无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (6): 633-640.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180372
张峰1,2,张凯立1,周明明2,陈超3,蔡志威3,魏国辉4,姜兴茂4,5,张诚1,劳伦·鲁尔曼6,吕耀康1( )
)
收稿日期:2018-08-09
修回日期:2018-09-04
出版日期:2019-06-20
网络出版日期:2019-05-23
作者简介:张 峰(1980-), 男, 副主任医师. E-mail: zfwl@zju.edu.cn
基金资助:
Feng ZHANG1,2,Kai-Li ZHANG1,Ming-Ming ZHOU2,Chao CHEN3,Zhi-Wei CAI3,Guo-Hui WEI4,Xing-Mao JIANG4,5,Cheng ZHANG1,RUHLMANN Laurent6,Yao-Kang LÜ1( )
)
Received:2018-08-09
Revised:2018-09-04
Published:2019-06-20
Online:2019-05-23
Supported by:摘要:
通过超声波辅助液相法将纳米银(AgNPs)与氧化石墨烯(GO)结合制得了一种新的负载纳米银的氧化石墨烯材料AgNPs@GO。分析表明在该材料中AgNPs主要被锚接在GO片层的含氧基团和缺陷上, 部分Ag单质被氧化为Ag +离子并有部分GO被还原。AgNPs@GO能有效抑制铜绿假单胞菌生长, 其抑菌能力显著强于AgNPs和GO。将AgNPs@GO作为添加剂引入聚乙烯(PE)基体, 进一步制备了新型的AgNPs@GO掺杂PE复合材料0.48wt%-AgNPs@GO/PE, 相比PE和AgNPs掺杂PE复合材料, 0.48wt%-AgNPs@GO/PE具有更好的抑菌能力和更强的阻隔水蒸气性能, 并且在水和乙醇溶液中都具有较好的耐溶出性能。
中图分类号:
张峰, 张凯立, 周明明, 陈超, 蔡志威, 魏国辉, 姜兴茂, 张诚, 劳伦·鲁尔曼, 吕耀康. 基于纳米银负载氧化石墨烯的新型聚乙烯复合材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 633-640.
Feng ZHANG, Kai-Li ZHANG, Ming-Ming ZHOU, Chao CHEN, Zhi-Wei CAI, Guo-Hui WEI, Xing-Mao JIANG, Cheng ZHANG, RUHLMANN Laurent, Yao-Kang LÜ. A New Polyethylene Composite Material Based on Nano Silver Particels Loaded Graphene Oxide[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(6): 633-640.
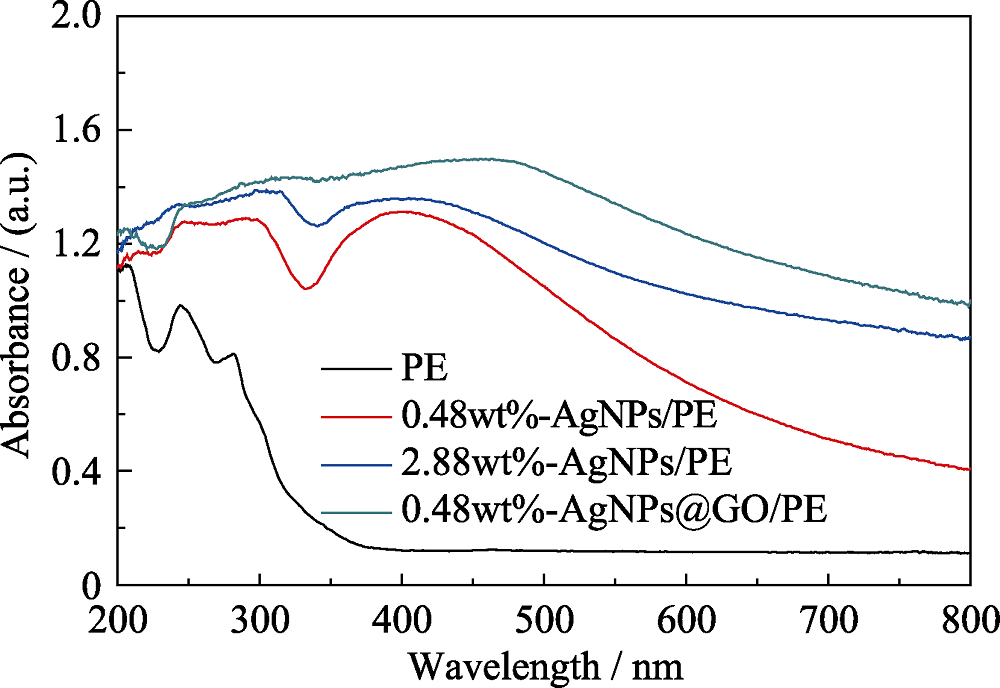
图S2 PE、0.48wt%-AgNPs/PE、2.88wt%-AgNPs/PE和0.48wt%-AgNPs@GO/PE的紫外-可见吸收光谱
Fig. S2 UV-Vis spectra of PE, 0.48wt%-AgNPs/PE, 2.88wt% -AgNPs/PE, and 0.48wt%-AgNPs@GO/PE
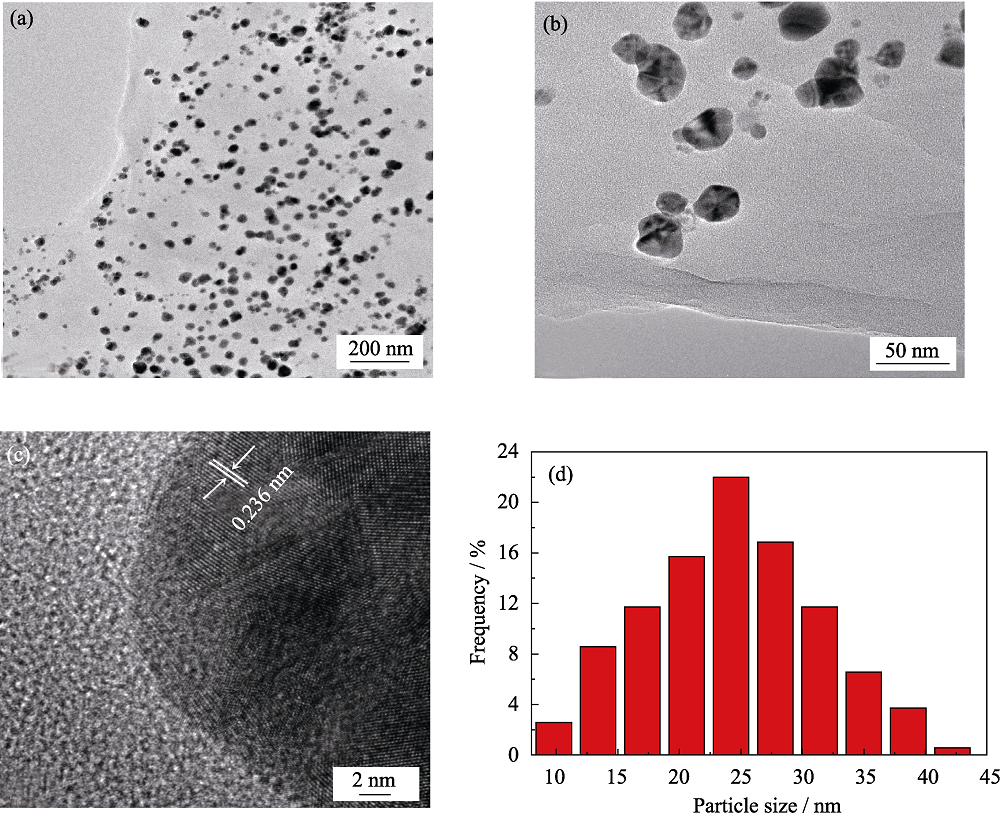
图3 AgNPs@GO的TEM(a,b)和HRTEM(c)照片以及AgNPs@GO上负载的AgNPs粒径分布的统计结果(d)
Fig. 3 TEM (a, b) and HRTEM (c) images of AgNPs@GO, and statistical result of the particle size distribution of AgNPs loaded on AgNPs@GO (d)
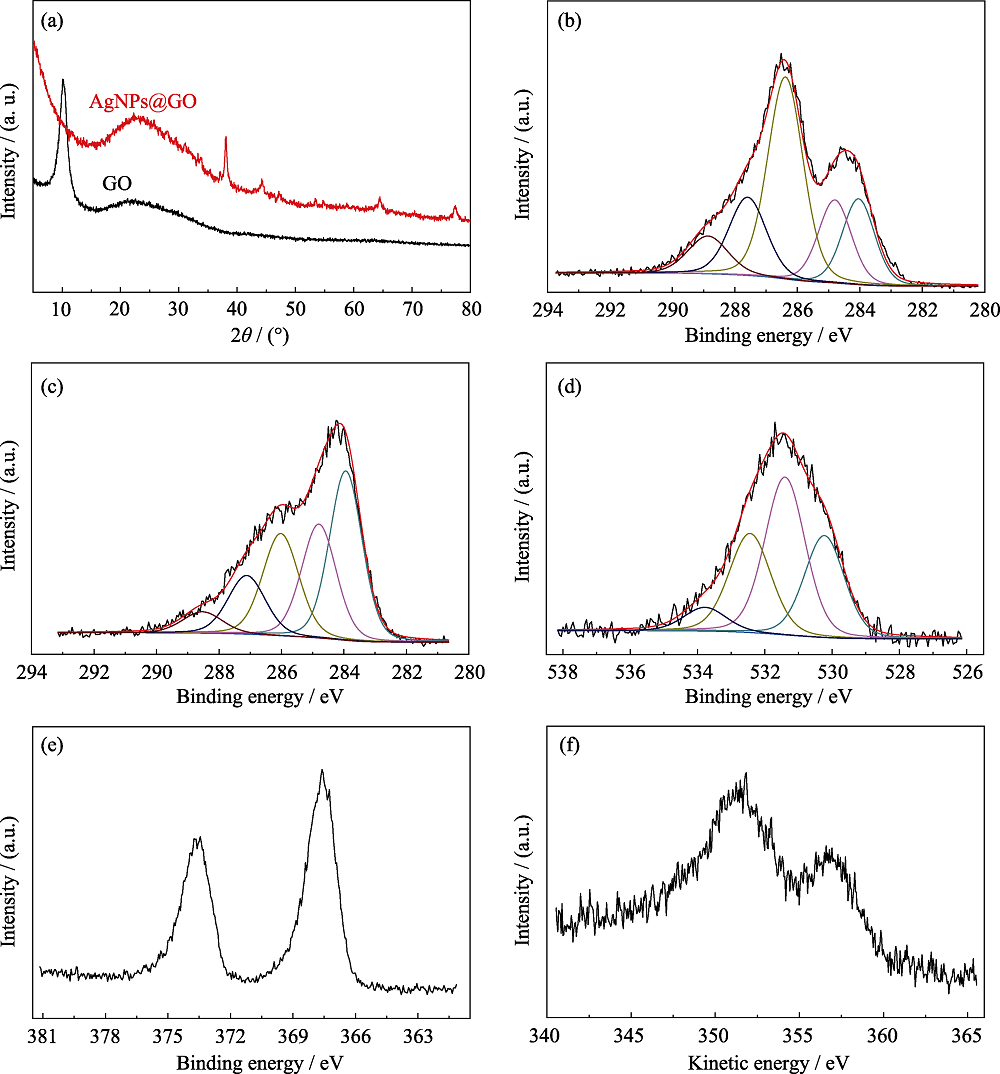
图4 GO和AgNPs@GO的XRD图谱(a); GO的XPS C1s图谱(b); AgNPS@GO的C1s(c)、O1s(d)、Ag3d(e)的XPS图谱和Ag(f)的AES 能谱
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of GO and AgNPs@GO(a); XPS C1s spectra of GO (b); XPS spectra C1s (c), O1s (d), Ag3d(e) of AgNPS@GO, and AES energy spectrum (f) of Ag
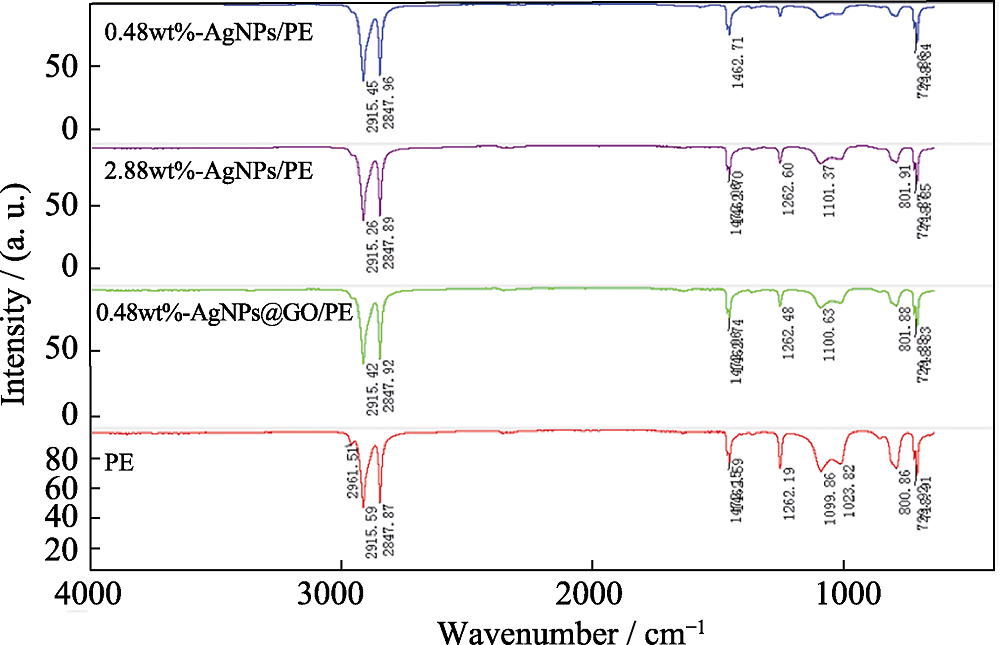
图S3 PE、0.48wt%-AgNPs/PE、2.88wt%-AgNPs/PE和0.48wt%-AgNPs@GO/PE的红外光谱
Fig. S3 IR spectra of PE, 0.48wt%-AgNPs/PE, 2.88wt%- AgNPs/PE, and 0.48wt%-AgNPs@GO/PE
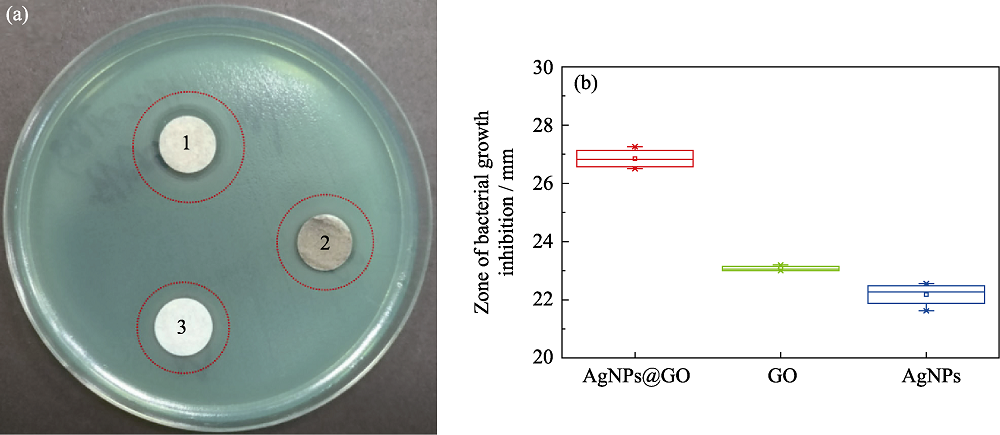
图5 AgNPs@GO、GO和AgNPs的铜绿假单胞菌的抑菌圈实验照片(a)((1)涂有AgNPs@GO的纸片, (2)涂有GO的纸片, (3)涂有AgNPs的纸片)和抑菌圈实验数据结果图(b)
Fig. 5 Photograph of inhibition zone of Pseudomonas aeruginosa ((1) paper coated with AgNPs@GO, (2) paper coated with GO, (3) paper coated with AgNPs) (a) and results of experimental data of inhibition zone of AgNPs@GO, GO and AgNPs (b)
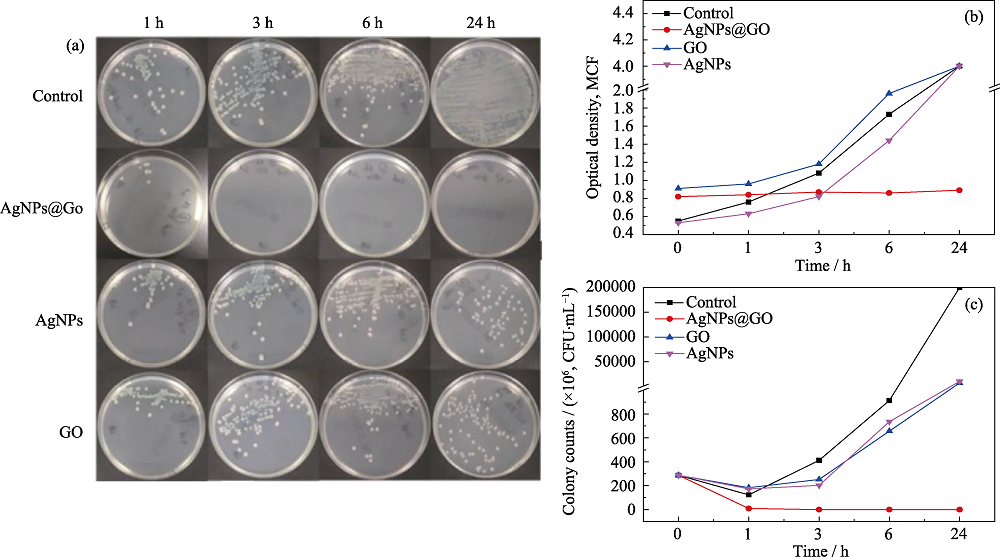
图6 不同时间取菌液接种于营养琼脂平板上进行的细菌培养照片(a)及其在不同时间的各试管中菌液的浊度(测量上限为4 MCF)(b) 和计数曲线(c)
Fig. 6 Photos (a) and turbidity (b) of the bacteria liquid in each test tube at different time (The upper limit of turbidity measurement is 4 MCF) and its counting curves of the bacterial culture on the nutrient agar plate at different time (c)
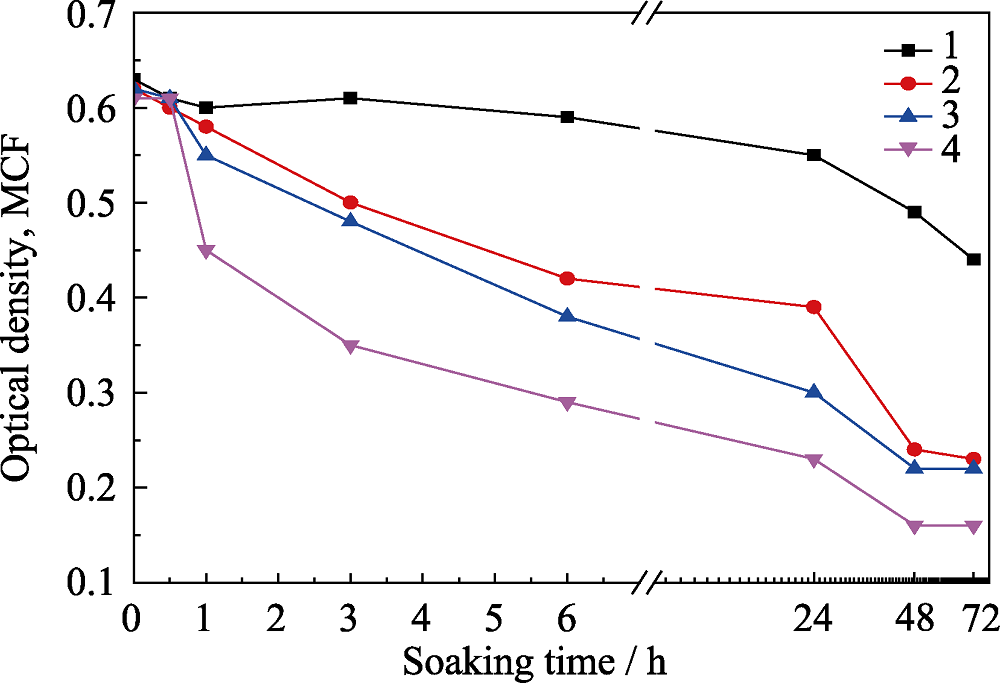
图7 抑制铜绿假单胞菌生长实验结果
Fig. 7 Inhibition of Pseudomonas aeruginosa growth test results Line 1: Blank control group; Line 2: 0.48wt%-AgNPs/PE; Line 3: 2.88wt%-AgNPs/PE; Line 4: 0.48wt%-AgNPs@GO/PE
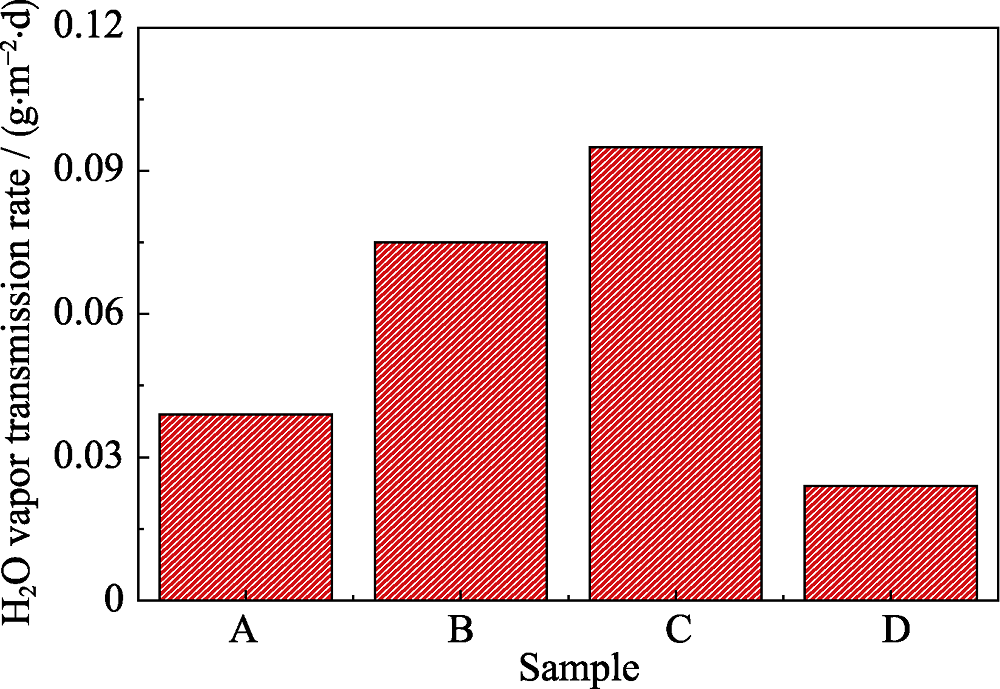
图8 水蒸气透过率实验结果 A: PE; B: 0.48wt%-AgNPs/PE; C: 2.88wt%-AgNPs/PE; D: 0.48wt%- AgNPs@GO/PE
Fig. 8 The results of water vapor transmission rate experiments
| [1] | ZAHRA S A, BUTT Y N, NASAR S , et al. Food packaging in perspective of microbial activity: a review.[J]. Microbiol. Biotech. Food Sci., 2018,6(2):752-757. |
| [2] |
LIM M, KIM D, SEO J . Enhanced oxygen-barrier and water- resistance properties of poly(vinyl alcohol) blended with poly(acrylic acid) for packaging applications. Polym. Int., 2016,65(4):400-406.
DOI URL |
| [3] |
JJOKAR M, RAHMAN R A, IBRAHIM N A , et al. Melt production and antimicrobial efficiency of low-density polyethylene (LDPE)-silver nanocomposite film. Food Bioprocess Tech., 2012,5(2):719-728.
DOI URL |
| [4] |
DAGLIA M . Polyphenols as antimicrobial agents. Curr. Opin. Biotechnol., 2012,23(2):174-181.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
KIM J S, KUK E, YU K N , et al. Antimicrobial effects of silver nanoparticles. Nanomed-Nanotechnol., 2007,3(1):95-101.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
SANCHEZ-VALDES S . Sonochemical deposition of silver nanoparticles on linear low density polyethylene/cyclo olefin copolymer blend films. Polym. Bull., 2014,71(7):1611-1624.
DOI URL |
| [7] | LUO CHEN, DONG ZHENG, LI ZHEN-XING , et al. The effect of nano-silver antibacterial package on the quality of shrimp meat during cold storage. Packging Engineering, 2018,39(7):60-64. |
| [8] | HE Y, QIAN L, LIU X , et al. Graphene oxide as an antimicrobial agent can extend the vase life of cut flowers. Nano Res., 2018: 1-13. |
| [9] |
GEORGAKILAS V, TIWARI J N, KEMP K C , et al. Noncovalent functionalization of graphene and graphene oxide for energy materials, biosensing, catalytic, and biomedical applications. Chem. Rev., 2016,116(9):5464-5519.
DOI URL |
| [10] |
PHAM T A, KUMAR N A, JEONG Y T . Covalent functionalization of graphene oxide with polyglycerol and their use as templates for anchoring magnetic nanoparticles. Synthetic Met., 2010,160(17/18):2028-2036.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
DU W, LÜ Y, LU H , et al. Surface modification by graphene oxide: an efficient strategy to improve the performance of activated carbon based supercapacitors. Chinese Chem. Lett., 2017,28(12):2285-2289.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
JI H, SUN H, QU X . Antibacterial applications of graphene-based nanomaterials: recent achievements and challenges. Adv. Drug Deliver. Rev., 2016,105:176-189.
DOI URL |
| [13] |
THAVANATHAN J, HUANG N M, THONG K L . Colorimetric detection of DNA hybridization based on a dual platform of gold nanoparticles and graphene oxide. Biosens. Bioelectron., 2014,55(10):91-98.
DOI URL |
| [14] |
RODRIGUEZ-GONZÁLEZ C, VELAZQUEZ-VILLALBA P, SALAS P , et al. Green synthesis of nanosilver-decorated graphene oxide sheets. Iet Nanobiotechnol., 2016,10(5):301-307.
DOI URL |
| [15] | DU W, LÜ Y, CAI Z , et al. Flexible all-solid-state supercapacitor based on three-dimensional porous graphene/titanium-containing copolymer composite film. Acta Phy.-Chim. Sin., 2017,33(9):1828-1837. |
| [16] | 姜兴茂, 闵建中, 黎珊 . 制备单分散超细颗粒的方法: 中国, CN104690295A. 2013. 12. 05 |
| [17] |
LU C, MAI Y W . Preparation, characterization and antibacterial properties of silver-modified graphene oxide.[J]. Mater. Chem., 2011,21(10):3350-3352.
DOI URL |
| [18] | MOULDER J F, STICKLE W F, SOBOL P E , et al. Handbook of X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy. Japan: ULVAC-PHI,Inc, 1992: 12-86. |
| [19] |
TANG J, CHEN Q, XU L , et al. Graphene oxide-silver nanocomposite as a highly effective antibacterial agent with species-specific mechanisms. ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013,5(9):3867-3874.
DOI URL |
| [20] |
DAS M R, SARMA R K, SAIKIA R , et al. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles in an aqueous suspension of graphene oxide sheets and its antimicrobial activity. Colloid. Surface. B, 2011,83(1):16-22.
DOI URL |
| [21] |
MESARO N, NORDMANN P, PLESIAT P , et al. Pseudomonas aeruginosa: resistance and therapeutic options at the turn of the new millennium. Clin. Microbiol. Infect., 2007,13(6):560-578.
DOI URL |
| [22] |
POLLACK M, YOUNG L . Protective activity of antibodies to exotoxin A and lipopolysaccharide at the onset of Pseudomonas aeruginosa septicemia in man,[J]. Clin. Invest., 1979,63(2):276-86.
DOI URL |
| [23] | SONG H, KO K, OH I , et al. Fabrication of silver nanoparticles and their antimicrobial mechanisms. Eur. Cells. Mater., 2006,11:58. |
| [24] |
FENG Q L, WU J, CHEN G Q , et al. A mechanistic study of the antibacterial effect of silver ions on Escherichia coli and Staphylococcus aureus.[J]. Biomed. Mater. Res., 2000,52(4):662-668.
DOI URL |
| [25] |
SONDI I, SALOPEK-SONDI B . Silver nanoparticles as antimicrobial agent: a case study on E. coli as a model for Gram-negative bacteria. Colloid Interface Sci., 2004,275(1):177-82.
DOI URL |
| [26] |
LIU Z, STOUT J E, BOLDIN M , et al. Intermittent use of copper- silver ionization for Legionella control in water distribution systems: a potential option in buildings housing individuals at low risk of infection. Clin. Infect. Dis., 1998,26(1):138-140.
DOI URL |
| [27] |
PARK H J, KIM J Y, KIM J , et al. Silver-ion-mediated reactive oxygen species generation affecting bactericidal activity. Water Res., 2009,43(4):1027-1032.
DOI URL |
| [28] |
ZHENG H, MA R, GAO M , et al. Antibacterial applications of graphene oxides: structure-activity relationships, molecular initiating events and biosafety. Sci. Bull., 2018,63(2):133-142.
DOI URL |
| [1] | 孙铭, 邵溥真, 孙凯, 黄建华, 张强, 修子扬, 肖海英, 武高辉. RGO/Al复合材料界面性质第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(6): 651-659. |
| [2] | 董淑蕊, 赵笛, 赵静, 金万勤. 离子化氨基酸对氧化石墨烯膜渗透汽化过程中水选择性渗透的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 387-394. |
| [3] | 李豪, 唐志红, 卓尚军, 钱荣. 基于ZIF8/rGO的高性能NO2室温传感器[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(12): 1277-1282. |
| [4] | 张伟,高鹏,侯成义,李耀刚,张青红,王宏志. 基于ZnO复合材料的芯片式pH和温度传感器[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(4): 416-422. |
| [5] | 赵超锋, 金佳人, 霍英忠, 孙陆, 艾玥洁. 氧化石墨烯吸附水体中酚类有机污染物的分子动力学模拟[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(3): 277-283. |
| [6] | 方美蓉,秦利梅,贾晓博,李永生,牛德超,胡泽岚. 聚乙烯亚胺改性的双介孔氧化硅基因载体构建[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 187-192. |
| [7] | 林启民, 崔建功, 颜鑫, 袁学光, 陈小瑜, 芦启超, 罗彦彬, 黄雪, 张霞, 任晓敏. 单点缺陷氧化石墨烯电子结构与光学特性的第一性原理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(10): 1117-1122. |
| [8] | 马志军, 莽昌烨, 赵海涛, 关智浩, 程亮. 石墨烯装载不同含量钴锌铁氧体及其电磁行为对比[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 407-416. |
| [9] | 王贵欣, 裴志彬, 叶长辉. 自供能柔性氧化石墨烯湿度传感器的喷墨印刷制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(1): 114-120. |
| [10] | 刘焕龙, 赵伟, 李睿哲, 黄谢意, 唐宇峰, 李冬梅, 黄富强. 还原氧化石墨烯原位包覆纳米MnTiO3颗粒的简易合成及储锂性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(9): 1022-1028. |
| [11] | 秦士林, 李继成, 李朝晖, 胡忠良, 丁燕怀, 雷钢铁, 肖启振. 基于共价键作用的四氧化三铁-还原氧化石墨烯复合材料的合成及其储锂性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(7): 741-748. |
| [12] | 阎鑫, 卢锦花, 惠小艳, 闫从祥, 高强, 孙国栋. g-C3N4/MoS2纳米片/氧化石墨烯三元复合催化剂的制备及可见光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(5): 515-520. |
| [13] | 王树江, 杨永恒, 温春阳, 张国馗, 苑春晖. 纳米银/伊利石复合材料的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(5): 570-576. |
| [14] | 王勇, 于云, 冯爱虎, 江峰, 胡学兵, 宋力昕. Nafion改性多级孔径石墨烯气凝胶制备与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(4): 469-474. |
| [15] | 廖 凡, 马剑琪, 葛红光. 磁性核壳Ag/PDA@SiO2@CoFe2O4复合纳米材料的制备、表征及其抑菌性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(5): 523-528. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||