无机材料学报 ›› 2020, Vol. 35 ›› Issue (2): 179-186.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190053
所属专题: 生物材料论文精选(2020)
代钊1,王铭2,王双1,李静1,陈翔1,汪大林1( ),祝迎春2(
),祝迎春2( )
)
收稿日期:2019-01-27
修回日期:2019-04-02
出版日期:2020-02-20
网络出版日期:2019-05-29
作者简介:代 钊(1989-), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: zhaodai313@126.com
基金资助:
DAI Zhao1,WANG Ming2,WANG Shuang1,LI Jing1,CHEN Xiang1,WANG Da-Lin1( ),ZHU Ying-Chun2(
),ZHU Ying-Chun2( )
)
Received:2019-01-27
Revised:2019-04-02
Published:2020-02-20
Online:2019-05-29
Supported by:摘要:
氧化锆陶瓷具有良好的力学性能和生物相容性, 是一种应用前景广阔的硬组织植入体材料。为促进植入体与骨组织形成稳定的骨结合, 本研究利用等离子喷涂制备了氧化锆增韧的锶、硅、氟微量掺杂羟基磷灰石(ZrO2-DHA)涂层, 对涂层物相、形貌以及力学性能和体外生物学性能进行了研究。结果表明, 锶、硅、氟的共掺杂通过成骨分化的信号转导通路提高了羟基磷灰石涂层对成骨细胞的黏附和分化等生物学性能; 不同复合组分的ZrO2-DHA涂层均不同程度地促进了小鼠成骨前体细胞的细胞活力和成骨分化相关基因的表达。在细胞培养的第7 d, DHA含量为70%的ZrO2-DHA涂层(7DHA) Alp和Col-I的相对表达量分别是对照组的约2.8倍和2.3倍; ZrO2-DHA涂层的力学性能随氧化锆组分的增加而增强, DHA涂层和7DHA涂层的硬度和结合强度分别为250.8、313HV和25.1、31.8 MPa; 7DHA涂层中的交织网络结构, 对残余热应力、压应力和拉伸力的承受能力较DHA涂层明显提升, 满足植入体应用需求。
中图分类号:
代钊,王铭,王双,李静,陈翔,汪大林,祝迎春. 氧化锆基微量元素共掺杂羟基磷灰石增韧涂层研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 179-186.
DAI Zhao,WANG Ming,WANG Shuang,LI Jing,CHEN Xiang,WANG Da-Lin,ZHU Ying-Chun. Zirconia Reinforced Trace Element Co-doped Hydroxyapatite Coating[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(2): 179-186.
| Parameter | HA/DHA coating | ZrO2-DHA coatings |
|---|---|---|
| Primary gas flow rate/(L?min-1) | Ar/40-41 | Ar/40-42 |
| Auxiliary gas flow rate/(L?min-1) | H2/6-7 | H2/8-9 |
| Carrier gas flow rate/(L?min-1) | Ar/6-6.5 | Ar/6-6.5 |
| Powder feed rate/(g?min-1) | 18 | 20 |
| Current/A | 650 | 570 |
| Gun transverse speed/(mm?s-1) | 500 | 500 |
| Standoff distance/mm | 100 | 100 |
表1 喷涂参数
Table 1 Plasma spraying parameters
| Parameter | HA/DHA coating | ZrO2-DHA coatings |
|---|---|---|
| Primary gas flow rate/(L?min-1) | Ar/40-41 | Ar/40-42 |
| Auxiliary gas flow rate/(L?min-1) | H2/6-7 | H2/8-9 |
| Carrier gas flow rate/(L?min-1) | Ar/6-6.5 | Ar/6-6.5 |
| Powder feed rate/(g?min-1) | 18 | 20 |
| Current/A | 650 | 570 |
| Gun transverse speed/(mm?s-1) | 500 | 500 |
| Standoff distance/mm | 100 | 100 |
| Gene | Sequence |
|---|---|
| Alp | F: 5-AACGTGGCCAAGAACATCATCA-3 R: 5-TGTCCATCTCCAGCCGTGTC-3 |
| Col-I | F: 5-CCAGAAGAACTGGTACATCAGCAA-3 R: 5-CGCCATACTCGAACTGGAATC-3 |
| Gapdh | F: 5-GGCATTGCTCTCAATGACAA-3 R: 5-TGTGAGGGAGATGCTCAGTG-3 |
表2 引物序列
Table 2 Sequence of primers
| Gene | Sequence |
|---|---|
| Alp | F: 5-AACGTGGCCAAGAACATCATCA-3 R: 5-TGTCCATCTCCAGCCGTGTC-3 |
| Col-I | F: 5-CCAGAAGAACTGGTACATCAGCAA-3 R: 5-CGCCATACTCGAACTGGAATC-3 |
| Gapdh | F: 5-GGCATTGCTCTCAATGACAA-3 R: 5-TGTGAGGGAGATGCTCAGTG-3 |
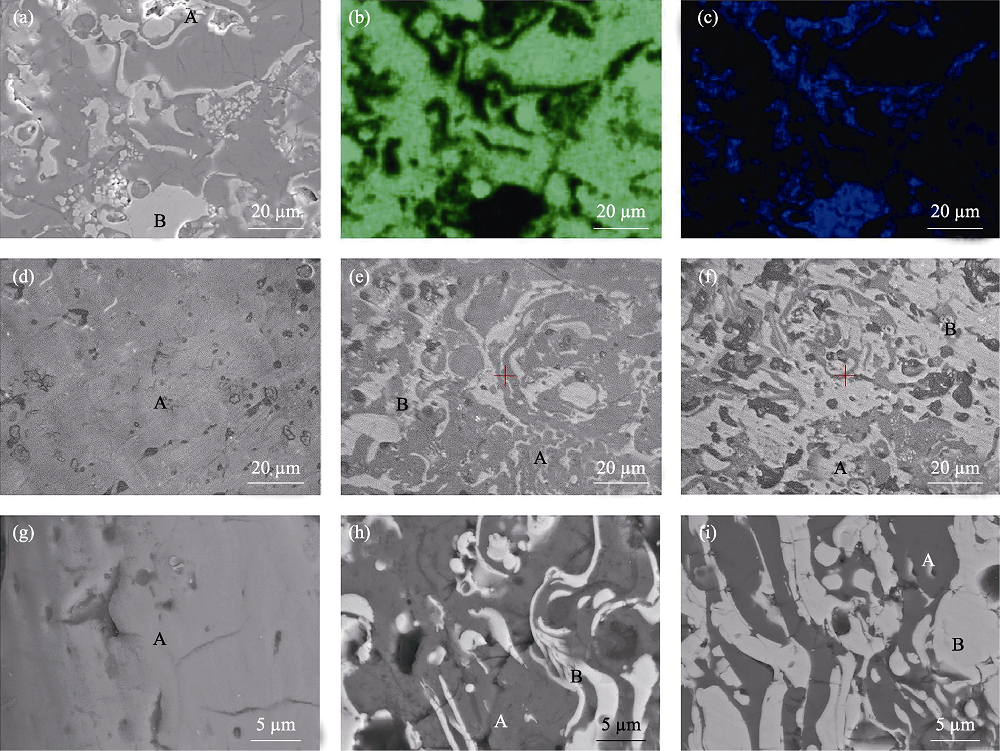
图2 7DHA涂层的SEM照片(a)和元素分布扫描照片(Ca(b)和Zr(c)); 涂层平面(d~f)和截面(g~i)的SEM照片: DHA(d, g)、7DHA (e, h)、3DHA (f, i)
Fig. 2 SEM images (a) and elemental mapping of Ca (green) (b) and Zr (blue) (c) of 7DHA coating, and SEM images of surface (d-f) and cross sections (g-i) of DHA (d, g), 7DHA (e, h) and 3DHA (f, i)
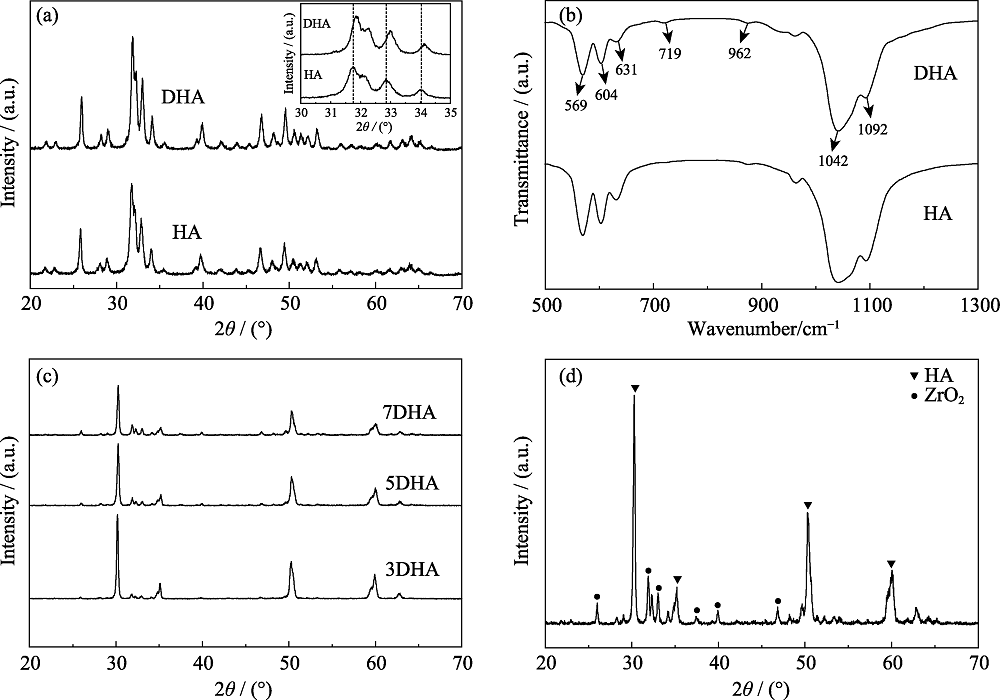
图3 HA和DHA粉体的XRD图谱(a)及FT-IR谱图 (b), DHA涂层的XRD图谱(c)及7DHA涂层的放大XRD图谱(d)
Fig. 3 XRD patterns of HA and DHA powders with inset showing the enlarged parts (a), FT-IR spectra of HA and DHA powders (b), and XRD patterns of 7DHA, 5DHA and 3DHA coatings (c) with enlarged pattern of 7DHA coating (d)
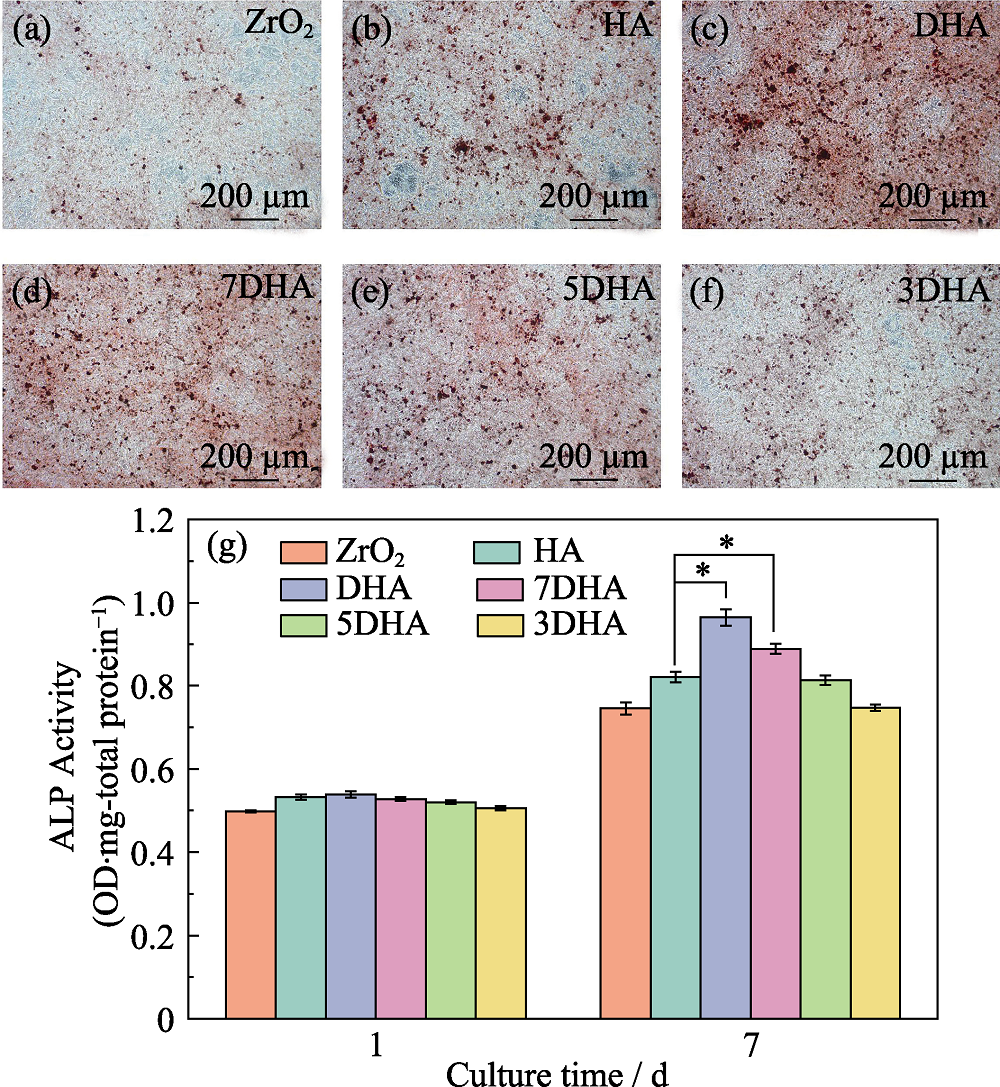
图7 MC3T3-E1细胞茜素红染色照片(a~f)和ALP活性比较(g)
Fig. 7 Optical images of MC3T3-E1 cell Alizarin red S staining (a-f) and comparison of ALP activity (g) (*p<0.05)
| [1] | PAYER M, HESCHL A, KOLLER M , et al. All-ceramic restoration of zirconia two-piece implants--a randomized controlled clinical trial. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 2015,26(4):371-376. |
| [2] | BANKOGLU G M, AYDIN C, YILMAZ H , et al. An overview of zirconia dental implants basic properties and clinical application of three cases. Journal of Oral Implantology, 2014,40(4):485-494. |
| [3] | BAN S . Reliability and properties of core materials for all-ceramic dental restorations. Japanese Dental Science Review, 2008,44(1):3-21. |
| [4] | GAHLERT M, ROEHLING S, SPRECHER C M , et al. In vivo performance of zirconia and titanium implants: a histomorphometric study in mini pig maxillae. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 2012,23(3):281-286. |
| [5] | KOHAL R J, WOLKEWITZ M, HINZE M , et al. Biomechanical and histological behavior of zirconia implants: an experiment in the rat. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 2009,20(4):333-339. |
| [6] | BIANCO P D, DUCHEYNE P, CUCKLE J M . Local accumulation of titanium released from a titanium implant in the absence of wear. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 1996,31:227-234. |
| [7] | TSCHEMITSCHEK H, BORCHERS L, GEURTSEN W . Nonalloyed titanium as a bioinert metal—a review. The Journal of Prosthetic Dentistry, 2006,96(1):523-530. |
| [8] | FRANSSON C, LEKHOLM U, JEMT T , et al. Prevalence of subjects with progressive bone loss at implants. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 2005,16(4):440-446. |
| [9] | ZHOU H, LEE J . Nanoscale hydroxyapatite particles for bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomaterialia, 2011,7(7):2769-2781. |
| [10] | SUN T, WANG M, SHAO Y , et al. The effect and osteoblast signaling response of trace silicon doping hydroxyapatite. Biological Trace Element Research, 2018,181(1):82-94. |
| [11] | XIAO S, WANG M, WANG L , et al. Environment-friendly synthesis of trace element Zn, Sr, and F codoping hydroxyapatite with non- cytotoxicity and improved osteoblast proliferation and differentiation. Biological Trace Element Research, 2018,185(1):148-161. |
| [12] | GAO J, WANG M, SHI C , et al. A facile green synthesis of trace Si, Sr and F multi-doped hydroxyapatite with enhanced biocompatibility and osteoconduction. Materials Letters, 2017,196:406-409. |
| [13] | GAO J, WANG M, SHI C , et al. Synthesis of trace element Si and Sr codoping hydroxyapatite with non-cytotoxicity and enhanced cell proliferation and differentiation. Biological Trace Element Research, 2016,174(1):208-217. |
| [14] | WANG L, WANG M, LI M , et al. Trace fluorine substituted calcium deficient hydroxyapatite with excellent osteoblastic activity and antibacterial ability. CrystEngComm, 2018,20(38):5744-5753. |
| [15] | YUGESWARAN S, YOGANAND C P, KOBAYASHI A , et al. Mechanical properties, electrochemical corrosion and in-vitro bioactivity of yttria stabilized zirconia reinforced hydroxyapatite coatings prepared by gas tunnel type plasma spraying. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials, 2012,9:22-33. |
| [16] | KHOR K A, GU Y W, PAN D , et al. Microstructure and mechanical properties of plasma sprayed HA/YSZ/Ti-6Al-4V composite coatings. Biomaterials, 2004,25(18):4009-4017. |
| [17] | 吴永智 . 等离子喷涂羟基磷灰石纳米氧化锆梯度涂层的研究. 北京: 北京工业大学硕士学位论文, 2008. |
| [18] | XIE L, WU X, LI W , et al. Latest research on zirconia implant surface treatment. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2017,21(10):1623-1628. |
| [19] | SZURKOWSKA K, KOLMAS J . Hydroxyapatites enriched in silicon-bioceramic materials for biomedical and pharmaceutical applications. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International, 2017,27(4):401-409. |
| [20] | ZIPKIN I, MCCLURE F J, LEE W A . Relation of the fluoride content of human bone to its chemical composition. Arch Oral Biol, 1960,2:190-195. |
| [21] | TRUEMAN CN, TUROSS N . Trace elements in recent and fossil bone apatite. Reviews in Mineralogy and Geochemistry, 2002,48(1):489-521. |
| [22] | GBT16886.12-2017/ISO10993-12:20012, Biological evaluation of medical devices-Part 12: Sample preparation and reference materials. |
| [23] | FRASNELLI M, CRISTOFARO F, SGLAVO V M , et al. Synthesis and characterization of strontium-substituted hydroxyapatite nanoparticles for bone regeneration. Materials Science & Engineering C: Materials for Biological Applications, 2017,71:653-662. |
| [24] | NI GX, SHU B, HUANG G , et al. The effect of strontium incorporation into hydroxyapatites on their physical and biological properties. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 2012,100(2):562-568. |
| [25] | TANG Q, BROOKS R, RUSHTON N , et al. Production and characterization of HA and SiHA coatings. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2010,21(1):173-181. |
| [26] | CANALIS E, HOTT M, DELOFFRE P , et al. The divalent strontium salt S12911 enhances bone cell replication and bone formation in vitro. Bone, 1996,18(6):517-523. |
| [27] | BONNELYE E, CHABADEL A, SALTEL F , et al. Dual effect of strontium ranelate: stimulation of osteoblast differentiation and inhibition of osteoclast formation and resorption in vitro. Bone, 2008,42(1):129-138. |
| [28] | TAKAHASHI N, SASAKI T, TSOUDEROS Y , et al. S 12911-2 inhibits osteoclastic bone resorption in vitro. Journal of Bone and Mineral Research, 2003,18(6):1082-1087. |
| [29] | BUEHLER J, CHAPPUIS P, SAFFAR J L ,et al. Strontium ranelate inhibits bone resorption while maintaining bone formation in alveolar bone in monkeys(Macaca fascicularis). Bone, 2001,29(2):176-179. |
| [30] | LI Z, HUANG B, MAI S , et al. Effects of fluoridation of porcine hydroxyapatite on osteoblastic activity of human MG63 cells. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2015,16(3):035006. |
| [31] | HONDA M, KIKUSHIMA K, KAWANOBE Y , et al. Enhanced early osteogenic differentiation by silicon-substituted hydroxyapatite ceramics fabricated via ultrasonic spray pyrolysis route. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Medicine, 2012,23(12):2923-2932. |
| [32] | HONDA M, KIKUSHIMA K, KAWANOBE Y , et al. Cell proliferation, morphology and differentiation of transgenic-cloned pig calvarial osteoblasts on the silicon-substituted hydorxyapatite ceramics fabricated via ultrasonic spray-pyrolysis technique. Journal of the Australian Ceramic Society, 2011,47(1):37-41. |
| [33] | ZHOU J, LI B, LU S , et al. Regulation of osteoblast proliferation and differentiation by interrod spacing of Sr-HA nanorods on microporous titania coatings. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013,5(11):5358-5365. |
| [34] | YANG F, YANG D, TU J , et al. Strontium enhances osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells and in vivo bone formation by activating Wnt/catenin signaling. Stem Cells, 2011,29(6):981-991. |
| [1] | 潘洋洋, 梁波, 洪督, 祁志祥, 牛亚然, 郑学斌. TiAl合金表面TiAlCrY/YSZ涂层高温长时间服役性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 105-112. |
| [2] | 安文然, 黄晶琪, 卢祥荣, 蒋佳宁, 邓龙辉, 曹学强. 热处理温度对LaMgAl11O19涂层热/力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 925-932. |
| [3] | 张叶, 曾宇平. 自蔓延高温合成氮化硅多孔陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 853-864. |
| [4] | 夏乾, 孙是昊, 赵义亮, 张翠萍, 茹红强, 王伟, 岳新艳. 碳化硼颗粒级配对硅反应结合碳化硼复合材料结构与性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 636-642. |
| [5] | 洪督, 牛亚然, 李红, 钟鑫, 郑学斌. 等离子喷涂TiC-Graphite复合涂层摩擦磨损性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 643-650. |
| [6] | 徐谱昊, 张相召, 刘桂武, 张明芬, 桂新易, 乔冠军. Al-Ti合金钎焊SiC陶瓷接头界面微观结构与力学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 683-690. |
| [7] | 丁健翔, 张凯歌, 柳东明, 郑伟, 张培根, 孙正明. Ti3AlC2陶瓷及其衍生物Ti3C2Tx增强的Ag基电接触材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 567-573. |
| [8] | 蔚海浪, 曹学强, 邓龙辉, 蒋佳宁. LaMeAl11O19/YSZ热障涂层热力学性能和热循环寿命[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1259-1266. |
| [9] | 孙扬善, 杨治华, 蔡德龙, 张正义, 柳琪, 房树清, 冯良, 石丽芬, 王友乐, 贾德昌. 粉末烧结法制备α-堇青石基玻璃陶瓷的析晶动力学和性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1351-1357. |
| [10] | 吴西士, 朱云洲, 黄庆, 黄政仁. 树脂基多孔碳孔结构对Cf/SiC复合材料连接性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1275-1280. |
| [11] | 孙鲁超, 周翠, 杜铁锋, 吴贞, 雷一明, 李家麟, 苏海军, 王京阳. 光悬浮区熔定向凝固Al2O3/Er3Al5O12和Al2O3/Yb3Al5O12共晶陶瓷的制备与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(6): 652-658. |
| [12] | 吕莎莎, 祖宇飞, 陈国清, 赵伯俊, 付雪松, 周文龙. 陶瓷颗粒增强Cr0.5MoNbWTi难熔高熵合金复合材料的制备及其力学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 386-392. |
| [13] | 王皓轩, 刘巧沐, 王一光. 高熵过渡金属碳化物陶瓷的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 355-364. |
| [14] | 金敏, 白旭东, 赵素, 张如林, 陈玉奇, 周丽娜. 坩埚下降法生长SnSe单晶及其力学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(3): 313-318. |
| [15] | 李陇彬, 薛玉冬, 胡建宝, 杨金山, 张翔宇, 董绍明. 碳化硅纳米线增韧碳化硅纤维/碳化硅基体损伤行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1111-1117. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||