无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (3): 335-340.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180273
檀小芳1,2, 端思晨1, 王泓翔1,3, 吴庆松4, 李苗苗5, 刘国强1,3, 徐静涛1,3, 谈小建1, 3, 邵和助1,3, 蒋俊1,3
收稿日期:2018-06-21
出版日期:2019-03-20
网络出版日期:2019-02-26
作者简介:檀小芳. E-mail: txf082@mail.ustc.edu.cn
TAN Xiao-Fang1,2, DUAN Si-Chen1, WANG Hong-Xiang1,3, WU Qing-Song4, LI Miao-Miao5, LIU Guo-Qiang1,3, XU Jing-Tao1,3, TAN Xiao-Jian1,3, SHAO He-Zhu1,3, JIANG Jun1,3
Received:2018-06-21
Published:2019-03-20
Online:2019-02-26
About author:TAN Xiao-Fang (1993-), female, Master. E-mail: txf082@mail.ustc.edu.cn
Supported by:摘要:
碲化锡(SnTe)是一种碲化铅的无铅替代物, 在热电领域有广阔的应用前景。但是, 纯相碲化锡样品具有较高的热导率与较低的塞贝克系数, 导致热电性能较差。本研究通过多重掺杂可以显著降低热导率, 提升塞贝克系数, 从而提升热电性能。SnTe热压样品的晶格热导率随着Se和S的引入明显降低,比如SnTe0.7S0.15Se0.15室温下晶格热导率仅为0.99 W•m-1•K-1。透射电子显微镜显示, SnTe掺杂样品内存在大量的纳米沉淀相与晶格位错。在此基础上, 掺杂In在价带顶引入共振态大幅提高了样品的塞贝克系数。实验表明通过多重掺杂可以有效提升碲化锡的热电性能, 其中样品Sn0.99In0.01Te0.7S0.15Se0.15在850 K时峰值ZT值达到0.8, 这说明碲化锡的确是一种有应用前景的中温区热电材料。
中图分类号:
檀小芳, 端思晨, 王泓翔, 吴庆松, 李苗苗, 刘国强, 徐静涛, 谈小建, 邵和助, 蒋俊. 多掺杂协同调控碲化锡热导率和功率因子提升热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(3): 335-340.
TAN Xiao-Fang, DUAN Si-Chen, WANG Hong-Xiang, WU Qing-Song, LI Miao-Miao, LIU Guo-Qiang, XU Jing-Tao, TAN Xiao-Jian, SHAO He-Zhu, JIANG Jun. Multi-doping in SnTe: Improvement of Thermoelectric Performance due to Lower Thermal Conductivity and Enhanced Power Factor[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(3): 335-340.
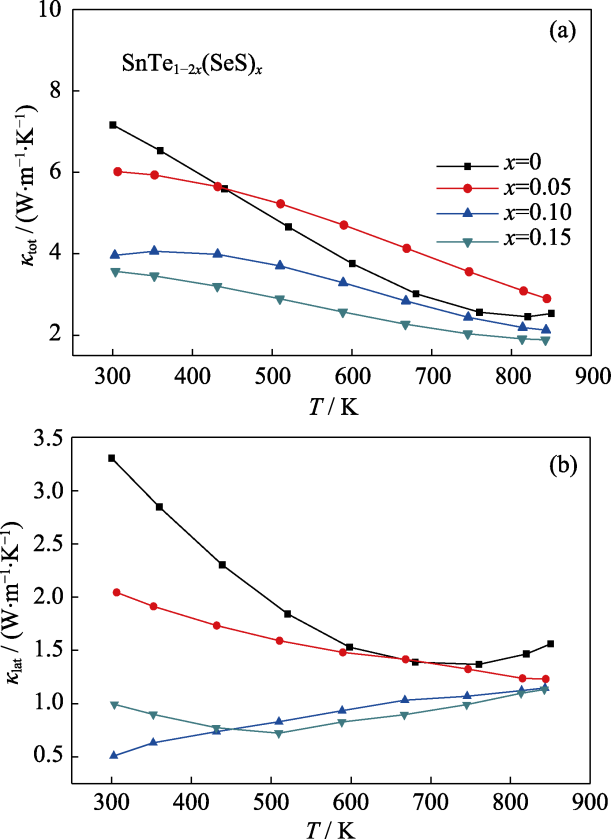
Fig.1 Temperature-dependent (a) total thermal conductivities(κtot) and (b) lattice thermal conductivities (κlat) of SnTe1-2xSxSex (x = 0, 0.05, 0.1, and 0.15) samples

Fig. 2 Temperature-dependent (a) total thermal conductivities(κtot) and (b) lattice thermal conductivities (κlat) of Sn1-yInyTe0.7S0.15Se0.15 (y=0, 0.0025, 0.005, 0.01, and 0.015) samples

Fig.3 Microstructures of Sn0.99In0.01Te0.7S0.15Se0.15(a) Medium-magnification TEM and (b) low-magnification images show the presence of nanoscale secondary phase; The inset in (a) is the SAED pattern along [004]; (c) HRTEM image focusing on the secondary phase with distorted connection between the precipitate and the matrix; The top-right and bottom-right insets are the respective FFT images showing lattice distortion between them; (d) the same TEM image with (c) showing the IFFT image (the bottom-right inset) of the selected region reflecting lattice distortion; and strain maps reflect high strain states inside (e) and around (f) the precipitates

Fig.4 Temperature dependent thermoelectric properties: (a) electrical conductivity σ, (b) the Seebeck coefficients S,(c) the power factors S2σ, and (d) ZT values for Sn1-yInyTe0.7S0.15Se0.15 (y=0, 0.0025, 0.005, 0.01, and 0.015) samples
| Samples | ρ/(g•cm-3) | N/(× 1020, cm-3) | μ/(cm2•V-1•s-1) | σ/(S•cm-1) | S/(μV•K-1) | S2σ/(μW•cm-1•K-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y=0 | 6.247 | 1.3 | 164 | 3480 | 7.6 | 0.2 |
| y=0.0025 | 6.209 | 1.4 | 100 | 2300 | 34 | 2.7 |
| y=0.005 | 6.161 | 1.6 | 57 | 1510 | 50 | 3.7 |
| y=0.01 | 6.161 | 2.0 | 39 | 1240 | 63 | 4.9 |
| y=0.015 | 6.195 | 2.2 | 26 | 910 | 71 | 4.6 |
Table 1 The density ρ, hole concentration n, mobility μ, electrical conductivity σ, Seebeck coefficient S, and power factor S2σ for Sn1-yInyTe0.7S0.15Se0.15 (y=0, 0.0025, 0.005, 0.01, and 0.015) samples at room temperature
| Samples | ρ/(g•cm-3) | N/(× 1020, cm-3) | μ/(cm2•V-1•s-1) | σ/(S•cm-1) | S/(μV•K-1) | S2σ/(μW•cm-1•K-2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| y=0 | 6.247 | 1.3 | 164 | 3480 | 7.6 | 0.2 |
| y=0.0025 | 6.209 | 1.4 | 100 | 2300 | 34 | 2.7 |
| y=0.005 | 6.161 | 1.6 | 57 | 1510 | 50 | 3.7 |
| y=0.01 | 6.161 | 2.0 | 39 | 1240 | 63 | 4.9 |
| y=0.015 | 6.195 | 2.2 | 26 | 910 | 71 | 4.6 |
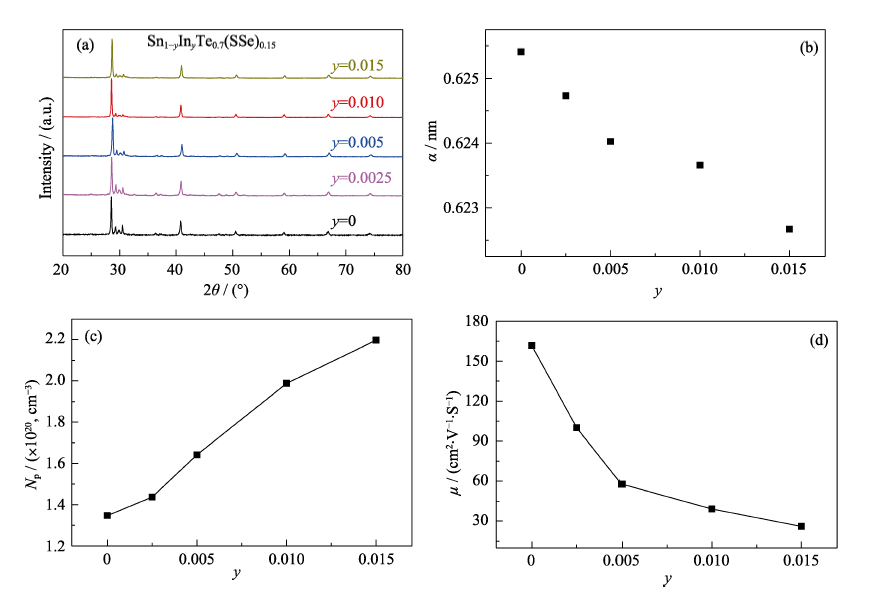
Fig.S3 Room temperature (a) powder XRD patterns, (b) lattice parameter a, (c) Hall carrier density Np, and (d) carrier mobility μ of Sn1-yInyTe0.7S0.15Se0.15 (y=0, 0.0025, 0.005, 0.01, and 0.015) samples
| [1] | SOOTSMAN J R, CHUNG D Y, KANATZIDIS M G.New and old concepts in thermoelectric materials.Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2009, 48(46): 8616-8639. |
| [2] | KANATZIDIS M G.Nanostructured thermoelectrics: the new paradigm? Chemistry of Materials, 2009, 22(3): 648-659. |
| [3] | ZHAO L D, DRAVID V P, KANATZIDIS M G.The panoscopic approach to high performance thermoelectrics. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 7(1): 251-268. |
| [4] | VINEIS C J, SHAKOURI A, MAJUMDAR A, et al.Nanostructured thermoelectrics: big efficiency gains from small features. Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(36): 3970-3980. |
| [5] | HEREMANS J P, JOVOVIC V, TOBERER E S, et al.Enhancement of thermoelectric efficiency in PbTe by distortion of the electronic density of states. Science, 2008, 321(5888): 554-557. |
| [6] | JAWORSKI C M, KULBACHINSKII V, HEREMANS J P. Resonant level formed by tin in Bi2Te3 and the enhancement of room-temperature thermoelectric power. Physical Review B, 2009, 80(23): 233201-1-4. |
| [7] | BILC D, MAHANTI S D, QUAREZ E, et al. Resonant states in the electronic structure of the high performance thermoelectrics AgPbmSbTe2+m: the role of Ag-Sb microstructures. Physical Review Letters, 2004, 93(14): 146403-1-4. |
| [8] | AHN K, HAN M K, HE J, et al.Exploring resonance levels and nanostructuring in the PbTe-CdTe system and enhancement of the thermoelectric figure of merit. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(14): 5227-5235. |
| [9] | AHMAD S, MAHANTI S D, HOANG K, et al. Ab initio studies of the electronic structure of defects in PbTe. Physical Review B, 2006, 74(15): 155205-1-13. |
| [10] | ZHANG Q, WANG H, LIU W, et al.Enhancement of thermoelectric figure-of-merit by resonant states of aluminium doping in lead selenide. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(1): 5246-5251. |
| [11] | HEREMANS J P, WIENDLOCHA B, CHAMOIRE A M.Resonant levels in bulk thermoelectric semiconductors. Energy & Environmental Science, 2012, 5(2): 5510-5530. |
| [12] | PEI Y, SHI X, LALONDE A, et al.Convergence of electronic bands for high performance bulk thermoelectrics. Nature, 2011, 473(7345): 66. |
| [13] | LIU W, TAN X, YIN K, et al. Convergence of conduction bands as a means of enhancing thermoelectric performance of n-type Mg2Si1-xSnx solid solutions. Physical Review Letters, 2012, 108(16): 166601- 1-5. |
| [14] | ZHAO L D, WU H J, HAO S Q, et al.All-scale hierarchical thermoelectrics: MgTe in PbTe facilitates valence band convergence and suppresses bipolar thermal transport for high performance. Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(11): 3346-3355. |
| [15] | YANG J, MEISNER G P, CHEN L.Strain field fluctuation effects on lattice thermal conductivity of ZrNiSn-based thermoelectric compounds. Applied Physics Letters, 2004, 85(7): 1140-1142. |
| [16] | ABELES B.Lattice thermal conductivity of disordered semiconductor alloys at high temperatures. Physical Review, 1963, 131(5): 1906-1911. |
| [17] | ZEIER W G, PEI Y, POMREHM G, et al.Phonon scattering through a local anisotropic structural disorder in the thermoelectric solid solution Cu2Zn1-xFexGeSe4. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(2): 726-732. |
| [18] | TAN G, LIU W, CHI H, et al.Realization of high thermoelectric performance in p-type unfilled ternary skutterudites FeSb2+xTe1-xvia band structure modification and significant point defect scattering. Acta Materialia, 2013, 61(20): 7693-7704. |
| [19] | ZHAO L D,TAN G,HAO S, et al.Ultrahigh power factor and thermoelectric performance in hole-doped single-crystal SnSe. Science, 2015, 351(6269): 141-144. |
| [20] | MINNICH A J, DRESSELHAUS M S, REN Z F, et al.Bulk nanostructured thermoelectric materials: current research and future prospects. Energy & Environmental Science, 2009, 2(5): 466-479. |
| [21] | ZHANG Q, LIAO B, LAN Y, et al.High thermoelectric performance by resonant dopant indium in nanostructured SnTe. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 2013, 110(33): 13261-13266. |
| [22] | TAN G, LIU W, WANG S, et al.Rapid preparation of CeFe4Sb12 Skutterudite by melt spinning: rich nanostructures and high thermoelectric performance. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2013, 1(40): 12657-12668. |
| [23] | ZHAO L D, LO S H, HE J, et al.High performance thermoelectrics from earth-abundant materials: enhanced figure of merit in PbS by second phase nanostructures. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2011, 133(50): 20476-20487. |
| [24] | ZHAO L D, HE J, WU C I, et al.Thermoelectrics with earth abundant elements: high performance p-type PbS nanostructured with SrS and CaS. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(18): 7902-7912. |
| [25] | ZHAO L D, HE J, HAO S, et al.Raising the thermoelectric performance of p-type PbS with endotaxial nanostructuring and valence-band offset engineering using CdS and ZnS. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(39): 16327-16336. |
| [26] | LEE Y, LO S H, ANDROULAKIS J, et al.High-performancetellurium-free thermoelectrics: all-scale hierarchical structuring of p-type PbSe-MSe systems (M=Ca, Sr, Ba). Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(13): 5152-5160. |
| [27] | BISWAS K, HE J, ZHANG Q, et al.Strained endotaxial nanostructures with high thermoelectric figure of merit. Nature Chemistry, 2011, 3(2): 160-166. |
| [28] | BISWAS K, HE J, BLUM I D, et al.High-performance bulk thermoelectrics with all-scale hierarchical architectures. Nature, 2012, 489(7416): 414-418. |
| [29] | TAN G, ZHENG Y, TANG X. High thermoelectric performance of nonequilibrium synthesized CeFe4Sb12 composite with multi-scaled nanostructures. Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 103(18): 7837-1-5. |
| [30] | TAN G J, SHI F Y, HAO S Q, et al.Valence band modification and high thermoelectric performance in SnTe heavily alloyed with MnTe. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015,137(35):11507-11516. |
| [31] | ROGERS L M.Drift mobility of light-mass holes in PbTe heavily doped with Na. Journal of Physics D Applied Physics, 1968, 1(8): 1067. |
| [32] | HE J, XU J, LIU G, et al.Enhanced thermopower in rock-salt SnTe-CdTe from band convergence. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(38): 32189-32192. |
| [33] | TAN G, ZHAO L D, SHI F, et al.High thermoelectric performance of p-type SnTe via a synergistic band engineering and nanostructuring approach. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(19):7006-7017. |
| [34] | TAN G J, SHI F Y, HAO S Q, et al.Codoping in SnTe: enhancement of thermoelectric performance through synergy of resonance levels and band convergence. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(15): 5100-5112. |
| [35] | TAN G, SHI F, DOAK J, et al.Extraordinary role of Hg in enhancing the thermoelectric performance of p-type SnTe. Energy & Environmental Science, 2014, 8(1): 267-277. |
| [36] | WEN L, ZHENG L, GE B, et al. Promoting SnTe as an eco-friendly solution for p-PbTe thermoelectric via band convergence and interstitial defects. Advanced Materials, 2017, 29(17): 1605887-1-8. |
| [37] | HE J, TAN X, XU J, et al.Valence band engineering and thermoelectric performance optimization in SnTe by Mn-alloying via a zone-melting method. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(39): 19974-19979. |
| [38] | TAN G J, SHI F Y, HAO S Q, et al.Valence band modification and high thermoelectric performance in SnTe heavily alloyed with MnTe. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2015, 137(35): 11507-11516. |
| [39] | LI W, CHEN Z, LIN S, et al.Band and scattering tuning for high performance thermoelectric Sn1-xMnxTe alloys. Journal of Materiomics, 2015, 1(4): 307-315. |
| [40] | ZHENG L, LI W, LIN S, et al.Interstitial defects improving thermoelectric SnTe in addition to band convergence. ACS Energy Letters, 2017, 2(3): 563-568. |
| [41] | WU H, CHANG C, FENG D, et al.Synergistically optimized electrical and thermal transport properties of SnTe via alloying high-solubility MnTe. Energy & Environmental Science, 2015, 8(11): 3298-3312. |
| [42] | BANIK A, SHENOY U S, ANAND S, et al.Mg alloying in SnTe facilitates valence band convergence and optimizes thermoelectric properties. Chemistry of Materials, 2015, 27(2): 581-587. |
| [43] | TAN X, SHAO H, HU T, et al.High thermoelectric performance in two-dimensional graphyne sheets predicted by first-principles calculations. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2015, 17(35): 22872-22881. |
| [44] | WU H, LU X, WANG G, et al. Sodium-doped tin sulfide single crystal: a nontoxic earth-abundant material with high thermoelectric performance. Advanced Energy Materials, 2018, 8(20): 1800087-1-8. |
| [45] | ZHAO L D, HAO S, LO S H, et al.High thermoelectric performance via hierarchical compositionally alloyed nanostructures. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2013, 135(19): 7364-7370. |
| [46] | POUDEL B, HAO Q, MA Y, et al.High thermoelectric performance of nanostructured bismuth antimony telluride bulk alloys. Science, 2008, 320(5876): 634-638. |
| [47] | ZHAO L D, ZHANG X, WU H, et al.Enhanced thermoelectric properties in the counter-doped SnTe system with strained endotaxial SrTe. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2016, 138(7): 2366-2373. |
| [48] | LIU H, SHI X, XU F, et al.Copper ion liquid-like thermoelectrics. Nature Materials, 2012, 11(5): 422-425. |
| [49] | HEY, DAY T, ZHANG T, et al.High thermoelectric performance in non-toxic earth-abundant copper sulfide. Advanced Materials, 2014, 26(23): 3974-3978. |
| [50] | ANANYA B, KANISHKA B.Lead-free thermoelectrics: promising thermoelectric performance in p-type SnTe1-xSex system. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(25): 9620-9625. |
| [51] | TAN X, TAN X, LIU G, et al.Optimizing the thermoelectric performance of In-Cd codoped SnTe by introducing Sn vacancies. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, 5(30): 7504-7509. |
| [52] | TAN X J, LIU G Q, XU J T, et al.Element-selective resonant state in M-doped SnTe (M=Ga, In, and Tl). Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2016, 18(30): 20635-20639. |
| [1] | 汪波, 余健, 李存成, 聂晓蕾, 朱婉婷, 魏平, 赵文俞, 张清杰. Gd/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3热电磁梯度复合材料的服役稳定性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 663-670. |
| [2] | 贺丹琪, 魏明旭, 刘蕤之, 汤志鑫, 翟鹏程, 赵文俞. 一步法制备重费米子YbAl3热电材料及其性能提升[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 577-582. |
| [3] | 林思琪, 李艾燃, 付晨光, 李荣斌, 金敏. Zintl相Mg3X2(X=Sb, Bi)基晶体生长及热电性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [4] | 王鹏将, 康慧君, 杨雄, 刘颖, 程成, 王同敏. 熵调控抑制ZrNiSn基half-Heusler热电材料的晶格热导率[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 717-723. |
| [5] | 程成, 李建波, 田震, 王鹏将, 康慧君, 王同敏. In2O3/InNbO4复合材料的热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 724-730. |
| [6] | 娄许诺, 邓后权, 李爽, 张青堂, 熊文杰, 唐国栋. Ge掺杂MnTe材料的热电输运性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 209-214. |
| [7] | 刘丹, 赵亚欣, 郭锐, 刘艳涛, 张志东, 张增星, 薛晨阳. 退火条件对磁控溅射MgO-Ag3Sb-Sb2O4柔性薄膜热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1302-1310. |
| [8] | 任培安, 汪聪, 訾鹏, 陶奇睿, 苏贤礼, 唐新峰. Te与In共掺杂对Cu2SnSe3热电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1079-1086. |
| [9] | 逯旭, 侯绩翀, 张强, 樊建锋, 陈少平, 王晓敏. Mg含量对Mg3(1+z)Sb2化合物热电传输性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(8): 835-840. |
| [10] | 杨枭, 苏贤礼, 鄢永高, 唐新峰. (GeTe)nBi2Te3的结构与热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(1): 75-80. |
| [11] | 周星圆, 柳伟, 张程, 华富强, 张敏, 苏贤礼, 唐新峰. Nb掺杂Mo1-xWxSeTe固溶体的热-电输运性能优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(12): 1373-1379. |
| [12] | 沈家骏, 方腾, 傅铁铮, 忻佳展, 赵新兵, 朱铁军. 热电材料中的晶格热导率[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(3): 260-268. |
| [13] | 李周, 肖翀. 异层等价离子双掺杂策略优化BiCuSeO的热电性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(3): 294-300. |
| [14] | 胡慧珊, 杨君友, 辛集武, 李思慧, 姜庆辉. SnO的歧化反应对SnTe热电性能的优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(3): 315-320. |
| [15] | 黄志成, 姚瑶, 裴俊, 董金峰, 张波萍, 李敬锋, 尚鹏鹏. n型SnS热电材料的制备与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(3): 321-327. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||