无机材料学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (10): 1089-1096.DOI: 10.15541/jim20180004
程丹1, 黄斌1, 陈涛1, 景凤娟1, 谢东2, 冷永祥1, 黄楠1
收稿日期:2018-01-02
修回日期:2018-01-31
出版日期:2018-10-20
网络出版日期:2018-09-25
作者简介:程 丹(1993-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: chengdan1193@163.com
基金资助:CHENG Dan1, HUANG Bin1, CHEN Tao1, JING Feng-Juan1, XIE Dong2, LENG Yong-Xiang1, HUANG Nan1
Received:2018-01-02
Revised:2018-01-31
Published:2018-10-20
Online:2018-09-25
About author:CHENG Dan. E-mail: chengdan1193@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
采用直流磁控溅射技术, 在Si片和316L SS基体上制备了不同Cu含量的TiCuO薄膜。采用X射线衍射仪(XRD)、透射电镜(TEM)、X 射线能谱仪(EDS)和X射线光电子能谱(XPS)对薄膜的显微结构和化学组成进行了分析。采用电化学腐蚀和模拟体液浸泡实验评价了薄膜的腐蚀性能和Cu离子释放特性。体外静态培养内皮细胞后, 采用细胞计数试剂盒(CCK-8)评价了TiCuO薄膜的细胞活性。研究结果表明, 未掺杂的TiO2薄膜为金红石相, 掺入Cu后的TiCuO薄膜由非晶基体上含有Cu2O的纳米晶粒构成。薄膜中的富Cu区引起了薄膜腐蚀。含Cu量高的TiCuO薄膜更易被腐蚀, 并释放出较多Cu离子。TiCuO薄膜释放出一定浓度的Cu离子促进了内皮细胞活性。研究表明, TiCuO薄膜的含Cu量和显微结构影响了Cu离子释放, 对其内皮细胞活性起了关键作用。
中图分类号:
程丹, 黄斌, 陈涛, 景凤娟, 谢东, 冷永祥, 黄楠. TiCuO薄膜的显微结构对Cu离子释放和内皮细胞行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(10): 1089-1096.
CHENG Dan, HUANG Bin, CHEN Tao, JING Feng-Juan, XIE Dong, LENG Yong-Xiang, HUANG Nan. Microstructure of TiCuO Films on Copper Ion Release and Endothelial Cell Behavior[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(10): 1089-1096.
| Sample | Cu/at% | Ti/at% | O/at% |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiCuO-1 | 12.4 | 12.3 | 75.3 |
| TiCuO-2 | 23.1 | 6.7 | 70.2 |
表1 采用EDS检测TiCuO薄膜中的Ti、Cu、O元素的相对原子含量
Table 1 Atomic concentration of TiCuO films evaluated by EDS
| Sample | Cu/at% | Ti/at% | O/at% |
|---|---|---|---|
| TiCuO-1 | 12.4 | 12.3 | 75.3 |
| TiCuO-2 | 23.1 | 6.7 | 70.2 |
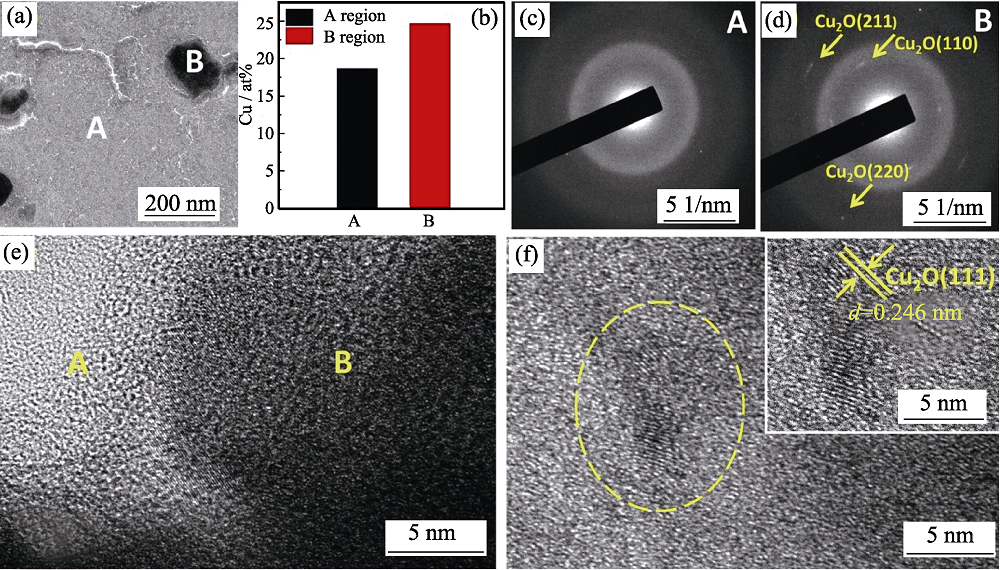
图2 TiCuO-1样品的TEM照片(a), A和B区域Cu原子百分比(b), A(c)和B(d)区域的选区电子衍射图(c)及其HRTEM形貌(e)~(f)
Fig. 2 TEM image (a), Cu contents evaluated by EDS (b), the selected area electron diffraction results of A region (c) and B region (d), and their corresponding HRTEM images (e, f), respectively, of the TiCuO-1 sample
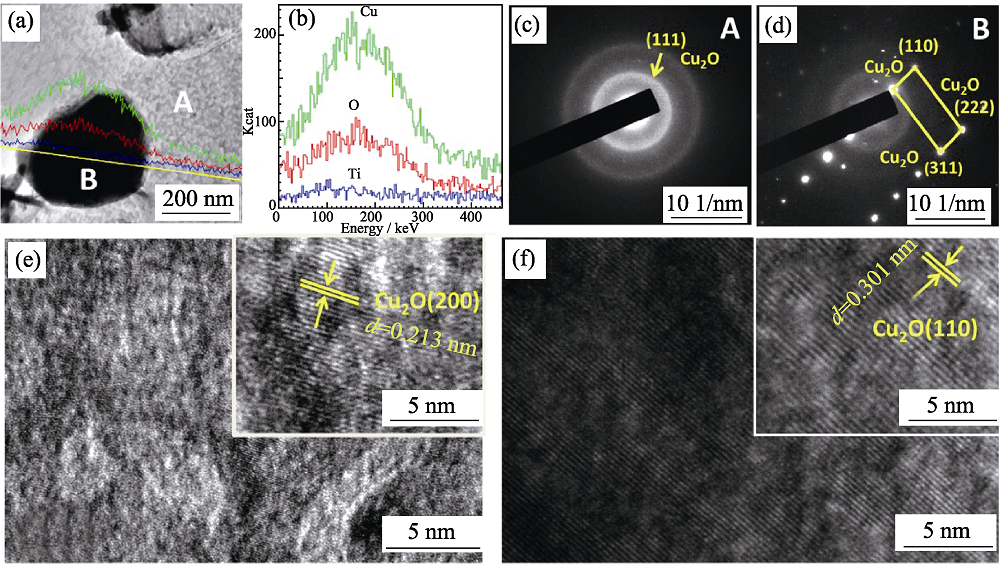
图3 TiCuO-2样品的TEM形貌照片(a), Cu、O、Ti元素的EDS 线扫描结果(b), A(c)和B(d)区域的选区电子衍射图及其HRTEM形貌图(e)~(f)
Fig. 3 TEM image(a), corresponding line-scanning of Cu, O, Ti elements (b) across a selected area (yellow line in (a)), the selected area electron diffraction results of A region (c) and B region (d), and their corresponding HRTEM images (e, f) respectively of the TiCuO-2 sample
| Sample | Ti2p | Cu2p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti4+ | Ti2+ | Ti3+ | Cu2+ | Cu+ | |
| TiCuO-2 | 47at% | 53at% | 0 | 30.2at% | 69.8at% |
| TiCuO-1 | 39at% | 43at% | 18at% | 6.2at% | 93.8at% |
| TiO2 | 32at% | 34at% | 34at% | - | - |
表2 TiO2、TiCuO-1、TiCuO-2 样品中的Ti2p和Cu2p拟合后的Ti4+、Ti3+、Ti2+在Ti2p图谱中所占面积的百分含量及Cu2+、Cu+在Cu2p图谱中的所占面积的百分含量
Table 2 The area percentages of Ti4 +, Ti3 + and Ti2 + in the Ti2p spectra and the area percentage of Cu2 + and Cu + in Cu2p spectra of TiO2, TiCuO-1 and TiCuO-2 samples
| Sample | Ti2p | Cu2p | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ti4+ | Ti2+ | Ti3+ | Cu2+ | Cu+ | |
| TiCuO-2 | 47at% | 53at% | 0 | 30.2at% | 69.8at% |
| TiCuO-1 | 39at% | 43at% | 18at% | 6.2at% | 93.8at% |
| TiO2 | 32at% | 34at% | 34at% | - | - |
| Sample | SS | TiO2 | TiCuO-1 | TiCuO-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecorr /V(vs.SCE) | -0.13 | -0.06 | -0.16 | -0.17 |
| Icorr /(μA·cm-2) | 0.49 | 0.03 | 0.62 | 3.89 |
表3 TiO2、TiCuO和SS的自腐蚀电位(Ecorr)及其自腐蚀电流密度(Icorr)
Table 3 Corrosion potential (Ecorr) and current densities (Icorr) of SS, TiO2 and TiCuO films derived from potentiodynamic polarization curves
| Sample | SS | TiO2 | TiCuO-1 | TiCuO-2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ecorr /V(vs.SCE) | -0.13 | -0.06 | -0.16 | -0.17 |
| Icorr /(μA·cm-2) | 0.49 | 0.03 | 0.62 | 3.89 |
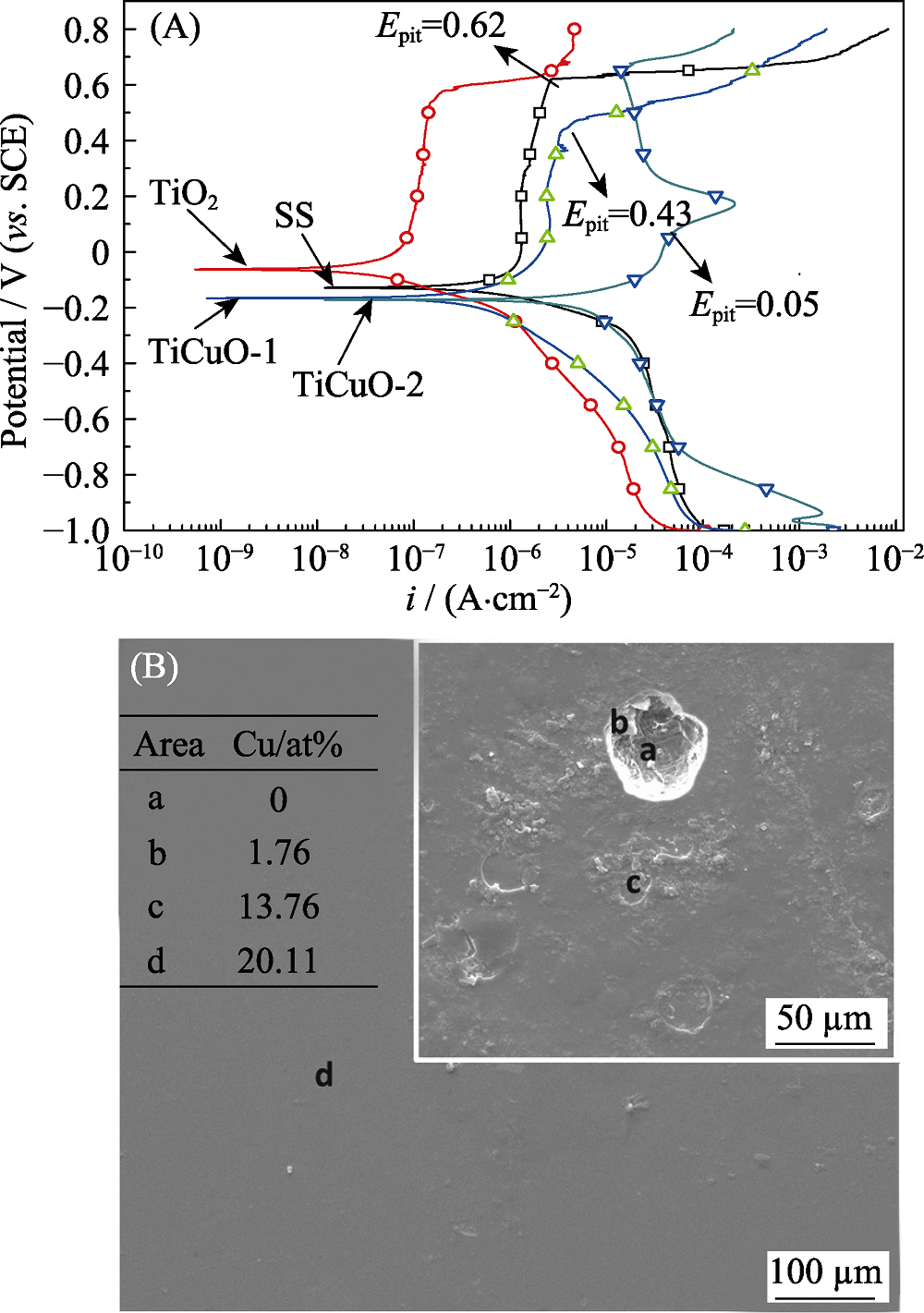
图5 TiO2、TiCuO样品和SS的电化学腐蚀极化曲线(A)及TiCuO-2样品的腐蚀形貌图和a, b, c, d四个不同腐蚀区域的EDS结果(B)
Fig. 5 Electrochemical corrosion polarization curves of TiO2, TiCuO and 316 L SS samples (A) and morphology of the TiCuO-2 sample with its EDS results of the four different corroded areas labeled with a, b, c and d (B)
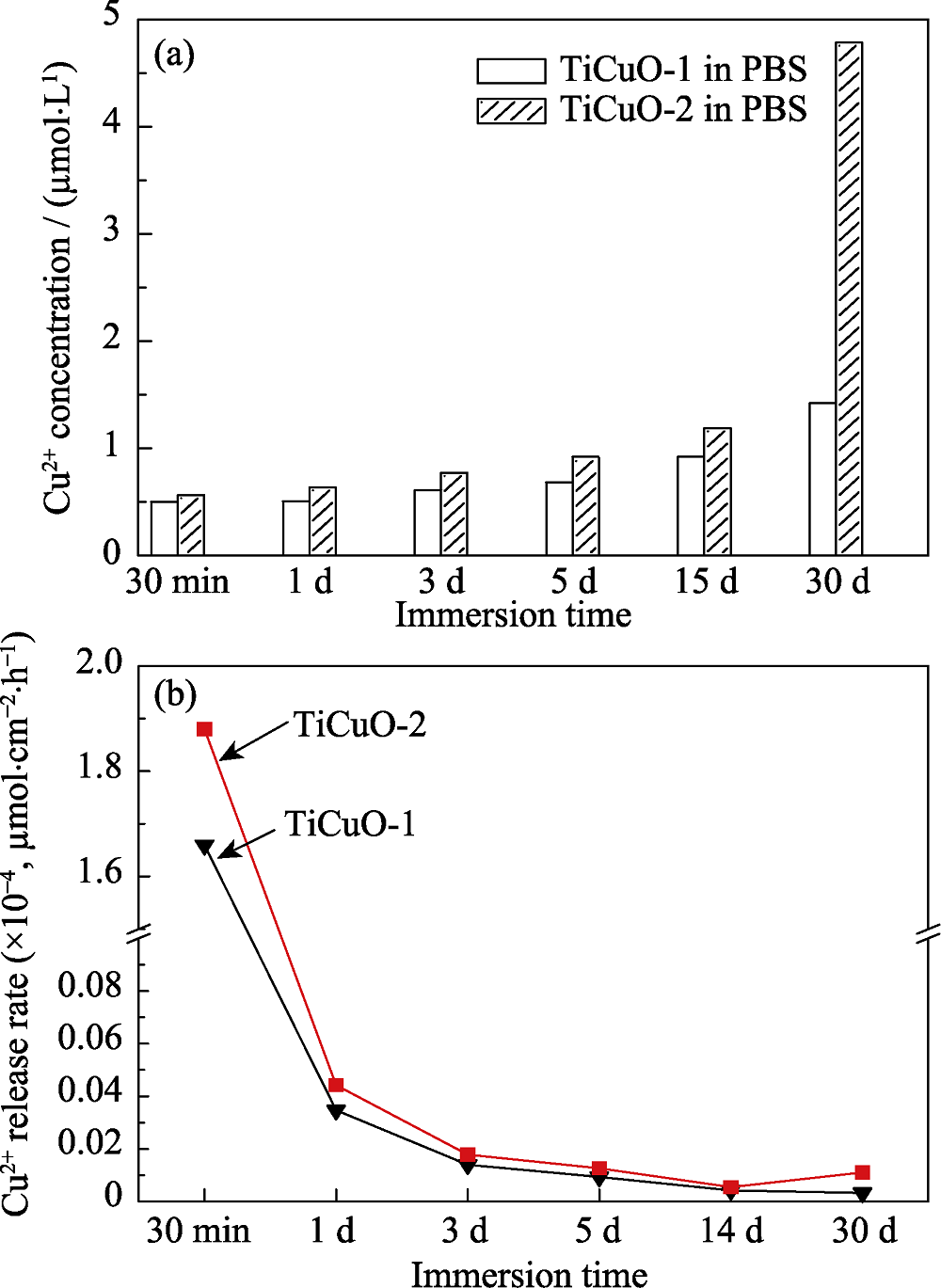
图6 TiCuO-1和TiCuO-2样品释放Cu离子累积浓度(a)和Cu离子平均释放速率(b)
Fig. 6 Accumulated Cu ions concentration (a) and release rate (b) of Cu ions released from TiCuO-1 and TiCuO-2 samples

图7 TiO2、TiCuO样品体外静态培养内皮细胞的细胞活性(a)和罗丹明荧光染色照片(b)
Fig. 7 ECs viability detected by CCK-8 assay (a) and fluorescence microscopic images stained by rhodamine (b) after being cultured on the samples of TiO2 and TiCuO
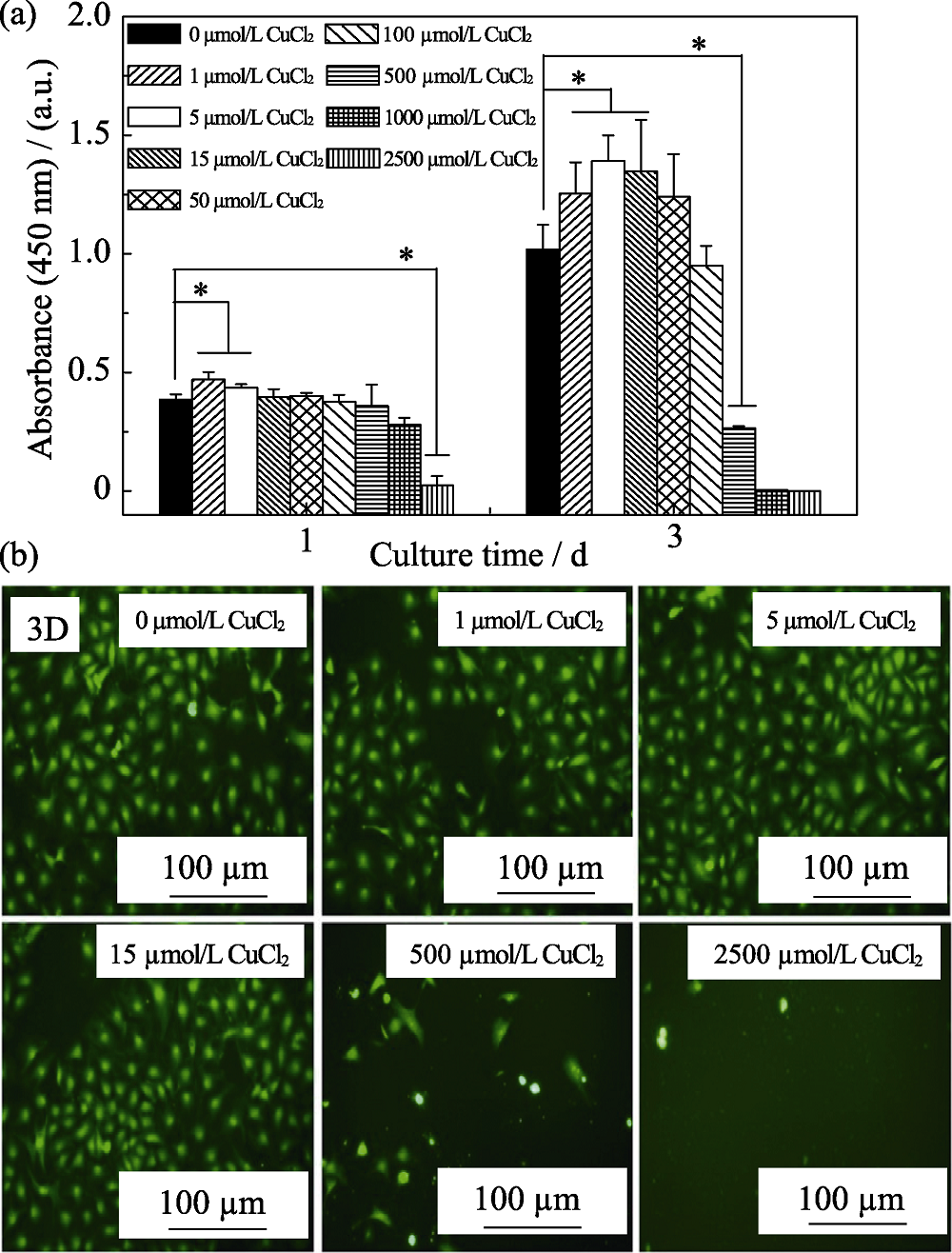
图8 TiO2、TiCuO样品体外静态培养内皮细胞的细胞活性(a)和罗丹明荧光染色照片(b)
Fig. 8 ECs viability detected by CCK-8 assay (a) and fluorescence microscopic images stained by rhodamine (b) after being cultured under condition medium with CuCl2 solution at different concentration
| [1] | WARD M R, STEWART D J, KUTRYK M J.Endothelial progenitor cell therapy for the treatment of coronary disease, acute MI, and pulmonary arterial hypertension: current perspectives.Catheterization and Cardiovascular Interventions, 2007, 70(7): 983-998. |
| [2] | NISIO D M, MIDDELDORP S, BÜLLER H R. Direct thrombin inhibitors.New England Journal of Medicine, 2005, 353(10): 1028-1040. |
| [3] | AKAHORI T, NIINOMI M.Fracture characteristics of fatigued Ti-6Al-4V ELI as an implant material.Materials Science & Engineering A, 1998, 243(1/2): 237-243. |
| [4] | LENG Y X, CHEN J Y, YANG P, et al. Structure and properties of passivating titanium oxide films fabricated by DC plasma oxidation. Surface & Coatings Technology, 2003, 166(2/3): 176-182. |
| [5] | TSYGANOV I A, MAITZ M F, RICHTER E,et al. Hemocompatibility of titanium-based coatings prepared by metal plasma immersion ion implantation and deposition. Nuclear Instruments & Methods in Physics Research, 2007, 257(1/2): 122-127. |
| [6] | KLESZCZEWSKI T, MODZELEWSKA B, BAL W,et al. Cu(II) complexation does not affect oxytocin action on pregnant human myometrium in vitro. Reproductive Toxicology, 2015, 59: 60-65. |
| [7] | AGGETT P J.An overview of the metabolism of copper.European Journal of Medical Research, 1999, 4(6): 214-216. |
| [8] | GAETKE L M, CHOW C K.Copper toxicity, oxidative stress, and antioxidant nutrients.Toxicology, 2003, 189(1/2): 147-163. |
| [9] | HU G.Copper stimulates proliferation of human endothelial cells under culture.Journal of Cellular Biochemistry, 1998, 69(3): 326-335. |
| [10] | REN L, XU L, FENG J,et al. In vitro study of role of trace amount of Cu release from Cu-bearing stainless steel targeting for reduction of in-stent restenosis. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Medicine, 2012, 23(5): 1235-1245. |
| [11] | SEN C K, KHANNA S, VENOJARVI M,et al. Copper-induced vascular endothelial growth factor expression and wound healing. Am. J. Physiol.-Heart Circ. Physiol., 2002, 282(5): H1821-H1827. |
| [12] | YIN R, LING L, XIANG Y,et al. Enhanced photocatalytic reduction of chromium (VI) by Cu-doped TiO2 under UV-A irradiation. Separation & Purification Technology, 2017, 190: 53-59. |
| [13] | ZONG M, LONG B, LIU Y,et al. Antibacterial ability and angiogenic activity of Cu-TiO2 nanotube arrays. Materials Science & Engineering C, 2017, 71: 93-99. |
| [14] | NORAMBUENA G A, PATEL R, KARAU M,et al. Antibacterial and bio compatible titanium-copper oxide coating may be a potential strategy to reduce periprosthetic infection: an in vitro study. Clinical Orthopaedics & Related Research, 2016, 475(3): 1-11. |
| [15] | WANG H, LI Y, BA X,et al. TiO2 thin films with rutile phase prepared by DC magnetron co-sputtering at room temperature: effect of Cu incorporation. Applied Surface Science, 2015, 345: 49-56. |
| [16] | TOMOLYA K, JANOVSZKY D, SYCHEVA A, et al. Peculiarities of ball-milling induced crystalline-amorphous transformation in Cu-Zr-Al-Ni-Ti alloys. Intermetallic, 2015, 65: 117-121. |
| [17] | NABIAŁEK M. Soft magnetic and microstructural investigation in Fe-based amorphous alloy.Journal of Alloys & Compounds, 2015, 642: 98-103. |
| [18] | OLEKSAK RP, DEVARAJ A, HERMAN GS.Atomic-scale structural evolution of Ta-Ni-Si amorphous metal thin films.Materials Letters, 2016, 164: 9-14. |
| [19] | TSENG I H, WU J C S, CHOU H Y. Effects of Sol-Gel procedures on the photocatalysis of Cu/TiO2 in CO2 photoreduction. Journal of Catalysis, 2004, 221(2): 432-440. |
| [20] | SUN C, ZHU J, LV Y,et al. Dispersion, reduction and catalytic performance of CuO supported on ZrO2-doped TiO2 for NO removal by CO. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2011, 103(1): 206-220. |
| [21] | LIU J, LI X, ZHAO Q,et al. The selective catalytic reduction of NO with propene over Cu-supported Ti-Ce mixed oxide catalysts: promotional effect of ceria. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2013, 378: 115-123. |
| [22] | LONG R, ENGLISH N J.Electronic properties of anatase-TiO2, co-doped by cation-pairs from hybrid density functional theory calculations.Chemical Physics Letters, 2011, 513(4): 218-223. |
| [23] | NAKAYAMA S, KIMURA A, SHIBATA M,et al. Voltammetric characterization of oxide films formed on copper in air. Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2001, 148(11): B467-B472. |
| [24] | NAKAYAMA S, NOTOYA T, OSAKAI T.Highly selective determination of copper corrosion products by voltammetric reduction in a strongly alkaline electrolyte.Analytical Sciences the International Journal of the Japan Society for Analytical Chemistry, 2012, 28(4): 323. |
| [25] | BELOUSOV V V.Mechanisms of accelerated oxidation of copper in the presence of molten oxides.Oxidation of Metals, 2007, 67(5/6): 235-250. |
| [26] | AL-MAYOUF A M, AL-SWAYIH A A, AL-MOBARAK N A,et al. Corrosion behavior of a new titanium alloy for dental implant applications in fluoride media. Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2004, 86(2/3): 320-329. |
| [27] | LIU H, LENG Y, HUANG N.Corrosion resistance of Ti-O film modified 316L stainless steel coronary stentsin vitro. Journal of Materials Engineering & Performance, 2012, 21(3): 424-428. |
| [28] | LIU H, ZHANG D, FENG S,et al. Corrosion and ion release behavior of Cu/Ti film prepared via physical vapor deposition in vitro as potential biomaterials for cardiovascular devices. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258(19): 7286-7291. |
| [29] | JACEK BANAS, ANDRZEJ MAZURKIEWICZ.The effect of copper on passivity and corrosion behaviour of ferritic and ferritic- austenitic stainless steels.Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2000, 277(1/2): 183-191. |
| [30] | STRANAK V, WULFF H, REBL H,et al. Deposition of thin titanium copper films with antimicrobial effect by advanced magnetron sputtering methods. Materials Science & Engineering C, 2011, 31(7): 1512-1519. |
| [31] | SEO Y, CHO Y S, HUH Y D,et al. Copper ion from Cu2O crystal induces AMPK-mediated autophagy via superoxide in endothelial cells. Molecules & Cells, 2016, 39(3): 195-203. |
| [32] | LIU H, PAN C, ZHOU S,et al. Improving hemocompatibility and accelerating endothelialization of vascular stents by a copper-titanium film. Materials Science & Engineering C Materials for Biological Applications, 2016, 69: 1175-1182. |
| [33] | MIDANDER K, CRONHOLM P, KARLSSON H L,et al. Surface characteristics, copper release, and toxicity of nano-and micrometer- sized copper and copper(II) oxide particles: a cross-disciplinary study. Small, 2009, 5(3): 389-399. |
| [34] | ARIMA Y, IWATA H.Effect of wettability and surface functional groups on protein adsorption and cell adhesion using well-defined mixed self-assembled monolayers.Biomaterials, 2007, 28(20): 3074-3082. |
| [35] | ESHAGHI A, ESHAGHI A.Preparation and hydrophilicity of TiO2 Sol-Gel derived nanocomposite films modified with copper loaded TiO2 nanoparticles.Materials Research Bulletin, 2011, 46(12): 2342-2345. |
| [36] | HUANG L, NING C Q, DING D Y,et al. Wettability and in vitro bioactivity of doped TiO2 nanotubes. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2010, 25(7): 775-779. |
| [37] | BRAMMER K S, OH S, GALLAGHER J O,et al. Enhanced cellular mobility guided by TiO2 nanotube surfaces. Nano Letters, 2008, 8(3): 786-793. |
| [1] | 王影, 张文龙, 邢彦锋, 曹苏群, 戴新义, 李晶泽. 非晶态磷酸锂包覆钛酸锂电极在0.01~3.00 V电压范围的性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 999-1005. |
| [2] | 赵长江,马超,刘俊成,刘治钢,陈燕. 溅射功率对磁控溅射法制备MgF2薄膜组织和性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(9): 1064-1070. |
| [3] | 王美涵, 温佳星, 陈昀, 雷浩. 掠射角溅射沉积纳米结构氧化钨薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(12): 1303-1308. |
| [4] | 王红燕, 张 浩, 姜 宏, 汪国庆, 熊春荣. 高可见光透过、高紫外截止镀膜玻璃的制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(7): 758-764. |
| [5] | 王佛根, 陈蕴璐, 任胜强, 张家远, 武莉莉, 冯良桓. 磁控溅射法制备的CdS:Al薄膜的性质研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(4): 413-417. |
| [6] | 李淼磊, 王恩青, 岳建岭, 黄小忠. TiAlN/VN纳米多层膜的微结构与力学和摩擦学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(12): 1280-1284. |
| [7] | 朱玉婵, 袁 敏, 张 欢, 王 乐, 全姗姗, 柴 波, 任占冬. 沿[111]方向择优生长Pt/Ti电极制备及析氯电催化活性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(5): 510-516. |
| [8] | 吴志立, 李玉阁, 吴 彼, 雷明凯. 高功率调制脉冲磁控溅射沉积TiAlSiN纳米复合涂层结构调控与性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(12): 1254-1260. |
| [9] | 张志伟, 邓 元. 磁控溅射法可控制备有序碲纳米线阵列[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(1): 107-112. |
| [10] | 张 辉, 马永军, 王艺程, 文丹丹, 叶 飞, 白飞明. 离轴磁控溅射法生长1-3维PZT-NFO纳米复合薄膜[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(4): 371-376. |
| [11] | 曹丽莉,王 瑶,邓 元,罗炳威,祝 薇,史永明, 林 桢. 铜对双靶共溅制备热电薄膜输运性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(2): 215-219. |
| [12] | 王伟君, 何 俊, 张克智, 陶加华, 孙 琳, 陈 晔, 杨平雄, 褚君浩. 单靶磁控溅射制备铜铟硒和铜铟锌硒薄膜及其结构、光学性质研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(11): 1223-1227. |
| [13] | 童 贝, 杨晓非, 林更琪, 陈 实, 欧阳君. AlN/FeCoSiB磁电复合薄膜的制备及其逆磁电效应研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(9): 982-986. |
| [14] | 许俊华, 薛雅平, 曹 峻, 喻利花. V含量对TaVN复合膜微结构、力学性能和摩擦性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(7): 769-774. |
| [15] | 曹 峻, 许俊华, 喻利花. TiN/VCN多层膜的力学性能及摩擦磨损性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(2): 195-200. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||