无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (9): 925-932.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180497
所属专题: 药物载体与防护材料
肖文谦,张静,李克江,邹新宇,蔡昱东,李波( ),刘雪(
),刘雪( ),廖晓玲
),廖晓玲
收稿日期:2018-10-18
修回日期:2018-12-24
出版日期:2019-09-20
网络出版日期:2019-05-29
作者简介:肖文谦(1982-), 男, 博士, 讲师. E-mail: wqxiao@cqust.edu.cn
基金资助:
XIAO Wen-Qian,ZHANG Jing,LI Ke-Jiang,ZOU Xin-Yu,CAI Yu-Dong,LI Bo( ),LIU Xue(
),LIU Xue( ),LIAO Xiao-Ling
),LIAO Xiao-Ling
Received:2018-10-18
Revised:2018-12-24
Published:2019-09-20
Online:2019-05-29
Supported by:摘要:
为了克服常规的生物陶瓷微球缺乏靶向功能的缺点, 本研究制备了内核为CaCO3, 外壳为磁性可调控羟基磷灰石(HA)的新型荔枝状多孔微球。结果表明: 抗肿瘤药物阿霉素(DOX)能有效地负载于磁性HA微球上, 并具备磁性靶向功能。此外, HA外壳具有良好的生物相容性和pH响应特性, 可在模拟酸性肿瘤细胞环境中控制DOX的释放, 有效杀死肿瘤细胞, 并在模拟正常细胞培养环境中减少对正常细胞的毒副作用。这种新型的微球材料具有超顺磁性能, 且微结构可控, 是一种智能化药物控释微球载体, 可以灵敏地释放DOX, 从而有效地实现抗肿瘤活性。
中图分类号:
肖文谦,张静,李克江,邹新宇,蔡昱东,李波,刘雪,廖晓玲. 荔枝状CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4磁性介孔多级微球的制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 925-932.
XIAO Wen-Qian,ZHANG Jing,LI Ke-Jiang,ZOU Xin-Yu,CAI Yu-Dong,LI Bo,LIU Xue,LIAO Xiao-Ling. Litchi-like Superparamagnetic Hydroxyapatite Microspheres with Hierarchically Mesoporous Microspheres[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(9): 925-932.
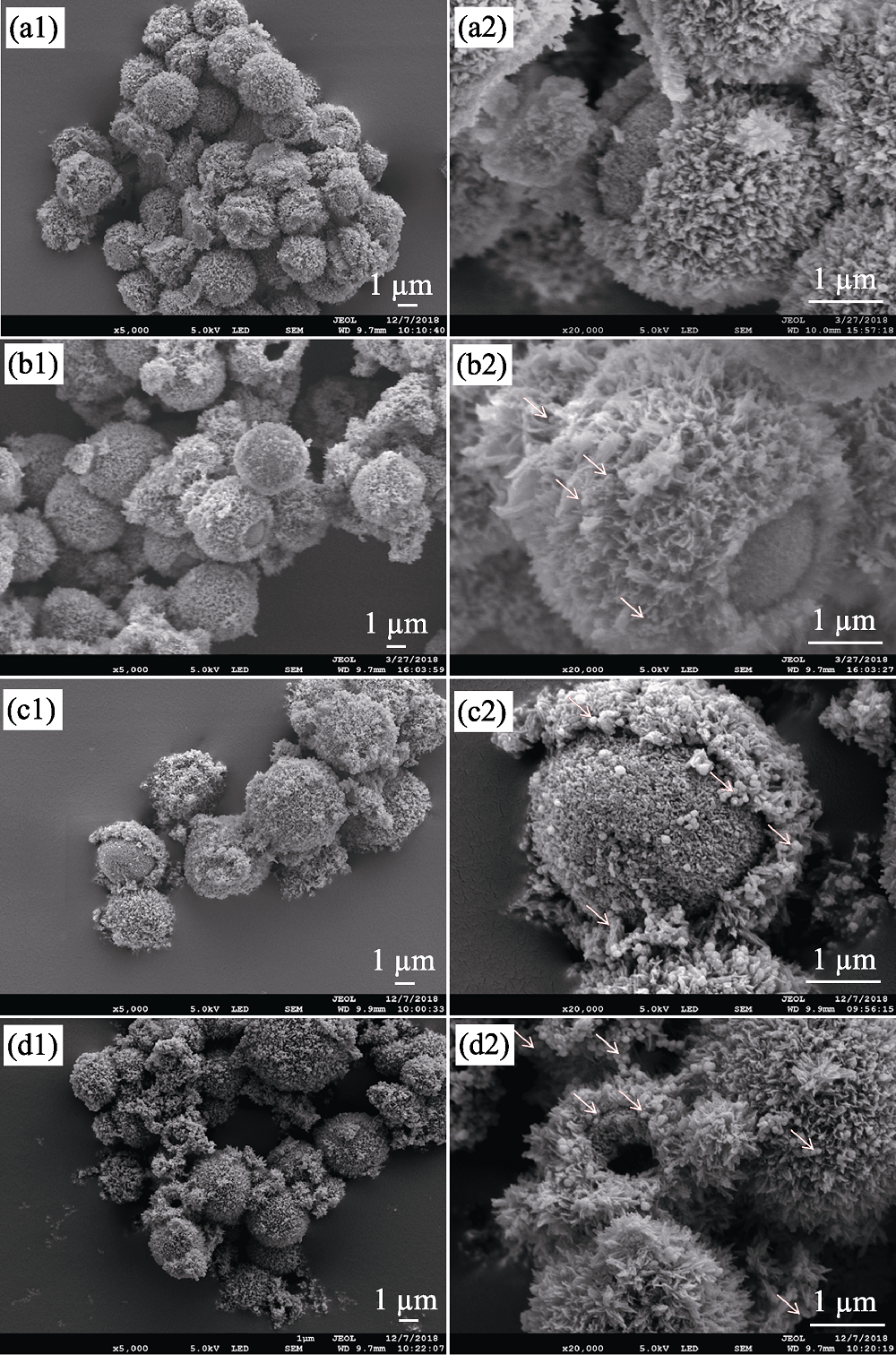

图1 不同Fe3O4含量的超顺磁性CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4微球的SEM照片
Fig. 1 SEM images of superparamagnetic CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4 microspheres with different Fe3O4 component. Note: S0 (a1, a2), S1 (b1, b2), S2 (c1, c2), S3 (d1, d2)
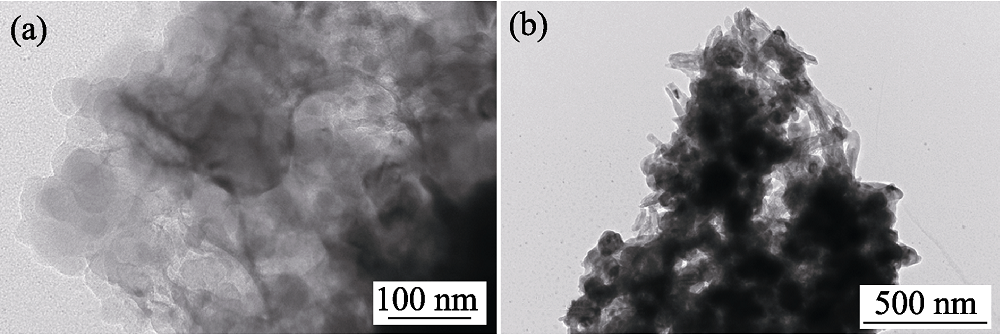
图2 Fe3O4为25wt%的CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4微球水热转化前(a)后(b)的TEM照片
Fig. 2 TEM images before (a) and after (b) hydrothermal conversion of CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4 microspheres with 25wt% Fe3O4 component
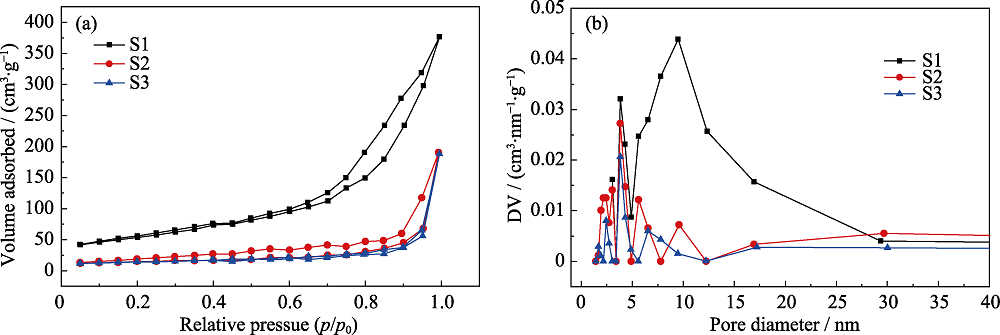
图5 不同Fe3O4掺杂含量的磁性CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4微球的等温吸附曲线(a)和孔径结构分布图(b)
Fig. 5 Typical nitrogen isothermal adsorption curves (a) and mesopore distribution (b) analysis of CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4 microspheres with different Fe3O4 content
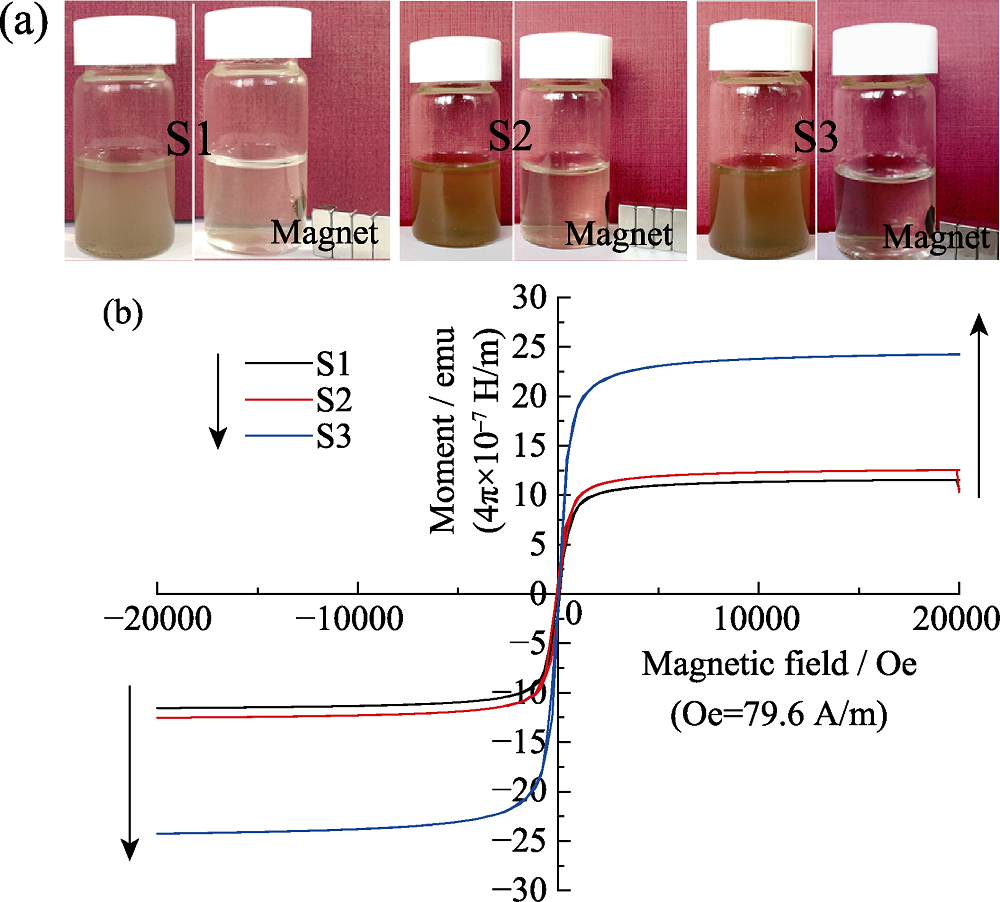
图7 (a)荔枝状超顺磁性CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4微球悬浮液受磁铁吸引的数码照片, 及(b)300 K 下不同Fe3O4含量的CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4微球的磁滞回线
Fig. 7 Digital photographs (a) of the litchi-like CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4 magnetic HA microspheres in aqueous suspension and (b) magnetization of different samples as a function of the applied field measured at 300 K
| Sample | Fe3O4 content/wt% | SBET /(m2·g-1) | DLA /(mg·g-1) | DLE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 16.08 | 196.481 | 96.88 | 96.88 |
| S2 | 17.69 | 50.749 | 96.14 | 96.14 |
| S3 | 37.98 | 46.623 | 97.96 | 97.96 |
表1 不同Fe3O4含量的CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4微球的比表面积(SBET)、载药量(DLA)和药物装载率(DLE)
Table 1 Fe3O4 content, specific surface area (SBET), drug loading amount (DLA) and drug loading efficiency (DLE) of CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4 microspheres
| Sample | Fe3O4 content/wt% | SBET /(m2·g-1) | DLA /(mg·g-1) | DLE/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| S1 | 16.08 | 196.481 | 96.88 | 96.88 |
| S2 | 17.69 | 50.749 | 96.14 | 96.14 |
| S3 | 37.98 | 46.623 | 97.96 | 97.96 |
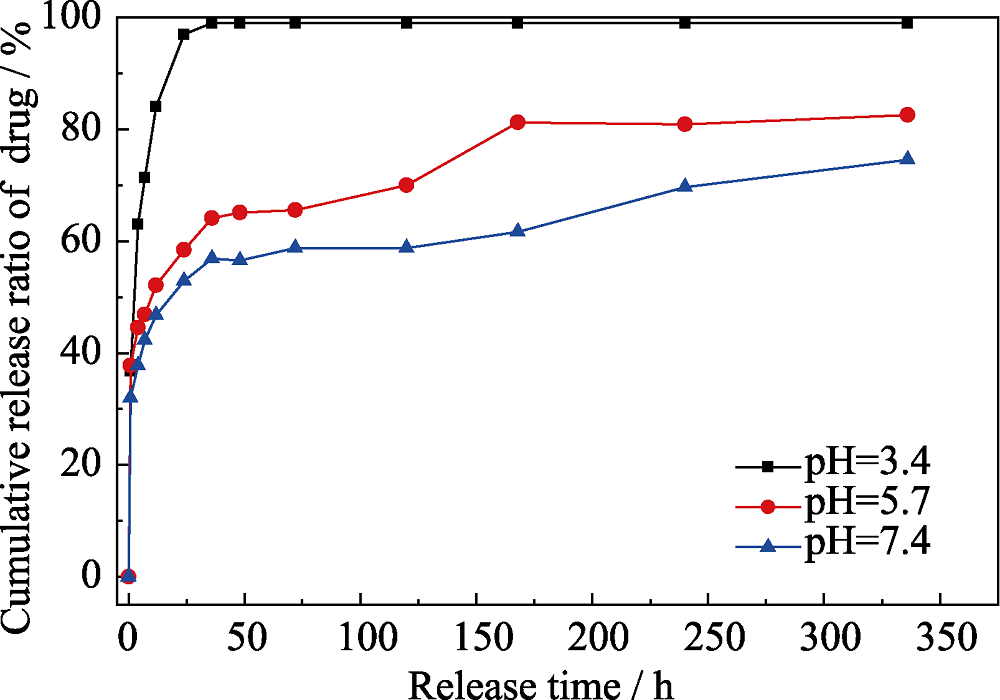
图8 37 ℃下载药CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4微球在不同pH (3.4、5.7、7.4)的PBS中的DOX累计释放曲线
Fig. 8 DOX release profiles of the DOX-loaded litchi-like magnetic HA microspheres in PBS with different pH of 3.4, 5.7 and 7.3 at 37 ℃
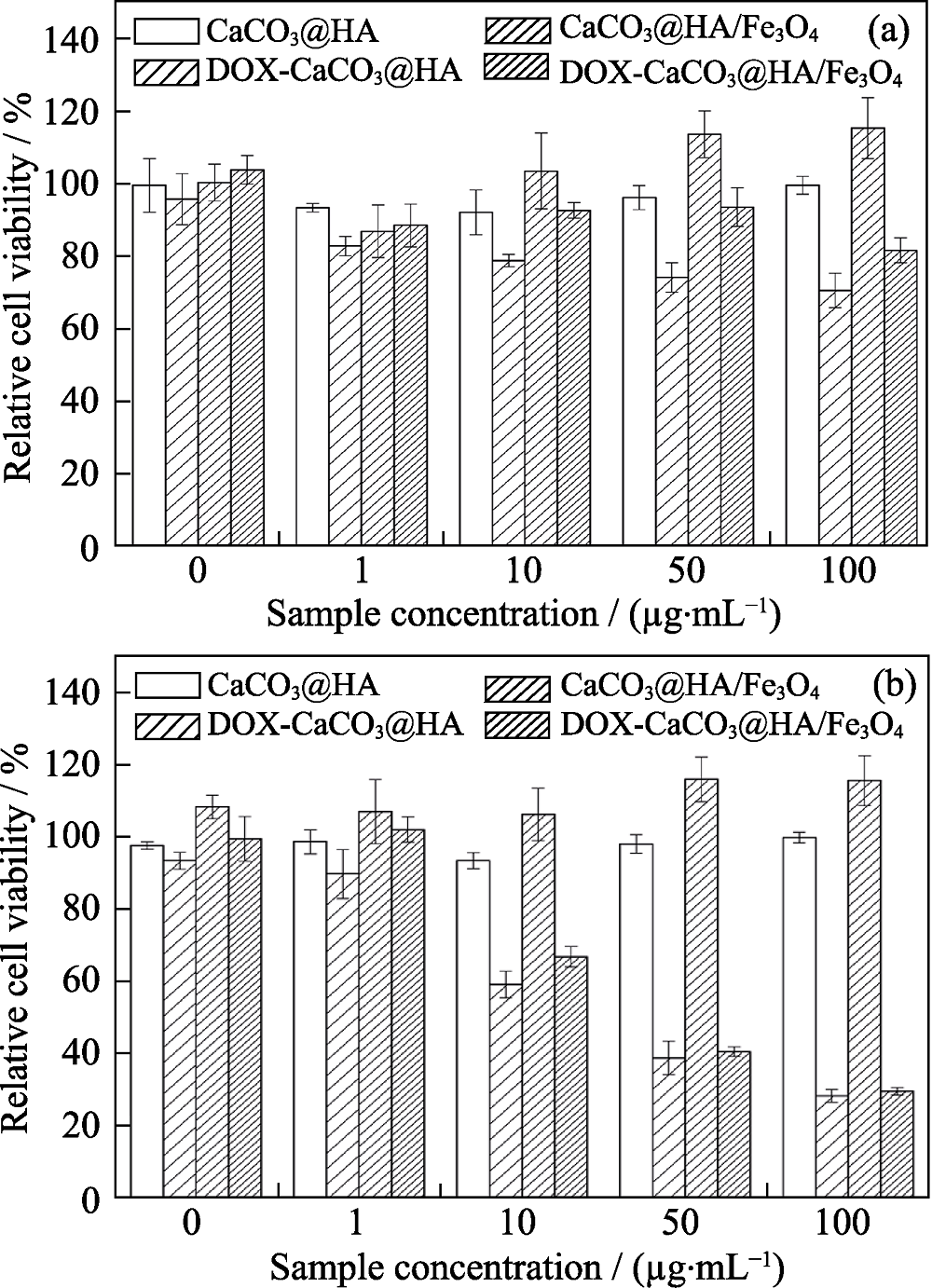
图9 CCK8试验法测定正常细胞HaCaT(a)和肿瘤细胞HN6(b)在载DOX和不载DOX的CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4和CaCO3@HA微球下的24 h存活率柱状图
Fig. 9 CCK-8 assay of HaCaT (a) and HN6 tumor cells (b) co-cultured with unloaded or DOX-loaded litchi-like magnetic HA microspheres and litchi-like HA microspheres for 24 h
| [1] | WANG H, LEEUWENBURGH SC, LI Y , et al. The use of micro- and nanospheres as functional components for bone tissue regeneration. Tissue Engineering Part B Reviews, 2012,18(1):24-39. |
| [2] | FAN J B, HUANG C, JIANG L , et al. Nanoporous microspheres: from controllable synthesis to healthcare applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013,1(17):2222-2235. |
| [3] | PARK J H, PÉREZ R A, JIN G Z, , et al. Microcarriers designed for cell culture and tissue engineering of bone. Tissue Engineering Part B Reviews, 2013,19(2):172-190. |
| [4] | LIU J, QIAO S Z, CHEN J S , et al. Yolk/shell nanoparticles: new platforms for nanoreactors, drug delivery and lithium-ion batteries. ChemInform, 2011,47(47):12578-12591. |
| [5] | MAHMOUDI M, SANT S, WANG B , et al. Superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles (SPIONs): development, surface modification and applications in chemotherapy. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2011,63(1/2):24-46. |
| [6] | KIM D H, LI W, CHEN J , et al. Multimodal Imaging of nanocomposite microspheres for transcatheter intra-arterial drug delivery to liver tumors. Scientific Reports, 2016,6:29653. |
| [7] | LIU Y, YANG F, YUAN C , et al. Magnetic nanoliposomes as in situ microbubble bombers for multimodality image-guided cancer theranostics. ACS Nano, 2017,11(2):1509-1519. |
| [8] | PARK J, AN K, HWANG Y , et al. Ultra-large-scale syntheses of monodisperse nanocrystals. Nature Materials, 2004,3(12):891-895. |
| [9] | CHEN Y, CHEN H, GUO L , et al. Hollow/rattle-type mesoporous nanostructures by a structural difference-based selective etching strategy. ACS Nano, 2010,4(1):529-539. |
| [10] | WANG Y, WANG F, CHEN B , et al. Facile one-pot synthesis of yolk-shell superparamagnetic nanocomposites via ternary phase separations. Chemical Communications, 2011,47(37):10350-10352. |
| [11] | LATTUADA M, HATTON TA . Synthesis, properties and applications of Janus nanoparticles. Nano Today, 2011,6(3):286-308. |
| [12] | XIA L Y, ZHANG M Q, YUAN C E , et al. A facile heteroaggregate- template route to hollow magnetic mesoporous spheres with tunable shell structures. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011,21(25):9020-9026. |
| [13] | GUO Y P, LONG T, TANG S , et al. Hydrothermal fabrication of magnetic mesoporous carbonated hydroxyapatite microspheres: biocompatibility, osteoinductivity, drug delivery property and bactericidal property. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2014,2(19):2899-2909. |
| [14] | LIN K, CHEN L, LIU P , et al. Hollow magnetic hydroxyapatite microspheres with hierarchically mesoporous microstructure for pH- responsive drug delivery. CrystEngComm, 2013,15(15):2999-3008. |
| [15] | QI C, LIN J, FU LH , et al. Calcium-based biomaterials for diagnosis, treatment, and theranostics. Chemical Society Reviews, 2017,47(2):357-403. |
| [16] | HONG Y, FAN H, LI B , et al. Fabrication, biological effects, and medical applications of calcium phosphate nanoceramics. Materials Science and Engineering: R, 2010,70(3-6):225-242. |
| [17] | YUAN H, FERNANDES H, HABIBOVIC P , et al. Osteoinductive ceramics as a synthetic alternative to autologous bone grafting. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2010,107(31):13614-13619. |
| [18] | QIAO W, LAN X, TSOI J K H , et al. Biomimetic hollow mesoporous hydroxyapatite microsphere with controlled morphology, entrapment efficiency and degradability for cancer therapy. RSC Adv., 2017,7(71):44788-44798. |
| [19] | LI R, CHEN K, LI G , et al. Structure design and fabrication of porous hydroxyapatite microspheres for cell delivery. Journal of Molecular Structure, 2016,1120:34-41. |
| [20] | WU H C, WANG T W, BOHN M C , et al. Novel magnetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles as non-viral vectors for the glial cell line-derived neurotrophic factor gene. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010,20(1):67-77. |
| [21] | GUO Y P, GUO L H, YAO Y B , et al. Magnetic mesoporous carbonated hydroxyapatite microspheres with hierarchical nanostructure for drug delivery systems. Chemical Communications, 2011,47(44):12215-12217. |
| [22] | HUANG C, ZHOU Y, TANG Z , et al. Synthesis of multifunctional Fe3O4 core/hydroxyapatite shell nanocomposites by biomineralization. Dalton Transactions, 2011,40(18):5026-5031. |
| [23] | BOCK N, RIMINUCCI A, DIONIGI C , et al. A novel route in bone tissue engineering: magnetic biomimetic scaffolds. Acta Biomaterials, 2010,6(3):786-796. |
| [24] | LONG T, GUO YP, TANG S , et al. Emulsion fabrication of magnetic mesoporous carbonated hydroxyapatite microspheres for treatment of bone infection. RSC Advances, 2014,4(23):11816-11825. |
| [25] | INUKAI A, SAKAMOTO N, AONO H , et al. Synthesis and hyperthermia property of hydroxyapatite-ferrite hybrid particles by ultrasonic spray pyrolysis. Journal of Magnetism & Magnetic Materials, 2011,323(7):965-969. |
| [26] | TEO B M, SUH S K, HATTON T A , et al. Sonochemical synthesis of magnetic Janus nanoparticles. Langmuir, 2011,27(1):30-33. |
| [27] | MENG J, ZHANG Y, QI X , et al. Paramagnetic nanofibrous composite films enhance the osteogenic responses of pre-osteoblast cells. Nanoscale, 2010,2(12):2565-2569. |
| [28] | ZHANG Y, WANG H, YAN B , et al. A reusable piezoelectric immunosensor using antibody-adsorbed magnetic nanocomposite. Journal of Immunological Methods, 2008,332(1):103-111. |
| [29] | SAFAVI A, MOMENI S . Highly efficient degradation of azo dyes by palladium/hydroxyapatite/Fe3O4 nanocatalyst. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012,201(1):125-131. |
| [30] | JIANG X, WANG F, CAI W , et al. Trisodium citrate-assisted synthesis of highly water-dispersible and superparamagnetic mesoporous Fe3O4 hollow microspheres via solvothermal process. Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2015,636 34-39. |
| [31] | WANG Y, HASSAN MS, GUNAWAN P , et al. Polyelectrolyte mediated formation of hydroxyapatite microspheres of controlled size and hierarchical structure. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science, 2009,339(1):69-77. |
| [32] | BRETCANU O, SPRIANO S, VERNÉ E , et al. The influence of crystallised Fe3O4 on the magnetic properties of coprecipitation- derived ferrimagnetic glass-ceramics. Acta Biomaterials, 2005,1(4):421-429. |
| [33] | YANG Y H, LIU C H, LIANG Y H , et al. Hollow mesoporous hydroxyapatite nanoparticles (hmHANPs) with enhanced drug loading and pH-responsive release properties for intracellular drug delivery. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013,1(19):2447-2450. |
| [1] | 吴锐, 张敏慧, 金成韵, 林健, 王德平. 光热核壳TiN@硼硅酸盐生物玻璃纳米颗粒的降解和矿化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [2] | 马晓森, 张丽晨, 刘砚超, 汪全华, 郑家军, 李瑞丰. 13X@SiO2合成及其甲苯吸附性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [3] | 迟聪聪, 屈盼盼, 任超男, 许馨, 白飞飞, 张丹洁. SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2核壳结构的制备及其光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [4] | 陈亚玲, 舒松, 王劭鑫, 李建军. Mn-HAP基低温SCR催化剂的制备及抗硫中毒性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1065-1072. |
| [5] | 陈小梅, 陈颖, 袁霞. 核壳材料Co3O4@SiO2催化环己基过氧化氢分解[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 65-71. |
| [6] | 朱雨桐, 谭佩洁, 林海, 朱向东, 张兴栋. 可注射透明质酸/羟基磷灰石复合材料: 制备、理化性能和细胞相容性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 981-990. |
| [7] | 林子扬, 常宇辰, 吴章凡, 包荣, 林文庆, 王德平. 不同模拟体液对硼硅酸盐生物活性玻璃基骨水泥矿化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 745-752. |
| [8] | 吴重草, 郇志广, 朱钰方, 吴成铁. 3D打印HA微球支架的制备与表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(6): 601-607. |
| [9] | 吴永豪, 李向锋, 朱向东, 张兴栋. 高强度羟基磷灰石纳米陶瓷的构建及其促成骨细胞活性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 552-560. |
| [10] | 郭小炜, 李玉妍, 陈南春, 王秀丽, 解庆林. 负载二甲酸钾缓释抗菌微球的构建[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 181-187. |
| [11] | 宋可可, 黄浩, 鲁梦婕, 杨安春, 翁杰, 段可. 水热制备锌、硅、镁、铁等元素掺杂羟基磷灰石及其表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1091-1096. |
| [12] | 邵悦婷, 朱英杰, 董丽颖, 蔡安勇. 羟基磷灰石超长纳米线/植物纤维纳米复合“宣纸”及其防霉性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(1): 107-112. |
| [13] | 潘碧宸,任鹏禾,周特军,蔡圳阳,赵小军,周宏明,肖来荣. 树脂基复合材料表面隔热涂层的组织与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 947-952. |
| [14] | 孙团伟,朱英杰. 一步溶剂热法合成锶掺杂羟基磷灰石超长纳米线[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 724-728. |
| [15] | 刘子阳, 耿振, 李朝阳. 牡蛎壳为原料制备医用CaCO3/HA复合生物材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 601-607. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||