无机材料学报 ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (2): 191-196.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160247
王 锦1, 陶 科2, 李国峰1, 梁 科1, 蔡宏琨1
收稿日期:2016-04-12
修回日期:2016-06-29
出版日期:2017-02-20
网络出版日期:2017-01-13
WANG Jin1, TAO Ke2, LI Guo-Feng1, LIANG Ke1, CAI Hong-Kun1
Received:2016-04-12
Revised:2016-06-29
Published:2017-02-20
Online:2017-01-13
摘要:
采用反应型热化学气相沉积系统在硅(100)衬底上外延生长富锗硅锗薄膜。四氟化锗作为锗源, 乙硅烷作为还原性气体。通过设计表面反应, 在低温条件下(350℃)制备了高质量的富锗硅锗薄膜。研究了氢退火对低温硅锗外延薄膜微结构和电学性能的影响。结果发现退火温度高于700℃时, 外延薄膜的表面形貌随着退火温度的升高迅速恶化。当退火温度为650℃时, 获得了最佳的退火效果。在该退火条件下, 外延薄膜的螺旋位错密度从3.7×106 cm-2下降到4.3×105 cm-2, 表面粗糙度从1.27 nm下降到1.18 nm, 而外延薄膜的结晶质量也有效提高。霍尔效应测试表明, 经退火处理的样品载流子迁移率明显提高。这些结果表明, 经过氢退火处理后, 反应型热化学气相沉积制备的低温硅锗外延薄膜可以获得与高温下硅锗外延薄膜相比拟的性能。
中图分类号:
王 锦, 陶 科, 李国峰, 梁 科, 蔡宏琨. 氢气氛退火对硅上低温外延制备的硅锗薄膜性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(2): 191-196.
WANG Jin, TAO Ke, LI Guo-Feng, LIANG Ke, CAI Hong-Kun. Effect of Hydrogen Annealing on the Property of Low-temperature Epitaxial Growth of Sige Thin Films on Si Substrate[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(2): 191-196.
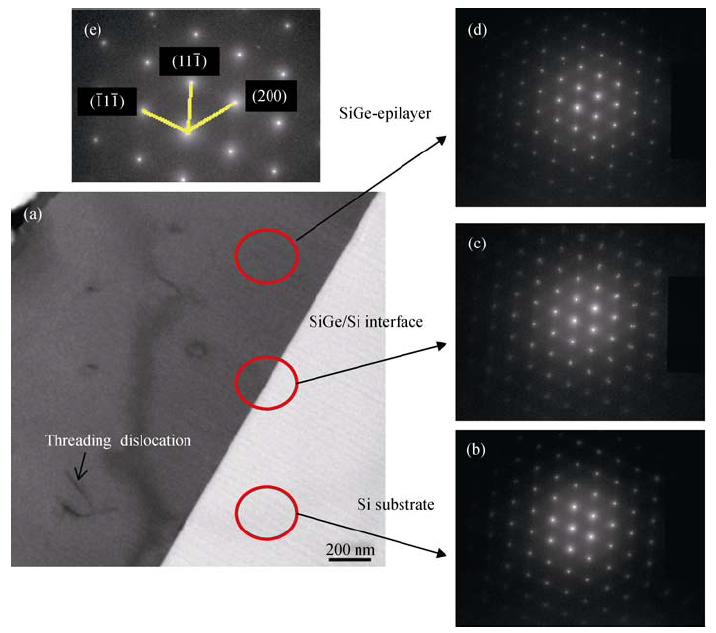
图1 硅锗外延薄膜的断面透射电镜照片(a)及样品不同深度的电子衍射谱(b~d)
Fig. 1 (a) Cross-sectional TEM image of epitaxial SiGe films on silicon substrate, (b)-(d) electron diffraction patterns for Si substrate, SiGe/Si interface and SiGe epilayer (e) which extracted from (d) for calculation The red circles mark the position for measurement of electron diffraction patterns
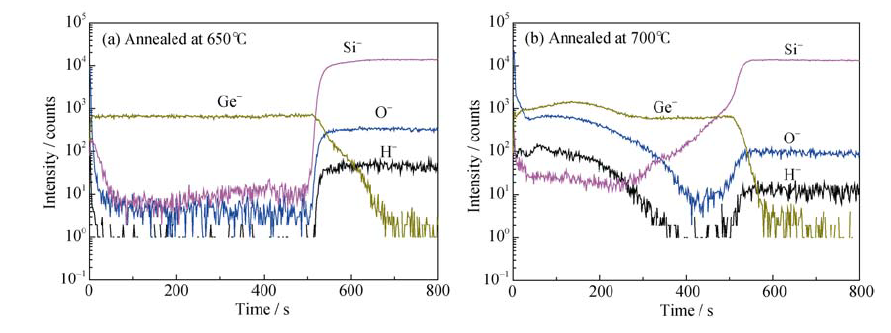
图3 经不同温度退火处理后硅锗外延薄膜由TOF-SIMS测得的离子组分深度分布
Fig. 3 Composition depth profile of ions detected by TOF-SIMS measurement from epitaxial SiGe films annealed at different temperatures
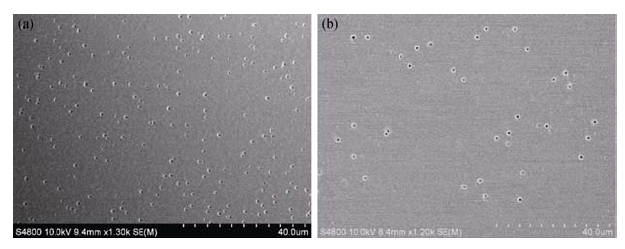
图5 硅锗外延薄膜经选择性湿法腐蚀后的表面扫描电镜照片
Fig. 5 SEM images of SiGe films after a selective wet etch, and pits with reversed pyramidal structure exhibited on the surface(a) As-deposited sample; (b) 650℃-annealed sample
| SixGe1-x | Resistance /(Ω·cm) | Carrier concentration/cm-3 | Mobility/ (cm2·V-1·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-grown | 0.402 | 6.35×1016 | 244 |
| Annealed | 1.470 | 1.07×1016 | 409 |
表1 由霍尔仪测得的硅锗外延薄膜的电学性能(膜厚900 nm)
Table 1 Electrical properties of SiGe thin films by Hall-effect measurement
| SixGe1-x | Resistance /(Ω·cm) | Carrier concentration/cm-3 | Mobility/ (cm2·V-1·s-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| As-grown | 0.402 | 6.35×1016 | 244 |
| Annealed | 1.470 | 1.07×1016 | 409 |
| Ref. | Temp./℃ | Thickness /nm | RMS roughness/nm | TDD/cm-2 | Mobility/(cm2·V-1·s-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-grown | Annealed | As-grown | Annealed | Annealed | ||||
| [21] | LT | 400 | 1224 | 0.40 | 0.7 | 1.70×108 | 1.00×107 | NA |
| HT | 670 | |||||||
| [22] | LT | 350 | 50 | 0.70 | NA | 5.00×105 | NA | 550 |
| HT | 600 | 300 | ||||||
| [23] | LT | 335 | 2000 | 0.60 | 1.6 | NA | 2.00×107 | NA |
| HT | 670 | |||||||
| [24] | LT | 400 | 2500 | 1.20 | 1.0 | NA | 6.00×106 | NA |
| HT | 750 | |||||||
| [25] | LT | 400 | 980 | 3.19 | 0.9 | NA | 6.00×106 | NA |
| HT | 670 | |||||||
表2 文献中报道的采用低温/高温法制备的锗外延薄膜的性能参数
Table 2 Summary of the process parameters and film quality from literatures which reported the epitaxial growth of Ge by using low temperature/high temperature method
| Ref. | Temp./℃ | Thickness /nm | RMS roughness/nm | TDD/cm-2 | Mobility/(cm2·V-1·s-1) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| As-grown | Annealed | As-grown | Annealed | Annealed | ||||
| [21] | LT | 400 | 1224 | 0.40 | 0.7 | 1.70×108 | 1.00×107 | NA |
| HT | 670 | |||||||
| [22] | LT | 350 | 50 | 0.70 | NA | 5.00×105 | NA | 550 |
| HT | 600 | 300 | ||||||
| [23] | LT | 335 | 2000 | 0.60 | 1.6 | NA | 2.00×107 | NA |
| HT | 670 | |||||||
| [24] | LT | 400 | 2500 | 1.20 | 1.0 | NA | 6.00×106 | NA |
| HT | 750 | |||||||
| [25] | LT | 400 | 980 | 3.19 | 0.9 | NA | 6.00×106 | NA |
| HT | 670 | |||||||
| [1] | PAUL D J.Silicon-germanium strained layer materials in microelectronics.Advanced Materials, 1999, 11(17): 191-204. |
| [2] | CHANG S T, LIAO M H, LIN W K.Si/SiGe hetero-junction solar cell with optimization design and theoretical analysis.Thin Solid Films, 2011, 519(15): 5022-5025. |
| [3] | HADI S A,HASHEMI P, NAYFEH A,et al. Thin film a-Si/c- Si1-xGex/c-Si heterojunction solar cells: design and material quality requirements, thin-film si cells.ECS Transactions, 2011, 41(4): 3-14. |
| [4] | CANNON D D, LIU J, DANIELSON D T,et al. Germanium-rich silicon-germanium films epitaxially grown by ultrahigh vacuum chemical-vapor deposition directly on silicon substrates.Applied Physics Letters, 2007, 91(25): 252111. |
| [5] | CHEN J X, ERNST F, HANSSON P O,et al. Liquid phase epitaxy of GeSi on {111} Si substrates: lattice defect structure and electronic properties.Journal of Crystal Growth, 1992, 118(s 3-4): 452-460. |
| [6] | CURRIEM T, SAMAVEDAM S B, LANGDO T A,et al. Controlling threading dislocation densities in Ge on Si using graded SiGe layers and chemical-mechanical polishing.Applied Physics Letters, 1998, 72(14): 1718-1720. |
| [7] | LOH T H, NGUYEN H S, TUNG C H, et al.Ultrathin low temperature SiGe buffer for the growth of high quality Ge epilayer on Si(100) by ultrahigh vacuum chemical vapor deposition.Applied Physics Letters.2007, 90(90): 092108-1-3. |
| [8] | GUO L, ZHAO S, WANG J,et al. Fabrication of strained Ge film using a thin SiGe virtual substrate.Journal of Semiconductors, 2009, 30(9): 16-20. |
| [9] | LOO R, SOURIAU L, ONG P,et al. Smooth and high quality epitaxial strained Ge grown on SiGe strain relaxed buffers with 70-85% Ge.Journal of Crystal Growth, 2011, 324(1): 15-21. |
| [10] | CHOI D, GE Y, HARRIS J S,et al. Low surface roughness and threading dislocation density Ge growth on Si (001) .Journal of Crystal Growth, 2008, 310(18): 4273-4279. |
| [11] | KIM H-W, SHIN K W, LEE G D,et al. High quality Ge epitaxial layers on Si by ultrahigh vacuum chemical vapor deposition.Thin Solid Films, 2009, 517(14): 3990-3994. |
| [12] | YAMAMOTO M, HANNA J, MIYAUCHI M.New low pressure chemical vapor deposition technique for Ge crystalline thin films.Applied Physics Letter, 1993, 63(18): 2508-2510. |
| [13] | YAMAMOTO M, TAKADA Y, HANNA J.Selective growth of Ge in GeF4-Si2H6 system.Applied Physics Letter, 1994, 64(25): 3467-3469. |
| [14] | HANNA J, SHIMIZU K.Low-temperature growth of polycrystalline Si and Ge films by redox reactions of Si2H6 and GeF4.Journal of Organometallic Chemistry, 2000, 611(1): 531-536. |
| [15] | TAO K, KUROSAWA Y, HANNA J.Low-temperature epitaxial growth of high quality Si1-xGex (x≥0.99) films on Si(001) wafer by reactive thermal chemical vapor deposition.Applied Physics Letters, 2013, 102: 182109-1-5. |
| [16] | NAYFEH A, CHUI C O, SARASWATK C,et al. Effects of hydrogen annealing on heteroepitaxial-Ge layers on Si: surface roughness and electrical quality.Applied Physics Letters, 2004, 85(14): 2815-2817. |
| [17] | HARTMANN J M, ABBADIEA,BARNES J P,et al.Impact of the H2 anneal on the structural and optical properties of thin and thick Ge layers on Si; low temperature surface passivation of Ge by Si.Journal of Crystal Growth, 2010, 312(4): 532-541. |
| [18] | KOBAYASHI S, NISHI Y, SARASWAT K C.Effect of isochronal hydrogen annealing on surface roughness and threading dislocation density of epitaxial Ge films grown on Si.Thin Solid Films, 2010, 518(6): S136-S139. |
| [19] | LUAN H C, LIM D R, LEE K K,et al. High-quality Ge epilayers on Si with low threading-dislocation densities.Applied Physics Letters, 1999, 75(19): 2909-2911. |
| [20] | PEZZOLI F, BONERA E, GRILLI E,et al. Raman spectroscopy determination of composition and strain in image heterostructures.Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2008, 11(s 5-6): 279-284. |
| [21] | SHAH V A, DOBBIE A, MYRONOV M,et al. High quality relaxed Ge layers grown directly on a Si(001) substrate.Solid-State Electronics, 2011, 62(1): 189-194. |
| [22] | ZHOU Z, LI C, LAI H,et al. The influence of low-temperature Ge seed layer on growth of high-quality Ge epilayer on Si(100) by ultrahigh vacuum chemical vapor deposition.Journal of Crystal Growth, 2008, 310(10): 2508-2513. |
| [23] | OLUBUYIDE O O, DANIELSON D T,KIMERLING L C,et al. Impact of seed layer on material quality of epitaxial germanium on silicon deposited by low pressure chemical vapor deposition.Thin Solid Films, 2006, 508(1): 14-19. |
| [24] | HARTMANN J M, DAMLENCOURT J F, BOGUMILOWICZ Y,et al. Reduced pressure-chemical vapor deposition of intrinsic and doped ge layers on Si(001) for microelectronics and optoelectronics purposes.Journal of Crystal Growth, 2005, 274(1/2): 90-99. |
| [25] | TAN Y H, TAN C S.Growth and characterization of germanium epitaxial film on silicon (001) using reduced pressure chemical vapor deposition. Thin Solid Films, 2012, 520(7): 2711-2716. |
| [1] | 顾薛苏, 殷杰, 王康龙, 崔崇, 梅辉, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 颗粒级配对黏结剂喷射打印碳化硅陶瓷性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 216-. |
| [2] | 陈雨, 林埔安, 蔡冰, 张文华. 钙钛矿太阳能电池无机空穴传输材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 105-. |
| [3] | 田煜彬, 田超凡, 李森, 赵永鑫, 邢涛, 李智, 陈萧如, 向帅蓉, 代鹏程. 高导电性生物质碳布的制备及其燃料电池气体扩散层性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 127-. |
| [4] | 江润璐, 吴鑫, 郭昊骋, 郑琦, 王连军, 江莞. UiO-67基导电复合材料的制备及其热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 197-. |
| [5] | 李海燕, 旷峰华, 吴昊龙, 刘小根, 包亦望, 万德田. 残余拉应力的温度依赖性及其对裂纹扩展行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 214-. |
| [6] | 方万丽, 沈黎丽, 李海燕, 陈薪羽, 陈宗琦, 寿春晖, 赵斌, 杨松旺. NiOx介孔层的成膜过程对碳电极钙钛矿太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 2-. |
| [7] | 丁统顺, 丰平, 孙学文, 单沪生, 李琪, 宋健. Fmoc-FF-OH钝化钙钛矿薄膜及其太阳能电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 50-. |
| [8] | 徐昊, 钱伟, 花银群, 叶云霞, 戴峰泽, 蔡杰. 皮秒激光加工的微织构对碳化硅润湿性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 73-. |
| [9] | 邱海洋, 苗广潭, 李辉, 栾奇, 刘国侠, 单福凯. 等离子体处理对突触晶体管长程塑性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 406-412. |
| [10] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [11] | 杨洋, 崔航源, 祝影, 万昌锦, 万青. 柔性神经形态晶体管研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [12] | 吴俊林, 丁继扬, 黄新友, 朱丹阳, 黄东, 代正发, 杨文钦, 蒋兴奋, 周健荣, 孙志嘉, 李江. Gd2O2S:Tb闪烁陶瓷的制备与结构: 水浴合成中H2SO4/Gd2O3摩尔比的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 452-460. |
| [13] | 陈鑫力, 李岩, 王伟胜, 石智文, 竺立强. 明胶/羧化壳聚糖栅控氧化物神经形态晶体管[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 421-428. |
| [14] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [15] | 方仁瑞, 任宽, 郭泽钰, 徐晗, 张握瑜, 王菲, 张培文, 李悦, 尚大山. 基于氧化物基电解质栅控晶体管突触的关联学习[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 399-405. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||