无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (7): 748-754.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180443
收稿日期:2018-09-20
修回日期:2018-11-13
出版日期:2019-07-20
网络出版日期:2019-06-26
作者简介:郭 钰(1983-), 女, 副研究员. E-mail:guoyu03201@sina.com
基金资助:
GUO Yu1,2,PENG Tong-Hua1,2( ),LIU Chun-Jun1,YANG Zhan-Wei1,CAI Zhen-Li1
),LIU Chun-Jun1,YANG Zhan-Wei1,CAI Zhen-Li1
Received:2018-09-20
Revised:2018-11-13
Published:2019-07-20
Online:2019-06-26
Supported by:摘要:
本研究探讨了同质外延生长的4H-SiC晶片表面堆垛层错(SF)的形貌特征和起因。依据表面缺陷检测设备KLA-Tencor CS920的光致发光(PL)通道和形貌通道的特点, 将SF分为五类。其中I类SF在PL通道图中显示为梯形, 在形貌图中不显示; II类SF在PL通道图中显示为三角形, 且与I类SF重合, 在形貌图中显示为胡萝卜形貌。III-V类SF在PL通道图中均显示为三角形, 在形貌图中分别显示为胡萝卜、无对应图像或三角形。研究结果表明, I类SF起源于衬底的基平面位错(BPD)连线, 该连线平行于<1$\bar{1}$00>方向, 在生长过程中沿着<11$\bar{2}$0>方向移动, 形成基平面SF。II类和大部分的III-IV类SF起源于衬底的BPD, 其中一个BPD在外延过程中首先转化为刃位错(TED), 并在外延过程中延<0001>轴传播, 其余BPD或由TED分解形成的不全位错(PDs)在(0001)面内传播形成三角形基平面SF。其余的III-V类SF起源于衬底的TED或其它。II-III类SF在形貌通道中显示为胡萝卜, 而IV类SF不显示, 主要区别在于外延过程中是否有垂直于(0001)面的棱镜面SF与表面相交。上述研究说明减少衬底的BPD, 对减少外延层中的SF尤为重要。
中图分类号:
郭钰, 彭同华, 刘春俊, 杨占伟, 蔡振立. 4H-SiC外延层中堆垛层错与衬底缺陷的关联性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(7): 748-754.
GUO Yu, PENG Tong-Hua, LIU Chun-Jun, YANG Zhan-Wei, CAI Zhen-Li. Correlation between Stacking Faults in Epitaxial Layers of 4H-SiC and Defects in 4H-SiC Substrate[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(7): 748-754.
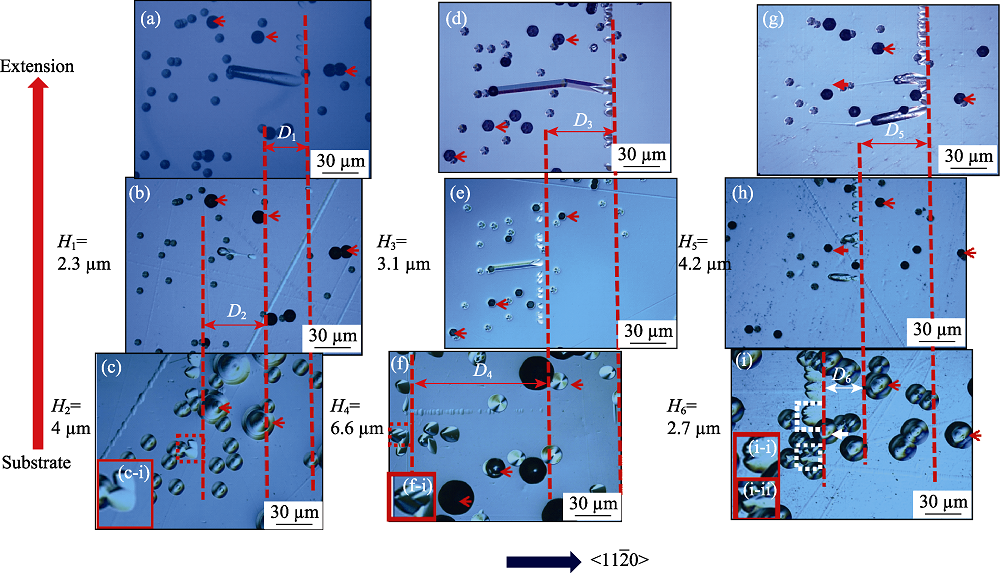
图2 I类和II类SF的起因和繁衍特征, <11$\bar{2}$0>方向是晶体生长的下台阶方向, D1~D6标记平行条纹的移动距离, H1~H6标记外延层的去除厚度
Fig. 2 Originations and propagations of SF I and SF II<11$\bar{2}$0> is the direction of lower steps of crystal growth. D1-D6 are the moving distances of BPD lines. H1-H6 are the removing thickness of epitaxial layers
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moving distance of BPD lines, D/μm | 33 | 57 | 44 | 94 | 60 | 39 |
| Removing thickness, H/μm | 2.3 | 4 | 3.1 | 6.6 | 4.2 | 2.7 |
表1 图2中平行条纹移动的距离D和外延层去除厚度H的对应关系
Table 1 Relationship of moving distance D of BPD lines and removing thickness H of epitaxial layers in Fig. 2
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moving distance of BPD lines, D/μm | 33 | 57 | 44 | 94 | 60 | 39 |
| Removing thickness, H/μm | 2.3 | 4 | 3.1 | 6.6 | 4.2 | 2.7 |
| Test position | Substrate | Epitaxial layers |
|---|---|---|
| N concentration | 8×1012 | <1010 |
表2 二次离子质谱(SIMS)检测衬底和外延层中的N含量
Table 2 Nitrogen concentration in substrate and epitaxial layers tested by SIMS
| Test position | Substrate | Epitaxial layers |
|---|---|---|
| N concentration | 8×1012 | <1010 |
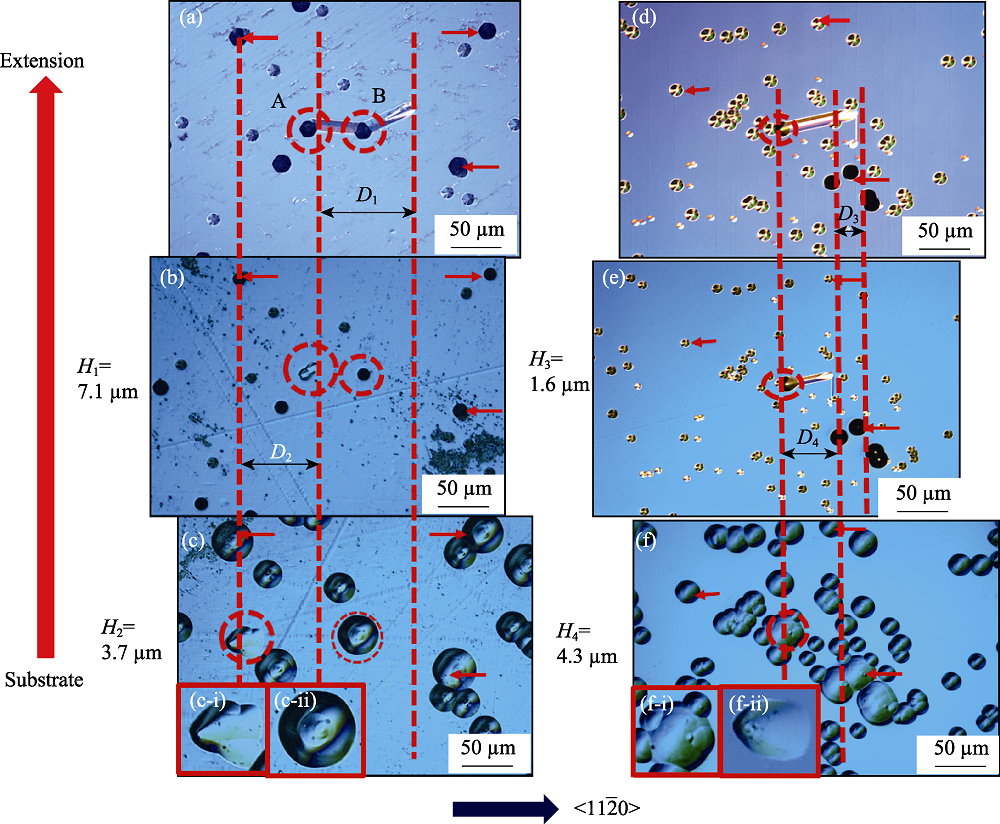
图4 III类SF的起因和繁衍特征, <11$\bar{2}$0>方向是晶体生长的下台阶方向, D1~D4标记胡萝卜尾部的移动距离, H1~H4标记外延层的去除厚度
Fig. 4 Originations and propagations of SF III<11$\bar{2}$0> is the direction of lower steps of crystal growth. D1-D4 are the moving distances of BPD lines. H1-H4 are the removing thickness of epitaxial layers
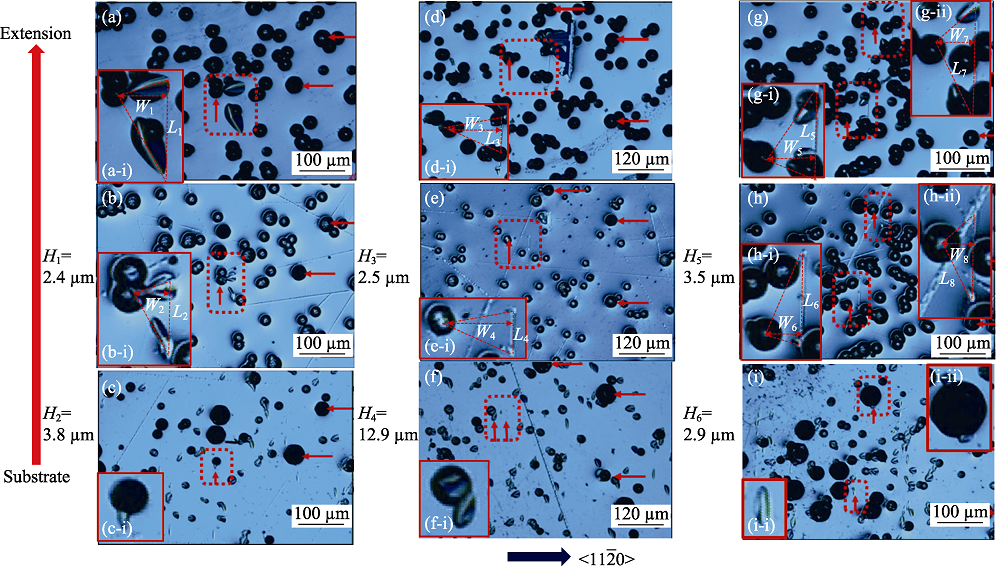
图5 IV类SF起因和繁衍特征, <11$\bar{2}$0>方向是晶体生长的下台阶方向, H1~H6标记外延层的去除厚度, L1~L8是三角形底边长度, W1~W8是三角形顶点到底边的垂直距离
Fig. 5 Originations and propagations of SF IV<11$\bar{2}$0> is the direction of lower steps of crystal growth. H1~H6 are the removing thickness of epitaxial layers. L1~L8 are bottom lengths of triangle defects. W1~W8 are widths of triangle defects
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moving distance of BPD lines, D/μm | 102 | 53 | 23 | 61 |
| Removing thickness, H/μm | 7.1 | 3.7 | 1.6 | 4.3 |
表3 图3中平行条纹移动的距离D和外延层去除厚度H的对应关系
Table 3 Relationship of the moving distance D of BPD lines and the removing thickness H of epitaxial layers in Fig. 3
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moving distance of BPD lines, D/μm | 102 | 53 | 23 | 61 |
| Removing thickness, H/μm | 7.1 | 3.7 | 1.6 | 4.3 |
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moving distance of BPD lines, D/μm | 34 | - | 36 | - | 50 | - | - | - |
| Removing thickness, H/μm | 2.4 | 3.8 | 2.5 | 12.9 | 3.5 | 2.9 | - | - |
| With triangle defects, W/μm | 85 | 51 | 85 | 49.0 | 85 | 35 | 85 | 35 |
| Bottom lengths of triangle defects, L/μm | 105 | 63 | 90 | 52 | 60 | 25 | 110 | 45 |
表4 图5中平行条纹移动的距离D、外延层去除厚度H、三角形缺陷宽度W和底边长度L的对应关系表
Table 4 Relationship of the moving distance D of BPD lines, the removing thickness H of epitaxial layers and width of trianagle defects W with bottom lengths of triangle defects in Fig. 3
| No. | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Moving distance of BPD lines, D/μm | 34 | - | 36 | - | 50 | - | - | - |
| Removing thickness, H/μm | 2.4 | 3.8 | 2.5 | 12.9 | 3.5 | 2.9 | - | - |
| With triangle defects, W/μm | 85 | 51 | 85 | 49.0 | 85 | 35 | 85 | 35 |
| Bottom lengths of triangle defects, L/μm | 105 | 63 | 90 | 52 | 60 | 25 | 110 | 45 |
| [1] | PENG T H, LIU C J, WANG B , et al. Progress in growth and physical properties of wide band gap semiconductor silicon carbide single crystals. Journal of Synthetic Crystal, 2012,S1:234-241. |
| [2] |
PENG T H, YANG H, JIAN J K , et al. Factors affecting the formation of misoriented domains in 6H-SiC single crystals grown by PVT method.[J]. Cryst. Res. Technol., 2009,44(4):357-362.
DOI URL |
| [3] | CHANG S H, LIU X C, HUANG W , et al. Preparation and properties of lateral contact structure SiC photoconductive semiconductor switches. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012,27(10):1058-1062. |
| [4] |
WANG B, PENG T H, LIANG J K , et al. Characterizations and formation mechanism of a new type of defect related to nitrogen doping in SiC crystals. Appl. Phys.A, 2014,117(3):1563-1569.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LIU C J, CHEN X L, PENG T H , et al. Step flow and polytype transformation in growth of 4H-SiC crystals. J. Cryst. Growth, 2014,394:126-131.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SUN W, SONG Y T, LIU C J , et al. Basal plane dislocation- threading edge dislocation complex dislocations in 6H-SiC single crystals. Mater.Express, 2015,5(1):63-67.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
LIU C J, PENG T H, WANG S C , et al. Formation mechanism of type 2 micropipe defects in 4H-SiC crystals. CrystEngComm, 2013,15(7):1307-1313.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
ZHAO N, LIU C J, WANG B , et al. Stacking faults in 4H-SiC single crystal. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018,33(5):540-544.
DOI URL |
| [9] |
LIU K X, STAHLBUSH R E, TWIGG M E , et al. Photoluminescence and electroluminescence imaging of carrot defect in 4H-SiC epitaxy. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2007,36(4):297-306.
DOI URL |
| [10] | ZHANG X, HA S Y, BENAMARA S , et al. Structure of carrot defects in 4H-SiC epilayers. Materials Science Forum, 2006, 527-529:327-332. |
| [11] |
MIAO M S, WALTER R L . Stacking faults and 3C quantum wells in hexagonal SiC polytypes. Mater.Sci.Forum, 2006, 527-529:351-354.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
WANG Y, CHERT L, MILDAOV M K , et al. Characterization of stacking fault induced behavior in 4H-SiC p-i-n diodes.Mater. Sci.Forum, 2006, 527-529:363-366.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
HIDEYUKI U, KEISUKE F, MASANHIKO I , et al. Analysis and reduction of stacking faults in fast epitaxial growth. Materials Science Forum, 2016 858:173-176.
DOI URL |
| [14] | RADU H, STEFAN G S, DENIS E T , et al. Identification of stacking faults in silicon carbide by polarization-resolved second harmonic generation microscopy. Scientific Reports, 2017, 7(1): 4870-1-9. |
| [15] | HIDEKAZU Y . Assessment of stacking faults in silicon carbide crystals. Sensors and Materials, 2013,25(3):177-187. |
| [16] |
HASSAN J, HENRY A, IVANOV I G , et al. In-grown stacking faults in 4H-SiC epilayers grown on off-cut substrates. Journal of Applied Physics, 2009,105(12):123513.
DOI URL |
| [17] |
ZHOU R W, LIU X C, GUO H J , et al. Study of triangle-shaped defects on nearly on-axis 4H-SiC substrates. Materials Science Forum, 2016,858:225-228.
DOI URL |
| [18] |
HASSAN J, BERGMAN J P . Single Shockley stacking faults in as-grown 4H-SiC epilayers. Materials Science Forum, 2010, 645-648:327-330.
DOI URL |
| [19] |
LIJIMA A, KAMATA I , TSUCHIDA, H, et al. Correlation between shapes of Shockley stacking faults and structures of basal plane dislocations in 4H-SiC epilayers. Philosophical Magazine, 2017,97(30):2736-2752.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
STAHLBUSH R E, MYERS-WARD R L, VANMIL B L , et al. A pictorial tracking of basal plane dislocations in SiC epitaxy. Materials Science Forum, 2010, 645-648:271-276.
DOI URL |
| [21] | OKOJIE R S, HUANG X, DUDLEY M , et al. Process-induced deformations and stacking faults in 4H-SiC. MRS Proceedings, 2011,911:B07-02. |
| [22] |
LIU K X, STAHLBUSH R E, TWIGG M E , et al. Photoluminescence and electroluminescence imaging of carrot defect in 4H-SiC epitaxy. Journal of Electronic Materials, 2007,36(4):297-306.
DOI URL |
| [23] | YUTARO M, SHUHEI Y, YASUTO H , et al. Photoluminescence study of oxidation-induced stacking faults in 4H-SiC epilayers. Materials Science Forum Vols., 2015,5(12):327-330. |
| [24] | LI Z Y, LIU L T, DONG X , et al. Defects in homogeneous epitaxial layers of 4H-SiC. Equipment for Electronic Products Manufacturing, 2005,11(130):62-64. |
| [25] |
MIAO M S, WALTER R L . Stacking faults and 3C quantum wells in hexagonal SiC polytypes. Mater. Sci. Forum, 2006, 527-529:351-354.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
KATSUNO M, NAKABAYASHI M, FUJIMOTO T , et al. Stacking fault formation in highly nitrogen-doped 4H-SiC substrates with different surface preparation conditions. Mater.Sci.Forum, 2008, 600-603:341-344.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
KUHR T A, LIU J Q, CHUNG H J , et al. Spontaneous formation of stacking faults in highly doped 4H-SiC during annealing.[J]. Appl. Phys., 2002,92(10):5863-5871.
DOI URL |
| [28] | GALECKAS A, LINNROS J, PIROUZ P , et al. Recombination- induced stacking faults: evidence for a general mechanism in hexagonal SiC. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2006, 96(2): 025502-1-4. |
| [29] |
OHNO T, YAMAGUCHI H, KURODA S , et al. Direct observation of dislocations propagated from 4H-SiC substrate to epitaxial layer by X-ray topograghy. Joumal of Crystal Growth, 2004,260:209-216.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
HASSAN J, HENRY A, MCNALLY P J , et al. Characterization of the carrot defect in 4H-SiC epitaxial layers. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2010,312(11):1828-1837.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 陈强, 白书欣, 叶益聪. 热管理用高导热碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [2] | 王华进, 寇华敏, 王墉哲, 姜大朋, 张博, 钱小波, 王静雅, 朱琳玲, 曾爱军, 杨秋红, 苏良碧. 193 nm激光下不同含量Y杂质CaF2晶体辐照损伤研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 219-224. |
| [3] | 欧阳琴, 王艳菲, 徐剑, 李寅生, 裴学良, 莫高明, 李勉, 李朋, 周小兵, 葛芳芳, 张崇宏, 何流, 杨磊, 黄政仁, 柴之芳, 詹文龙, 黄庆. 核用碳化硅纤维增强碳化硅复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 821-840. |
| [4] | 阮景, 杨金山, 闫静怡, 游潇, 王萌萌, 胡建宝, 张翔宇, 丁玉生, 董绍明. 三维碳化硅纳米线增强碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料的电磁屏蔽性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 579-584. |
| [5] | 阮景, 杨金山, 闫静怡, 游潇, 王萌萌, 胡建宝, 张翔宇, 丁玉生, 董绍明. 碳化硅纳米线增强多孔碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料的制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 459-466. |
| [6] | 李陇彬, 薛玉冬, 胡建宝, 杨金山, 张翔宇, 董绍明. 碳化硅纳米线增韧碳化硅纤维/碳化硅基体损伤行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1111-1117. |
| [7] | 罗清,苑青,蒋前勤,于乃森. Cu-SSZ-13/碳化硅废料复合材料的合成及其 NH3-SCR性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 953-960. |
| [8] | 田兆波, 陈克新, 孙思源, 张杰, 崔巍, 刘光华. 无催化剂碳热还原法制备SiC@SiO2纳米电缆[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(11): 1217-1221. |
| [9] | 崔潆心, 胡小波, 徐现刚. 物理气相传输法生长碳化硅单晶原生表面形貌研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(8): 877-882. |
| [10] | 施徐国, 李明远, 马维刚, 周新贵, 张兴. KD-II型碳化硅纤维热输运性质的实验研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(7): 756-760. |
| [11] | 赵宁, 刘春俊, 王波, 彭同华. 4H-SiC晶体中的层错研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(5): 540-544. |
| [12] | 黄毅华, 江东亮, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 张先锋, 廖振魁, 黄政仁. rGO/SiC复合材料的制备与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(11): 1147-1153. |
| [13] | 邢媛媛, 吴海波, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 颗粒级配对固相烧结碳化硅陶瓷的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(11): 1167-1172. |
| [14] | 余洁意, 黄 昊, 高 见, 周 雷, 高 嵩, 董星龙, 全 燮. 直流电弧等离子体制备纳米SiC及其催化特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(4): 351-356. |
| [15] | 王 锦, 陶 科, 李国峰, 梁 科, 蔡宏琨. 氢气氛退火对硅上低温外延制备的硅锗薄膜性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(2): 191-196. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||