无机材料学报 ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (1): 1-16.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180171
所属专题: MAX相和MXene材料; 二维材料; 2019~2020年度优秀作者作品欣赏:功能材料
• 综述 • 下一篇
王人焱, 甘霖, 翟天佑
收稿日期:2018-04-19
修回日期:2018-06-03
出版日期:2019-01-21
网络出版日期:2018-12-17
作者简介:王人焱(1994-),男,博士研究生. E-mail: Renyanwang@hust.edu.cn
基金资助:WANG Ren-Yan, GAN Lin, ZHAI Tian-You
Received:2018-04-19
Revised:2018-06-03
Published:2019-01-21
Online:2018-12-17
About author:WANG Ren-Yan. E-mail: Renyanwang@hust.edu.cn
摘要:
二维材料因其不同于体相的超薄原子结构、大的比表面积和量子限域效应等受到了人们的广泛关注。二维各向异性材料作为二维材料家族的一员, 其取向依赖的物理和化学性质, 使得对该类材料性能的选择性优化成为可能。过渡金属Re基硫属化合物作为各向异性材料的典型代表, 具有可调的可见光波段吸收带隙, 极弱的层间耦合作用力, 以及各向异性的光学、电学性能, 现已成为电子和光电子领域的研究热点之一。本文主要介绍了ReX2 (X=S, Se)的晶体结构和基本性质, 总结目前该材料体系主流的合成方法, 研究其各向异性物理特性及优化的手段和条件, 并对ReX2的制备和发展进行了展望。
中图分类号:
王人焱, 甘霖, 翟天佑. ReX2 (X=S, Se): 二维各向异性材料发展的新机遇[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(1): 1-16.
WANG Ren-Yan, GAN Lin, ZHAI Tian-You. ReX2 (X=S, Se): A New Opportunity for Development of Two-dimensional Anisotropic Materials[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(1): 1-16.
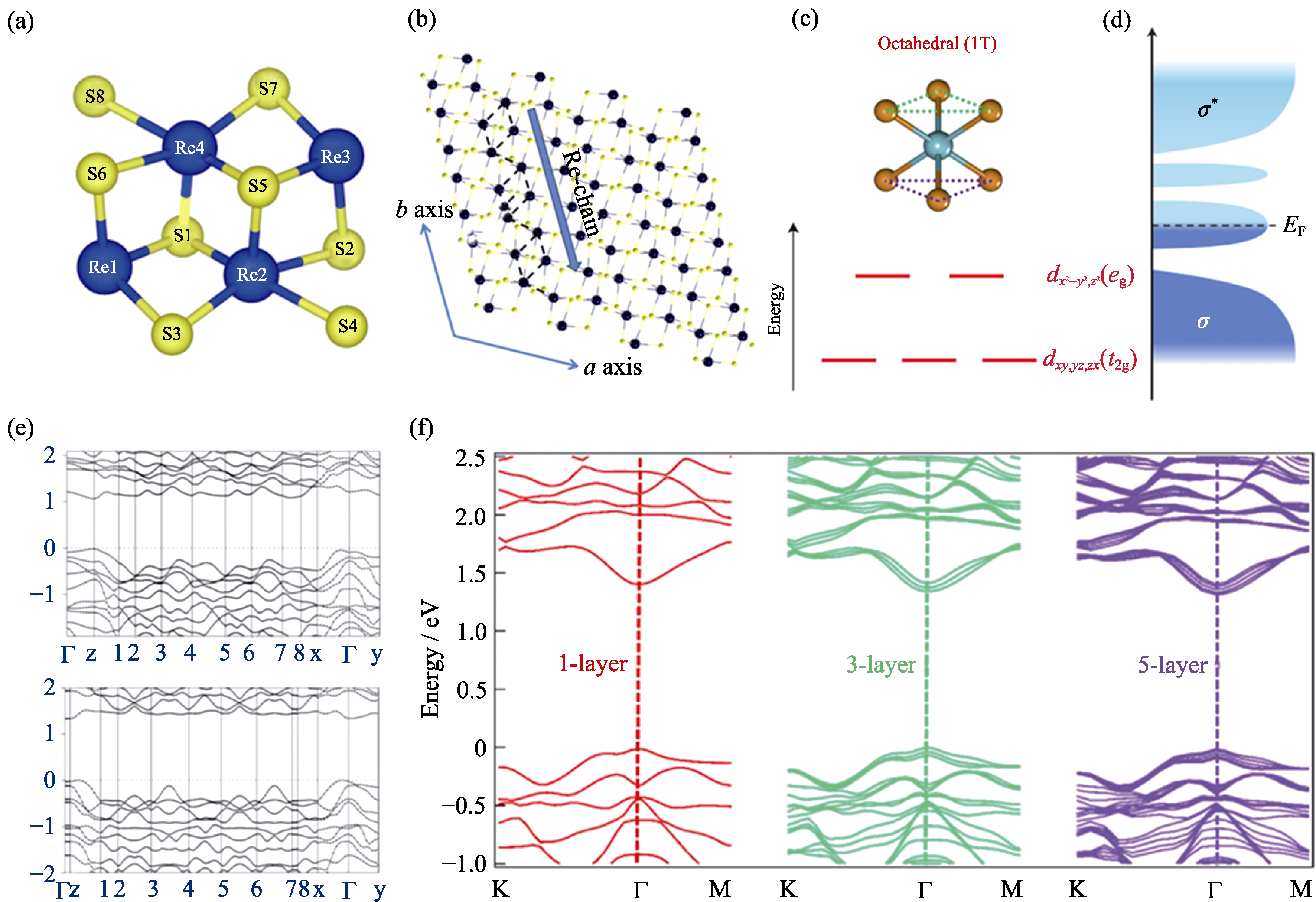
图1 (a)ReS2单胞结构图[33]; (b)ReX2晶体结构顶视图; (c) ~(d)1T相结构轨道成键和能级示意图[39,40]; (e)ReSe2块体(上)和单层(下)带隙结构[50]; (f)1层、3层、5层的ReS2能带模拟图[51]
Fig. 1 (a) The model unitcell view of ReS2[33]; (b) Top view of the crystalline structure of distorted-1T phase of monolayer ReX2(Black balls represent Re atoms and yellow balls represent S or Se atoms); (c, d) Schematic images of 1T lattice symmetries and energy levels of d-orbital electrons induced by the crystal field[39,40]; (e) First-principles scalar relativistic projector augmented wave calculations of electronic band structures for bulk (top) and single-layer (down) ReSe2[50]; (f) Band structure of monolayer, trilayer and five-layer ReS2 by ab initio-calculations[51]
| Materials | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ReS2 | 0.6417 | 0.6510 | 0.6461 | 121.10 | 88.38 | 106.47 | 0.21930 |
| ReSe2 | 0.6603 | 0.6717 | 0.6718 | 91.87 | 104.93 | 118.95 | 0.24753 |
表1 ReS2和ReSe2单胞晶格参数[36,37]
Table 1 Original unit-cell lattice parameters of ReS2 and ReSe2[36,37]
| Materials | a/nm | b/nm | c/nm | α/(°) | β/(°) | γ/(°) | V/nm3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ReS2 | 0.6417 | 0.6510 | 0.6461 | 121.10 | 88.38 | 106.47 | 0.21930 |
| ReSe2 | 0.6603 | 0.6717 | 0.6718 | 91.87 | 104.93 | 118.95 | 0.24753 |

图2 (a)ReS2不同层数的PL光谱; (b)ReS2, MoS2, MoSe2, WS2和WSe2的PL强度和层数依赖关系[50]; (c)ReS2和(d) ReSe2单层到块体厚度的拉曼光谱[58]; (e)ReS2纳米卷自组装机制[59]; (f)单层ReS2纳米墙热弯曲示意图[60]
Fig. 2 PL spectra of ReS2 flakes with different number of layers; (b) Integrated PL intensity as a function of number of layers (normalized to that of monolayer) in ReS2, MoS2, MoSe2, WS2 and WSe2[50]; Raman spectra recorded on (c) N-layer ReS2 and (d) N-layer ReSe2 in the parallel polarization configuration[58]; (e) Schematic for the process of oriented self assembly of ReS2 nanoscrolls[59]; (f) Schematic for the TIB of a single ReS2 nanowall[60]
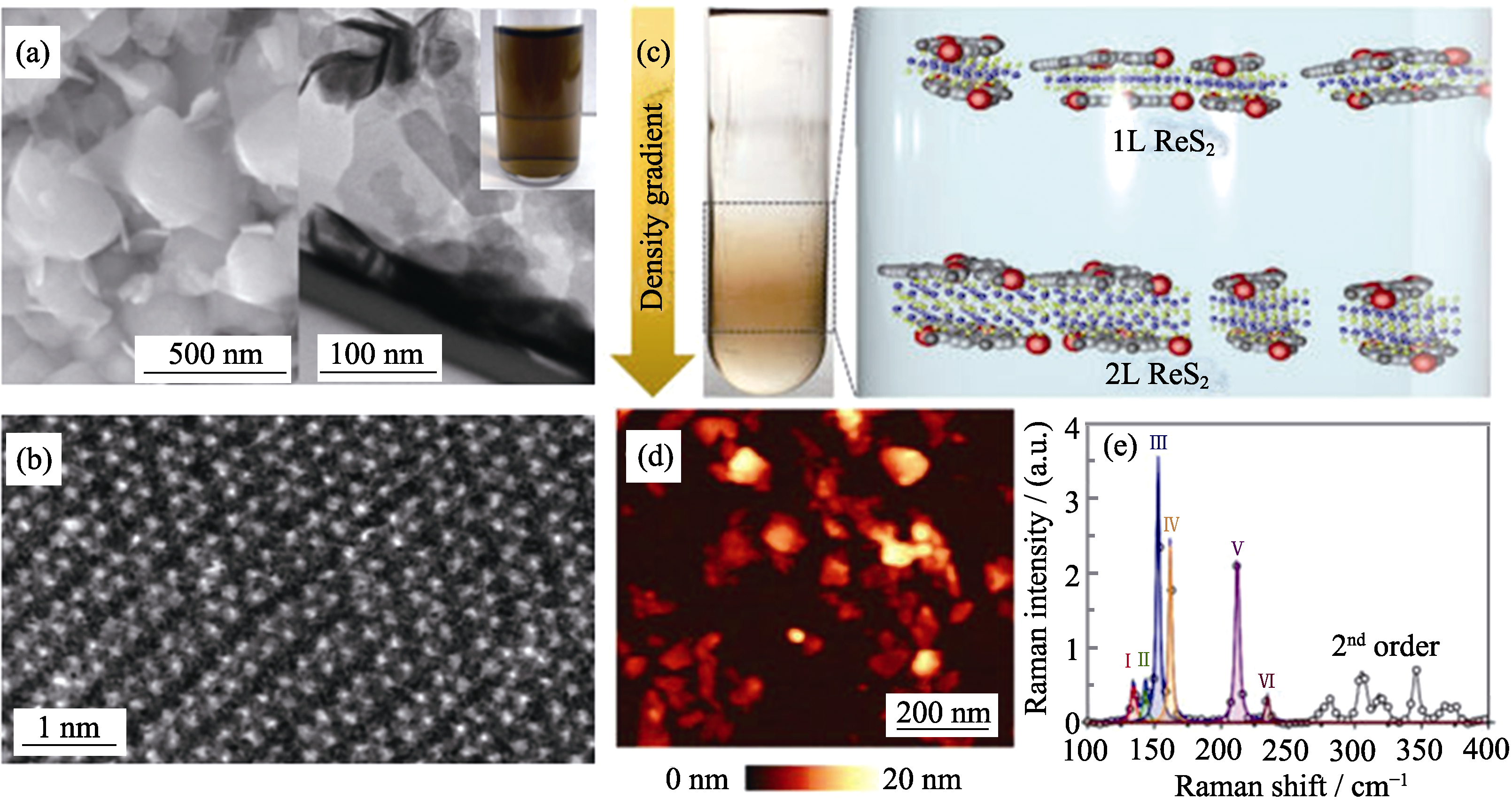
图3 (a)分离前ReS2纳米片SEM照片(左)和分离后TEM照片(右), 插图:剥离样品水溶液光学照片; (b)HRTEM照片[70]; (c)等密度梯度超速离心分离不同密度梯度ReS2纳米片示意图; (d)AFM照片; (e)ReS2拉曼光谱图[63]
Fig. 3 (a) SEM image of ReS2 powders and TEM image of as-exfoliated ReS2 nanosheets with inset showing photograph of a typical dark-brown exfoliated ReS2 suspension in water; (b) High-resolution STEM image of as-exfoliated ReS2 nanosheets[70]; (c) Schematics for different density gradient ultracentrifugation ReS2 nanosheets through iDGU; (d) Atomic force microscopy image of solution-processed ReS2 following deposition on a Si wafer; (e) Raman spectrum of ReS2 nanosheets[63]

图4 (a)PVD制备ReS2薄膜示意图; (b)ReS2薄膜Raman光谱图; (c)光学照片, 插图:AFM照片和TEM照片[88]; (d)蓝宝石衬底和ReS2薄膜光学照片; (e)SiO2/Si衬底CVD生长ReS2纳米片光学照片[74]
Fig. 4 (a) Schematic diagram of synthesized ReS2 film by PVD; (b) Raman spectrum of ReS2 film ; (c) Optical photograph of grown ReS2 film on the SiO2/Si substrate with inset showing the AFM and TEM images[88]; (d) A picture of bare and as-grown ReS2 bilayer film on sapphire wafer by CVD; (e) Optical microscope image of the ReS2 hexagons[74]
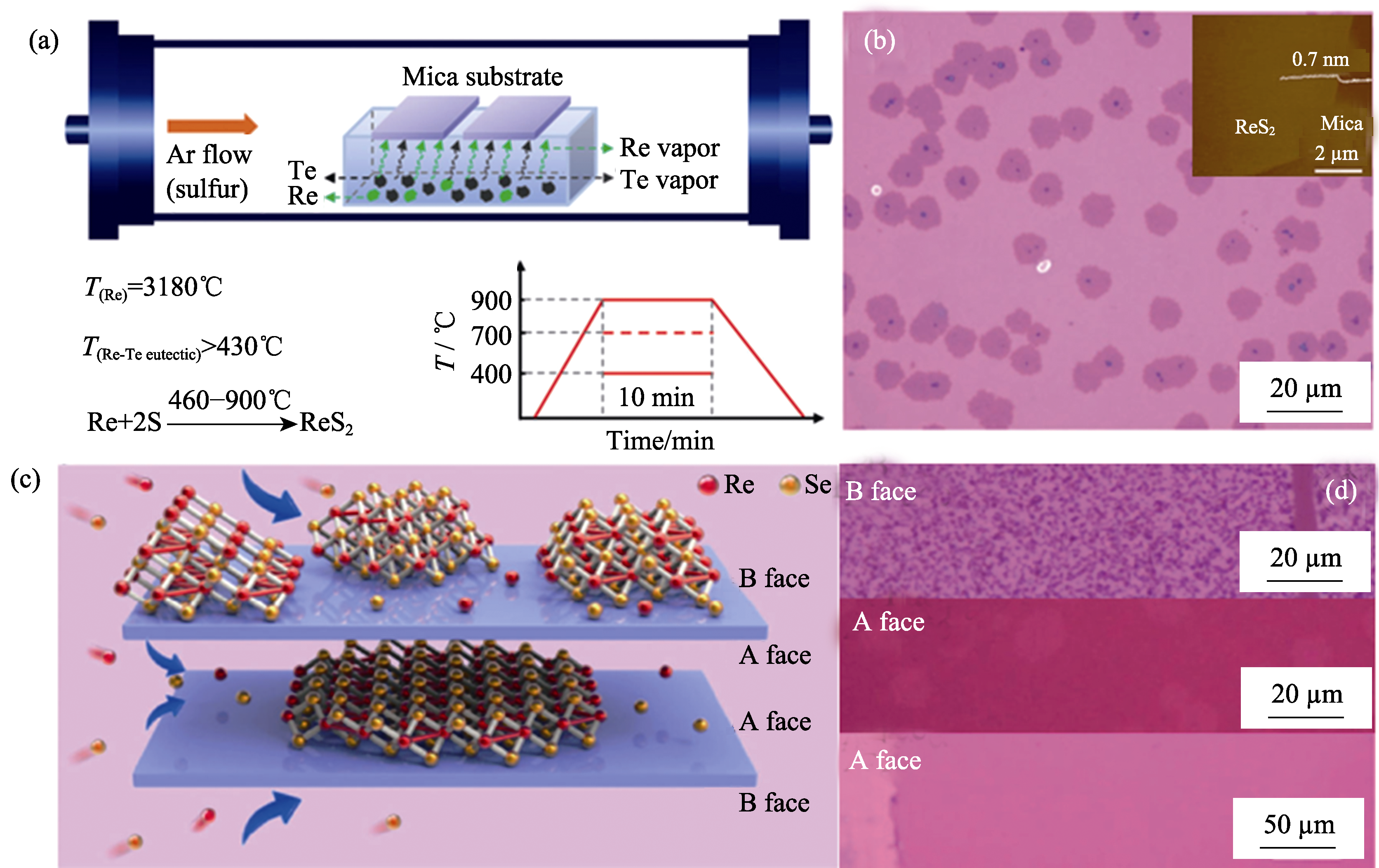
图5 (a)Te辅助CVD合成ReS2示意图; (b)转移至SiO2/Si衬底ReS2光学照片, 插图为AFM照片[77]; (c)夹层限域生长ReSe2表面反应机制示意图; (d)A、B面的ReSe2形貌光学照片[89]
Fig. 5 (a) Schematic for the tellurium-assisted CVD growth approach; (b) Optical image of ReS2 after transferred onto SiO2/Si (300 nm) substrate with inset showing AFM image of ReS2 on mica substrate[77]; (c) Schematic of the CVD growth of ReSe2 in the confined reaction space and the surface reaction during the epitaxial growth of the ReSe2 atomic layer on mica; (d) Optical image of ReSe2 in A and B face[89]
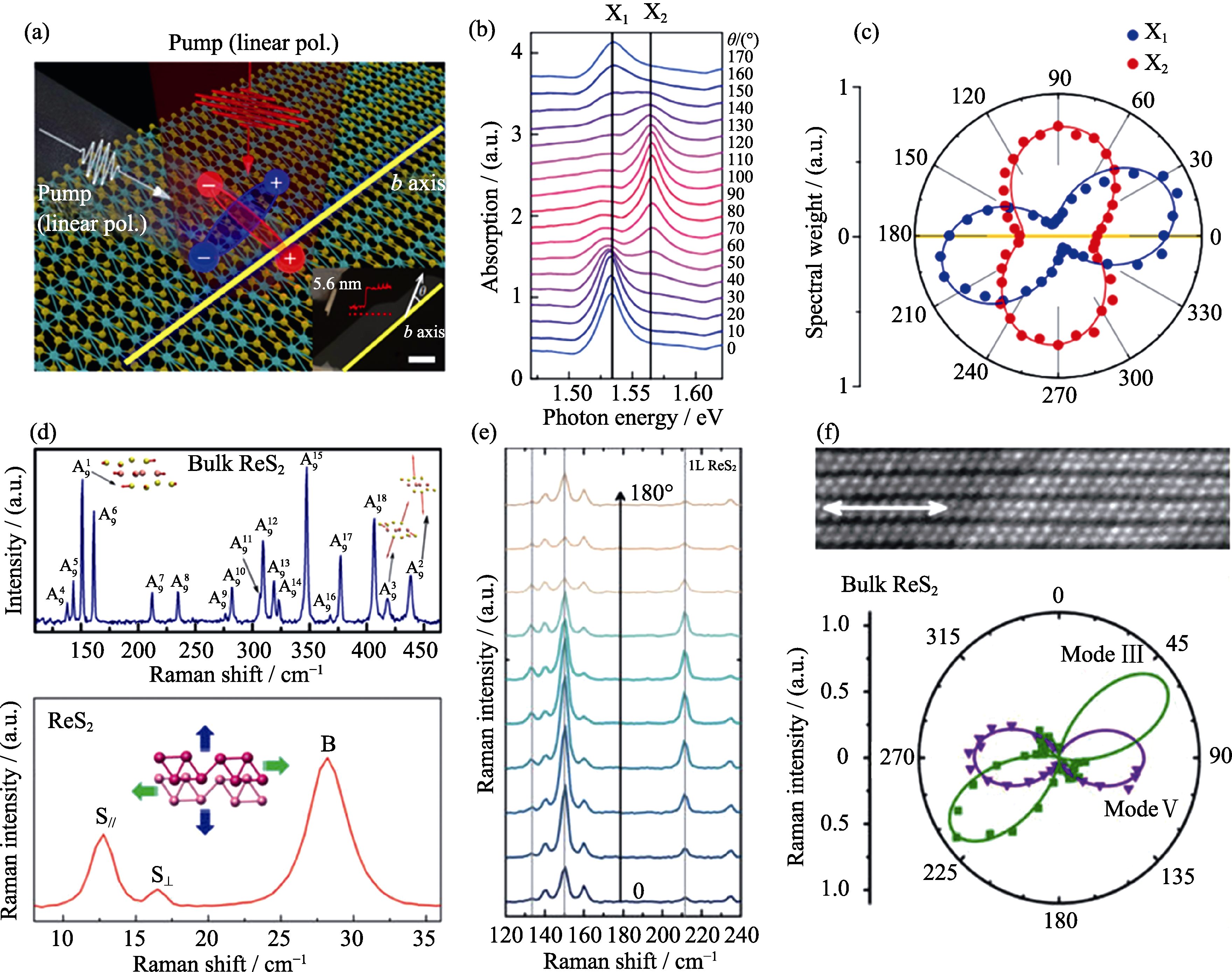
图6 (a)泵浦探测少层ReS2纳米片实验示意图, 插图:剥离ReS2光学照片; (b)角度依赖的少层ReS2纳米片光吸收谱; (c)X1, X2激子角度依赖的光吸收极化图[122]; (d)ReS2 Raman光谱[128]和低频Raman光谱[131]; (e)ReS2 不同旋转角度的Raman光谱; (f)少层ReS2纳米片高分辨TEM照片和对应偏振Raman极化图[130]
Fig. 6 (a) A schematic illustrating the pump-probe experiment of few-layer ReS2 with inset showing optical image of few-layer ReS2; (b) Polarization-dependent absorption spectra of few-layer ReS2; (c) Corresponding spectral weights of Lorentzian contributions of X1 (blue dots) and X2(red dots). Yellow line represents the b-axis[122]; (d) Raman spectrum for bulk ReS2[128] and Low-frequency Raman spectroscopy of few layer ReS2[131]; (e) Unpolarized Raman spectra as a function of sample orientation angle; (f) High-magnification ADF-STEM image and corresponded polarization-and orientation-resolved Raman spectra[130]
| Symmetry | Bulk/cm-1 | Monolayer/cm-1 | Origin of phonon mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 140.3 | 139.2 | Out-of-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Ag | 145.9 | 145.3 | Out-of-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 153.1 | 153.6 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 163.6 | 163.6 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 217.2 | 217.7 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 237.1 | 237.7 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Cp | 278.3 | 278.3 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of Re and S atoms |
| Cp | 284.2 | 284.7 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of Re and S atoms |
| Eg | 307.8 | 307.8 | In-plane vibrations of S atoms |
| Eg | 311.0 | 311.0 | In-plane vibrations of S atoms |
| Cp | 320.6 | 320.6 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 324.9 | 324.9 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 348.8 | 348.8 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 368.9 | 369.5 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 377.9 | 377.4 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 407.3 | 408.3 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Ag | 418.7 | 419.3 | Out-of-plane vibrations of S atoms |
| Ag | 438.0 | 437.5 | Out-of-plane vibrations of S atoms |
表2 633 nm激光激发块体和单层ReS2的18种Raman振动光谱[35]
Table 2 The 18 Raman active frequencies in bulk and monolayer ReS2 under 633 nm solid state laser excitation[35]
| Symmetry | Bulk/cm-1 | Monolayer/cm-1 | Origin of phonon mode |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ag | 140.3 | 139.2 | Out-of-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Ag | 145.9 | 145.3 | Out-of-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 153.1 | 153.6 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 163.6 | 163.6 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 217.2 | 217.7 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Eg | 237.1 | 237.7 | In-plane vibrations of Re atoms |
| Cp | 278.3 | 278.3 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of Re and S atoms |
| Cp | 284.2 | 284.7 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of Re and S atoms |
| Eg | 307.8 | 307.8 | In-plane vibrations of S atoms |
| Eg | 311.0 | 311.0 | In-plane vibrations of S atoms |
| Cp | 320.6 | 320.6 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 324.9 | 324.9 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 348.8 | 348.8 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 368.9 | 369.5 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 377.9 | 377.4 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Cp | 407.3 | 408.3 | In- and out-of-plane vibration of S atoms |
| Ag | 418.7 | 419.3 | Out-of-plane vibrations of S atoms |
| Ag | 438.0 | 437.5 | Out-of-plane vibrations of S atoms |

图7 (a)ReS2晶体管光学照片; (b)对应(a)图ReS2的TEM照片; (c)不同电极的I-V曲线; (d)不同电极之间的ReS2转移特性曲线[137]; (e)各向异性ReS2晶体管转移特性曲线, 插图为器件光学照片和R-Vbg曲线; (f)角度依赖的FET迁移率极化图, 插图:器件光学照片[51]; (g)ReS1.23Se0.77合金各向异性转移特性曲线, 插图为器件光学照片[76]
Fig. 7 (a) Optical microscope image of ReS2 four probe transistor; (b) The magnified ADF images taken from the sample in (a); (c) The direction-dependent I-V characteristics with inset showing nonlinear I-V behavior indicate the Schottky Au/ReS2 contacts; (d) The direction-dependent transfer characteristics[137]; (e) Transfer curves of anisotropic ReS2 FETs along two sides with top inset showing optical image of the devices (Scale bar, 10 μm) and low inset showing the 4-probe resistance of the same devices. (f) Normalized field-effect mobility of a six-layer device with inset showing the optical image of the device[51]; (g) Angle-dependent transfer curves of ReS1.23Se0.77 alloy device with inset showing optical image of ReS2 device[76]

图8 (a)角度依赖的ReS2极化光电流图; (b)极化光电流曲线[112]; (c)偏振光I-t曲线; (d)偏振光电流极化图[76]; (e)ReSe2偏振光电器件示意图; (f)器件SEM照片和不同角度的入射光电流分布图[15]
Fig. 8 (a) The photocurrent of ReS2 change as a function of drain bias under different polarization light illuminations; (b) The change of the photocurrent under different drain biases plotted as a function of polarization angle[112]; (c) Photocurrent response of ReS1.06Se0.94 alloy device under light on and off irradiation, and under light with different polarization direction; (d) Polar plots for the photocurrent with respect to the polarization angle of the incident light[76]; (e) Schematic structure of ReSe2 photodetectors; (f) The SEM image and polarization-dependent photocurrent mapping of the device[15]
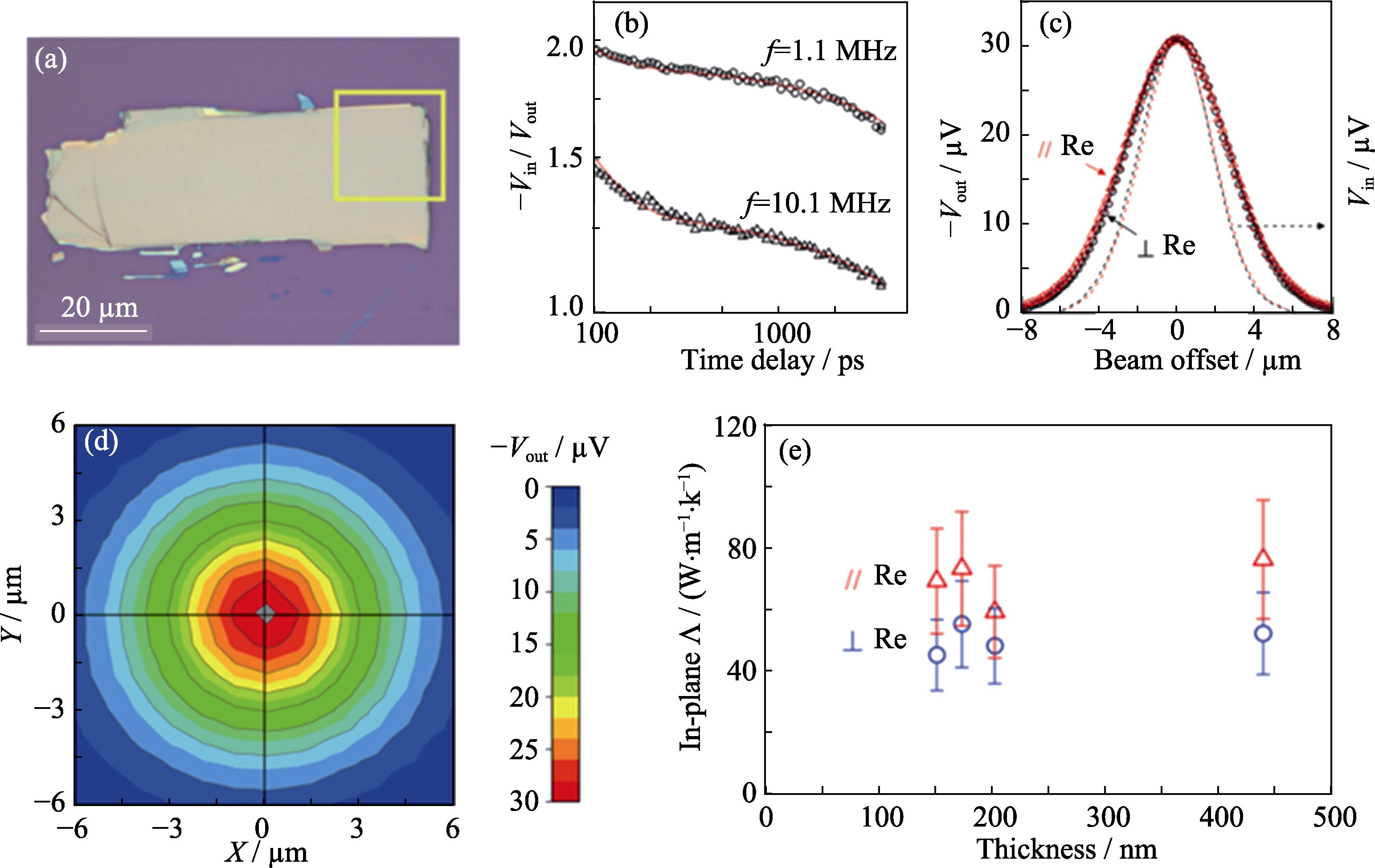
图9 (a)剥离层状ReS2光学照片; (b)面外热传导曲线; (c)极化方向的热传导曲线; (d)面内热传导分布图; (e)不同厚度的面内极化热导率[151]
Fig. 9 (a) Optical microscopy image of an exfoliated ReS2 ?ake; (b) Through-plane TDTR data at two modulation frequencies; (c) In-plane TDTR data at f = 1.1 MHz and time delay of -50 ps. The dashed lines are the intensity profile of the laser beam; (d) 2D beam-offset scan of the TDTR signal; (e) In-plane thermal conductivity of exfoliated ReS2 ?akes as a function of thickness[151]
| [1] | GONG C, ZHANG Y, CHEN W, et al. Electronic and optoelectronic applications based on 2D novel anisotropic transition metal dichalcogenides. Adv. Sci., 2017, 4(12): 1700231-1-19. |
| [2] | TIAN H, TICE J, FEI R, et al.Low-symmetry two-dimensional materials for electronic and photonic applications. Nano Today, 2016, 11(6): 763-777. |
| [3] | LIU X, RYDER C R, WELLS S A, et al. Resolving the in-plane anisotropic properties of black phosphorus. Small Methods, 2017, 1(6): 1700143-1-9. |
| [4] | XIA F N, WANG H, JIA Y C, et al. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 4458-1-6. |
| [5] | ZHAO L D, LO S H, ZHANG Y, et al.Ultralow thermal conductivity and high thermoelectric figure of merit in SnSe crystals. Nature, 2014, 508(7496): 373-377. |
| [6] | YANG Y, LIU S C, YANG W, et al.Air-stable in-plane anisotropic GeSe2 for highly polarization-sensitive photodetection in short wave region. [J]. Am. Chem. Soc., 2018, 140(11): 4150-4156. |
| [7] | XU J, CHEN L, DAI Y W, et al. A two-dimensional semiconductor transistor with boosted gate control and sensing ability. Sci.Adv., 2017, 3(5): 1602246-1-8. |
| [8] | SHIM J, OH S, KANG D H, et al. Phosphorene/rhenium disulfide heterojunction-based negative differential resistance device for multi-valued logic. Nat. Commun., 2016, 7: 13413-1-8. |
| [9] | WANG X, HUANG L, PENG Y, et al.Enhanced rectification, transport property and photocurrent generation of multilayer ReSe2/MoS2 p-n heterojunctions. Nano Res., 2016, 9(2): 507-516. |
| [10] | DATHBUN A, KIM Y, KIM S, et al.Large-area CVD-grown sub-2 V ReS2 transistors and logic gates. Nano Lett., 2017, 17(5): 2999-3005. |
| [11] | MOHAMMED O B, MOVVA H C P, PRASAD N, et al. ReS2-based interlayer tunnel field effect transistor. J. Appl. Phys., 2017, 122(24): 245701-1-7. |
| [12] | CORBETT C M, MCCLELLAN C, RAI A, et al.Field effect transistors with current saturation and voltage gain in ultrathin ReS2. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(1): 363-370. |
| [13] | CHO A J, NAMGUNG S D, KIM H, et al. Electric and photovoltaic characteristics of a multi-layer ReS2/ReSe2 heterostructure. APL Materials, 2017, 5(7): 076101-1-8. |
| [14] | ZHANG E, JIN Y, YUAN X, et al.ReS2-based field-effect transistors and photodetectors. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25(26): 4076-4082. |
| [15] | ZHANG E, WANG P, LI Z, et al.Tunable ambipolar polarization- sensitive photodetectors based on high-anisotropy ReSe2 nanosheets. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(8): 8067-8077. |
| [16] | QIN J K, REN D D, SHAO W Z, et al.Photoresponse enhancement in monolayer ReS2 phototransistor decorated with CdSe-CdS-ZnS quantum dots. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2017, 9(45): 39456-39463. |
| [17] | YANG S, TONGAY S, LI Y, et al.Layer-dependent electrical and optoelectronic responses of ReSe2 nanosheet transistors. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(13): 7226-7231. |
| [18] | CUI Y, LU F, LIU X. Nonlinearsaturable and polarization- induced absorption of rhenium disulfide. Sci. Rep., 2017, 7: 40080-1-9. |
| [19] | ZHANG Q, TAN S, MENDES R G, et al.Extremely weak Van Der Waals coupling in vertical ReS2 nanowalls for high-current- density lithium-ion batteries. Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(13): 2616-2623. |
| [20] | QI F, CHEN Y, ZHENG B, et al.Hierarchical architecture of ReS2/rGO composites with enhanced electrochemical properties for lithium-ion batteries. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 413: 123-128. |
| [21] | QI F, HE J, CHEN Y, et al.Few-layered ReS2 nanosheets grown on carbon nanotubes: a highly efficient anode for high-performance lithium-ion batteries. Chem. Eng. J., 2017, 315: 10-17. |
| [22] | QI F, CHEN Y, ZHENG B, et al.3D chrysanthemum-like ReS2 microspheres composed of curly few-layered nanosheets with enhanced electrochemical properties for lithium-ion batteries. [J]. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52(7): 3622-3629. |
| [23] | ESCALONA N, LLAMBIAS F J G, VRINAT M, et al. Highly active ReS2/gamma-Al2O3 catalysts: effect of calcination and activation over thiophene hydrodesulfurization. Catal. Commun., 2007, 8(3): 285-288. |
| [24] | ALIAGA J A, ZEPEDA T N, PAWELEC B N, et al.Microspherical ReS2 as a high-performance hydrodesulfurization catalyst. Catal. Lett., 2017, 147(5): 1243-1251. |
| [25] | SEPULVEDA C, ESCALONA N, GARCIA R, et al.Hydrodeoxygenation and hydrodesulfurization co-processing over ReS2 supported catalysts. Catal. Today, 2012, 195(1): 101-105. |
| [26] | ANTONIO ALIAGA J, ZEPEDA T, FRANCISCO ARAYA J, et al. Low-dimensional ReS2/C composite as effective hydrodesulfurization catalyst. Catalysts, 2017, 7(12): 7120377-1-11. |
| [27] | QI F, WANG X, ZHENG B, et al.Self-assembled chrysanthemum- like microspheres constructed by few-layer ReSe2 nanosheets as a highly efficient and stable electrocatalyst for hydrogen evolution reaction. Electrochim. Acta, 2017, 224: 593-599. |
| [28] | HO T C, SHEN Q, MCCONNACHIE J M, et al.Kinetic characterization of unsupported ReS2 as hydroprocessing catalyst. [J]. Catal., 2010, 276(1): 114-122. |
| [29] | GAO J, LI L, TAN J, et al.Vertically oriented arrays of ReS2 nanosheets for electrochemical energy storage and electrocatalysis. Nano Lett., 2016, 16(6): 3780-3787. |
| [30] | RAHMAN M, DAVEY K, QIAO S Z. Advent of 2D rhenium disulfide (ReS2): fundamentals to applications. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(10): 1606129-1-21. |
| [31] | HAFEEZ M, GAN L, BHATTI A S, et al.Rhenium dichalcogenides (ReX2, X = S or Se): an emerging class of TMDs family. Mater. Chem. Front., 2017, 1(10): 1917-1932. |
| [32] | WILDERVANCK J C, JELLINEK F.The dichalcogenides of technetium and rhenium. Journal of the Less Common Metals, 1971, 24(1): 73-81. |
| [33] | YU Z G, CAI Y, ZHANG Y W. Robust direct bandgap characteristics of one- and two-dimensional ReS2. Sci. Rep., 2015, 5: 13783-1-9. |
| [34] | KEYSHAR K, GONG Y, YE G, et al.Chemical vapor deposition of monolayer rhenium disulfide (ReS2). Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(31): 4640-4648. |
| [35] | FENG Y, ZHOU W, WANG Y, et al. Raman vibrational spectra of bulk to monolayer ReS2 with lower symmetry. Phys. Rev. B, 2015, 92(5): 054110-1-24. |
| [36] | KAO Y C, HUANG T, LIN D Y, et al. Anomalous structural phase transition properties in ReSe2 and Au-doped ReSe2. J. Chem. Phys., 2012, 137(2): 024509-1-7. |
| [37] | TIONG K K, HO C H, HUANG Y S.The electrical transport properties of ReS2 and ReSe2 layered crystals. Solid State. Commun., 1999, 111(11): 635-640. |
| [38] | WANG Q H, KALANTAR-ZADEH K, KIS A, et al.Electronics and optoelectronics of two-dimensional transition metal dichalcogenides. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2012, 7(11): 699-712. |
| [39] | YANG H, KIM S W, LEE Y H, et al.Structural and quantum- state phase transitions in Van Der Waals layered materials. Nat. Phys., 2017, 13: 931-937. |
| [40] | CHHOWALLA M, SHIN H S, EDA G, et al.The chemistry of two-dimensional layered transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets. Nat. Chem., 2013, 5(4): 263-275. |
| [41] | YIN Z, LI H, JIANG L, et al.Single-layer MoS2 phototransistors. ACS Nano, 2012, 6(1): 74-80. |
| [42] | TONGAY S, FAN W, KANG J, et al.Tuning interlayer coupling in large-area heterostructures with CVD-grown MoS2 and WS2 monolayers. Nano Lett., 2014, 14(6): 3185-3190. |
| [43] | SPLENDIANI A, SUN L, ZHANG Y, et al.Emerging photoluminescence in monolayer MoS2. Nano Lett., 2010, 10(4): 1271-1275. |
| [44] | LI T, GALLI G.Electronic properties of MoS2 nanoparticles. J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(44): 16192-16196. |
| [45] | TONNDORF P, SCHMIDT R, BOTTGER P, et al.Photoluminescence emission and Raman response of monolayer MoS2, MoSe2, and WSe2. Opt. Express, 2013, 21(4): 4908-4916. |
| [46] | HART L, DALE S, HOYE S, et al.Rhenium dichalcogenides: layered semiconductors with two vertical orientations. Nano Lett., 2016, 16(2): 1381-1386. |
| [47] | HART L S, WEBB J L, DALE S, et al. Electronic bandstructure and Van Der Waals coupling of ReSe2 revealed by high-resolution angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Sci. Rep., 2017, 7: 5145-1-9. |
| [48] | WEBB J L, HART L S, WOLVERSON D, et al. Electronic band structure of ReS2 by high-resolution angle-resolved photoemission spectroscopy. Phys. Rev. B, 2017, 96(11): 115205-1-8. |
| [49] | WOLVERSON D, CRAMPIN S, KAZEMI A S, et al.Raman spectra of monolayer, few-layer, and bulk ReSe2: an anisotropic layered semiconductor. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(11): 11154-11164. |
| [50] | TONGAY S, SAHIN H, KO C, et al. Monolayer behaviour in bulk ReS2 due to electronic and vibrational decoupling. Nat.Commun., 2014, 5: 3252-1-6. |
| [51] | LIU E, FU Y, WANG Y, et al. Integrated digital inverters based on two-dimensional anisotropic ReS2 field-effect transistors. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6: 6991-1-7. |
| [52] | EDA G, YAMAGUCHI H, VOIRY D, et al.Photoluminescence from chemically exfoliated MoS2. Nano Lett., 2011, 11(12): 5111-5116. |
| [53] | MAK K F, LEE C, HONE J, et al. Atomically thin MoS2: a new direct-gap semiconductor. Phys. Rev. Lett., 2010, 105(13): 136805-1-4. |
| [54] | ZHAO W, GHORANNEVIS Z, CHU L, et al.Evolution of electronic structure in atomically thin sheets of WS2 and WSe2. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(1): 791-797. |
| [55] | GUTIERREZ H R, PEREA-LOPEZ N, ELIAS A L, et al.Extraordinary room-temperature photoluminescence in triangular WS2 monolayers. Nano Lett., 2013, 13(8): 3447-3454. |
| [56] | ZHAO H, WU J, ZHONG H, et al.Interlayer interactions in anisotropic atomically thin rhenium diselenide. Nano Res., 2015, 8(11): 3651-3661. |
| [57] | TONGAY S, ZHOU J, ATACA C, et al.Thermally driven crossover from indirect toward direct bandgap in 2D semiconductors: MoSe2 versus MoS2. Nano Lett., 2012, 12(11): 5576-5580. |
| [58] | LORCHAT E, FROEHLICHER G, BERCIAUD S.Splitting of interlayer shear modes and photon energy dependent anisotropic raman response in N-layer ReSe2 and ReS2. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(2): 2752-2760. |
| [59] | ZHANG Q, WANG W, KONG X, et al.Edge-to-edge oriented self-assembly of ReS2 nanoflakes. [J]. Am. Chem. Soc., 2016, 138(35): 11101-11104. |
| [60] | ZHANG Q, WANG W, ZHANG J, et al. Thermally induced bending of ReS2 nanowalls. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(3): 1704585-1-7. |
| [61] | JARIWALA B, VOIRY D, JINDAL A, et al.Synthesis and characterization of ReS2 and ReSe2 layered chalcogenide single crystals. Chem. Mater., 2016, 28(10): 3352-3359. |
| [62] | HU D, XU G, XING L, et al.Two-dimensional semiconductors grown by chemical vapor transport. Angew Chem. Int. Ed., 2017, 56(13): 3611-3615. |
| [63] | KANG J, SANGWAN V K, WOOD J D, et al.Layer-by-layer sorting of rhenium disulfide via high-density isopycnic density gradient ultracentrifugation. Nano Lett., 2016, 16(11): 7216-7223. |
| [64] | JAWAID A, NEPAL D, PARK K, et al.Mechanism for liquid phase exfoliation of MoS2. Chem. Mater., 2015, 28(1): 337-348. |
| [65] | ZHENG J, ZHANG H, DONG S, et al. High yield exfoliation of two-dimensional chalcogenides using sodium naphthalenide. Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 2995-1-7. |
| [66] | COLEMAN J N, LOTYA M, O'NEILL A, et al. Two-dimensional nanosheets produced by liquid exfoliation of layered materials. Science, 2011, 331(6017): 568-571. |
| [67] | NICOLOSI V, CHHOWALLA M, KANATZIDIS M G, et al.Liquid exfoliation of layered materials. Science, 2013, 340(6139): 1226419-1226419. |
| [68] | HUO C, YAN Z, SONG X, et al.2D materials via liquid exfoliation: a review on fabrication and applications. Sci. Bull., 2015, 60(23): 1994-2008. |
| [69] | ZHAO X, MA X, SUN J, et al.Enhanced catalytic activities of surfactant-assisted exfoliated WS2 nanodots for hydrogen evolution. ACS Nano, 2016, 10(2): 2159-2166. |
| [70] | FUJITA T, ITO Y, TAN Y, et al.Chemically exfoliated ReS2 nanosheets. Nanoscale, 2014, 6(21): 12458-12462. |
| [71] | XU K, DENG H X, WANG Z, et al.Sulfur vacancy activated field effect transistors based on ReS2 nanosheets. Nanoscale, 2015, 7(38): 15757-15762. |
| [72] | KIM Y, KANG B, CHOI Y, et al. Direct synthesis of large-area continuous ReS2 films on a flexible glass at low temperature. 2D Materials, 2017, 4(2): 025057-1-10. |
| [73] | QIN J K, SHAO W Z, XU C Y, et al.Chemical vapor deposition growth of degenerate p-type Mo-doped ReS2 films and their homojunction. ACS Appl. Mater. Inter., 2017, 9(18): 15583-15591. |
| [74] | HAFEEZ M, GAN L, LI H, et al.Large-area bilayer ReS2 film/multilayer ReS2 flakes synthesized by chemical vapor deposition for high performance photodetectors. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(25): 4551-4560. |
| [75] | CHEN B, WU K, SUSLU A, et al. Controlling structural anisotropy of anisotropic 2D layers in pseudo-1D/2D material heterojunctions. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(34): 1701201-1-8. |
| [76] | CUI F, FENG Q, HONG J, et al. Synthesis of large-size 1T ' ReS2xSe2(1-x) alloy monolayer with tunable bandgap and carrier type. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(46): 1705015-1-9. |
| [77] | CUI F, WANG C, LI X, et al.Tellurium-assisted epitaxial growth of large-area, highly crystalline ReS2 atomic layers on mica substrate. Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(25): 5019-5024. |
| [78] | HAFEEZ M, GAN L, LI H, et al.Chemical vapor deposition synthesis of ultrathin hexagonal ReSe2 flakes for anisotropic Raman property and optoelectronic application. Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(37): 8296-8301. |
| [79] | AL-DULAIMI N, LEWIS E A, LEWIS D J, et al.Sequential bottom-up and top-down processing for the synthesis of transition metal dichalcogenide nanosheets: the case of rhenium disulfide (ReS2). Chem. Commun., 2016, 52(50): 7878-7881. |
| [80] | YELLA A, THERESE H A, ZINK N, et al.Large scale MOCVD synthesis of hollow ReS2 nanoparticles with nested fullerene-like structure. Chem. Mater., 2008, 20(11): 3587-3593. |
| [81] | KIM S, YU H K, YOON S, et al.Growth of two-dimensional rhenium disulfide (ReS2) nanosheets with a few layers at low temperature. Crystengcomm, 2017, 19(36): 5341-5345. |
| [82] | CHATURVEDI A, SLABON A, HU P, et al.Rapid synthesis of transition metal dichalcogenide few-layer thin crystals by the microwave-induced-plasma assisted method. J. Cryst. Growth, 2016, 450: 140-147. |
| [83] | AL-DULAIMI N, LEWIS D J, ZHONG X L, et al.Chemical vapour deposition of rhenium disulfide and rhenium-doped molybdenum disulfide thin films using single-source precursors. J. Mater. Chem. C, 2016, 4(12): 2312-2318. |
| [84] | AL-DULAIMI N, LEWIS E A, SAVJANI N, et al.The influence of precursor on rhenium incorporation into Re-doped MoS2 (Mo1-xRexS2) thin films by aerosol-assisted chemical vapour deposition (AACVD). J. Mater. Chem. C, 2017, 5(35): 9044-9052. |
| [85] | SIMCHI H, WALTER T N, CHOUDHURY T H, et al.Sulfidation of 2D transition metals (Mo, W, Re, Nb, Ta): thermodynamics, processing, and characterization. J. Mater. Sci., 2017, 52(17): 10127-10139. |
| [86] | BOROWIEC J, GILLIN W P, WILLIS M A C, et al. Room temperature synthesis of ReS2 through aqueous perrhenate sulfidation. J. Phys: Condens. Matter, 2018, 30(5): 055702-1-11. |
| [87] | HU S Y, CHEN Y Z, TIONG K K, et al.Growth and characterization of molybdenum-doped rhenium diselenide. Mater. Chem. Phys., 2007, 104(1): 105-108. |
| [88] | QI F, CHEN Y, ZHENG B, et al.Facile growth of large-area and high-quality few-layer ReS2 by physical vapour deposition. Mater. Lett., 2016, 184: 324-327. |
| [89] | CUI F, LI X, FENG Q, et al.Epitaxial growth of large-area and highly crystalline anisotropic ReSe2 atomic layer. Nano Res., 2017, 10(8): 2732-2742. |
| [90] | LI X, CUI F, FENG Q, et al.Controlled growth of large-area anisotropic ReS2 atomic layer and its photodetector application. Nanoscale, 2016, 8(45): 18956-18962. |
| [91] | ZHANG T, JIANG B, XU Z, et al. Twinned growth behaviour of two-dimensional materials. Nat. Commun., 2016, 7: 13911- 1-7. |
| [92] | CHEN P, WANG J, LU Y, et al.The fabrication of ReS2 flowers at controlled locations by chemical vapor deposition. Physica E, 2017, 89: 115-118. |
| [93] | QIN J K, SHAO W Z, LI Y, et al.Van der Waals epitaxy of large-area continuous ReS2 films on mica substrate. RSC Adv., 2017, 7(39): 24188-24194. |
| [94] | HE X, LIU F, HU P, et al.Chemical vapor deposition of high-quality and atomically layered ReS2. Small, 2015, 11(40): 5423-5429. |
| [95] | YANG S, TONGAY S, YUE Q, et al. High-performance few-layer Mo-doped ReSe2 nanosheet photodetectors. Sci. Rep., 2014, 4: 5442-1-6. |
| [96] | WU K, CHEN B, YANG S, et al.Domain architectures and grain boundaries in chemical vapor deposited highly anisotropic ReS2 monolayer films. Nano Lett., 2016, 16(9): 5888-5894. |
| [97] | CHEN Y, GAN L, LI H, et al. Achieving uniform monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides film on silicon wafer via silanization treatment: a typical study on WS2. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(7): 160550-1-6. |
| [98] | YAN C, GAN L, ZHOU X, et al. Space-confined chemical vapor deposition synthesis of ultrathin HfS2 flakes for optoelectronic application. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(39): 1702918- 1-9. |
| [99] | JIN B, HUANG P, ZHANG Q, et al. Self-limited epitaxial growth of ultrathin non-layered CdS flakes for high-performance photodetectors. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2018, 28: 1800181- 1-9. |
| [100] | JU M, LIANG X, LIU J, et al.Universal substrate-trapping strategy to grow strictly monolayer transition metal dichalcogenides crystals. Chem. Mater., 2017, 29(14): 6095-6103. |
| [101] | ZHANG Q, XIAO Y, ZHANG T, et al.Iodine-mediated chemical vapor deposition growth of metastable transition metal dichalcogenides. Chem. Mater., 2017, 29(11): 4641-4644. |
| [102] | HUANG W, GAN L, YANG H, et al. Controlled synthesis of ultrathin 2D β-In2S3 with broadband photoresponse by chemical vapor deposition. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27(36): 1702448- 1-9. |
| [103] | GONG Y, LIN Z, YE G, et al.Tellurium-assisted low-temperature synthesis of MoS2 and WS2 monolayers. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(12): 11658-11666. |
| [104] | ZHOU S, GAN L, WANG D, et al. Space-confined vapor deposition synthesis of two dimensional materials. Nano Res., 2017: 12274-1-23. |
| [105] | SONG J G, PARK J, LEE W, et al.Layer-controlled, wafer scale, and conformal synthesis of tungsten disulfide nanosheets using atomic layer deposition. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(12): 11333-11340. |
| [106] | JANG Y, YEO S, LEE H B R, et al. Wafer-scale, conformal and direct growth of MoS2 thin films by atomic layer deposition. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2016, 365: 160-165. |
| [107] | MEMARIAN N, ROZATI S M, CONCINA I, et al. Deposition of nanostructured CdS thin films by thermal evaporation method: effect of substrate temperature. Mater., 2017, 10(7): 773-1-8. |
| [108] | MAZUR M, HOWIND T, GIBSON D, et al.Modification of various properties of HfO2 thin films obtained by changing magnetron sputtering conditions. Surf. Coat. Technol., 2017, 320: 426-431. |
| [109] | ZHAN L, WAN W, ZHU Z, et al. MoS2 materials synthesized on SiO2/Si substrates via MBE. J. Phys.: Conf. Ser., 2017, 864: 012037-1-5. |
| [110] | HAMALAINEN J, MATTINEN M, MIZOHATA K, et al. Atomic layer deposition of rhenium disulfide. Adv. Mater., 2018, 30(24): 1703622-1-6. |
| [111] | BISWAS D, GANOSE A M, YANO R, et al. Narrow-band anisotropic electronic structure of ReS2. Phys. Rev. B, 2017, 96(8): 085205-1-7. |
| [112] | LIU F, ZHENG S, HE X, et al.Highly sensitive detection of polarized light using anisotropic 2D ReS2. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(8): 1169-1177. |
| [113] | HUANG C C, KAO C C, LIN D Y, et al. A comprehensive study on the optical properties of thin gold-doped rhenium disulphide layered single crystals. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2013, 52(4): 04CH11-1-6. |
| [114] | HO C H, HSIEH M H, WU C C, et al.Dichroic optical and electrical properties of rhenium dichalcogenides layer compounds. [J]. Alloys Compd., 2007, 442(1/2): 245-248. |
| [115] | CUI Q, HE J, BELLUS M Z, et al.Transient absorption measurements on anisotropic monolayer ReS2. Small, 2015, 11(41): 5565-5571. |
| [116] | ASLAN O B, CHENET D A, VAN DER ZANDE A M, et al. Linearly polarized excitons in single- and few-layer ReS2 crystals. ACS Photonics, 2016, 3(1): 96-101. |
| [117] | ZHENG J Y, LIN D Y, HUANG Y S. Piezoreflectance study of band-edge excitons of ReS2:Au. Jpn. J. Appl. Phys., 2009, 48(5): 052302-1-6. |
| [118] | WU S, SHAN Y, GUO J, et al.Phase-engineering-induced generation and control of highly anisotropic and robust excitons in few-layer ReS2. [J]. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8(12): 2719-2724. |
| [119] | HO C H, LEE H W, WU C C.Polarization sensitive behaviour of the band-edge transitions in ReS2 and ReSe2 layered semiconductors. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2004, 16(32): 5937-5944. |
| [120] | ARORA A, NOKY J, DRUEPPEL M, et al.Highly anisotropic in-plane excitons in atomically thin and bulklike 1T’-ReSe2. Nano Lett., 2017, 17(5): 3202-3207. |
| [121] | SIM S, LEE D, TRIFONOV A V, et al. Ultrafast quantum beats of anisotropic excitons in atomically thin ReS2. Nat. Commun., 2018, 9(1): 351-1-7. |
| [122] | SIM S, LEE D, NOH M, et al. Selectively tunable optical Stark effect of anisotropic excitons in atomically thin ReS2. Nat. Commun., 2016, 7: 13569-1-6. |
| [123] | CHAVES A, LOW T, AVOURIS P, et al. Anisotropic exciton Stark shift in black phosphorus. Phys. Rev. B, 2015, 91(15): 155311-1-7. |
| [124] | SAITO R, TATSUMI Y, HUANG S, et al. Raman spectroscopy of transition metal dichalcogenides. J. Phys.: Condens. Matter, 2016, 28(35): 353002-1-37. |
| [125] | ZHANG S, MAO N, ZHANG N, et al.Anomalous polarized raman scattering and large circular intensity differential in layered triclinic ReS2. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(10): 10366-10372. |
| [126] | TAUBE A, LAPINSKA A, JUDEK J, et al. Temperature dependence of Raman shifts in layered ReSe2 and SnSe2 semiconductor nanosheets. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2015, 107(1): 013105- 1-5. |
| [127] | MIAO P, QIN J K, SHEN Y, et al. Unraveling the Raman enhancement mechanism on 1T'-phase ReS2 nanosheets. Small, 2018: 1704079-1-8. |
| [128] | MCCREARY A, SIMPSON J R, WANG Y, et al.Intricate resonant Raman response in anisotropic ReS2. Nano Lett., 2017, 17(10): 5897-5907. |
| [129] | PRADHAN N R, MCCREARY A, RHODES D, et al.Metal to insulator quantum-phase transition in few-layered ReS2. Nano Lett., 2015, 15(12): 8377-8384. |
| [130] | CHENET D A, ASLAN O B, HUANG P Y, et al.In-plane anisotropy in mono- and few-layer ReS2 probed by Raman spectroscopy and scanning transmission electron microscopy. Nano Lett., 2015, 15(9): 5667-5672. |
| [131] | HE R, YAN J A, YIN Z, et al.Coupling and stacking order of ReS2 atomic layers revealed by ultralow-frequency Raman spectroscopy. Nano Lett., 2016, 16(2): 1404-1409. |
| [132] | WU J, MAO N, XIE L, et al.Identifying the crystalline orientation of black phosphorus using angle-resolved polarized Raman spectroscopy. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 127(8): 2396-2399. |
| [133] | TAO J, SHEN W, WU S, et al.Mechanical and electrical anisotropy of few-layer black phosphorus. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(11): 11362-11370. |
| [134] | XIA F, WANG H, JIA Y. Rediscovering black phosphorus as an anisotropic layered material for optoelectronics and electronics. Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 4458-1-6. |
| [135] | QIAO J, KONG X, HU Z X, et al. High-mobility transport anisotropy and linear dichroism in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 4475-1-7. |
| [136] | LI L, GONG P, WANG W, et al.Strong in-plane anisotropies of optical and electrical response in layered dimetal chalcogenide. ACS Nano, 2017, 11(10): 10264-10272. |
| [137] | LIN Y C, KOMSA H P, YEH C H, et al.Single-layer ReS2: two-dimensional semiconductor with tunable in-plane anisotropy. ACS Nano, 2015, 9(11): 11249-11257. |
| [138] | LI L, PI L, LI H, et al.Photodetectors based on two-dimensional semiconductors: progress, opportunity and challenge. Chin. Sci. Bull., 2017, 62(27): 3134-3153. |
| [139] | YAN K, WEI Z, ZHANG T, et al.Near-infrared photoresponse of one-sided abrupt MAPbI3/TiO2 heterojunction through a tunneling process. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2016, 26(46): 8545-8554. |
| [140] | ZENG L, TAO L, TANG C, et al. High-responsivity UV-Vis photodetector based on transferable WS2 film deposited by magnetron sputtering. Sci. Rep., 2016, 6: 20343-1-8. |
| [141] | LI L, WANG W, CHAI Y, et al. Few-layered PtS2 phototransistor on h-BN with high gain. Adv. Funct. Mater., 2017, 27: 1701011-1-8. |
| [142] | JIANG J W. Thermal conduction in single-layer black phosphorus: highly anisotropic? Nanotechnology, 2015, 26(5): 055701-1-6. |
| [143] | LUO Z, MAASSEN J, DENG Y, et al. Anisotropic in-plane thermal conductivity observed in few-layer black phosphorus. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6: 8572-1-8. |
| [144] | LEE S, YANG F, SUH J, et al. Anisotropic in-plane thermal conductivity of black phosphorus nanoribbons at temperatures higher than 100 K. Nat. Commun., 2015, 6: 8573-1-7. |
| [145] | MA J L, CHEN Y N, HAN Z, et al. Strong anisotropic thermal conductivity of monolayer WTe2. 2D Materials, 2016, 3(4): 045010-1-8. |
| [146] | LIU G, SUN H Y, ZHOU J, et al. First-principles study of lattice thermal conductivity of Td-WTe2. New J. Phys., 2016, 18(3): 033017-1-9. |
| [147] | CARRETE J, MINGO N, CURTAROLO S. Low thermal conductivity and triaxial phononic anisotropy of SnSe. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2014, 105(10): 101907-1-5. |
| [148] | LI Y L, SHI X, REN D D, et al.Investigation of the anisotropic thermoelectric properties of oriented polycrystalline SnSe. Energies, 2015, 8(7): 6275-6285. |
| [149] | GUO R Q, WANG X J, KUANG Y D, et al. First-principles study of anisotropic thermoelectric transport properties of IV-VI semiconductor compounds SnSe and SnS. Phys. Rev. B, 2015, 92(11): 115202-1-13. |
| [150] | SUN B Z, MA Z, HE C, et al.Anisotropic thermoelectric properties of layered compounds in SnX2(X = S, Se): a promising thermoelectric material. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17(44): 29844-29853. |
| [151] | JANG H, RYDER C R, WOOD J D, et al. 3D anisotropic thermal conductivity of exfoliated rhenium disulfide. Adv. Mater., 2017, 29(35): 1700650-1-6. |
| [152] | YU S, ZHU H, ESHUN K, et al. Strain-engineering the anisotropic electrical conductance in ReS2 monolayer. Appl. Phys. Lett., 2016, 108(19): 191901-1-6. |
| [153] | MENG M, SHI C G, LI T, et al.Magnetism induced by cationic defect in monolayer ReSe2 controlled by strain engineering. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 425: 696-701. |
| [154] | MIN Y M, WANG A Q, REN X M, et al.Defect formation and electronic structure regulated by strain engineering in ReS2. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2018, 427: 942-948. |
| [155] | ZHOU Z H, WEI B C, HE C Y, et al.Anisotropic Raman scattering and mobility in monolayer 1Td-ReS2 controlled by strain engineering. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2017, 404: 276-281. |
| [156] | ZHANG X O, LI Q F. Strain-induced magnetism in ReS2 monolayer with defects. Chin. Phys. B, 2016, 25(11): 117103-1-5. |
| [157] | LI T H, ZHOU Z H, GUO J H, et al. Raman scattering modification in monolayer ReS2 controlled by strain engineering. Chin. Phys. Lett., 2016, 33(4): 046201-1-5. |
| [158] | LI Y L, LI Y, TANG C.Strain engineering and photocatalytic application of single-layer ReS2. Int. [J]. Hydrogen Energy, 2017, 42(1): 161-167. |
| [159] | KAO Y C, HUANG T, LIN D Y, et al. Anomalous structural phase transition properties in ReSe2 and Au-doped ReSe2. J. Chem. Phys., 2012, 137(2): 024509-1-7. |
| [160] | YAN Y, JIN C, WANG J, et al.Associated lattice and electronic structural evolutions in compressed multilayer ReS2. [J]. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2017, 8(15): 3648-3655. |
| [161] | HOU D, MA Y, DU J, et al.High pressure X-ray diffraction study of ReS2. J. Phys. Chem. Solids, 2010, 71(11): 1571-1575. |
| [162] | NAUMOV P G, ELGHAZALI M A, MIRHOSSEINI H, et al. Pressure-induced metallization in layered ReSe2. J. Phys. Condens Matter, 2017, 30(3): 035401-1-6. |
| [163] | YANG S, WANG C, SAHIN H, et al.Tuning the optical, magnetic, and electrical properties of ReSe2 by nanoscale strain engineering. Nano Lett., 2015, 15(3): 1660-1666. |
| [164] | ZHOU D, ZHOU Y, PU C, et al.Pressure-induced metallization and superconducting phase in ReS2. npj Quantum Mater., 2017, 2(19): 1-7. |
| [165] | YAGMURCUKARDES M, BACAKSIZ C, SENGER R T, et al. Hydrogen-induced structural transition in single layer ReS2. 2D Materials, 2017, 4(3): 035013-1-8. |
| [166] | JO S H, PARK H Y, KANG D H, et al.Broad detection range rhenium diselenide photodetector enhanced by (3-aminopropyl) triethoxysilane and triphenylphosphine treatment. Adv. Mater., 2016, 28(31): 6711-6718. |
| [167] | ALI M H, KANG D H, PARK J H.Rhenium diselenide (ReSe2) infrared photodetector enhanced by (3-aminopropyl) trimethoxysilane (APTMS) treatment. Org. Electron., 2018, 53: 14-19. |
| [168] | ZHANG X, LI Q. Electronic and magnetic properties of nonmetal atoms adsorbed ReS2 monolayers. J. Appl. Phys., 2015, 118(6): 064306-1-7. |
| [169] | LUO M, SHEN Y H, YIN T L.Structural, electronic, and magnetic properties of transition metal doped ReS2 monolayer. JETP Letters, 2017, 105(4): 255-259. |
| [170] | LOH G C, PANDEY R.Robust magnetic domains in fluorinated ReS2 monolayer. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2015, 17(28): 18843-18853. |
| [171] | OBODO K O, OUMA C N M, OBODO J T, et al. Influence of transition metal doping on the electronic and optical properties of ReS2 and ReSe2 monolayers. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2017, 19(29): 19050-19057. |
| [1] | 丁玲, 蒋瑞, 唐子龙, 杨运琼. MXene材料的纳米工程及其作为超级电容器电极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | 杨卓, 卢勇, 赵庆, 陈军. X射线衍射Rietveld精修及其在锂离子电池正极材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | 陈强, 白书欣, 叶益聪. 热管理用高导热碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | 林俊良, 王占杰. 铁电超晶格的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [5] | 牛嘉雪, 孙思, 柳鹏飞, 张晓东, 穆晓宇. 铜基纳米酶的特性及其生物医学应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [6] | 苑景坤, 熊书锋, 陈张伟. 聚合物前驱体转化陶瓷增材制造技术研究趋势与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [7] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [8] | 杨洋, 崔航源, 祝影, 万昌锦, 万青. 柔性神经形态晶体管研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [9] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [10] | 齐占国, 刘磊, 王守志, 王国栋, 俞娇仙, 王忠新, 段秀兰, 徐现刚, 张雷. GaN单晶的HVPE生长与掺杂进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [11] | 张超逸, 唐慧丽, 李宪珂, 王庆国, 罗平, 吴锋, 张晨波, 薛艳艳, 徐军, 韩建峰, 逯占文. 新型GaN与ZnO衬底ScAlMgO4晶体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [12] | 陈昆峰, 胡乾宇, 刘锋, 薛冬峰. 多尺度晶体材料的原位表征技术与计算模拟研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [13] | 林思琪, 李艾燃, 付晨光, 李荣斌, 金敏. Zintl相Mg3X2(X=Sb, Bi)基晶体生长及热电性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [14] | 刘岩, 张珂颖, 李天宇, 周菠, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 陶瓷材料电场辅助连接技术研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 113-124. |
| [15] | 谢兵, 蔡金峡, 王铜铜, 刘智勇, 姜胜林, 张海波. 高储能密度聚合物基多层复合电介质的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||