无机材料学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 1215-1222.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170041
所属专题: 药物载体与防护材料
马芳, 崔名芳, 朱建华, 李雅丽
收稿日期:2017-01-18
修回日期:2017-03-13
出版日期:2017-11-20
网络出版日期:2017-10-20
作者简介:马 芳(1992-), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: 1649304362@qq.com
基金资助:MA Fang, CUI Ming-Fang, ZHU Jian-Hua, LI Ya-Li
Received:2017-01-18
Revised:2017-03-13
Published:2017-11-20
Online:2017-10-20
摘要:
选用聚烯丙基氯化铵(PAH)作为晶体生长调节剂, 在水热条件下成功制备了多孔羟基磷灰石(Hydroxyapatite, HAP)中空微球。详细研究了反应时间和添加剂浓度等因素的影响: 150℃水热反应12 h, 控制PAH 浓度0.3~0.5 g/L, 可合成尺寸均匀、孔径密集的HAP中空微球。微球生长经历早期前驱体微结构、异相成核、相转化等不同阶段, 聚合物在各阶段都起到重要的调节作用。以典型的布洛芬(ibuprofen, IBU)作为模型药物, 研究微球的药物负载和脱附能力。结果显示: 多孔微球具有良好的药物负载和释放能力, 吸附量较好, 可达到413.65 mg/g。且药物具有较好的pH响应释放行为, 可作为pH敏感靶向药物载体应用到生物医学等领域。
中图分类号:
马芳, 崔名芳, 朱建华, 李雅丽. 聚烯丙基氯化铵调控下多孔羟基磷灰石微球的合成及作为药物载体的应用研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(11): 1215-1222.
MA Fang, CUI Ming-Fang, ZHU Jian-Hua, LI Ya-Li. Porous Hydroxyapatite Microspheres Prepared by Using Poly (Allylamine Hydrochloride) and Its Application in Drug Delivery[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(11): 1215-1222.
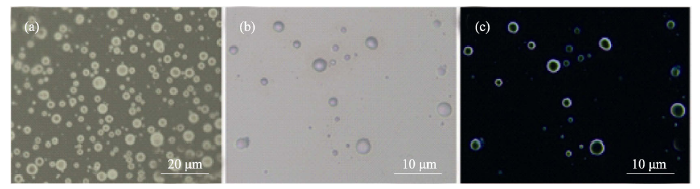
图2 0.42 g/L PAH和磷酸氢二钠溶液混合后形成的类“囊泡”结构
Fig. 2 Optical images of “vesicles” after addition of Na2HPO4 with PAH (0.42 g/L) (a) “Vesicles” before introduction of calcium ions; (b) Aggregations after addition of Ca2+; (c) Polarized image after adding Ca2+
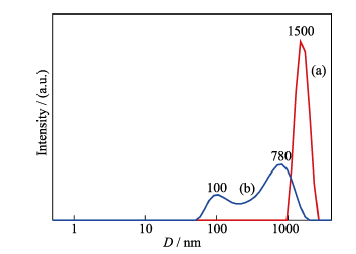
图3 PAH和磷酸氢二钠复合物的粒径分布分析(a)和钙离子加入后, 纳米颗粒的粒径分布(b)
Fig. 3 Diameter distributions of "vesicles", which were synthesized by 0.42 g/L PAH and disodium hydrogen phosphate solution before adding calcium ions (a) and calcium phosphate "vesicle structure" after adding calcium ions (b)
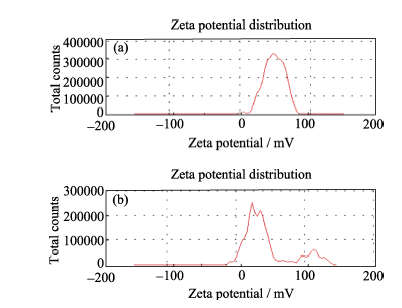
图4 钙离子加入前(a)后(b), 溶液中颗粒的Zeta电位
Fig. 4 Zeta potential of "vesicles" before introduction of calcium ions (a); Zeta potential of nucleated particles after addition of calcium ions (b)([PAH]=0.42 g/L)
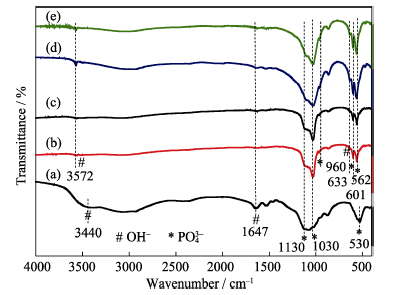
图8 不同水热时间合成产物的FTIR图谱
Fig. 8 FTIR spectra of the products synthesized by hydrthermal method for different time (a) 0 h; (b) 0.5 h; (c) 1.5 h; (d) 8 h; (e) 12 h
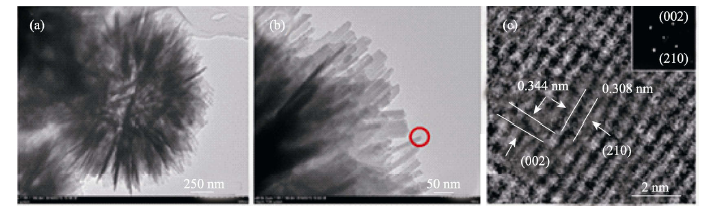
图9 水热反应12 h产物的TEM照片(a, b)和HRTEM分析结果(c), (c)图中的插入图为选区电子衍射花样
Fig. 9 TEM (a, b) and HRTEM (c) images of HAP microspheres after reacting for 12 h. Inset in (c) shows the selected area diffraction (SAED) pattern([PAH]=0.42 g/L)
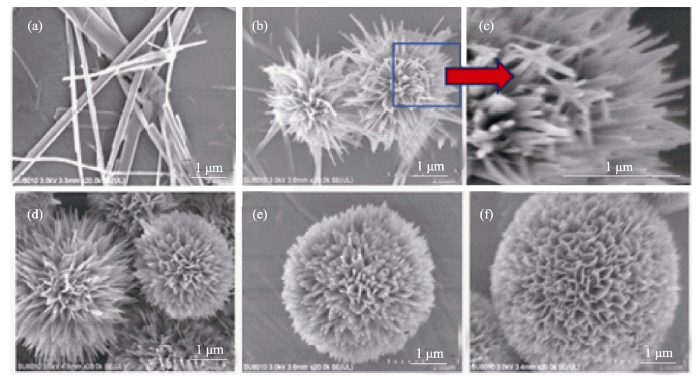
图10 不同PAH浓度下水热合成产物的SEM图片
Fig. 10 SEM images of the HAP samples synthesized by hydrothermal method with different PAH concentrations (a) 0 g/L; (b) 0.06 g/L; (c) 0.06 g/L; (d) 0.24 g/L; (e) 0.36 g/L; (f) 0.42 g/L
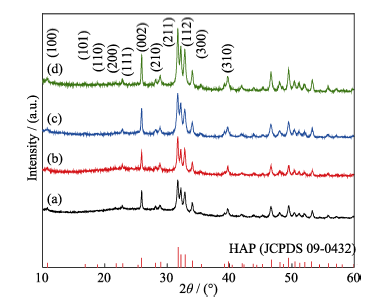
图11 不同PAH浓度条件下产物的XRD图谱
Fig. 11 XRD patterns of the HAP samples synthesized by hydrothermal method with different PAH concentrations (a) 0.06 g/L; (b) 0.24 g/L; (c) 0.36 g/L; (d) 0.42 g/L
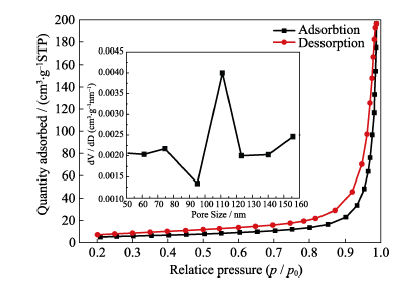
图13 HAP的N2吸脱附等温曲线及孔径分布图
Fig. 13 N2 adsorption-desorption isotherm and the pore size distribution of HAP porous microspheres prepared by a hydrothermal method at 150℃ for 12 h
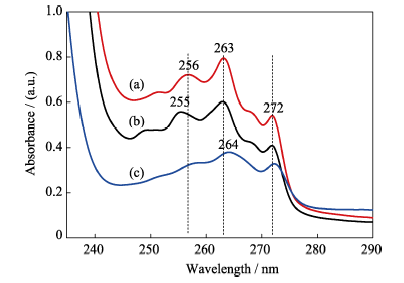
图14 (a) IBU正己烷溶液和(b)IBU被HAP吸附后溶液的紫外-可见光谱; (c)IBU释放6 h后, PBS溶液中的紫外-可见光谱
Fig. 14 UV-Vis spectra of IBU before (a) and after (b) adsorption onto the surface of porous microspheres, UV-Vis spectrum of IBU in the PBS solution after releasing for 6 h (c)
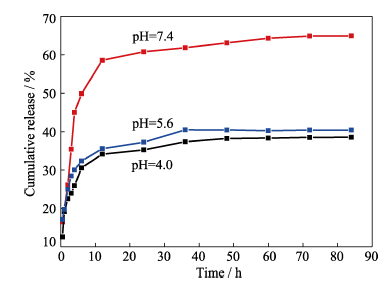
图15 负载IBU的多孔HAP微球在pH=4.0、5.6和7.4的PBS溶液中的释放曲线, 37℃
Fig. 15 IBU release profiles of porous microspheres in PBS solution of pH at 4.0, 5.6 and 7.4, under 37℃
| [1] | DOROZHKIN S V.Calcium orthophosphates in nature, biology and medicine.Materials, 2009, 2(2): 399-498. |
| [2] | PALMER L C, NEWCOMB C J, KALTZ S R,et al. Biomimetic systems for hydroxyapatite mineralization in inspired by bone and enamel. Chemical Reviews, 2009, 108(6): 4754-4783. |
| [3] | WANG K W, ZHU Y J, CHEN X Y,et al. Flower-like hierarchically nanostructured hydroxyapatite hollow spheres: facile preparation and application in anticancer drug cellular delivery. Chemistry-An Asian Journal, 2010, 5(12): 2477-2482. |
| [4] | TANG Q L, ZHU Y J, WU J,et al. Calcium phosphate drug nanocarriers with ultrahigh and adjustable drug-loading capacity one-step synthesis, in situ drug loading and prolonged drug release. Nanomedicine Nanotechnology Biology & Medicine, 2011, 7(4): 428-434. |
| [5] | DEVILLE S, SAIZ E, TOMSIA A P.Freeze casting of hydroxyapatite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering.Biomaterials, 2006, 27(32): 5480-5489. |
| [6] | WANG C, WANG Y, MENG H Y,et al. Research progress regarding nanohydroxyapatite and its composite biomaterials in bone defect repair. International Journal of Polymeric Materials and Polymeric Biomaterials, 2016, 65(12): 601-610. |
| [7] | ZHANG G D, CHEN J D, YANG S,et al. Preparation of amino-acid-regulated hydroxyapatite particles by hydrothermal method. Materials Letters, 2011, 65(3): 572-574. |
| [8] | DING G J, ZHU Y J, QI C,et al. Amorphous calcium phosphate nanowires prepared using beta-glycerophosphate disodium salt as an organic phosphate source by a microwave-assisted hydrothermal method and adsorption of heavy metals in water treatment. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(50): 40154-40162. |
| [9] | LU B Q, ZHU Y J, CHEN F,et al. Solvothermal transformation of a calcium oleate precursor into large-sized highly ordered arrays of ultralong hydroxyapatite microtubes. Chemistry, 2014, 20(23): 7116-7121. |
| [10] | LIU D M, YANG Q, TROCZYNSKI T,et al. Structural evolution of Sol-Gel derived hydroxylapatite. Biomaterials, 2002, 23(7): 1679-1687. |
| [11] | KIM W, SAITO F.Sonochemical synthesis of hydroxyapatite from H3PO4 solution with Ca(OH)2.Ultrasonics Sonochemistry, 2001, 8(2): 85-88. |
| [12] | WANG K W, ZHU Y J, CHEN F,et al. Microwave-assisted synthesis of hydroxyapatite hollow microspheres in aqueous solution. Materials Letters, 2011, 65(15): 2361-2363. |
| [13] | LIN K L, CHEN L, LIU P Y,et al. Hollow magnetic hydroxyapatite microspheres with hierarchically mesoporous microstructure for pH-responsive drug delivery. CrystEngComm, 2013, 15(15): 2999-3008. |
| [14] | MA L, ZHU J H, HUANG L.Rapid synthesis of hydroxyapatite nanorods at low temperature controlled by sodium alginate.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(3): 311-317. |
| [15] | ZHAO H, ZHU Y D, SUN J,et al. Synthesis of hollow hydroxyapatite nanospheres by the control of nucleation and growth in a two phase system. Chemical Communications, 2014, 50(83): 12519-12522. |
| [16] | WU Y J, TSENG Y H, CHAN J C C. Morphology control of fluorapatite crystallites by citrate ions. Crystal Growth & Design. 2010, 10(10): 4240. |
| [17] | LEE G S, PARK J H, SHIN U S,et al. Direct deposited porous scaffolds of calcium phosphate cement with alginate for drug delivery and bone tissue engineering. Acta Biomaterialia, 2011, 7(8): 3178-3186. |
| [18] | CANTAERT B, KIM Y Y, LUDWIG H,et al. Think positive: phase separation enables a positively charged additive to induce dramatic changes in calcium carbonate morphology. Advanced Functional Materials, 2012, 22(5): 907-915. |
| [19] | HIROFUMI D, EITARO M, SATOSHI M.Fabrication of hollow poly-allylamine hydrochloride/poly-sodium styrene sulfonate microcapsules from microbubble templates.Soft Matter, 2010, 6(9): 1892-1897. |
| [20] | SUZUKI O, KAMAKURA S, KATAGIRI T,et al. Bone formation enhanced by implanted octacalcium phosphate involving conversion into Ca-deficient hydroxyapatite. Biomaterials, 2006, 27(13): 2671-2681. |
| [21] | DING H C, PAN H H, XU X R,et al. Toward a detailed understanding of magnesium ions on hydroxyapatite crystallization inhibition. Crystal Growth & Design, 2014, 14(2): 763-769. |
| [22] | ZHAN J, TSENG Y, CHAN J C C,et al. Biomimetic formation of hydroxyapatite nanorods by a single-crystal-to-single-crystal transformation. Advanced Functional Materials, 2005, 15(12): 2005-2010. |
| [23] | LIN K, CHANG J, ZHU Y,et al. A facile one-step surfactant-free and low-temperature hydrothermal method to prepare uniform 3D structured carbonated apatite flowers. Crystal Growth & Design, 2009, 9(1): 177-178. |
| [24] | ZHANG Y J, LU J J, WANG J Q,et al. Synthesis of nanorod and needle-like hydroxyapatite crystal and role of pH adjustment. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2009, 311(23/24): 4740-4746. |
| [25] | REN F, LENG Y, DING Y,et al. Hydrothermal growth of biomimetic carbonated apatite nanoparticles with tunable size, morphology and ultrastructure. CrystEngComm, 2013, 15(11): 2137-2146. |
| [26] | VISWANATH B, RAVISHANKAR N.Controlled synthesis of plate-shaped hydroxyapatite and implications for the morphology of the apatite phase in bone.Biomaterials, 2008, 29(36): 4855-4863. |
| [27] | ZHANG X J, LIN D Y, YAN X H,et al. Evolution of the magnesium incorporated amorphous calcium phosphate to nano- crystallized hydroxyapatite in alkaline solution. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2011, 336(1): 60-66. |
| [28] | GORDON L M, COHEN M J, MACRENARIS K W,et al. Amorphous intergranular phases control the properties of rodent tooth enamel. Science, 2015, 347(6223): 726-750. |
| [29] | CHEN F, ZHU Y J, ZHAO X Y,et al. Solvothermal synthesis of oriented hydroxyapatite nanorod/nanosheet arrays using creatine phosphate as phosphorus source. CrystEngComm, 2013, 15(22): 4527-4531. |
| [30] | QI C, ZHU Y J, LU B Q,et al. Hydroxyapatite hierarchically nanostructured porous hollow microspheres: rapid, sustainable microwave-hydrothermal synthesis by using creatine phosphate as an organic phosphorus source and application in drug delivery and protein adsorption. Chemistry, 2013, 19(17): 5332-5341. |
| [31] | VALLET-REGÍ, GONZÁLEZ-CALBET J M. Calcium phosphates as substitution of bone tissues.Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2004, 32(1): 1-31. |
| [1] | 庞力斌, 王德平. 介孔硼硅酸盐玻璃微球药物载体的制备及其性能表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 780-786. |
| [2] | 陈亚玲, 舒松, 王劭鑫, 李建军. Mn-HAP基低温SCR催化剂的制备及抗硫中毒性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1065-1072. |
| [3] | 朱雨桐, 谭佩洁, 林海, 朱向东, 张兴栋. 可注射透明质酸/羟基磷灰石复合材料: 制备、理化性能和细胞相容性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(9): 981-990. |
| [4] | 林子扬, 常宇辰, 吴章凡, 包荣, 林文庆, 王德平. 不同模拟体液对硼硅酸盐生物活性玻璃基骨水泥矿化性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(7): 745-752. |
| [5] | 吴永豪, 李向锋, 朱向东, 张兴栋. 高强度羟基磷灰石纳米陶瓷的构建及其促成骨细胞活性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(5): 552-560. |
| [6] | 宋可可, 黄浩, 鲁梦婕, 杨安春, 翁杰, 段可. 水热制备锌、硅、镁、铁等元素掺杂羟基磷灰石及其表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(10): 1091-1096. |
| [7] | 邵悦婷, 朱英杰, 董丽颖, 蔡安勇. 羟基磷灰石超长纳米线/植物纤维纳米复合“宣纸”及其防霉性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(1): 107-112. |
| [8] | 孙团伟,朱英杰. 一步溶剂热法合成锶掺杂羟基磷灰石超长纳米线[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(6): 724-728. |
| [9] | 刘子阳, 耿振, 李朝阳. 牡蛎壳为原料制备医用CaCO3/HA复合生物材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(5): 601-607. |
| [10] | 代钊,王铭,王双,李静,陈翔,汪大林,祝迎春. 氧化锆基微量元素共掺杂羟基磷灰石增韧涂层研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 179-186. |
| [11] | 付亚康,翁杰,刘耀文,张科宏. 钛网表面含hBMP-2的复合涂层制备及hBMP-2的释放研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(2): 173-178. |
| [12] | 周子航, 王群, 葛翔, 李朝阳. 掺锶羟基磷灰石纳米颗粒的合成、表征及模拟研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(11): 1283-1289. |
| [13] | 高龙, 张赵文斌, 常江. 生物玻璃/聚乳酸多孔微球的制备及其作为细胞载体的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(10): 1163-1168. |
| [14] | 肖文谦,张静,李克江,邹新宇,蔡昱东,李波,刘雪,廖晓玲. 荔枝状CaCO3@HA/Fe3O4磁性介孔多级微球的制备[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(9): 925-932. |
| [15] | 吴金结, 李艳, 魏仁初, 汪建新, 屈树新, 翁杰, 智伟. 微振动应力环境影响羟基磷灰石陶瓷生物活性及力学稳定性的体外评价[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 417-424. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||