无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (4): 387-393.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180263
陈仁德1,郭鹏1,左潇1,许世鹏2,柯培玲1,3,汪爱英1,3( )
)
收稿日期:2018-06-19
修回日期:2018-09-25
出版日期:2019-04-20
网络出版日期:2019-04-15
作者简介:陈仁德(1988-), 男, 硕士, 工程师. E-mail:chenrd@nimte.ac.cn
基金资助:
Ren-De CHEN1,Peng GUO1,Xiao ZUO1,Shi-Peng XU2,Pei-Ling KE1,3,Ai-Ying WANG1,3( )
)
Received:2018-06-19
Revised:2018-09-25
Published:2019-04-20
Online:2019-04-15
Supported by:摘要:
采用反应磁控溅射技术, 通过改变溅射靶电流实现了不同Ag掺杂含量0.7at%~41.4at%非晶碳膜(a-C:Ag)的可控制备, 并系统研究了Ag含量对薄膜组分、结构、机械特性的影响规律, 以及薄膜的电学特性。结果表明: 当Ag含量在0.7at%~1.2at%时, Ag原子固溶于非晶碳基质; 当Ag含量在13.0at%~41.4at%范围, 薄膜中出现尺寸约为6 nm的Ag纳米晶。随着Ag含量增加, 碳网络结构的sp 2团簇尺寸增大, 结构无序度降低。应力测试表明, 在低Ag含量范围, Ag原子固溶于碳膜网络结构中, 起到枢纽作用, 促进碳网络结构键长、键角畸变弛豫, 从而降低薄膜应力。随着Ag含量增加, 部分Ag原子将形成Ag纳米晶粒, 薄膜通过Ag纳米晶与非晶碳界面处的滑移以及扩散作用释放过高的畸变能降低应力。Ag含量为37.8at%时, 在11.6 K附近, 薄膜出现金属-半导体特性转变。而Ag含量为41.4at%的薄膜, 在2~400 K测试温度范围内, 均表现为半导体特性, 其中在164~400 K范围内, 薄膜表现出典型的热激活导电机制。
中图分类号:
陈仁德, 郭鹏, 左潇, 许世鹏, 柯培玲, 汪爱英. Ag掺杂非晶碳膜结构、力学与电学行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 387-393.
Ren-De CHEN, Peng GUO, Xiao ZUO, Shi-Peng XU, Pei-Ling KE, Ai-Ying WANG. Ag Doped Amorphous Carbon Films: Structure, Mechanical and Electrical Behaviors[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(4): 387-393.
| Sputtering current /A | Sputtering power /W | Ag concentration /at% | O concentration /at% | Thickness /nm | Deposition rate /(nm?min-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.3 | 582 | 0.7 | 30.2 | 364.5 | 18.2 |
| 1.4 | 602 | 0.8 | 26.5 | 358.3 | 17.9 |
| 1.5 | 647 | 1.2 | 27.2 | 508.5 | 25.4 |
| 1.6 | 859 | 13.0 | 45.2 | 725.4 | 36.3 |
| 1.8 | 788 | 37.8 | 32.9 | 1409.1 | 70.5 |
| 2.0 | 856 | 41.4 | 32.2 | 1720.4 | 86.0 |
表1 Ag掺杂含量、O含量、薄膜厚度和沉积速率随溅射电流和功率的变化关系
Table 1 Ag concentration, O concentration, film thickness and average deposition rate varied with sputtering current and power
| Sputtering current /A | Sputtering power /W | Ag concentration /at% | O concentration /at% | Thickness /nm | Deposition rate /(nm?min-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.3 | 582 | 0.7 | 30.2 | 364.5 | 18.2 |
| 1.4 | 602 | 0.8 | 26.5 | 358.3 | 17.9 |
| 1.5 | 647 | 1.2 | 27.2 | 508.5 | 25.4 |
| 1.6 | 859 | 13.0 | 45.2 | 725.4 | 36.3 |
| 1.8 | 788 | 37.8 | 32.9 | 1409.1 | 70.5 |
| 2.0 | 856 | 41.4 | 32.2 | 1720.4 | 86.0 |

图1 不同Ag掺杂含量a-C:Ag薄膜的C1s精细XPS图谱(a)和Ag含量为41.4at%薄膜的Ag3d精细XPS图谱(b)
Fig. 1 Typical XPS spectra for the a-C:Ag films (a), and representative Ag 3d spectra of the films with 41.4at% Ag (b)
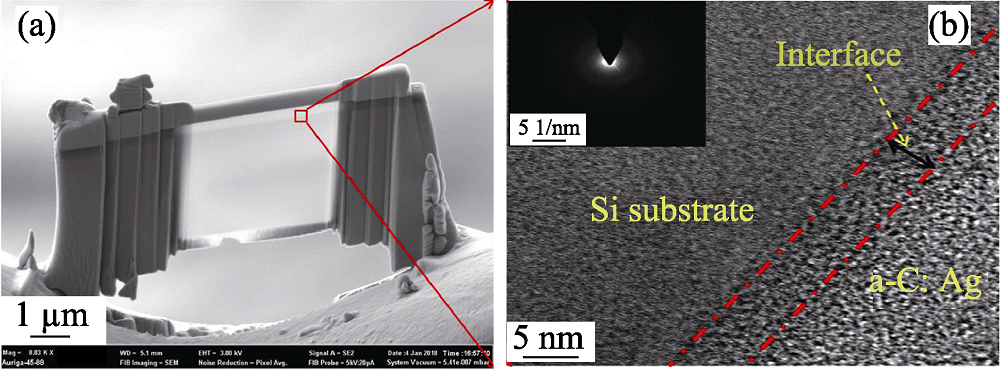
图3 掺杂含量1.2at%的a-C:Ag薄膜FIB样品形貌(a), 界面处的透射电子显微高分辨照片以及a-C:Ag薄膜选区电子衍射花样(b)
Fig. 3 (a) Sample for TEM prepared by FIB, (b) HRTEM and SAED of sample with 1.2at% a-C:Ag
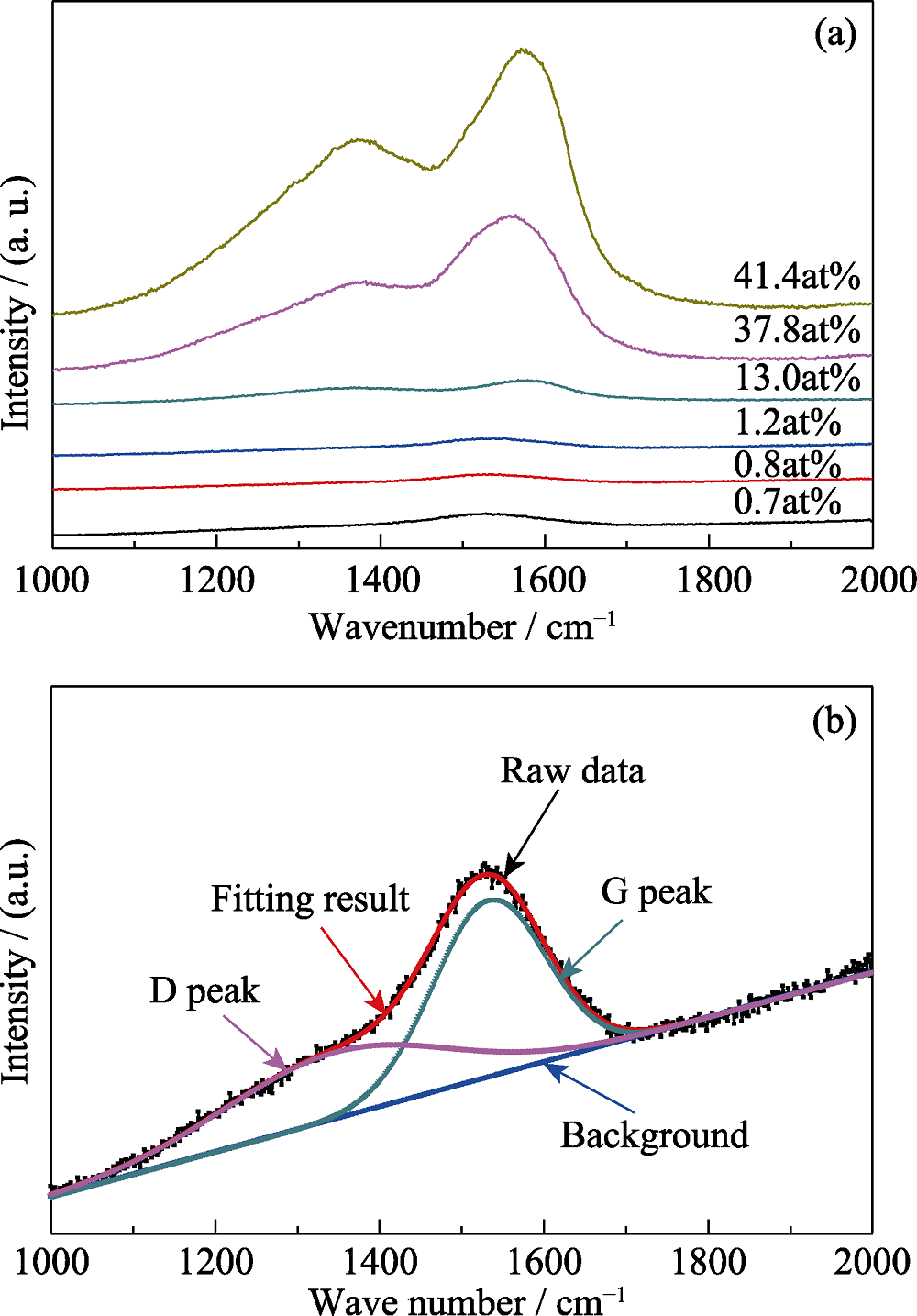
图4 不同Ag掺杂含量a-C:Ag的Raman光谱图(a), 掺杂含量0.7at%的a-C:Ag的Raman拟合结果(b)
Fig. 4 Typical Raman spectra a-C:Ag films with different Ag concentrations (a) and the fitting result of a-C:Ag film with 0.7at% Ag atoms (b)
| Ag concentration /at% | G-peak position/cm-1 | ID/IG | FWHM of G-peak/cm-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 1533.0 | 0.75 | 159.4 |
| 0.8 | 1535.9 | 0.79 | 151.6 |
| 1.2 | 1539.8 | 0.85 | 151.4 |
| 13.0 | 1582.5 | 1.94 | 122.5 |
| 37.8 | 1566.4 | 2.15 | 123.6 |
| 41.4 | 1580.7 | 2.68 | 110.0 |
表2 不同Ag掺杂含量a-C:Ag的Raman拟合结果
Table 2 The fitted G-peak position, ID/IG and FWHM of G-peak varied with different Ag concentrations
| Ag concentration /at% | G-peak position/cm-1 | ID/IG | FWHM of G-peak/cm-1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.7 | 1533.0 | 0.75 | 159.4 |
| 0.8 | 1535.9 | 0.79 | 151.6 |
| 1.2 | 1539.8 | 0.85 | 151.4 |
| 13.0 | 1582.5 | 1.94 | 122.5 |
| 37.8 | 1566.4 | 2.15 | 123.6 |
| 41.4 | 1580.7 | 2.68 | 110.0 |
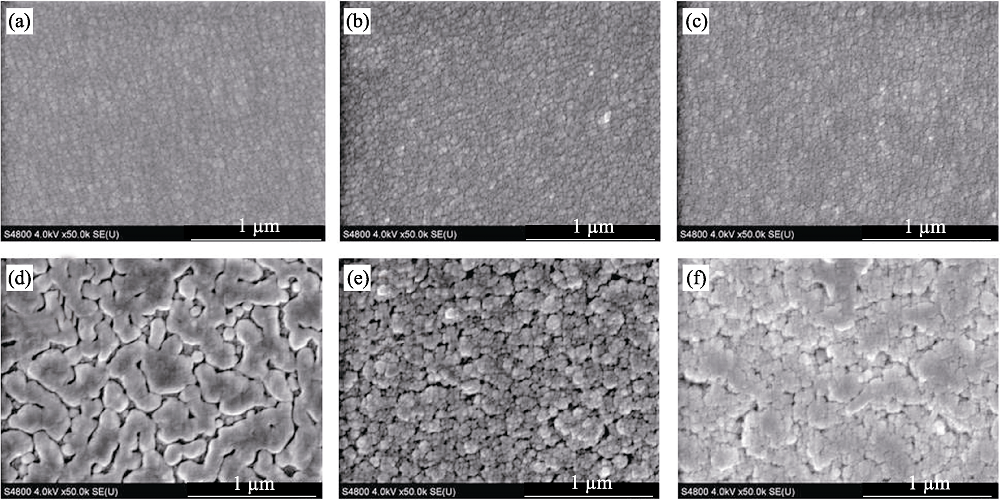
图5 不同Ag含量a-C:Ag表面SEM形貌
Fig. 5 Surface topographies of a-C:Ag films with different Ag concentrations (a) 0.7at%; (b) 0.8at%; (c) 1.2at%; (d) 13.0at%; (e) 37.8at%; (f) 41.4at%
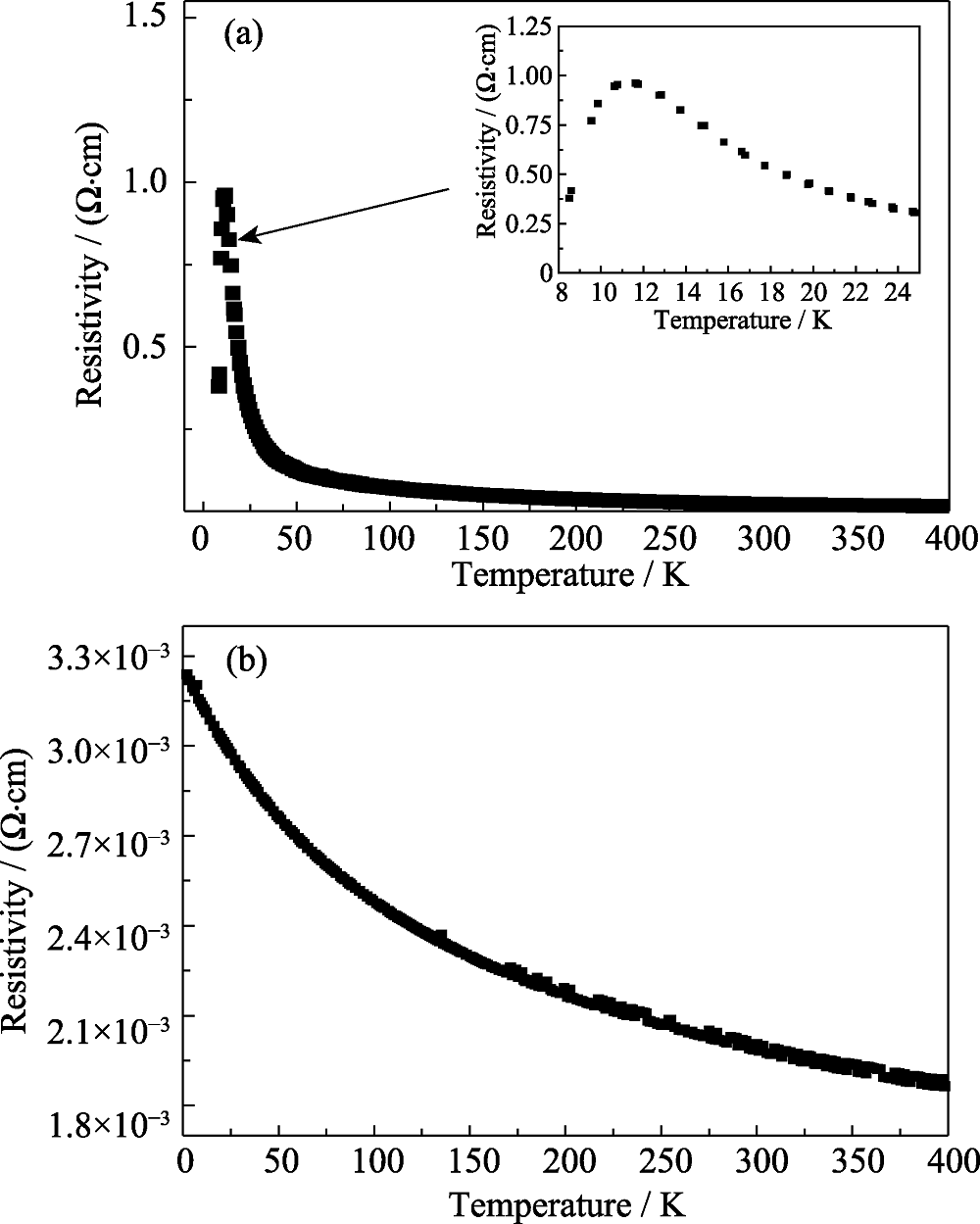
图8 (a)在8~400 K测试温度范围内, 掺杂含量为37.8at%的a-C:Ag电阻率随温度的变化曲线, 插图是2~24 K区域的放大图;(b)在2~400 K测试温度范围内, 金属含量为41.4at%的a-C:Ag电阻率随温度的变化曲线
Fig. 8 Temperature dependence of resistivity in a-C:Ag film with 37.8at% Ag in the range of 8~400 K (a) and the a-C:Ag with 41.4at% Ag in the range of 2~400 K (b)
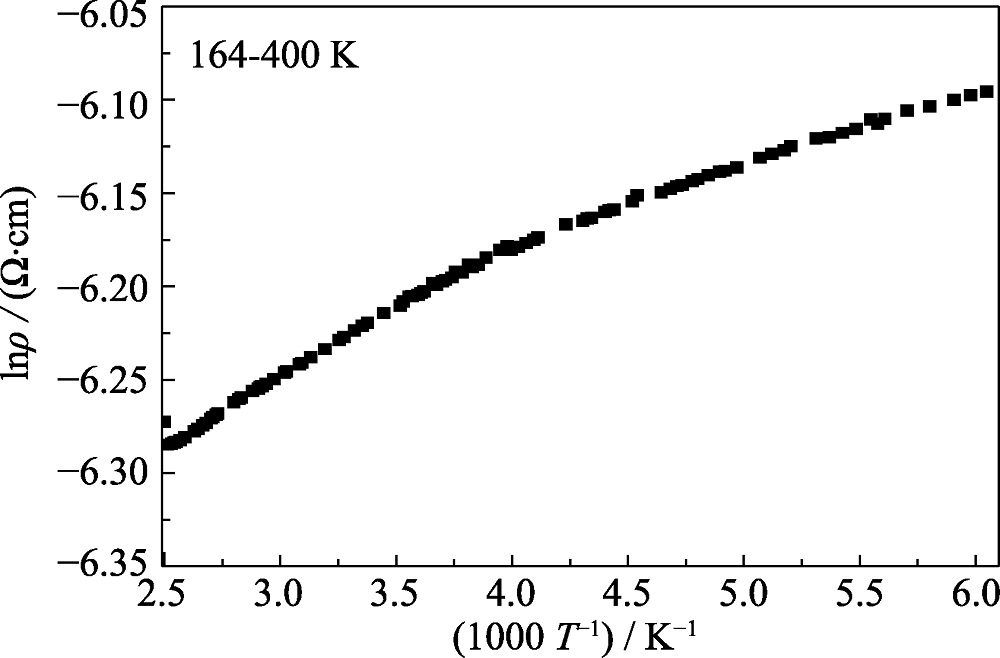
图9 Ag含量为41.4at%的a-C:Ag的lnρ 随1000/T变化关系曲线, 温度区间164~400 K
Fig. 9 Plot of lnρ vs reciprocal temperature in the range of 164-400 K for a-C:Ag film with 41.4at% Ag
| [1] | 薛群基, 王立平 . 类金刚石碳基薄膜材料. 北京: 科学出版社, 2012. |
| [2] | ROBERTSON J . Diamond-like amorphous carbon. Mater. Sci. Eng.B, 2002,37(4/5/6):129-281. |
| [3] | DAI W . Research on the synthesis, structure and properties of metal doped diamond-like carbon nanocomposite films. New Technology & New Process, 2015,7:128-131. |
| [4] | ZHANG S, WU Y, ZHU L , et al. Research progress of metal doped diamond-like carbon films. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2017,13:77-82. |
| [5] | TAMULEVICIUS S, MESKINIS S, TAMULEVICIUS T , et al. Diamond like carbon nanocomposites with embedded metallic nanoparticles. Rep. Prog. Phys., 2018, 81(2): 024501-1-31. |
| [6] | PU J, WANG L, XUE Q . Progress in strengthening and toughening carbon-based films. China Surface Engineering, 2014,27(6):4-27. |
| [7] | WU Y, CHEN J, LI H , et al. Preparation and properties of Ag/DLC nanocomposite films fabricated by unbalanced magnetron sputtering. Appl. Surf.Sci, 2013,284:165-170. |
| [8] | MAZARE A, ANGHEL A, SURDU-BOB C , et al. Silver doped diamond-like carbon antibacterial and corrosion resistance coatings on titanium. Thin Solid Films, 2018,657:16-23. |
| [9] | CONSTANTINOU M, PERVOLARAKI M, NIKOLAOU P , et al. Microstructure and nanomechanical properties of pulsed excimer laser deposited DLC:Ag films: enhanced nanotribological response. Surf. Coat. Technol, 2017,309:320-330. |
| [10] | DWIVEDI N, KUMAR S, CAREY J D , et al. Influence of silver incorporation on the structural and electrical properties of diamond-like carbon thin films. ACS Appl Mater Interfaces, 2013,5:2725-2732. |
| [11] | MEŠKINIS Š, VASILIAUSKAS A, ŠLAPIKAS K , et al. Bias effects on structure and piezoresistive properties of DLC:Ag thin films. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2014,255:84-89. |
| [12] | PEINER E, TIBREWALA A, BANDORF R , et al. Diamond-like carbon for MEMS.[J]. Micromech. Microeng., 2007,17(7):S83-S90. |
| [13] | CHUA D H C, MILNE W I, SHEEJA D , et al. Fabrication of diamond- like amorphous carbon cantilever resonators. J. Vac. Sci. Technol. B, 2004,22(6):2680-2684. |
| [14] | SARSEMBINOV S S, PRIKHODKO O Y, RYAGUZOV A P , et al. Electronic properties of diamond-like carbon films modified by silver nanoclusters. Phys. Status Solidi C, 2009,7:805-807. |
| [15] | ABDOLGHADERI S, ASTINCHAP B, SHAFIEKHANI A . Electrical percolation threshold in Ag-DLC nanocomposite films prepared by RF-sputtering and RF-PECVD in acetylene plasma. J Mater Sci: Mater Electron, 2016,27(7):6713-6720. |
| [16] | MUSIL J, LOUDA M, SOUKUP Z , et al. Relationship between mechanical properties and coefficient of friction of sputtered a-C/Cu composite thin films. Diamond Relat. Mater., 2008,17(11):1905-1911. |
| [17] | MATSUNAMI N, YAMAMURA Y, ITIKAWA Y , et al. Energy dependence of the ion-induced sputtering yields of monatomic solids. At. Data Nucl.Data Tables, 1984,31:1-80. |
| [18] | SMENTKOWSKI V S . Trends in sputtering. Prog. Surf. Sci., 2000,64:1-58. |
| [19] | TAKI T, TAKAI O . XPS structural characterization of hydrogenated amorphous carbon thin films prepared by shielded arc ion plating. Thin Solid Films, 1998,316:45-50. |
| [20] | KIM H W, LEE N E . Conformal electroless filling of Cu into patterned amorphous carbon layer modified by oxygen plasma and aminosilane treatments. J. Vac. Sci. Technol.B, 2010,28(4):715-719. |
| [21] | WARREN B E . X-ray diffraction, New edition, US: Dover Publications, 1990. |
| [22] | FERRARI A C, ROBERTSON J . Interpretation of Raman spectra of disordered and amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev.B, 2000,61(20):14095-14107. |
| [23] | FERRARI A C, ROBERTSON J . Resonant Raman spectroscopy of disordered,amorphous,diamondlike carbon. Phys. Rev. B, 2001, 64(7): 075414-1-13. |
| [24] | CASIRAGHI C, FERRARI A C, ROBERTSON J. Raman spectroscopy of hydrogenated amorphous carbon. Phys. Rev. B, 2005, 72: 085401-1-14. |
| [25] | ZOU C W, WANG H J, FENG L , et al. Effects of Cr concentrations on the microstructure, hardness, and temperature-dependent tribological properties of Cr-DLC coatings. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013,286:137-141. |
| [26] | DAI W, KE P, MOON M W , et al. Investigation of the microstructure, mechanical properties and tribological behaviors of Ti- containing diamond-like carbon films fabricated by a hybrid ion beam method. Thin Solid Films, 2012,520(19):6057-6063. |
| [27] | QUAN J, ZHANG J, QI X , et al. A study on the correlation between the dewetting temperature of Ag film and SERS intensity. Sci. Rep., 2017,7(1):14771-14782. |
| [28] | GUO P, SUN L, LI X , et al. Structural properties and surface wettability of Cu-containing diamond-like carbon films prepared by a hybrid linear ion beam deposition technique. Thin Solid Films, 2015,584:289-293. |
| [29] | SINGH V, JIANG J C, MELETIS E I . Cr-diamondlike carbon nanocomposite films: synthesis, characterization and properties. Thin Solid Films, 2005,489(1/2):150-158. |
| [30] | SONODA T, NAKAO S, IKEYAMA M . Deposition of Ti/C nano-composite DLC films by magnetron DC sputtering with dual targets. Vacuum, 2009,84(5):666-668. |
| [31] | WANG A Y, LEE K R, AHN J P , et al. Structure and mechanical properties of W incorporated diamond-like carbon films prepared by a hybrid ion beam deposition technique. Carbon, 2006,44(9):1826-1832. |
| [32] | GUO P, LI X, SUN L , et al. Stress reduction mechanism of diamond- like carbon films incorporated with different Cu contents. Thin Solid Films, 2017,640:45-51. |
| [33] | DONNET C, ERDEMIR A . Tribology of Diamond-like Carbon Films. US: Springer, 2008. |
| [34] | WAN C, ZHANG X, VANACKEN J , et al. Electro- and magneto- transport properties of amorphous carbon films doped with iron. Diamond Relat. Mater., 2011,20(1):26-30. |
| [35] | TAKENO T, MIKI H, TAKAGI T , et al. Electrically conductive properties of tungsten-containing diamond-like carbon films. Diamond Relat. Mater., 2006,15(11/12):1902-1905. |
| [36] | HUANG Q F, YOON S F, RUS LI , et al. Conduction mechanism in molybdenum-containing diamond-like carbon deposited using electron cyclotron resonance chemical vapor deposition.[J]. Appl. Phys., 2000,88(7):4191-4195. |
| [1] | 魏婷婷, 高希光, 宋迎东. 2D SiC/SiC复合材料电阻率对服役环境的响应特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(4): 420-426. |
| [2] | 刘云鹏, 盛伟繁, 吴忠华. 同步辐射及其在无机材料中的应用进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 901-918. |
| [3] | 夏芳芳, 王发坤, 胡海龙, 许翔, 李阳, 翟天佑. 二次谐波在二维材料结构表征中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1022-1030. |
| [4] | 李汉超, 刘盼盼, 孙丽丽, 柯培玲, 崔平, 汪爱英. 金属催化非晶碳转化制备石墨烯方法的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(6): 587-595. |
| [5] | 李蕾, 郭鹏, 刘林林, 孙丽丽, 柯培玲, 汪爱英. 金属过渡层类型对非晶碳膜结构性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(3): 331-338. |
| [6] | 魏菁, 李汉超, 柯培玲, 汪爱英. 不同厚度四面体非晶碳薄膜的高通量制备及表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(11): 1173-1178. |
| [7] | 李 磊, 梁笠智, 吴 恒, 梁 爽, 朱瑛莺, 朱信华. 钙钛矿锰氧化物低维纳米结构研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(4): 337-344. |
| [8] | 原子健,朱夏明,王 雄,张莹莹,万正芬,邱东江,吴惠桢,杜滨阳. 氧化铟薄膜制备及其特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 15(2): 141-144. |
| [9] | 郑遗凡, 陆月萍, 莫卫民, 李国华, 赵 娜. WC/TiO2纳米复合材料的微结构及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2010, 25(11): 1139-1144. |
| [10] | 孙金峰,李晓普,梁宝岩,赵玉成,王明智. 反应球磨钛与尿素制备氮化钛的反应机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(4): 759-763. |
| [11] | 马小叶,姜雪宁,孟宪芹,庞胜利,孟昕,张庆瑜. 沉积温度对Gd掺杂CeO2电解质薄膜生长及电学特性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(5): 912-916. |
| [12] | 张化宇,檀满林,韩杰才,朱嘉琦,贾泽纯. 掺硼四面体非晶碳膜的微观结构及光谱表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(1): 180-184. |
| [13] | 刘爱萍,朱嘉琦,韩杰才,韩潇,吴化平. 掺磷四面体非晶碳薄膜电极的电化学伏安特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(6): 1056-1060. |
| [14] | 肖慧明,王建明. Al含量对α-Ni(OH)2结构及其电化学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2004, 19(3): 463-470. |
| [15] | 王智民,韩基新,刘静波. 掺镧改性钛酸钡湿敏陶瓷元件[J]. 无机材料学报, 2002, 17(6): 1187-1193. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||