无机材料学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 596-602.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160472
王舒玮1, 2, 胡和丰1, 王德宇2, 沈 彩2
收稿日期:2016-08-17
修回日期:2016-11-13
出版日期:2017-06-20
网络出版日期:2017-05-27
作者简介:王舒玮(1992–), 女, 硕士研究生.
基金资助:WANG Shu-Wei1, 2, HU He-Feng1, WANG De-Yu2, SHEN Cai2
Received:2016-08-17
Revised:2016-11-13
Published:2017-06-20
Online:2017-05-27
About author:WANG Shu-Wei.
Supported by:摘要:
固体电解质界面膜(Solid Electrolyte Interphase, SEI)在钠离子电池(Sodium Ion Battery, NIB)中扮演着重要作用。迄今为止, 对于钠离子电池SEI膜的探索仍然十分有限。本研究利用电化学原子力显微镜(Electrochemical AFM, EC-AFM), 通过循环伏安法研究了钠离子电池负极材料高定向热解石墨(Highly Oriented Pyrolytic Graphite, HOPG), 在碳酸乙烯酯(Ethylene Carbonate, EC)和氟代碳酸乙烯酯(Fluoroethylene Carbonate, FEC)电解液中首次充放电过程SEI膜的结构变化。通过纳米刻蚀的方法, 进一步获得首次充放电结束后SEI的厚度。结合X射线光电子能谱(X-ray Photoelectron Spectroscopy, XPS)分析了HOPG在EC和FEC电解液中所形成的SEI膜的化学组成区别。研究结果表明, 在EC电解液中, 所生成的SEI膜在HOPG表面非台阶处较薄, 但在HOPG的台阶处较厚; 在FEC电解液中, 所生成的SEI膜很厚, 具有明显的双层结构。其中上层是由体积较大的颗粒组成, 下层则由致密的小颗粒组成。
中图分类号:
王舒玮, 胡和丰, 王德宇, 沈 彩. 钠离子电池HOPG负极固体电解质界面膜的AFM研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(6): 596-602.
WANG Shu-Wei, HU He-Feng, WANG De-Yu, SHEN Cai. AFM Investigation of Solid Electrolyte Interphase on HOPG Anode in Sodium Ion Battery[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(6): 596-602.

图1 在1 mol/L NaClO4/EC/DMC电解液中和1 mol/L NaClO4/FEC/DMC电解液中的第一圈循环伏安曲线(电压范围: 3.0~0 V, 速率: 0.5 mV/s)
Fig. 1 Cyclic voltammogram of HOPG electrode in 1 mol/L NaClO4/EC/DMC and 1 mol/L NaClO4/FEC/DMC at scan rate of 0.5 mV/s
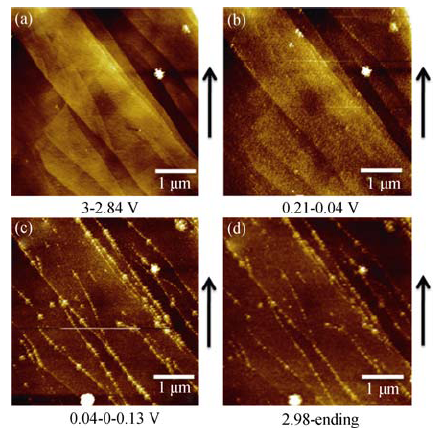
图2 在1 mol/L NaClO4/EC/DMC电解液中首次电化学循环伏安的原位AFM图片
Fig. 2 In situ AFM images of HOPG electrode cycled at a scanning rate of 0.5 mV/s between 3.0 and 0 V in 1 mol/L NaClO4/EC/DMC(a) During discharging, potential range of 3.0-2.84 V; (b) During discharging, potential range of 0.24-0.04 V; (c) The potential is sweeped from 0.04 V to 0 V then rised to 0.13 V; (d) During charging, potential range of 2.98-3.0 V. The arrow indicates AFM scanning direction
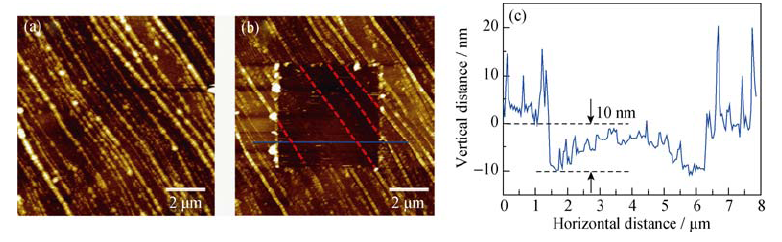
图3 (a)HOPG负极在1 mol/L NaClO4/EC/DMC电解液中首次循环伏安结束后的图像; (b)中间SEI膜被刮除后HOPG负极的图像; (c)蓝色实线所示的高度剖面图
Fig. 3 (a) AFM image of HOPG electrode after first CV cycle in the 1 mol/L NaClO4/EC/DMC; (b) AFM image of the HOPG anode after the SEI in the middle of the image being scraped off and (c) cross-section analysis of the location marked by blue line
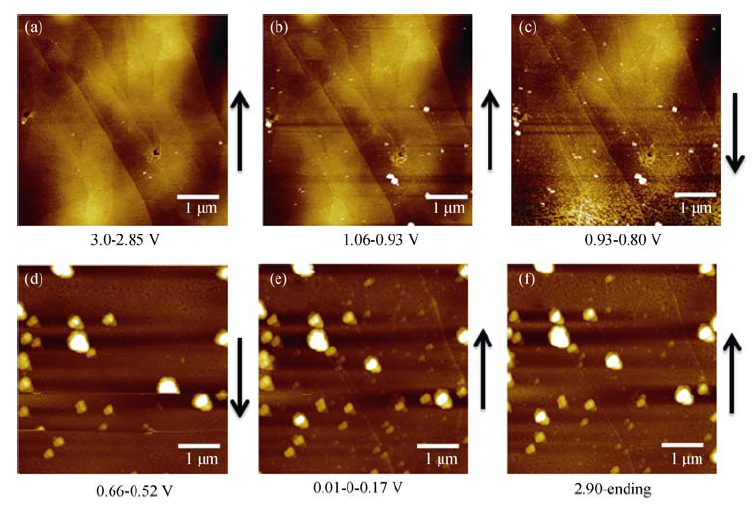
图 4 在1 mol/L NaClO4/FEC/DMC电解液中进行首次循环伏安测试的原位AFM图片
Fig. 4 In situ AFM images of HOPG electrode cycled at a scanning rate of 0.5 mV/s between 3.0 and 0.0 V in 1 mol/L NaClO4/FEC/DMC(a) During discharging, potential range of 3.0-2.85 V; (b) During discharging, potential range of 1.06-0.93 V; (c) During discharging, potential range: of 0.93-0.80 V; (d) During discharging, the potential range of 0.66-0.52 V; (e) The potential is sweeped from 0.01 V to 0 V then rised to 0.17 V; (f) During charging, the potential range of 2.90-3.0 V; The arrow indicates AFM scanning direction
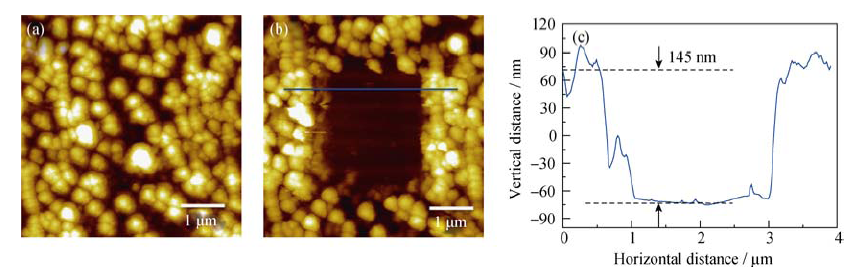
图5 (a) HOPG负极在1 mol/L NaClO4/FEC/DMC电解液中首次循环伏安结束后的图像; (b) 中间SEI膜被刮除后HOPG负极的图像; (c) 蓝色实线所示的高度剖面图
Fig. 5 (a) AFM image of HOPG electrode after first CV cycle in the 1 mol/L NaClO4/FEC/DMC; (b) AFM image of the HOPG anode after the SEI in the middle of the image being scraped off; and (c) cross-section analysis of the location marked by blue line
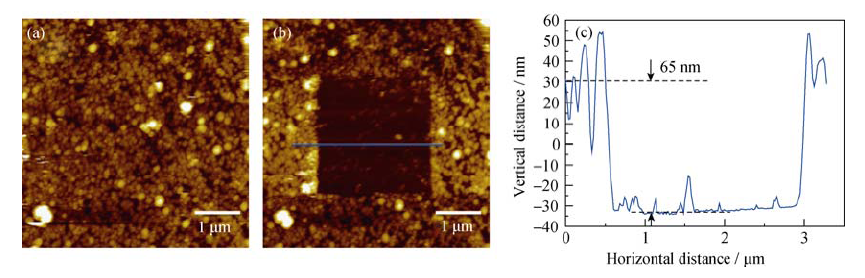
图6 (a) HOPG负极在1 mol/L NaClO4/FEC/DMC电解液中首次循环伏安结束后下层SEI膜的图像; (b) 中间SEI膜被刮除后HOPG负极的图像; (c) 蓝色实线所示的高度剖面图
Fig. 6 (a) AFM image of under SEI layer on HOPG electrode after first CV cycle in the 1 mol/L NaClO4/FEC/DMC; (b) AFM image of the HOPG anode after the SEI in the middle of the image being scraped off; (c) cross-section analysis of the location marked by blue line
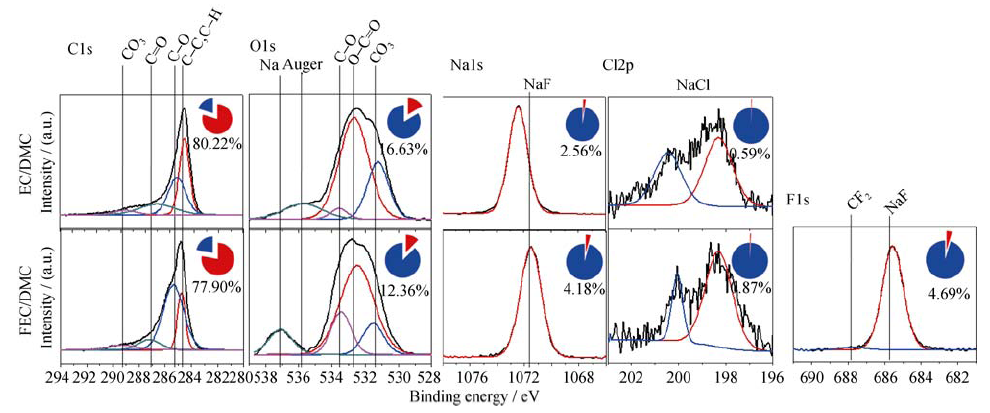
图7 在EC/DMC和FEC/DMC电解液中进行电化学循环伏安(电压范围: 3.0~0 V; 速率: 0.5 mV/s)后, HOPG负极上SEI膜的XPS图谱
Fig. 7 XPS spectra of the SEI on HOPG electrode cycled at a scanning rate of 0.5 mV/s between 3.0 and 0 V in the EC/DMC and FEC/DMC electrolytes
| HOPG | Atomic concentration /% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Na | Cl | F | ||
| 1 mol/L NaClO4 /EC/DMC | Before etching | 80.22 | 16.63 | 2.56 | 0.59 | - |
| After etching | 83.16 | 11.62 | 3.42 | 1.80 | - | |
| 1 mol/L NaClO4 /FEC/DMC | Before etching | 77.90 | 12.36 | 4.18 | 0.87 | 4.69 |
| After etching | 78.02 | 5.21 | 6.95 | 2.03 | 7.79 | |
表1 XPS测试结果C、O、Na、Cl和F的原子百分比
Table 1 Atomic concentrations of C, O, Na, Cl and F obtained from XPS
| HOPG | Atomic concentration /% | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | O | Na | Cl | F | ||
| 1 mol/L NaClO4 /EC/DMC | Before etching | 80.22 | 16.63 | 2.56 | 0.59 | - |
| After etching | 83.16 | 11.62 | 3.42 | 1.80 | - | |
| 1 mol/L NaClO4 /FEC/DMC | Before etching | 77.90 | 12.36 | 4.18 | 0.87 | 4.69 |
| After etching | 78.02 | 5.21 | 6.95 | 2.03 | 7.79 | |
| [1] | XU K.Electrolytes and interphases in Li-ion batteries and beyond.Chemical Reviews, 2014, 114(23): 11503-11618. |
| [2] | SHEN CBUCK M.Nanoscale patterning of a self-assembled monolayer by modification of the molecule-substrate bond.Beilstein journal of nanotechnology, 2014, 5: 258-267. |
| [3] | SHEN C, CEBULA I, BROWN C, et al.Structure of isophthalic acid based monolayers and its relation to the initial stages of growth of metal-organic coordination layers.Chemical Science, 2012, 3(6): 1858-1865. |
| [4] | CEBULA I, SHEN CBUCK M.Isophthalic acid: a basis for highly ordered monolayers.Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 49(35): 6220-6223. |
| [5] | CRAMER J R, NING Y, SHEN C, et al.Oligo (naphthylene- ethynylene) Molecular Rods.European Journal of Organic Chemistry, 2013, 2013(14): 2813-2822. |
| [6] | SHEN C, HARYONO M, Grohmann A, et al.Self-assembled monolayers of a bis(pyrazol-1-yl)pyridine-substituted thiol on Au(111).Langmuir, 2008, 24(22): 12883-12891. |
| [7] | SHEN C, CRAMER J R, JACOBSEN M F, et al.Steering supramolecular patterns by nucleobase-terminated molecules.Chemical communications, 2013, 49(5): 508-510. |
| [8] | ZHU J, FENG J, LU L, et al.In situ study of topography, phase and volume changes of titanium dioxide anode in all-solid-state thin film lithium-ion battery by biased scanning probe microscopy.Journal of Power Sources, 2012, 197: 224-230. |
| [9] | ZHANG J, WANG R, YANG X, et al.Direct observation of inhomogeneous solid electrolyte interphase on MnO anode with atomic force microscopy and spectroscopy.Nano letters, 2012, 12(4): 2153-2157. |
| [10] | LIU R R, DENG X, LIU X R, et al.Facet dependent SEI formation on the LiNi(0.5)Mn(1.5)O4 cathode identified by in situ single particle atomic force microscopy.Chemical communications, 2014, 50(99): 15756-15759. |
| [11] | ZHENG J, ZHENG H, WANG R, et al.3D visualization of inhomogeneous multi-layered structure and Young's modulus of the solid electrolyte interphase (SEI) on silicon anodes for lithium ion batteries.Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(26): 13229-13238. |
| [12] | INABA M, KAWATATE Y, FUNABIKI A, et al.STM study on graphite/electrolyte interface in lithium-ion batteries: solid electrolyte interface formation in trifluoropropylene carbonate solution.Electrochimica Acta, 1999, 45(1/2): 99-105. |
| [13] | V CRESCE A, RUSSELL S M, BAKER D R, et al. In situ and quantitative characterization of solid electrolyte interphases.Nano letters, 2014, 14(3): 1405-1412. |
| [14] | LIU X R, WANG L, WAN L J, et al.In situ observation of electrolyte-concentration-dependent solid electrolyte interphase on graphite in dimethyl sulfoxide.ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(18): 9573-9580. |
| [15] | LUCAS I T, POLLAK EKOSTECKI R.In situ AFM studies of SEI formation at a Sn electrode.Electrochemistry Communications, 2009, 11(11): 2157-2160. |
| [16] | DOMI Y, OCHIDA M, TSUBOUCHI S, et al.In Situ AFM study of surface film formation on the edge plane of HOPG for lithium-ion batteries.The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(51): 25484-25489. |
| [17] | DENG X, LIU X, YAN H, et al.Morphology and modulus evolution of graphite anode in lithium ion battery: an in situ AFM investigation.Science China-Chemistry, 2014, 57(1): 178-183. |
| [18] | HERRERA S E, TESIO A Y, CLARENC R, et al.AFM study of oxygen reduction products on HOPG in the LiPF6-DMSO electrolyte.Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2014, 16(21): 9925-9929. |
| [19] | WANG L, DENG D, LEV L C, et al.In-situ investigation of solid-electrolyte interphase formation on the anode of Li-ion batteries with atomic force microscopy.Journal of Power Sources, 2014, 265: 140-148. |
| [20] | LACEY S D, WAN J, VON WALD CRESCE A, et al. Atomic force microscopy studies on molybdenum disulfide flakes as sodium-ion anodes.Nano letters, 2015, 15(2): 1018-1024. |
| [21] | SHEN C, WANG S, JIN Y, et al.In situ AFM imaging of solid electrolyte interfaces on HOPG with ethylene carbonate and fluoroethylene carbonate-based electrolytes.ACS applied materials & interfaces, 2015, 7(45): 25441-25447. |
| [22] | JIAN Z, HAN W, LU X, et al.Superior electrochemical performance and storage mechanism of Na3V2(PO4)3 Cathode for Room-Temperature Sodium-Ion Batteries.Advanced Energy Materials, 2013, 3(2): 156-160. |
| [23] | PAN H, LU X, YU X, et al.Sodium storage and transport properties in layered Na2Ti3O7 for room-temperature sodium-ion batteries.Advanced Energy Materials, 2013, 3(9): 1186-1194. |
| [24] | XU KVON CRESCE A. Interfacing electrolytes with electrodes in Li ion batteries.Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2011, 21(27): 9849-9864. |
| [25] | AMINE K, BELHAROUAK I, CHEN Z, et al.Nanostructured anode material for high-power battery system in electric vehicles.Advanced materials, 2010, 22(28): 3052-3057. |
| [26] | LEE S W, GALLANT B M, BYON H R, et al.Nanostructured carbon-based electrodes: bridging the gap between thin-film lithium-ion batteries and electrochemical capacitors.Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(6): 1972-1985. |
| [27] | PALOMARES V, CASAS-CABANAS M, CASTILLO-MARTÍNEZ E, et al. Update on Na-based battery materials. A growing research path.Energy & Environmental Science, 2013, 6(8): 2312-2337. |
| [28] | SLATER M D, KIM D, LEE E, et al.Sodium-ion batteries.Advanced Functional Materials, 2013, 23(8): 947-958. |
| [29] | DARWICHE A, MARINO C, SOUGRATI M T, et al.Better cycling performances of bulk Sb in Na-ion batteries compared to Li-ion systems: an unexpected electrochemical mechanism.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(51): 20805-20811. |
| [30] | XIA XDAHN J R. Study of the reactivity of Na/hard carbon with different solvents and electrolytes.Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2011, 159(5): A515-A519. |
| [31] | ELLIS L D, HATCHARD T DOBROVAC M N. Reversible insertion of sodium in tin.Journal of the Electrochemical Society, 2012, 159(11): 32-42. |
| [32] | JI L W, GU M, SHAO Y Y, et al.Controlling SEI formation on SnSb-porous carbon nanofibers for improved Na ion storage.Advanced materials, 2014, 26(18): 2901-2908. |
| [33] | MU L, XU S, LI Y, et al.Prototype sodium-ion batteries using an air-stable and Co/Ni-Free O3-layered metal oxide cathode.Advanced materials, 2015, 27(43): 6928-6933. |
| [34] | LI Y, HU Y-S, QI X, et al.Advanced sodium-ion batteries using superior low cost pyrolyzed anthracite anode: towards practical applications.Energy Storage Materials, 2016, 5: 191-197. |
| [35] | KOMABA S, MURATA W, ISHIKAWA T, et al.Electrochemical Na insertion and solid electrolyte interphase for hard-carbon electrodes and application to Na-ion batteries.Advanced Functional Materials, 2011, 21(20): 3859-3867. |
| [36] | BREITUNG B, BAUMANN P, SOMMER H, et al.In situ and operando atomic force microscopy of high-capacity nano-silicon based electrodes for lithium-ion batteries.Nanoscale, 2016, 8(29): 14048-14056. |
| [1] | 孔国强, 冷明哲, 周战荣, 夏池, 沈晓芳. Sb掺杂O3型Na0.9Ni0.5Mn0.3Ti0.2O2钠离子电池正极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 656-662. |
| [2] | 江依义, 沈旻, 宋半夏, 李南, 丁祥欢, 郭乐毅, 马国强. 双功能电解液添加剂对锂离子电池高温高电压性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 710-716. |
| [3] | 赵伟, 徐阳, 万颖杰, 蔡天逊, 穆金潇, 黄富强. 金属氰胺化合物的结构、合成及电化学储能应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(2): 140-151. |
| [4] | 王晶, 徐守冬, 卢中华, 赵壮壮, 陈良, 张鼎, 郭春丽. 钠离子电池中空结构CoSe2/C负极材料的制备及储钠性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1344-1350. |
| [5] | 张晓君, 李佳乐, 邱吴劼, 杨淼森, 刘建军. 钠离子电池正极材料P2-Nax[Mg0.33Mn0.67]O2的电化学活性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(6): 623-628. |
| [6] | 刘勇, 白海军, 赵奇志, 杨金戈, 李宇杰, 郑春满, 谢凯. LiNi0.8Co0.15Al0.05O2/石墨锂离子电池高荷电存储老化机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(2): 175-180. |
| [7] | 曾凡鑫, 刘创, 曹余良. 去合金化制备具有高循环稳定性的纳米多孔Sb/MCNT储钠负极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1137-1144. |
| [8] | 李勇, 何玮鑫, 郑芯月, 于胜兰, 李海同, 黎弘毅, 张蓉, 王雨. 水系钠离子电池普鲁士蓝正极材料的制备与电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 365-372. |
| [9] | 王武练, 张军, 王秋实, 陈亮, 刘兆平. 高质量水系钠离子电池正极Fe4[Fe(CN)6]3的合成及其电化学性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(12): 1301-1308. |
| [10] | 王家虎, 王文馨, 杜鹏, 胡芳东, 姜晓蕾, 杨剑. Na3V2(PO4)2F3@V2O5-x复合材料的制备及储钠性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(10): 1097-1102. |
| [11] | 马国强, 蒋志敏, 陈慧闯, 王莉, 董经博, 张建君, 徐卫国, 何向明. 基于锂盐的新型锂电池电解质研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(7): 699-710. |
| [12] | 肖娜, 潘洋, 宋云, 吴晓京, 傅正文, 周永宁. 锑硅纳米复合薄膜作为钠离子电池负极材料的电化学行为研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(5): 494-500. |
| [13] | 罗军明, 吴小红, 徐吉林. 电解液组分对TiCP/Ti6Al4V复合材料微弧氧化膜耐蚀性及耐磨性影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(4): 418-424. |
| [14] | 李 玲, 肖俊莹, 崔米豆, 太优一, 庞永文, 韩 松, 李晓苇. 高效CdS量子点敏化B/S共掺杂纳米TiO2太阳能电池的制备及光电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(6): 627-633. |
| [15] | 杨汉西, 钱江锋. 水溶液钠离子电池及其关键材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(11): 1165-1171. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||