无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (12): 1325-1333.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190039
收稿日期:2019-01-18
修回日期:2019-03-08
出版日期:2019-12-20
网络出版日期:2019-05-29
作者简介:陈一凡(1995-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: pzhcyf@qq.com
基金资助:
CHEN Yi-Fan1,TANG Xiao-Ning1( ),ZHANG Bin2,LUO Yong1,LI Yang1
),ZHANG Bin2,LUO Yong1,LI Yang1
Received:2019-01-18
Revised:2019-03-08
Published:2019-12-20
Online:2019-05-29
Supported by:摘要:
采用溶胶-凝胶法制备载体SiO2, 并通过水解法制备出负载型TiO2@SiO2复合光催化抗菌材料, 采用SEM、XRD、BET、FT-IR、XPS和粒度仪对材料进行表征和分析。在UVA紫外光照下, 通过降解甲基橙溶液考察了复合材料的光催化性能, 在照射3 h后, 不同钛掺杂量复合材料的光催化降解率均能达到99.9%, 钛掺比为0.58时催化效率最高。通过平板涂布法检测了复合材料对大肠杆菌的抗菌效果, 发现抗菌性能随着钛含量的增加而提高, 在紫外照射条件下最高可达92%以上, 同时在可见光照射下也能表现出良好的抗菌性能。通过细菌荧光检测, 可以有效证明复合材料所产生的活性氧迁移到了细胞内部, 造成细胞体氧化损伤, 这是光催化材料抗菌机理研究的重要依据。
中图分类号:
陈一凡, 唐晓宁, 张彬, 罗勇, 李阳. TiO2@SiO2复合材料的制备及其光催化与抗菌性能的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(12): 1325-1333.
CHEN Yi-Fan, TANG Xiao-Ning, ZHANG Bin, LUO Yong, LI Yang. TiO2@SiO2 Composites: Preparation and Photocatalytic Antimicrobial Performance[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(12): 1325-1333.
| Element | wt % | at % |
|---|---|---|
| Ti | 28.40 | 13.57 |
| Si | 25.90 | 21.10 |
| O | 45.70 | 65.33 |
表1 TiO2@SiO2复合材料元素含量分析结果
Table 1 Analysis of element content about TiO2-doped SiO2 composites
| Element | wt % | at % |
|---|---|---|
| Ti | 28.40 | 13.57 |
| Si | 25.90 | 21.10 |
| O | 45.70 | 65.33 |
| Sample | BET/(m2·g-1) | BJH Pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|
| 0.58-TiO2@SiO2 | 177 | 12.4 |
| SiO2 | 83 | 20.6 |
| TiO2 | 115 | 4.4 |
表2 SiO2、TiO2和TiO2@SiO2的比表面积和BJH吸附平均孔径
Table 2 BET analysis and BJH adsorption pore size of SiO2, TiO2 and TiO2-doped SiO2 composites
| Sample | BET/(m2·g-1) | BJH Pore size/nm |
|---|---|---|
| 0.58-TiO2@SiO2 | 177 | 12.4 |
| SiO2 | 83 | 20.6 |
| TiO2 | 115 | 4.4 |
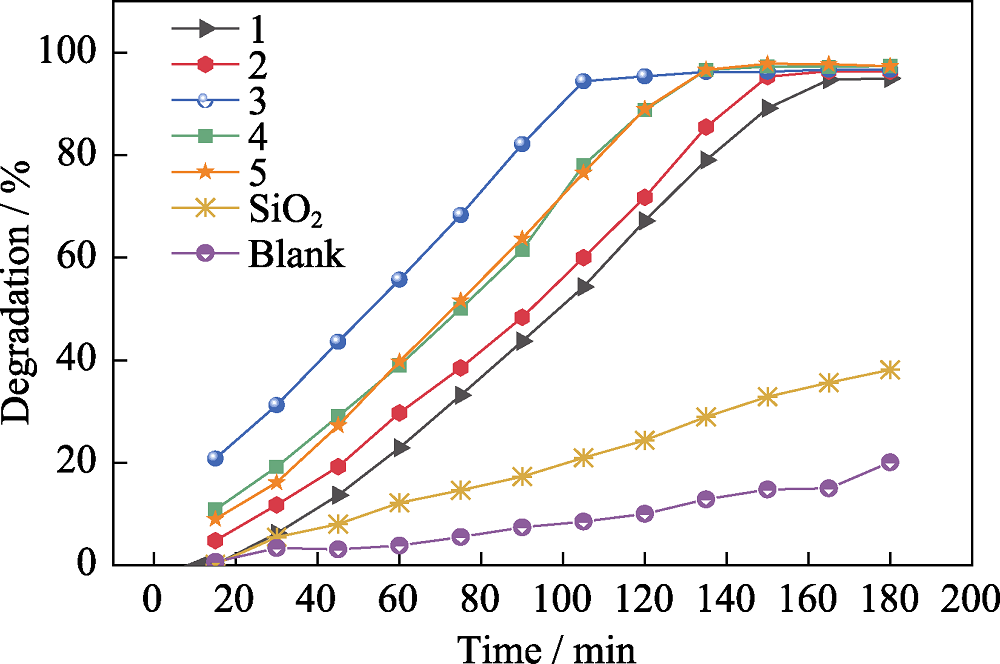
图8 不同Ti掺杂量TiO2@SiO2样品的光催化降解曲线
Fig. 8 Photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by using TiO2-doped SiO2 with different Ti contents (1) 0.3-TiO2@SiO2; (2) 0.44-TiO2@SiO2; (3) 0.58-TiO2@SiO2; (4) 0.74-TiO2@SiO2; (5) 0.88-TiO2@SiO2
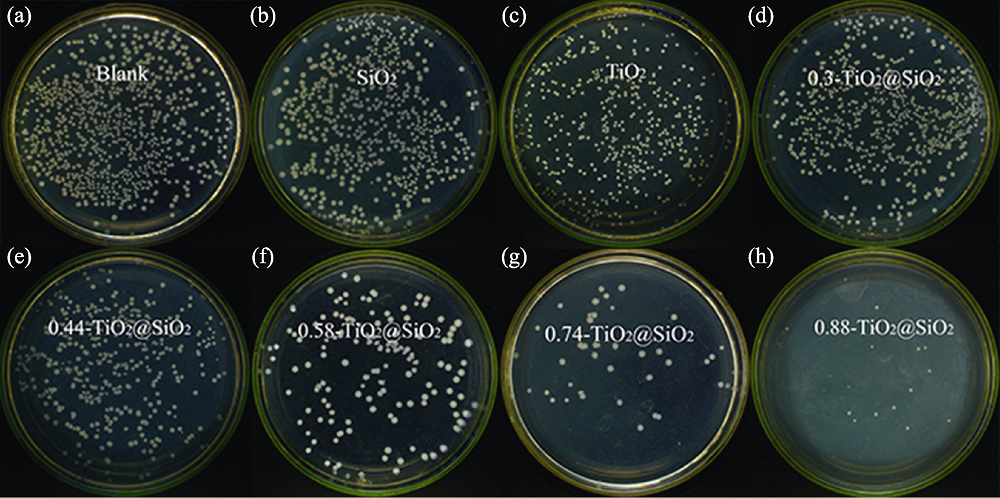
图9 UVA条件下SiO2、TiO2和不同钛掺杂量的TiO2@SiO2复合材料抗菌效果照片
Fig. 9 Antimicrobial effect of SiO2, TiO2 and TiO2-doped SiO2 composites with different Ti contents on E.coli under UVA irradiation
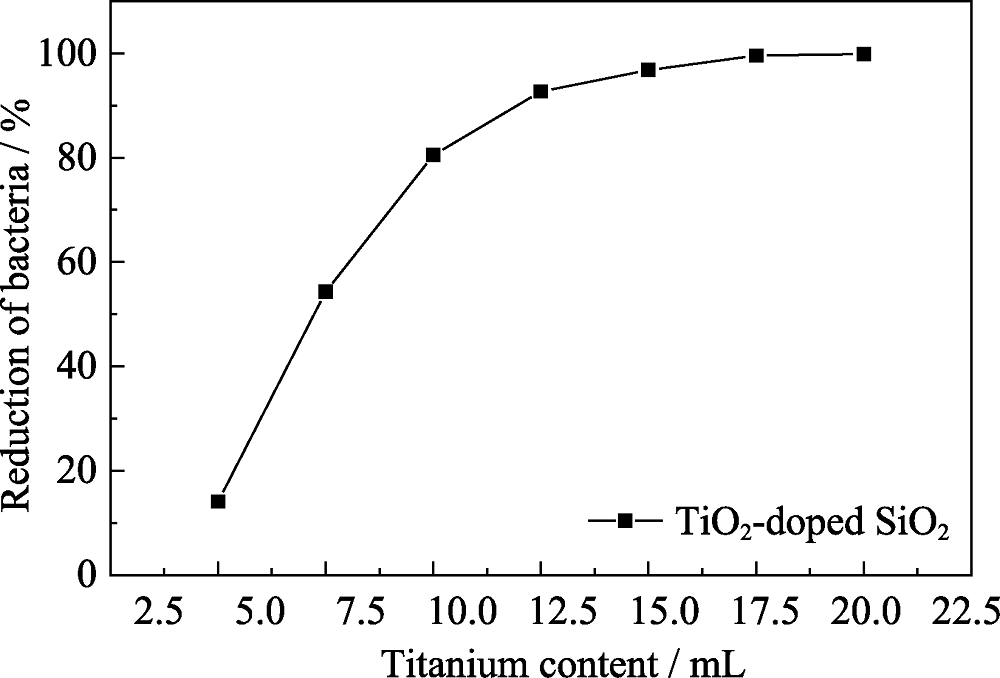
图10 UVA条件下不同钛掺杂量对TiO2@SiO2材料抗菌性能的影响
Fig. 10 Effect of the antimicrobial property using TiO2-doped SiO2 composites with different Ti contents under UVA irradiation
| Lamp-house | Material | E.coli-BL21 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number (after 24 h) | Reduction of bacteria/% | ||
| UVA | Blank | 833 | - |
| SiO2 | 788 | 5.4 | |
| 0.58-TiO2@SiO2 | 163 | 80.5 | |
| TiO2 | 586 | 29.6 | |
| Visible light | Blank | 808 | - |
| 0.58-TiO2@SiO2 | 198 | 65.5 | |
表3 不同光照条件下的抗菌性能结果
Table 3 Results of antibacterial activity with different irradiations
| Lamp-house | Material | E.coli-BL21 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Number (after 24 h) | Reduction of bacteria/% | ||
| UVA | Blank | 833 | - |
| SiO2 | 788 | 5.4 | |
| 0.58-TiO2@SiO2 | 163 | 80.5 | |
| TiO2 | 586 | 29.6 | |
| Visible light | Blank | 808 | - |
| 0.58-TiO2@SiO2 | 198 | 65.5 | |
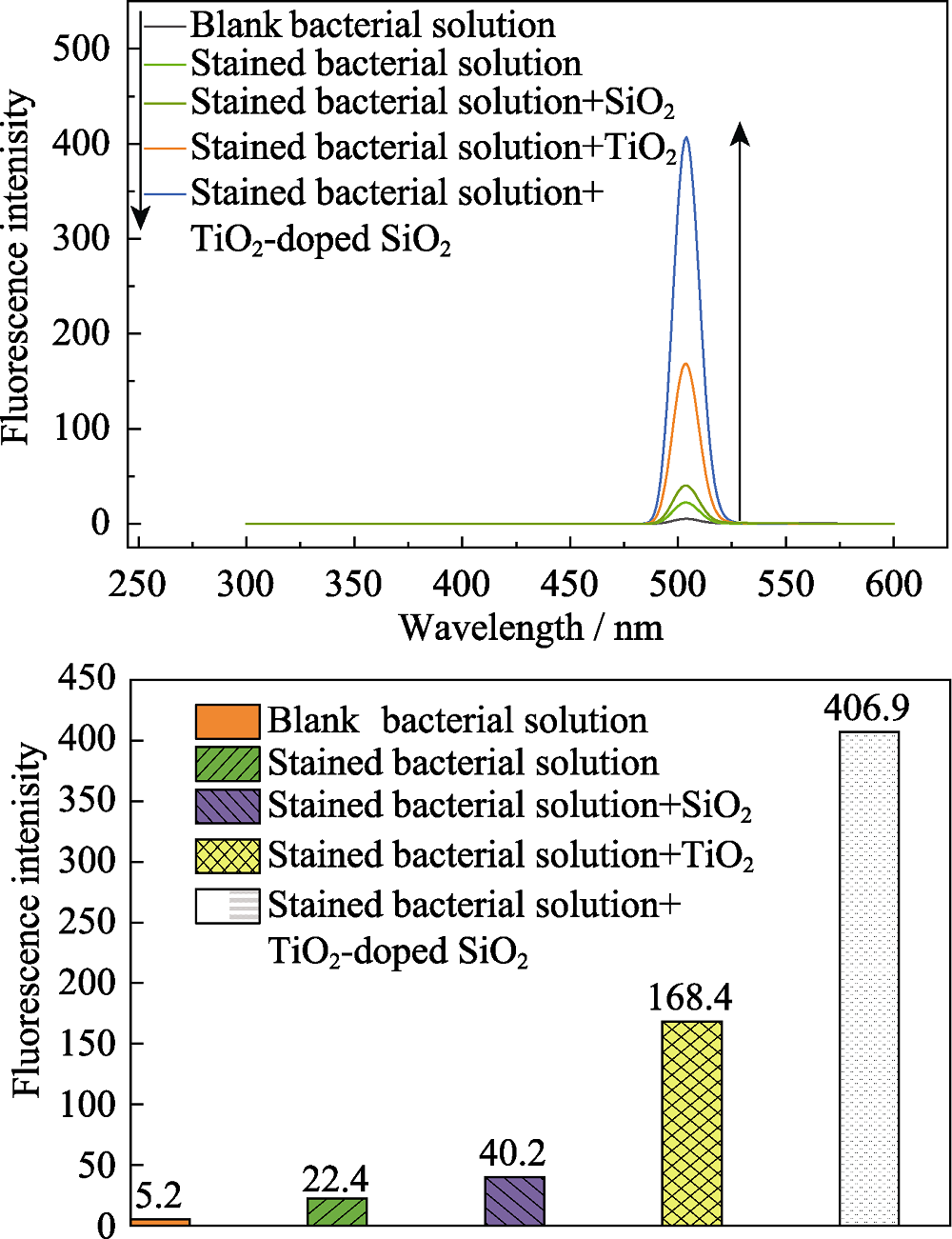
图12 TiO2、SiO2和0.58-TiO2@SiO2材料的荧光图谱
Fig. 12 Fluorescence spectra of TiO2, SiO2 and 0.58- TiO2@SiO2 Right diagram shows the values of fluorescence with an excitation wavelength of 492 nm and an emission wavelength of 504 nm
| [1] | GAYA U I, ABDULLAH A H . Heterogeneous photocatalytic degradation of organic contaminants over titanium dioxide: a review of fundamentals, progress and problems. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology C: Photochemistry Reviews, 2008,9(1):1-12. |
| [2] | ZHANG Q J, SUN C H, ZHAO Y , et al. Low Ag-doped titanium dioxide nanosheet films with outstanding antimicrobial property. Environmental science & technology, 2010,44(21):8270-8275. |
| [3] | LINIC S, BARTEAU M . Heterogeneous catalysis of alkene epoxidation. Handbook of Heterogeneous Catalysis: Online, 2008: 3448-3464. |
| [4] | BANERJEE S, GOPAL J, MURALEEDHARAN P , et al. Physics and chemistry of photocatalytic titanium dioxide: visualization of bactericidal activity using atomic force microscopy. Current Science, 2006,90(10):1378-1383. |
| [5] | TANG F Q, HOU L P, GUO G S . Preparation of TiO2 nanometer powders. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2001,16(4):615-619. |
| [6] | MANDZY N, GRULKE E, DRUFFEL T . Breakage of TiO2 agglomerates in electrostatically stabilized aqueous dispersions. Powder Technology, 2005,160(2):121-126. |
| [7] | XU Y H, LEI B, GUO L Q , et al. Preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of manganese doped TiO2 immobilized on silica gel. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2008,160(1):78-82. |
| [8] | HU C, WANG Y Z, TANG H X . Structure and photocatalytic performance of surface bond-conjugated TiO2/SiO2 Catalyst. Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2001,22(2):185-188. |
| [9] | SON S, HWANG S H, KIM C , et al. Designed synthesis of SiO2/TiO2 core/shell structure as light scattering material for highly efficient dye-sensitized solar cells. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013,5(11):4815-4820. |
| [10] | KIM J, SONG K C, FONCILLAS S , et al. Dopants for synthesis of stable bimodally porous titania. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2001,21(16):2863-2872. |
| [11] | GAO P, NG K, SUN D D . Sulfonated graphene oxide-ZnO-Ag photocatalyst for fast photodegradation and disinfection under visible light. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013,262:826-835. |
| [12] | LUO X Y, HUANG R Y, ZHAO D F , et al. Preparation and photocatalytic performance of silver modified white carbon black doped TiO2. New Chemical Materials, 2017,45(2):152-154. |
| [13] | LI Z J, HOU B, XU Y , et al. Hydrothermal synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic performance of silica-modified titanium dioxide nanoparticles. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2005,288(1):149-154. |
| [14] | ZHANG X, ZHANG F, CHAN K Y . Synthesis of titania-silica mixed oxide mesoporous materials, characterization and photocatalytic properties. Applied Catalysis A: General, 2005,284(1/2):193-198. |
| [15] | MAUČEC D, ŠULIGOJ A, RISTIĆ A , et al. Titania versus zinc oxide nanoparticles on mesoporous silica supports as photocatalysts for removal of dyes from wastewater at neutral pH. Catalysis Today, 2018,310:32-41. |
| [16] | SHI W Z, GUO B S, XUE H Q . Preparation, photocatalytic property and antibacterial property of Ag@TiO2@SiO2 composite nanomaterials. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016,31(5):466-472. |
| [17] | ZHANG S Q, WEI Y F . Recent advances in fluorescent probes for the detection of reactive oxygen species. Chinese Journal of Spectroscopy Laboratory, 2009,26(4):794-802. |
| [18] | RANJAN S, RAMALINGAM C . Titanium dioxide nanoparticles induce bacterial membrane rupture by reactive oxygen species generation. Environmental Chemistry Letters, 2016,14(4):487-494. |
| [19] | RUBIO J, OTEO J L, VILLEGAS M , et al. Characterization and sintering behaviour of submicrometre titanium dioxide spherical particles obtained by gas-phase hydrolysis of titanium tetrabutoxide. Journal of Materials Science, 1997,32(3):643-652. |
| [20] | DUTOIT D, SCHNEIDER M, BAIKER A . Titania-silica mixed oxides: I. Influence of Sol-Gel and drying conditions on structural properties. Journal of Catalysis, 1995,153(1):165-176. |
| [21] | GAO X T, WACHS I E . Titania-silica as catalysts: molecular structural characteristics and physico-chemical properties. Catalysis Today, 1999,51(2):233-254. |
| [22] | DAVIS R J, LIU Z F . Titania-silica: a model binary oxide catalyst system. Chemistry of Materials, 1997,9(11):2311-2324. |
| [23] | MURASHKEVICH A N, LAVITSKAYA A S, BARANNIKOVA T I , et al. Infrared absorption spectra and structure of TiO2-SiO2 composites. Journal of Applied Spectroscopy, 2008,75(5):730-734. |
| [24] | MIAO Y C, XU X L, LIU K Q , et al. Preparation of novel Cu/TiO2 mischcrystal composites and antibacterial activities for Escherichia coli under visible light. Ceramics International, 2017,43(13):9658-9663. |
| [25] | HE C X, TIAN B Z, ZHANG J L . Thermally stable SiO2-doped mesoporous anatase TiO2 with large surface area and excellent photocatalytic activity. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010,344(2):382-389. |
| [26] | ULLAH S, FERREIRA-NETO E P, PASA A A , et al. Enhanced photocatalytic properties of core@shell SiO2@TiO2 nanoparticles. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2015,179:333-343. |
| [27] | SING K S . Reporting physisorption data for gas/solid systems with special reference to the determination of surface area and porosity. Pure Applied Chemistry, 1985,57(4):603-619. |
| [28] | YANG W, FENG Y Y, XIAO D , et al. Fabrication of microporous and mesoporous carbon spheres for high-performance supercapacitor electrode materials. International Journal of Energy Research, 2015,39(6):805-811. |
| [29] | STANDARD A . G5-94 standard reference test method for making potentiostatic and potentiodynamic anodic polarization measurements. Annual Book of ASTM Standards, 1994,3:73-79. |
| [30] | FU X Z, CLARK L A, YANG Q , et al. Enhanced photocatalytic performance of titania-based binary metal oxides: TiO2/SiO2 and TiO2/ZrO2. Environmental Science Technology, 1996,30(2):647-653. |
| [31] | ZHANG M H, SHI L Y, YUAN S , et al. Synthesis and photocatalytic properties of highly stable and neutral TiO2/SiO2 hydrosol. Journal of Colloid Interface Science, 2009,330(1):113-118. |
| [32] | WANG J M, LI C, ZHUANG H , et al. Photocatalytic degradation of methylene blue and inactivation of gram-negative bacteria by TiO2 nanoparticles in aqueous suspension. Food Control, 2013,34(2):372-377. |
| [33] | MOHAPATRA P, PARIDA K . Photocatalytic activity of sulfate modified titania 3: decolorization of methylene blue in aqueous solution. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2006,258(1/2):118-123. |
| [34] | YU Y F, ZHENG S, CHAI L Y , et al. Progress of study on the anti-bacterial materials of Ag-embedding titanium oxide. Techniques and Equipment for Environmental Pollution Control, 2004,5(12):16-20. |
| [35] | XU Y M, YU H, HE Q Z , et al. Synthesis, characterization and antibacterial properties of core-shell structure Ag+-loaded nano-titania doped with rare earth ion antibacterial agent. Chinese Rare Earths, 2009,30(2):65-70. |
| [36] | YANG Y, DENG G D, YI Q , et al. Nanometer TiO2/SiO2 composite antibacterial materials for foodstuffs. Fine Chemicals, 2001,18(12):703-706. |
| [37] | ADITYA A, CHATTOPADHYAY S, JHA D , et al. Zinc oxide nanoparticles dispersed in ionic liquids show high antimicrobial efficacy to skin-specific bacteria. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2018,10(18):15401-15411. |
| [38] | HAN C, LEI Y P, WANG Y D . Recent progress on nano- heterostructure photocatalysts for solar fuels generation. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015,30(11):1121-1130. |
| [1] | 伍林, 胡明蕾, 王丽萍, 黄少萌, 周湘远. TiHAP@g-C3N4异质结的制备及光催化降解甲基橙[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [2] | 王磊, 李建军, 宁军, 胡天玉, 王洪阳, 张占群, 武琳馨. CoFe2O4@Zeolite催化剂活化过一硫酸盐对甲基橙的强化降解: 性能与机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 469-476. |
| [3] | 吴雪彤, 张若飞, 阎锡蕴, 范克龙. 纳米酶: 一种抗微生物感染新方法[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 43-54. |
| [4] | 马心全, 李喜宝, 陈智, 冯志军, 黄军同. S型异质结BiOBr/ZnMoO4的构建及光催化降解性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [5] | 陈瀚翔, 周敏, 莫曌, 宜坚坚, 李华明, 许晖. CoN/g-C3N4 0D/2D复合结构及其光催化制氢性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [6] | 盛丽丽, 常江. 光/磁热Fe2SiO4/Fe3O4双相生物陶瓷及其复合电纺丝膜制备及抗菌性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 983-990. |
| [7] | 薛虹云, 王聪宇, MAHMOOD Asad, 于佳君, 王焱, 谢晓峰, 孙静. 二维g-C3N4与Ag-TiO2复合光催化剂降解气态乙醛抗失活研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [8] | 王晓俊, 许文, 刘润路, 潘辉, 朱申敏. 水凝胶负载的纳米银/氮化碳光催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [9] | 洪佳辉, 马冉, 仵云超, 文涛, 艾玥洁. MOFs自牺牲模板法制备CoNx/g-C3N4纳米材料用作高效光催化还原U(VI)[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 741-749. |
| [10] | 迟聪聪, 屈盼盼, 任超男, 许馨, 白飞飞, 张丹洁. SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2核壳结构的制备及其光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [11] | 安琳, 吴淏, 韩鑫, 李耀刚, 王宏志, 张青红. 非贵金属Co5.47N/N-rGO助催化剂增强TiO2光催化制氢性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 534-540. |
| [12] | 周港怀, 刘耀, 石原, 刘绍军. 活性氧化铝催化剂载体的光固化浆料制备与成型[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 297-302. |
| [13] | 陈士昆, 王楚楚, 陈晔, 李莉, 潘路, 文桂林. 磁性Ag2S/Ag/CoFe1.95Sm0.05O4 Z型异质结的制备及光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1329-1336. |
| [14] | 刘雪晨, 曾滴, 周沅逸, 王海鹏, 张玲, 王文中. 改性氮化碳光催化剂在生物质氧化反应中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 38-44. |
| [15] | 张弦, 张策, 姜文君, 冯德强, 姚伟. 四元BiMnVO5的合成、电子结构与可见光催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||