无机材料学报 ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (12): 1269-1278.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160234
• • 下一篇
鲍 艳, 王 彤
收稿日期:2016-04-06
修回日期:2016-06-15
出版日期:2016-12-16
网络出版日期:2016-11-23
基金资助:BAO Yan, WANG Tong
Received:2016-04-06
Revised:2016-06-15
Published:2016-12-16
Online:2016-11-23
Supported by:摘要:
中空二氧化硅(SiO2)微球具有特殊的内部空腔、吸附渗透性好、物质传递可控等优异性能, 可储存负载并缓慢释放药物、香精、染料、菌素等客体分子, 因此在药物缓释、医学成像、环境保护以及化妆品等领域有着广阔的应用前景。根据国内外研究进展, 本文归纳对比了中空SiO2微球几种制备方法之间的优劣差异, 着重阐述了其作为缓控释载体表现出的持久性和高效性, 以及功能化的有机/无机杂化微球在响应性控释方面的优越性。并对中空SiO2微球作为新型缓控释载体的发展前景进行了展望。
中图分类号:
鲍 艳, 王 彤. 中空SiO2微球的制备及其在缓/控释应用中的新进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(12): 1269-1278.
BAO Yan, WANG Tong. Recent Advances in Fabrication and Sustained/Controlled-release Application of Hollow Silica Microspheres[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(12): 1269-1278.
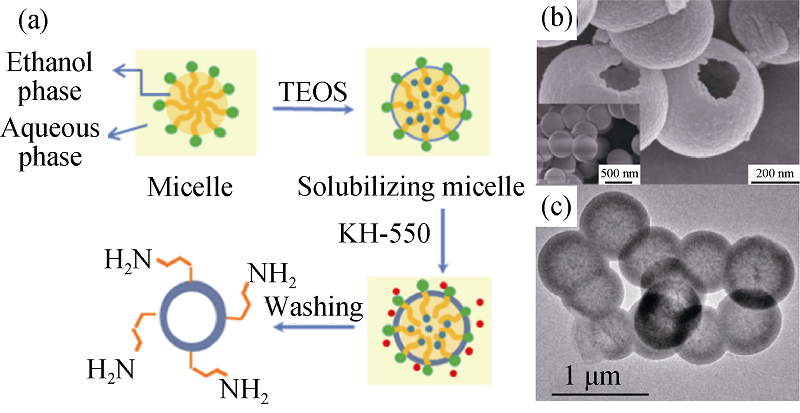
图3 (a)软模板法制备中空SiO2微球的机理图; 中空SiO2微球的(b)SEM和(c)TEM照片[44]
Fig. 3 (a) A schematic of the process for hollow silica microspheres preparation via soft-templating method; (b) SEM and (c)TEM images of hollow silica microspheres[44]
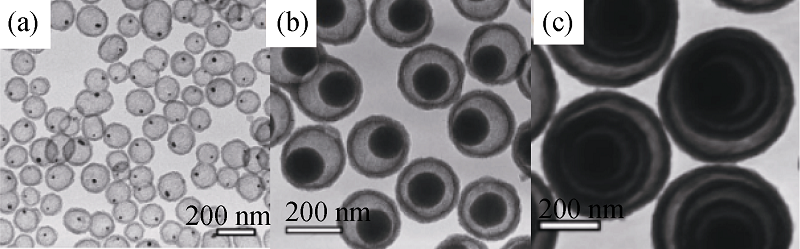
图4 (a)金/SiO2摇铃状中空微球, (b)SiO2/SiO2摇铃状中空微球和(c)SiO2/SiO2多重壳层状中空微球的TEM照片[46]
Fig. 4 TEM images of (a) Au/SiO2 yolk/shell hollow silica microspheres, (b) SiO2/SiO2 yolk/shell hollow silica microspheres and (c) SiO2/SiO2 multilayer shell hollow silica microspheres[46]
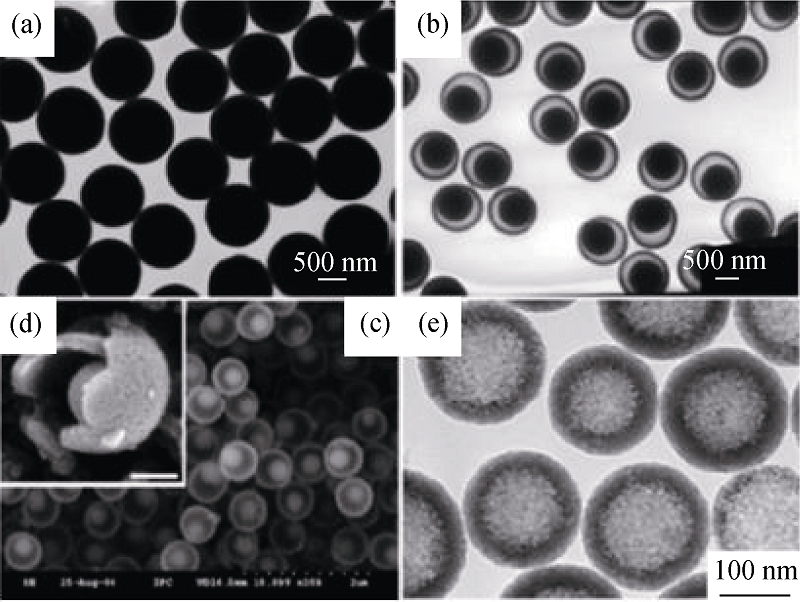
图6 (a)实心SiO2微球的TEM照片, 摇铃结构介孔中空SiO2微球的(b)TEM照片和(c、d)SEM照片和(e)介孔中空SiO2微球的TEM照片[58]
Fig. 6 (a) TEM image of solid silica spheres, (b) TEM and (c, d) SEM images of mesoporous hollow silica nanorattles, (e) TEM image of mesoporous hollow silica microspheres[58]
| Method | Characteristic | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Hard template | ① Adjustable particle size; ② Well-defined structure; ③ Uniform product morphology; ④ Foreseeable and high repetition rate | ① Difficult to remove the templates ② The shell easy to collapse; ③ Time-consuming and money-consuming |
| Soft template | ① Easy to prepare and remove the templates ② Simple technology; ③ Time-saving | ① Poor structural stability and monodispersity; ② Not easy to control shell thickness; ③ Wide particle size distribution; ④ Low efficiency |
| Self template | ① No additional template; ② Simple step and time-saving synthetic; ③ High repetition rate; ④ Controllable morphology | ① Various and complex influence factors; ② Large dependability on environment |
表1 各种制备方法的优劣对比
Table 1 Characteristics and limitations of various preparation methods
| Method | Characteristic | Limitation |
|---|---|---|
| Hard template | ① Adjustable particle size; ② Well-defined structure; ③ Uniform product morphology; ④ Foreseeable and high repetition rate | ① Difficult to remove the templates ② The shell easy to collapse; ③ Time-consuming and money-consuming |
| Soft template | ① Easy to prepare and remove the templates ② Simple technology; ③ Time-saving | ① Poor structural stability and monodispersity; ② Not easy to control shell thickness; ③ Wide particle size distribution; ④ Low efficiency |
| Self template | ① No additional template; ② Simple step and time-saving synthetic; ③ High repetition rate; ④ Controllable morphology | ① Various and complex influence factors; ② Large dependability on environment |
| [1] | LIU J, LIU F, GAO K,et al. Recent developments in the chemical synthesis of inorganic porous capsules. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2009, 19(34): 6073-6084. |
| [2] | ZHANG C, HOU T, CHEN J,et al. Preparation of mesoporous silica microspheres with multi-hollow cores and their application in sustained drug release. Particuology, 2010, 8(5): 447-452. |
| [3] | ZHU Y, SHI J, CHEN H,et al. A facile method to synthesize novel hollow mesoporous silica spheres and advanced storage property. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2005, 84(1): 218-222. |
| [4] | YANG X L, YAO K, ZHU Y H.Fabrication and sustained release property of nanostruetured hollow silica microspheres.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2005, 20(6): 1403-1408. |
| [5] | 鲍艳, 杨永强, 马建中, 等. 一种聚丙烯酸酯/ 中空二氧化硅纳米复合皮革涂饰剂的制备方法: 中国, 102704273A.2012-10-03. |
| [6] | ZHAO Y, SUN Y L, WANG H,et al. The application of hollow microspheres . Science and Technology in Chemical Industry, 2014, 22(5): 68-72. |
| [7] | CHEN J F, DING H M, WANG J X,et al. Preparation and characterization of porous hollow silica nanoparticles for drug delivery application . Biomaterials, 2004, 25(4): 723-727. |
| [8] | FENG X F, JIN W G, LIU F,et al. Advance in preparation of hollow mesoporous silica-based microsphere . Inorganic Chemical Industry, 2008, 40(12): 12-14. |
| [9] | WANG J X, WANG Z H, CHEN J F,et al. Direct encapsulation of water-soluble drug into silica microcapsules for sustained release applications . Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43(12): 3374-3381. |
| [10] | SLOWING I, VIVERO E J, WU C,et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers . Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2008, 60(11): 1278-1288. |
| [11] | ZHU Y, SHI J, SHEN W,et al. Stimuli-responsive controlled drug release from a hollow mesoporous silica sphere/polyelectrolyte multilayer core-shell structure. Angewandte Chemie, 2005, 117(32): 5213-5217. |
| [12] | LEE C, CHENG S, HUANG I,et al. Intracellular pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the controlled release of anticancer chemotherapeutics. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 122(44): 8390-8395. |
| [13] | CHANG F P, HUNG Y, CHANG J H,et al. Enzyme encapsulated hollow silica nanospheres for intracellular biocatalysis. ACS applied Materials & Interfaces, 2014, 6(9): 6883-6890. |
| [14] | CHEN Y, MENG Q, WU M,et al. Hollow mesoporous organosilica nanoparticles: a generic intelligent framework- hybridization approach for biomedicine. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2014, 136(46): 16326-16334. |
| [15] | RETSCH M, SCHMELAEISEN M, BUTT H J,et al. Visible Mie scattering in nonabsorbing hollow sphere powders. Nano Letters, 2011, 11(3): 1389-1394. |
| [16] | JIN L, XU L, MOREIN C,et al. Titanium containing γ‐MnO2(TM) hollow spheres: one-step synthesis and catalytic activities in Li/Air batteries and oxidative chemical reactions. Advanced Functional Materials, 2010, 20(19): 3373-3382. |
| [17] | ZHU Y, FANG Y, KASKEL S.Folate-conjugated Fe3O4@SiO2 hollow mesoporous spheres for targeted anticancer drug delivery.The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2010, 114(39): 16382-16388. |
| [18] | KOWALSKI A, VOGEL M, BLANKENSHIP R M.US Patent4, 427, 836, 1884. |
| [19] | ZHANG S, XU L, LIU H,et al. A dual template method for synthesizing hollow silica spheres with mesoporous shells. Materials Letters, 2009, 63(2): 258-259. |
| [20] | WANG Y, TANG C, DENG Q,et al. A versatile method for controlled synthesis of porous hollow spheres. Langmuir, 2010, 26(18): 14830-14834. |
| [21] | KATO N, KATO N.High-yield hydrothermal synthesis of mesoporous silica hollow capsules.Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2016, 219: 230-239. |
| [22] | DUAN Y W, YU A H, ZHAI G X.Progress of preparation methods of hollow microspheres.Chinese Journal of Pharmaceuticals, 2015, 46(6): 639-646. |
| [23] | SCHMID A, FUJII S, ARMES S P.Polystyrene silica nanocomposite particlesvia alcoholic dispersion polymerization using a cationic azo initiator. Langmuir, 2006, 22(11): 4923-4927. |
| [24] | SEN D, KHAN A, BAHADUR J,et al. Use of small-angel neutron scattering to investigate modifications of internal structure in self-assembled grains of nanoparticles synthesized by spray drying. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2010, 347(1): 25-30. |
| [25] | HAGURA N, NANDIYANTO A B D, ISKANDAR F,et al. A role of template surface charge in the preparation of porous and hollow particles using spray-drying. Chemistry Letters, 2009, 38(11): 1076-1077. |
| [26] | HU W, DU X, WU Y,et al. Novel -Cu0.95V2O5 hollow microspheres and α-CuV2O6 nanograins: Facile synthesis and application in lithium-ion batteriesv. Journal of Power Sources, 2013, 237(237): 112-118. |
| [27] | WEI J, DU A, JIN F,et al. The preparation and high-frequency electromagnetic properties of ferrimagnetic bisphthalonitrile-Fe3O4 core-shell hollow microspheres. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials, 2013, 340(8): 70-75. |
| [28] | 杨永强. 聚丙烯酸酯/中空二氧化硅纳米复合皮革涂饰剂的制备及应用研究. 陕西科技大学, 2014. |
| [29] | GU W J, LIAO Y, WU W B,et al. Progress in the preparation of hollow silica spheres. Silicone Material, 2009, 23(4): 257-264. |
| [30] | TENG Z, HAN Y, LI J,et al. Preparation of hollow mesoporous silica spheres by a Sol-Gel/emulsion approach. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2010, 127(1): 67-72. |
| [31] | BECKER AL, JOHNSTON APR, CARUSO F.Layer-by-layer- assembled capsules and films for therapeutic delivery.Small, 2010, 6(17): 1836-1852. |
| [32] | XIE F, QI M Z, LI W J,et al. Classification, fabrication methods and applications of inorganic hollow spheres. Progress in Chemistry, 2011, 23(12): 2522-2533. |
| [33] | MALGRAS V, JI Q, KAMACHI Y,et al. Templated synthesis for nanoarchitectured porous materials. Bulletin of the Chemical Society of Japan, 2015, 88(9): 1171-1200. |
| [34] | HSUEH H Y, YAO C T, HO R M.Well-ordered nanohybrids and nanoporous materials from gyroid block copolymer templates.Chemical Society Reviews, 2015, 44(7): 1974-2018. |
| [35] | NANDIYANTO A B D, KIM S G, ISKANDAR F,et al. Synthesis of spherical mesoporous silica nanoparticles with nanometer-size controllable pores and outer diameters. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2009, 120(3): 447-453. |
| [36] | YANG Z, CONG H, CAO W.Narrowly dispersed micrometer- sized composite spheres based on diazonium-polystyrene.Journal of Polymer Science Part A: Polymer Chemistry, 2004, 42(17): 4284-4288. |
| [37] | ZOU H, WU S, RAN Q,et al. A simple and low-cost method for the preparation of monodisperse hollow silica spheres. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(31): 11623-11629. |
| [38] | BAO Y, YANG Y Q, MA J Z.Fabrication of monodisperse hollow silica spheres and effect on water vapor permeability of polyacrylate membrane.Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2013, 407(10): 155-163. |
| [39] | SUHENDI A, NANDIYANTO A B, MUNIR M M,et al.Preparation of agglomeration-free spherical hollow silica particles using an electrospray method with colloidal templating. Materials Letters, 2013, 106(9): 432-435. |
| [40] | CHEN Z, CUI Z M, NIU F,et al. Pd nanoparticles in silica hollow spheres with mesoporous walls: a nanoreactor with extremely high activity. Chem. Commun., 2010, 46(35): 6524-6526. |
| [41] | BAO Y, YANG Y Q, MA J Z,et al. Fabrication of hollow silica microsphere using zinc oxide as template and its effect on polyacrylate film properies. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2014, 42(7): 914-925. |
| [42] | CAO F, LI D X, GUAN Z S.Preparation of silica hollow microspheres with special surface morphology by biotemplate method.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(3): 501-506. |
| [43] | WANG X, MIAO X R, LI Z M,et al. Fabrication of microporous hollow silica spheres templated by NP-10 micelles without calcinations. Applied Surface Science, 2011, 257(7): 2481-2488. |
| [44] | BAO Y, SHI C H, MA J Z.Fabrication of hollow silica spheres and their effect on water vapor permeability of waterborne polyurethane film.Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2015, 43(1): 35-41. |
| [45] | 李敏. 双子表面活性剂为模板制备中空二氧化硅纳米球及其载药性能研究. 湖北: 华中科技大学博士学位, 2013. |
| [46] | WU X J, XU D.Soft template synthesis of yolk/silica shell particles.Advanced Materials, 2010, 22(13): 1516-1520. |
| [47] | JAFELICCI JR M, DAVOLOS M R, DOS SANTOS F J,et al. Hollow silica particles from microemulsion. Journal of Non- crystalline Solids, 1999, 247(1): 98-102. |
| [48] | SINGH R K, GARG A, BANDYOPADHYAYA R,et al. Density fractionated hollow silica microspheres with high-yield by non-polymeric Sol-Gel/ emulsion route. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2007, 310(1): 39-45. |
| [49] | TENG Z, HAN Y, LI J,et al. Preparation of hollow mesoporous silica spheres by a Sol-Gel/ emulsion approach. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2010, 127(1): 67-72. |
| [50] | JZHANG C, HOU T, CHEN J,et al. Preparation of mesoporous silica microspheres with multi-hollow cores and their application in sustained drug release. Particuology, 2010, 8(5): 447-452. |
| [51] | CHUL O, CHUNG S, SHIN S,et al. Distribution of macropores in silica particles prepared by using multiple emulsions. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2002, 254(1): 79-86. |
| [52] | WU W, XIAO X H, ZHANG S F,et al. One-pot reaction and subsequent annealing to synthesis hollow spherical magnetite and maghemite nanocages. Nanoscale Research Letters, 2009, 4(8): 926-931. |
| [53] | FANG X, ZHAO X, FANG W,et al.Self-templating synthesis of hollow mesoporous silica and their applications in catalysis and drug delivery. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(6): 2205-2218. |
| [54] | WANG Q, LIU Y, YAN H.Mechanism of aself-templatingsynthesis of monodispersed hollow silica nanospheres with tunable size and shell thickness.Chemical Communications, 2007(23): 2339-2341. |
| [55] | BAO Y, YANG Y Q, MA J Z.Research progress of hollow structural materials prepared via templating method.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(5): 459-468. |
| [56] | ZHANG Q, ZHANG T, GE J,et al. Permeable silica shell through surface-protected etching. Nano letters, 2008, 8(9): 2867-2871. |
| [57] | HU J, WANG X, LIU L,et al. A facile and general fabrication method for organic silica hollow spheres and their excellent adsorption properties for heavy metal ions. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(46): 19771-19777. |
| [58] | CHEN D, LI L, TANG F,et al. Facile and scalable synthesis of tailored silica “nanorattle” structures. Advanced Materials, 2009, 21(37): 3804-3807. |
| [59] | CHEN Y, CHEN H R, SHI J L.Construction of homogenous/heterogeneous hollow mesoporous silica nanostructures by silica- etching chemistry: principles, synthesis, and applications.Accounts of Chemical Research, 2013, 47(1): 125-137. |
| [60] | CHEN Y, XU P, CHEN H,et al. Colloidal HPMO nanoparticles: silica-etching chemistry tailoring, topological transformation, and nano-biomedical applications. Advanced Materials, 2013, 25(22): 3100-3105. |
| [61] | JI Q, GUO C, YU X,et al. Flake-shell capsules: adjustable inorganic structures. Small, 2012, 8(15): 2345-2349. |
| [62] | TERENTYEVA T G, MATRAS A, VAN ROSSOM W,et al. Bioactive flake-shell capsules: soft silica nanoparticles for efficient enzyme immobilization. Journal of Materials Chemistry B, 2013, 1(26): 3248-3256. |
| [63] | SLOWING I, VIVERRO E J, WU C,et al. Mesoporous silica nanoparticles as controlled release drug delivery and gene transfection carriers. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 2008, 60(11): 1278-1288. |
| [64] | LEE C, CHENG S, HUANG I,et al. Intracellular pH-responsive mesoporous silica nanoparticles for the controlled release of anticancer chemotherapeutics. Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2010, 122(44): 8390-8395. |
| [65] | HWANG Y J, OH C, OH S G.Controlled release of retinol from silica particles prepared in O/W/O emulsion: The effects of surfactants and polymers.Journal of Controlled Release, 2005, 106(3): 339-349. |
| [66] | THEISINGER S, SCHOELLER K, OSBORN B,et al. Encapsulation of a fragrance via miniemulsion polymerization for temperature-controlled release. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics, 2009, 210(6): 411-420. |
| [67] | VALLET-REGI M, BALAS F, COLILLA M,et al. bone-regenerative bioceramic implants with drug and protein controlled delivery capability. Progress in Solid State Chemistry, 2008, 36(3): 163-191. |
| [68] | SHE X, CHEN L, VELLEMAN L,et al. Fabrication of high specificity hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles assisted by Eudragit for targeted drug delivery. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2015, 445: 151-160. |
| [69] | LI Z Z, WEN L X, SHAO L,et al. Fabrication of porous hollow silica nanoparticles and their applications in drug release control. Journal of Controlled Release, 2004, 98(2): 245-254. |
| [70] | BOTTERHUIS N E, SUN Q, MAGUSIN P C M M,et al. Hollow silica spheres with an ordered pore structure and their application in controlled release studies. Chemistry-A European Journal, 2006, 12(5): 1448-1456. |
| [71] | CHEN J F, DING H M, WANG J X,et al. Preparation and characterization of porous hollow silica nanoparticles for drug delivery application. Biomaterials, 2004, 25(4): 723-727. |
| [72] | HUDSON S P, PADERERA R F, LANGER R,et al. The biocompatibility of mesoporous silicates. Biomaterials, 2008, 29(30): 4045-4055. |
| [73] | WANG J X, WANG Z H, CHEN J F,et al. Direct encapsulation of water-soluble drug into silica microcapsules for sustained release applications. Materials Research Bulletin, 2008, 43(12): 3374-3381. |
| [74] | LANGER R.Polymer-controlled drug delivery systems.Accounts of Chemical Research, 1993, 26(10): 537-542. |
| [75] | JONES M N.Carbohydrate-mediated liposomal targeting and drug delivery.Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews, 1994, 13(3): 215-249. |
| [76] | LIU G, ZHU C, XU J,et al. Thermo-responsive hollow silica microgels with controlled drug release properties. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces, 2013, 111(6): 7-14. |
| [77] | CHEN F, ZHU Y.Chitosan enclosed mesoporous silica nanoparticles as drug nano-carriers: sensitive response to the narrow pH range.Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2012, 150(1): 83-89. |
| [78] | XUE M, FINDENEGG G H.Lysozyme as a pH-responsive valve for the controlled release of guest molecules from mesoporous silica.Langmuir, 2012, 28(50): 17578-17584. |
| [79] | YOU Y Z, KALEBAILA K K, BROCK S L.Temperature- controlled uptake and release in PNIPAM-modified porous silica nanoparticles.Chemistry of Materials, 2008, 20(10): 3354-3359. |
| [80] | CHEN L, WANG W, SU B,et al. A light-responsive release platform by controlling the wetting behavior of hydrophobic surface. ACS Nano, 2014, 8(1): 744-751. |
| [81] | CHEN M, HUANG C, HE C,et al. A glucose-responsive controlled release system using glucose oxidase-gated mesoporous silica nanocontainers. Chemical Communications, 2012, 48(76): 9522-9524. |
| [82] | RADHAKRISHNAN K, GUPTA S, GNANADHAS D P,et al. Protamine-capped mesoporous silica nanoparticles for biologically triggered drug release. Particle & Particle Systems Characterization, 2014, 31(4): 449-458. |
| [83] | ZHANG Z, BALOGH D, WANG F,et al. Biocatalytic release of an anticancer drug from nucleic-acids-capped mesoporous SiO2 Using DNA or molecular biomarkers as triggering stimuli. ACS Nano, 2013, 7(10): 8455-8468. |
| [84] | GUI W Y, WANG W Q, JIAO X Y,et al. pH-response controlled release system based on hollow mesoporous silica nanoparticles . Scientia Sinica Chimica, 2015, 45(7): 703-709. |
| [85] | HU J, LIU L, XIE Y,et al. Facile synthesis of thermal-responsive P(NIPAM-S)/SiO2 hybrid hollow spheres and their controllable release properties for fragrance. Polymer Chemistry, 2013, 4(11): 3293-3299. |
| [86] | HU J, CHEN M, TIAN H,et al. Preparation and pyrolysis characteristics of PNIPAM-grafted SiO2 hollow spheres loading vitamin C. RSC Advances, 2015, 5(99): 81134-81141. |
| [87] | ZHU Y, MENG W, GAO H,et al. Hollow mesoporous silica/poly (L-lysine) particles for codelivery of drug and gene with enzyme- triggered release property. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2011, 115(28): 13630-13636. |
| [1] | 丁玲, 蒋瑞, 唐子龙, 杨运琼. MXene材料的纳米工程及其作为超级电容器电极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | 杨卓, 卢勇, 赵庆, 陈军. X射线衍射Rietveld精修及其在锂离子电池正极材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | 陈强, 白书欣, 叶益聪. 热管理用高导热碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | 林俊良, 王占杰. 铁电超晶格的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [5] | 牛嘉雪, 孙思, 柳鹏飞, 张晓东, 穆晓宇. 铜基纳米酶的特性及其生物医学应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [6] | 苑景坤, 熊书锋, 陈张伟. 聚合物前驱体转化陶瓷增材制造技术研究趋势与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [7] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [8] | 杨洋, 崔航源, 祝影, 万昌锦, 万青. 柔性神经形态晶体管研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [9] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [10] | 林思琪, 李艾燃, 付晨光, 李荣斌, 金敏. Zintl相Mg3X2(X=Sb, Bi)基晶体生长及热电性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [11] | 张超逸, 唐慧丽, 李宪珂, 王庆国, 罗平, 吴锋, 张晨波, 薛艳艳, 徐军, 韩建峰, 逯占文. 新型GaN与ZnO衬底ScAlMgO4晶体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [12] | 陈昆峰, 胡乾宇, 刘锋, 薛冬峰. 多尺度晶体材料的原位表征技术与计算模拟研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [13] | 齐占国, 刘磊, 王守志, 王国栋, 俞娇仙, 王忠新, 段秀兰, 徐现刚, 张雷. GaN单晶的HVPE生长与掺杂进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [14] | 谢兵, 蔡金峡, 王铜铜, 刘智勇, 姜胜林, 张海波. 高储能密度聚合物基多层复合电介质的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| [15] | 冯静静, 章游然, 马名生, 陆毅青, 刘志甫. 冷烧结技术的研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 125-136. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||