无机材料学报 ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (8): 825-831.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170498
邓立儿1, 李妍2, 巩蕾1, 王佳1
收稿日期:2017-10-19
修回日期:2018-02-27
出版日期:2018-08-28
网络出版日期:2018-07-17
基金资助:DENG Li-Er1, LI Yan2, GONG Lei1, WANG Jia1
Received:2017-10-19
Revised:2018-02-27
Published:2018-08-28
Online:2018-07-17
Supported by:摘要:
光热治疗是近年来受到广泛关注的一种低副作用的癌症治疗方法, 治疗中使用的纳米光热剂的制备和性能是决定光热治疗效应的关键因素。本研究采用热解和表面配体置换相结合的方法制备得到二氢硫辛酸(DHLA)修饰的Ag2S纳米晶材料, 这种材料具有良好的水溶性、光热稳定性和生物相容性。研究结果显示浓度大于40 μg/mL的Ag2S纳米晶在波长为980 nm、功率密度为5 W/cm2的红外激光照射下对宫颈癌细胞具有明显的杀伤效果, 且光热稳定性良好。Ag2S纳米晶的光热效应与其良好的荧光成像功能相结合, 可实现光热治疗的可视化和精准化。
中图分类号:
邓立儿, 李妍, 巩蕾, 王佳. Ag2S纳米晶的制备及其近红外光热治疗应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(8): 825-831.
DENG Li-Er, LI Yan, GONG Lei, WANG Jia. Preparation of Ag2S Nanocrystals for NIR Photothermal Therapy Application[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(8): 825-831.
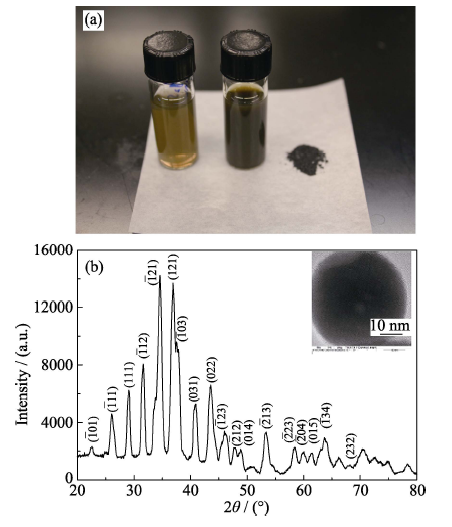
图1 Ag2S纳米晶粉末及不同浓度水溶液照片(a)和Ag2S纳米晶的XRD图谱(b)及其TEM照片(插图)
Fig. 1 Photograph of DHLA-Ag2S nanocrystals aqueous dispersion (a) and XRD pattern (b) with inset showing TEM image of Ag2S nanocrystals
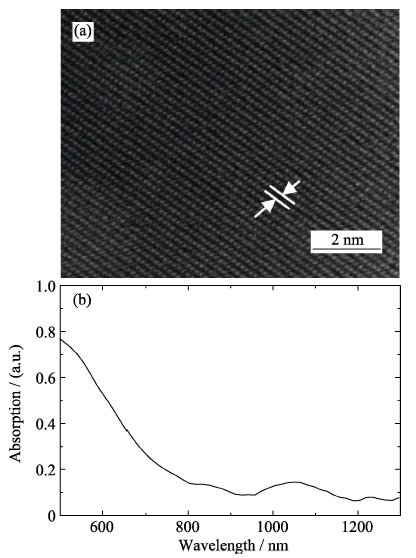
图2 Ag2S纳米晶HRTEM照片(a)及其水溶液的吸收光谱(b)
Fig. 2 HRTEM images of the synthesized Ag2S nanocrystals (a) and UV-Vis-NIR spectrum (b) of Ag2S nanocrystals suspended in water
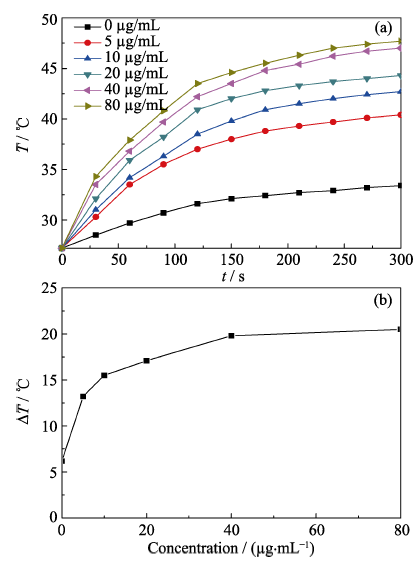
图3 不同浓度Ag2S纳米晶水溶液在激光照射下的升温曲线(a)和相同光照时间下(5 min)的温升值随溶液的浓度变化曲线(b)
Fig. 3 Temperature elevation of the aqueous dispersion of Ag2S nanocrystals with different concentrations as a function of irradiation time (a) and plot of temperature change (∆T) over a period of 5 min versus the concentration of the Ag2S nanocrystals aqueous dispersion (b)
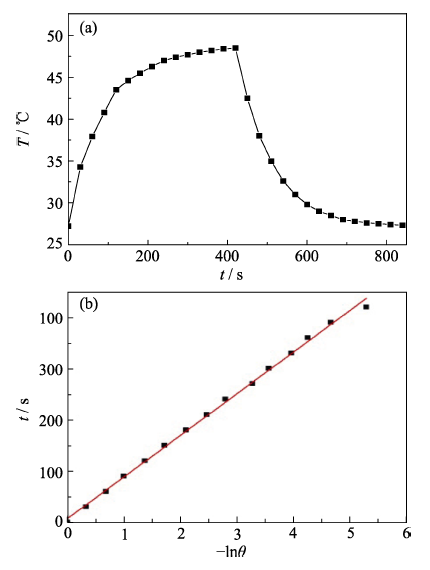
图4 80 μg/mL的Ag2S纳米晶水溶液在激光(980 nm, 5 W/cm2)照射下加热(激光开)和冷却(激光关)过程的温度变化曲线(a)及其t与lnθ的线性拟合曲线(b)
Fig. 4 Temperature evolution of Ag2S nanocrystals aqueous dispersion (80 μg/mL) during heating (laser on) and cooling (laser off) (a) and linear fitting curve between t and lnθ (b)
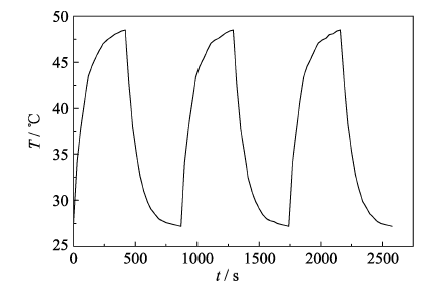
图5 三个周期激光开关过程的DHLA-Ag2S纳米晶水溶液温度值随时间的变化曲线
Fig. 5 Temperature varied with time of DHLA-Ag2S nanocrystals aqueous solution in three cycles of laser switching
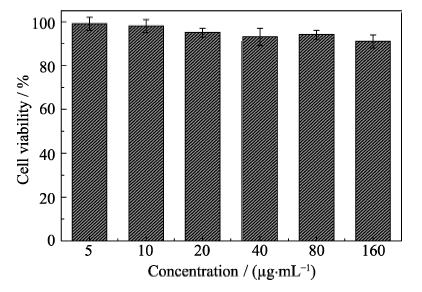
图6 与不同浓度的Ag2S纳米晶水溶液共培养24 h后HeLa细胞的存活率
Fig. 6 Cell viability of HeLa cells incubated with different concentrations of Ag2S nanocrystal aqueous solutions for 24 h
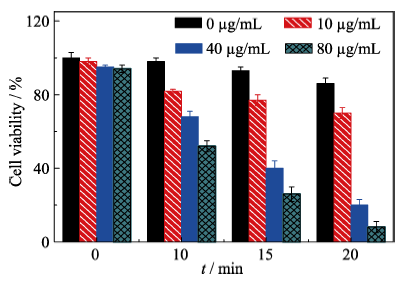
图7 不同光照时间和不同浓度的Ag2S纳米材料光热治疗后HeLa细胞的存活率
Fig. 7 Cell viability of HeLa cells incubated with different concentrations of Ag2S nanomaterials and then being irradiated by a NIR laser for different time
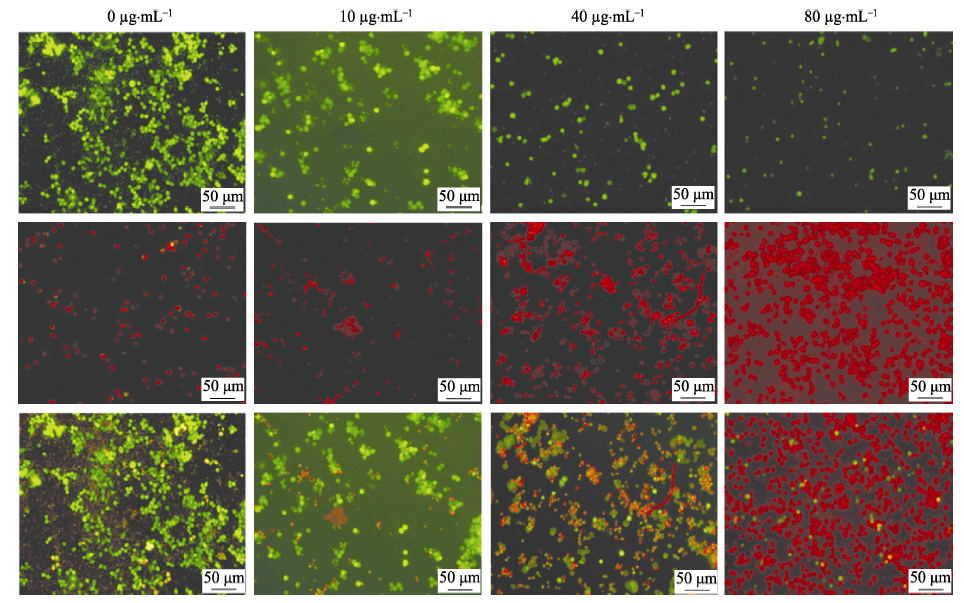
图8 光照20 min后不同浓度Ag2S纳米晶材料杀灭肿瘤细胞效果的荧光照片
Fig. 8 Fluorescence images of HeLa cells after photothermal treatment with different concentrations of Ag2S nanomaterials under NIR irradiation for 20 min Green fluorecence: live cells; Red fluorescence: dead cells. All bars are 50 μm
| [1] | LU W, XIONG C, ZHANG G D,et al. Targeted photothermal abltion of murnemelanomas with melanocyte-stimulating hormone analog conjugated hollow gold nanospheres.Clin. Cancer. Res., 2009, 15(3): 876-886. |
| [2] | TAKOR A S, GAMBHIR S S.Nanooncology: the future of cancer diagnosis and therapy.CA. Cancer J. Clin., 2013, 63(6): 395-399. |
| [3] | VOGEL A, VENUGOPALAN V.Mechanisms of pulsed laser ablation of biological tissues.Chem. Rev., 2003, 103(2): 577-581. |
| [4] | YANG J, CHOI J, BANG D,et al. Convertible organic nanoparticles for near-infrared photothermal ablation of cancer cells.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(2): 441-444. |
| [5] | ZHAI YUN GANG, DONG WEN JIE, GAO YONG PING,et al. Preparation of superparamagnetic gold nanocomposites with different diameters and their imaging and therapy applications.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(9): 950-956. |
| [6] | YANG J, CHOI J, BANG D,et al. Convertible organic nanoparticles for near-infrared photothermal ablation of cancer cells.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2011, 50(2): 441-444. |
| [7] | THAKARE V S, DAS M, JAIN A K,et al. Carbon nanotubes in cancer theragnosis.Nanomedicine, 2010, 5(8): 1277-1301. |
| [8] | HIESCH L R, STAFFORD R J, BANKSON J A.et al. Nanoshell- media-infrared thermal therapy of tumors under magnetic resonance guidance.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2003, 100(23): 13549-13554. |
| [9] | HUANG X, JAIN P K, El-SAYED I H.et al. Plasmonic photo-thermal therapy (PPTT) using gold nanoparticles. Alex. J. Med., 2011, 47(15): 1-9. |
| [10] | HAO Y W, ZHANG B X, ZHENG C X,et al.The tumor-targeting core-shell structured DTX-loaded PLGA@Au nanoparticles for chemo-photothermal therapy and X-ray imaging. Journal of Controlled Release, 2015, 220: 545-555. |
| [11] | LI J L, GU M.Gold-nanoparticle-enhanced cancer photothermal therapy.IEEE J. Sel. Top Quant Electron., 2010, 16(4): 989-996. |
| [12] | LI Z, HUANG P, ZHANG X,et al.RGD-conjugated dendrimer-modified gold nanorods for in vivo tumor targeting and photothermal therapy. Mol. Pharmaceutics., 2010, 7(1): 94-104. |
| [13] | LI Z B, HUANG H, TANGS Y,et al. Small gold nanorods laden mac rophages for enhanced tumor coverage in photothermal therapy. Biomaterials, 2016, 74(30): 144-154. |
| [14] | CHAKRAVARTY P, MARCHES R, ZIMMERMAN N S,et al.Thermal ablation of tumor cells with anti body-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotubes.Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2008, 105(25): 8697-8702. |
| [15] | ZHANG Z, LIU S, XIONG H.Electrospun PLA/MWCNTs composite nanofibers for combined chemo- and photothermaltherapy.Acta Biomaterialia, 2015, 26(20): 115-123. |
| [16] | POLAND C A, DUFFIN R, KINLOCH I,et al.Carbon nanotubes introduced into the abdominal cavity of mice show asbestos-like pathogenicity in a pilot study. Nat. Nanotechnol., 2008, 3(7): 423-428. |
| [17] | LANBERT T N, ANDREWS N L, GERUNG H, et al. (CdSe)ZnS core-shell quantum dots: synthesis and characterization of a size series of highly luminescent nanocrystallites. Biomaterials, 2008, 29(5): 1912-1919. |
| [18] | DABBOUSI B O, RODRIGUEZVIEJO J, FV MIKULEC F V,et al.(CdSe) ZnS core-shell quantum dots: synthesis and optical and structural characterization of a size series of highly luminescent materials. J. Bacterior., 1997, 182(13): 3649-3654. |
| [19] | LEE C, KIM H, HONG C,et al.Porous silicon as an agent for cancer thermotherapy based on near-infrared light irradiation. J. Mater. Chem., 2008, 18(40): 4790-4795. |
| [20] | YANG K, ZHANG S A, ZHANG G X,et al.Graphene in mice: ultra hig in vivo tumor uptake and efficient photothermal therapy. Nano Lett., 2010, 10(9): 3318-3323. |
| [21] | SHARKER S M, KIM S M, LEE J E,et al.Functionalized biocom-patible WO3 nanoparticles for triggered and targeted in vitro and in vivo photothermal therapy. J. Control. Release, 2015, 217: 211-220. |
| [22] | YANG C, MA L, ZOU X J,et al.Surface plasmon-enhanced Ag/CuS nanocomposites for cancer treatment. Cancer Nano, 2013, 4(4/5): 81-89. |
| [23] | SHERLOCK S P, TABAKAN S M, XIE L,et al.Photothermally enhanced drug delivery by ultra-small multifunctional FeCo/ graphitic-shell nanocrystals. ACS Nano, 2011, 5(2): 1505-1512. |
| [24] | KRYUKOV A I, STROYUK A L, ZIN'CHUK N N,et al. Optical and catalytic properties of Ag2S nanoparticles. Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2004, 221(1/2): 209-221. |
| [25] | WANG Q T, WANG X B, LOU W J,et al.Synthesis of bismuth sulfide nanostructures and their electrochemical hydrogen storage behavior. New Journal of Chemistry, 2010, 34(9): 1930-1935. |
| [26] | HONGG S, ROBINSON J T, ZHANG Y J,et al.In vivo fluorescence imaging with Ag2S quantum dots in the second near-infrared region. 2012, 51(39): 9818-9821. |
| [27] | LI C Y, ZHANG Y J, WANG M,et al.In vivo real-time visualization of tissue blood flow and angiogenesis using Ag2S quantum dots in the NIR-II window. Biomaterials, 2014, 35(1): 393-400. |
| [28] | ROPER D K, AHN W, HOEPFNER M.Microscale heat transfer transduced by surface plasmon resonant gold nanoparticles.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(9): 3636-9641. |
| [29] | YUWEN L H, ZHOU J J, ZHANG Y Q,et al.Aqueous phase preparation of ultrasmall MoSe2 nanodots for efficient photothermal therapy of cancer cells. Nanoscale, 2016, 8: 2720-2726. |
| [30] | TIAN Q W, JIANG F R, ZOU R J,et al. Hydrophilic Cu9S5 nanocrystals: a photothermal agent with a 25.7% heat conversion efficiency for photothermal ablation of cancer cells in vivo.ACS Nano, 2011, 5(12): 9761-9771. |
| [31] | HONG G S, ROBINSON T J, ZHANG Y J,et al.In-vivo fluorescence imaging with Ag2S quantum dots in the second near-infrared region.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 51(39): 9818-9821. |
| [32] | DU Y P, XU B, FU T,et al.Near-infrared photoluminescent Ag2S quantum dots from a single source precursor.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2010, 132(5): 1470-1471. |
| [1] | 孙炼, 顾全超, 杨雅萍, 王洪磊, 余金山, 周新贵. 二维过渡金属硫属化合物氧还原反应催化剂的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 697-709. |
| [2] | 李文博, 黄民松, 李月明, 李驰麟. 双盐镁电池CoS2正极材料的电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 173-181. |
| [3] | 蔡苗, 陈子航, 曾实, 杜江慧, 熊娟. CuS纳米片修饰Bi5O7I复合材料用于光催化还原Cr(VI)水溶液[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(6): 665-672. |
| [4] | 汤丹蕾, 贾丽华, 赵振龙, 杨瑞, 王欣, 郭祥峰. EDTA辅助合成Co3O4纳米材料及其气敏性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(11): 1214-1222. |
| [5] | 李泽晖,谭美娟,郑元昊,骆雨阳,经求是,蒋靖坤,李明杰. 导电金属有机骨架材料在超级电容器中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(7): 769-780. |
| [6] | 彭章美,赵安婷,付茂芬. Q[6]/CdS-Ag2S复合光催化剂的合成及光催化性质[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 703-708. |
| [7] | 陈钧,马培华,张诚,劳伦·鲁尔曼,吕耀康. 新型多功能无机/有机复合薄膜的制备及电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 217-223. |
| [8] | 肖剑飞, 乃学瑛, 苟生莲, 叶俊伟, 董亚萍, 李武. 邻苯二甲酸氢钾在制备碱式硫酸镁纳米线过程中的机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(11): 1181-1186. |
| [9] | 许云青,王海增. EDTA辅助水热法制备不同形貌的氟化镁钠[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 933-937. |
| [10] | 李思汉, 张超, 吴辰亮, 张荷丰, 严新焕. 低负载量Pd/CeO2/γ-Al2O3催化剂用于低温催化氧化VOCs[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(8): 827-833. |
| [11] | 张峰, 张凯立, 周明明, 陈超, 蔡志威, 魏国辉, 姜兴茂, 张诚, 劳伦·鲁尔曼, 吕耀康. 基于纳米银负载氧化石墨烯的新型聚乙烯复合材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 633-640. |
| [12] | 王树江, 杨永恒, 温春阳, 张国馗, 苑春晖. 纳米银/伊利石复合材料的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(5): 570-576. |
| [13] | 杨志胜, 柯蔚芳, 王艳香, 黄丽群, 郭平春, 朱 华. 杂化钙钛矿(HOC2H4NH3)2CuCl4的制备与表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(10): 1063-1067. |
| [14] | 湛 菁, 陆二聚, 蔡 梦, 马雅琳, 张传福. 棒状多孔NiCo2O4粉末的可控制备及其电催化性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(1): 11-17. |
| [15] | 赵新红, 高向平, 赵江波, 张晓晓, 郝志鑫. 低量结构导向剂改进离子热法高效合成LTA型磷酸铝分子筛[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(11): 1212-1218. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||