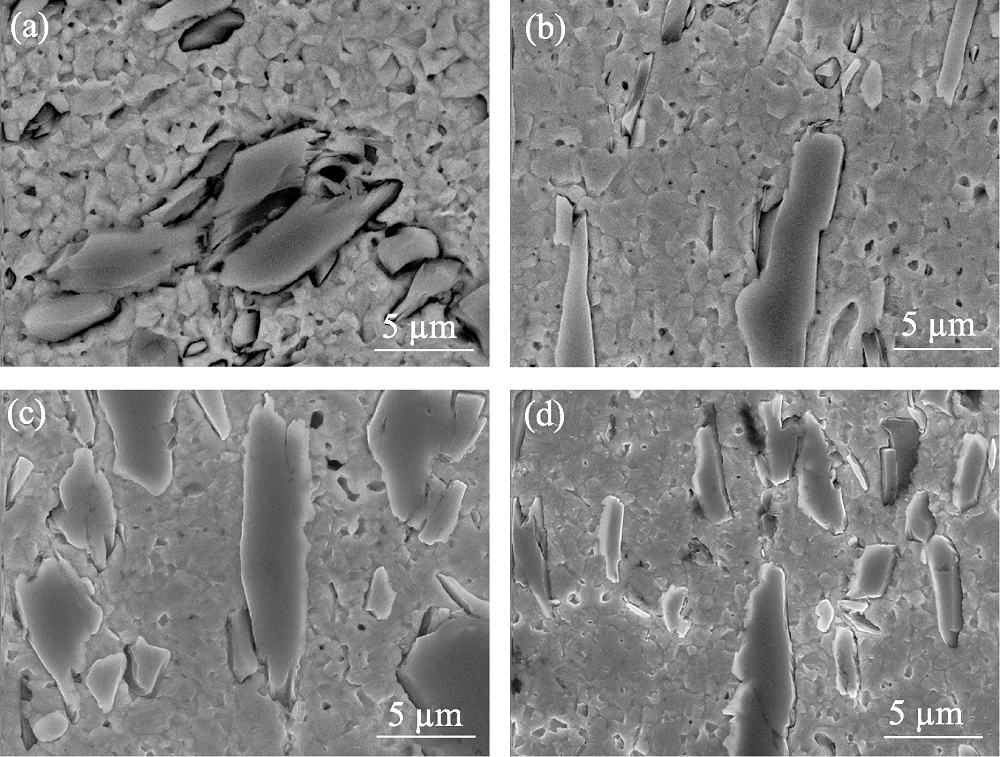
图6 Ag/Ti3AlC2 ECAP后在不同热处理条件下的SEM照片 (a) 400 ℃; (b) 600 ℃; (c) 700 ℃; (d) 800 ℃
Fig. 6 SEM images of the ECAPed Ag/Ti3AlC2 heat-treated at different temperatures
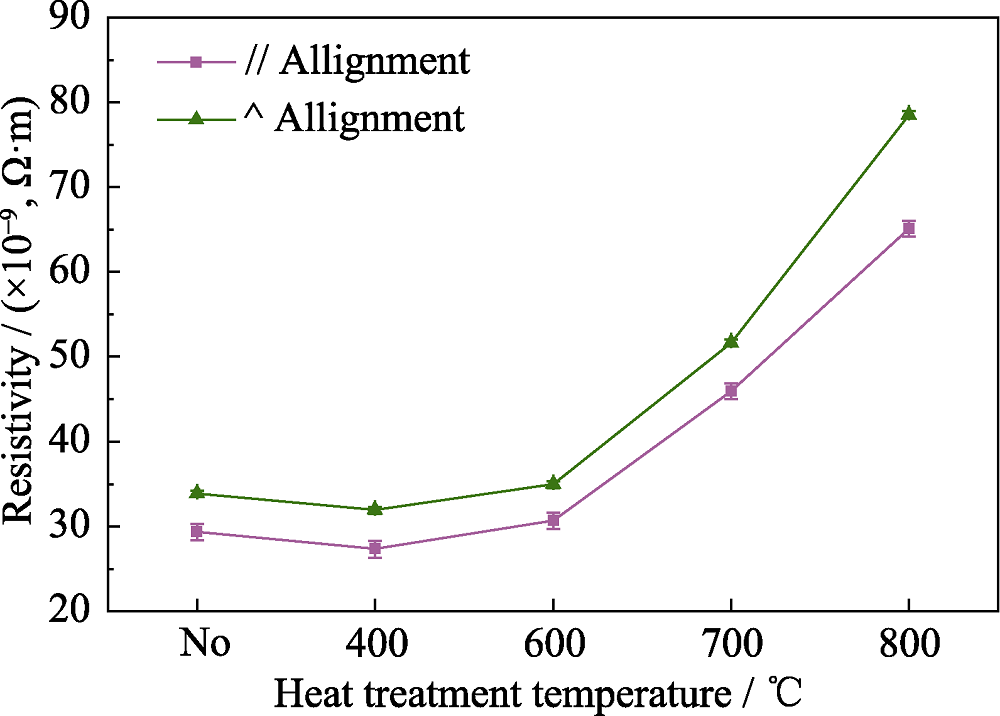
图8 Ag/Ti3AlC2 ECAP后平行和垂直于Ti3AlC2颗粒取向的电阻率
Fig. 8 Resistivity of the ECAPed Ag/Ti3AlC2 samples tested parallel to and perpendicular to the alignment of Ti3AlC2 particles
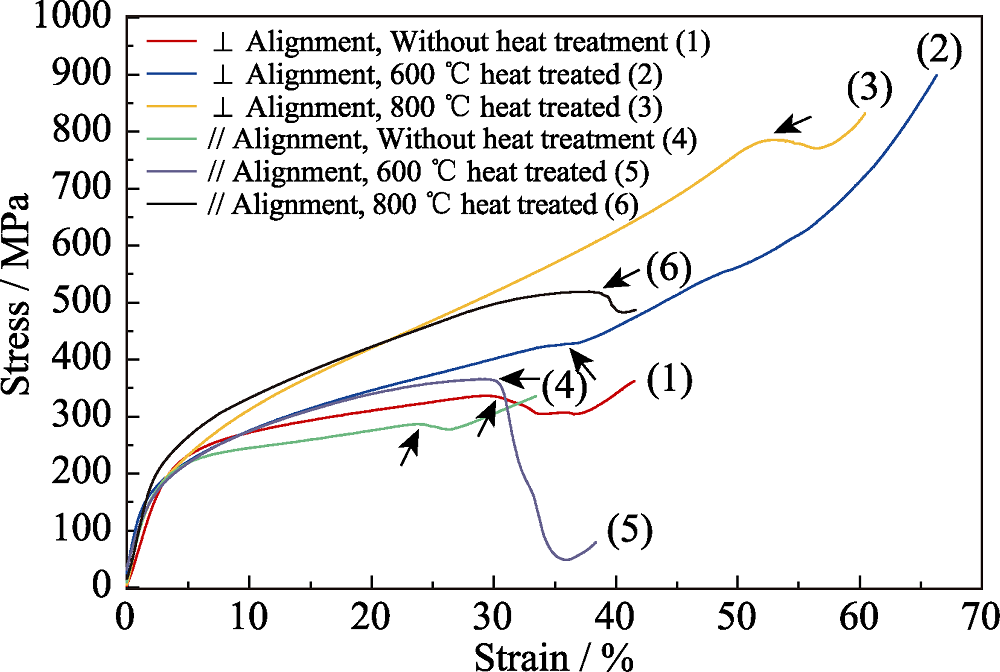
图10 Ag/Ti3AlC2 ECAP后平行和垂直于Ti3AlC2颗粒取向时的压缩应力-应变曲线
Fig. 10 Compressive stress-strain curves of the ECAPed Ag/Ti3AlC2 samples tested parallel and perpendicular to the alignment of Ti3AlC2 particles
| Heat treatment | Loaded // alignment | Loaded ^ alignment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| σM/MPa | εM/% | σM /MPa | εM/% | |
| N/A | 287.5 | 23.9 | 336.9 | 29.2 |
| 600 ℃ | 366.1 | 28.9 | 400.0 | 29.8 |
| 800 ℃ | 519.2 | 37.9 | 784.0 | 52.8 |
表1 Ag/Ti3AlC2 ECAP后最大压缩强度和应变量
Table 1 The maximum compressive strength and strain of the ECAPed Ag/Ti3AlC2 compacts
| Heat treatment | Loaded // alignment | Loaded ^ alignment | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| σM/MPa | εM/% | σM /MPa | εM/% | |
| N/A | 287.5 | 23.9 | 336.9 | 29.2 |
| 600 ℃ | 366.1 | 28.9 | 400.0 | 29.8 |
| 800 ℃ | 519.2 | 37.9 | 784.0 | 52.8 |
| Ag/MAX | Preparation method | Relative density/% | Resistivity/ (×10-9, Ω·m) | Vickers hardness/HV | Maximum compressive strength and strain | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/Ti3AlC2 | ECAPed at 37 MPa +800 ℃, 2 h | (97.8±0.8) | (65.1±1)(//alignment) (78.5±1)(⊥alignment) | (79±5) | 519 MPa, 37.9% (loaded // alignment) 784 MPa, 52.8% (loaded ^ alignment) | This work |
| Ag/Ti3AlC2 | Compacted at 800 MPa+800 ℃, 2 h | (96.0±0.4) | (60.6±1) | (95±5) | (446±15) MPa, (32.9±2.8)% | [6] |
| Ag/Ti3AlC2 | Compacted at 800 MPa+800 ℃, 2 h +ECAPed at 37 MPa | (99.8±0.2) | (59.3±1)(//alignment) (70.2±1)(⊥alignment) | (132±5) | (656±17) MPa, (30.3±2.7)% (loaded // alignment) (805±19) MPa, (43.8±2.2)% (loaded ^ alignment) | [6] |
| Ag/Ti3SiC2 | Compacted at 800 MPa+950 ℃, 1 h | (95.0) | (27.6±0.2) | (56) | N/A | [7] |
| Ag/Ti2AlC | Compacted at 800 MPa+800 ℃, 2 h | (95.7) | (79.5) | (88) | N/A | [10] |
| Ag/Ti2SnC | Compacted at 800 MPa+800 ℃, 2 h | (95.0) | (118.3) | (75) | N/A | [9] |
表2 Ag/10wt% MAX复合材料的基本物理性能
Table 2 Basic physical propery of Ag/10wt% MAX composites
| Ag/MAX | Preparation method | Relative density/% | Resistivity/ (×10-9, Ω·m) | Vickers hardness/HV | Maximum compressive strength and strain | Ref. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ag/Ti3AlC2 | ECAPed at 37 MPa +800 ℃, 2 h | (97.8±0.8) | (65.1±1)(//alignment) (78.5±1)(⊥alignment) | (79±5) | 519 MPa, 37.9% (loaded // alignment) 784 MPa, 52.8% (loaded ^ alignment) | This work |
| Ag/Ti3AlC2 | Compacted at 800 MPa+800 ℃, 2 h | (96.0±0.4) | (60.6±1) | (95±5) | (446±15) MPa, (32.9±2.8)% | [6] |
| Ag/Ti3AlC2 | Compacted at 800 MPa+800 ℃, 2 h +ECAPed at 37 MPa | (99.8±0.2) | (59.3±1)(//alignment) (70.2±1)(⊥alignment) | (132±5) | (656±17) MPa, (30.3±2.7)% (loaded // alignment) (805±19) MPa, (43.8±2.2)% (loaded ^ alignment) | [6] |
| Ag/Ti3SiC2 | Compacted at 800 MPa+950 ℃, 1 h | (95.0) | (27.6±0.2) | (56) | N/A | [7] |
| Ag/Ti2AlC | Compacted at 800 MPa+800 ℃, 2 h | (95.7) | (79.5) | (88) | N/A | [10] |
| Ag/Ti2SnC | Compacted at 800 MPa+800 ℃, 2 h | (95.0) | (118.3) | (75) | N/A | [9] |
| [1] |
DING J X, SUN Z M, ZHANG P G , et al. Current research status and outlook of Ag-based contact materials. Materials Reports, 2018,32(1):58-66.
DOI URL PMID |
| [2] |
SUN Z M . Progress in research and development on MAX phases: a family of layered ternary compounds. International Materials Reviews, 2011,56(3):143-166.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
DING J X, TIAN W B, ZHANG P G , et al. Arc erosion behavior of Ag/Ti3AlC2 electrical contact materials. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018,740:669-676.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
LIU M M, CHEN J L, CUI H , et al. Ag/Ti3AlC2 composites with high hardness, high strength and high conductivity. Materials Letters, 2018,213:269-273.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
DING J X, TIAN W B, WANG D D , et al. Corrosion and degradation mechanism of Ag/Ti3AlC2 composites under dynamic electric arc discharging. Corrosion Science, 2019,156:147-160.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WANG D D, TIAN W B, MA A B , et al. Anisotropic properties of Ag/Ti3AlC2 electrical contact materials prepared by equal channel angular pressing. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019,784:431-438.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHANG M, TIAN W B, ZHANG P G , et al. Microstructure and properties of Ag-Ti3SiC2 contact materials prepared by pressureless sintering. International Journal of Minerals. Metallurgy, and Materials, 2018,25(7):810-816.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
DING J X, TIAN W B, ZHANG P G , et al. Preparation and arc erosion properties of Ag/Ti2SnC composites under electric arc discharging. Journal of Advanced Ceramics, 2019,8(1):90-101.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
DING J X, TIAN W B, WANG D D , et al. Microstructure evolution, oxidation behavior and corrosion mechanism of Ag/Ti2SnC composite during dynamic electric arc discharging. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019,785:1086-1096.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
DING J X, TIAN W B, WANG D D , et al. Arc erosion and degradation mechanism of Ag/Ti2AlC composite. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2019,55(5):627-637.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
AFONIN M P, BOIKO A V . Effect of structural anisotropy on contact properties in a silver-graphite composite. Powder Metallurgy and Metal Ceramics, 2005,44(1):84-87.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
XU C, YI D, WU C , et al. Microstructures and properties of silver- based contact material fabricated by hot extrusion of internal oxidized Ag-Sn-Sb alloy powders. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2012,538:202-209.
DOI URL |
| [13] | CHEN YL, YANG CF, YEH JW , et al. A novel process for fabricating electrical contact SnO2/Ag composites by reciprocating extrusion. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions a-Physical Metallurgy and Materials Science, 2005,36A(9):2441-2447. |
| [14] |
BALOG M, SIMANCIK F, BAJANA O , et al. ECAP vs. direct extrusion-techniques for consolidation of ultra-fine Al particles. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2009,504(1):1-7.
DOI URL |
| [15] |
SEGAL V M . Materials processing by simple shear. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 1995,197(2):157-164.
DOI URL PMID |
| [16] |
MA A, NISHIDA Y, SUZUKI K , et al. Characteristics of plastic deformation by rotary-die equal-channel angular pressing. Scripta Materialia, 2005,52(6):433-437.
DOI URL PMID |
| [17] |
HAGHIGHI R D, JAHROMI S A J, MORESEDGH A , et al. A comparison between ECAP and conventional extrusion for consolidation of aluminum metal matrix composite. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2012,21(9):1885-1892.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
DERAKHSHANDEH H R, JAHROMI A J . An investigation on the capability of equal channel angular pressing for consolidation of aluminum and aluminum composite powder. Materials & Design, 2011,32(6):3377-3388.
DOI URL PMID |
| [19] |
LAPOVOK R . Damage evolution under severe plastic deformation. International Journal of Fracture, 2002,115(2):159-172.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
NAGASEKHAR A V, TICK-HON Y, RAMAKANTH K S . Mechanics of single pass equal channel angular extrusion of powder in tubes. Applied Physics A-Materials Science & Processing, 2006,85(2):185-194.
DOI URL PMID |
| [21] |
LIU M, CHEN J, CUI H , et al. Temperature-driven deintercalation and structure evolution of Ag/Ti3AlC2 composites. Ceramics International, 2018,44(15):18129-18134.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
SU L Y, WANG P F, XU Z B , et al. Oscillatory shear-induced alignment of ketjen black conductive particles in polylactic acid and its effect on the electrical anisotropy. Journal of Polymer Science Part B-Polymer Physics, 2016,54(3):369-373.
DOI URL |
| [23] |
XU W X, JIA M K, GONG Z . Thermal conductivity and tortuosity of porous composites considering percolation of porous network: from spherical to polyhedral pores. Composites Science and Technology, 2018,167:134-140.
DOI URL |
| [24] |
BARSOUM M W . The Mn+1AXn phases: a new class of solids; thermodynamically stable nanolaminates. Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2000,28(1-4):201-281.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 吴爽, 苟燕子, 王永寿, 宋曲之, 张庆雨, 王应德. 高温热处理对国产KD-SA型SiC纤维组成结构与力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 569-576. |
| [2] | 张硕, 付前刚, 张佩, 费杰, 李伟. C/C多孔体的高温热处理对C/C-SiC复合材料摩擦磨损行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 561-568. |
| [3] | 安文然, 黄晶琪, 卢祥荣, 蒋佳宁, 邓龙辉, 曹学强. 热处理温度对LaMgAl11O19涂层热/力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 925-932. |
| [4] | 祝泉, 胡建宝, 杨金山, 周海军, 董绍明. 采用定向SiC纳米线烧结制备高强多孔SiC陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 547-551. |
| [5] | 朱勇, 顾军, 于涛, 何海佟, 姚睿. 铂钴合金纳米电催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 299-305. |
| [6] | 魏玉全,杨勇,刘盟,郦其乐,黄政仁. 高温热处理对SiBCN/HfC复相陶瓷物相组成及微观结构的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 931-938. |
| [7] | 张博,张宁,杨建华,兰建成,王金渠. 两步晶化制备高性能a&b取向T型沸石膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 939-946. |
| [8] | 王志虎,张菊梅,白力静,张国君. AZ31镁合金微弧氧化陶瓷层表面Mg(OH)2膜层的制备及耐蚀性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 709-716. |
| [9] | 付亚康,翁杰,刘耀文,张科宏. 钛网表面含hBMP-2的复合涂层制备及hBMP-2的释放研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 173-178. |
| [10] | 廖春景, 董绍明, 靳喜海, 胡建宝, 张翔宇, 吴惠霞. 沉积温度及热处理对低压化学气相沉积氮化硅涂层的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(11): 1231-1237. |
| [11] | 王雅, 索红莉, 毛磊, 刘敏, 马麟, 王毅, KAUSARShaheen, 周宇琦. Nb掺杂YBCO薄膜钉扎机理的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(10): 1055-1059. |
| [12] | 郑海亚, 孟晨曦, 胡冬力, 顾辉, 刘海涛, 张国军. 织构化ZrB2-SiC超高温陶瓷中取向关系的EBSD研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4): 380-384. |
| [13] | 王浩, 罗永春, 邓安强, 赵磊, 姜婉婷. 退火温度对无镁La-Y-Ni系A2B7型合金相结构和电化学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4): 434-440. |
| [14] | 屈婧婧, 魏星, 刘飞, 袁昌来, 陈国华, 黄先培. 热处理对Mg-Al-Si-Ti-B系微晶玻璃析晶及介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(12): 1309-1315. |
| [15] | 李姝玲, 原鲜霞, 孔海川, 徐 进, 马紫峰. Fe-PPy-TsOH/C用作质子交换膜燃料电池氧电极催化剂的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(4): 393-399. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||