无机材料学报 ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (10): 1073-1080.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160173
杨广武1,2, 杨瑞霞1,3, 张守超2, 朱 飞2
收稿日期:2016-03-23
修回日期:2016-05-18
出版日期:2016-10-20
网络出版日期:2016-09-23
作者简介:杨广武(1970–), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: yanggw204@163.com
基金资助:YANG Guang-Wu1,2, YANG Rui-Xia1,3, ZHANG Shou-Chao2, ZHU Fei2
Received:2016-03-23
Revised:2016-05-18
Published:2016-10-20
Online:2016-09-23
About author:YANG Guang-Wu. E-mail: yanggw204@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
利用提拉法生长了掺杂浓度为1.0at%~10.0at%的YVO4:Ce3+单晶, XRD分析显示Ce3+ 的掺入没有改变晶体结构。晶体的激发和发射谱测试表明, 在325 nm激发下YVO4:Ce3+发射出峰值在445 nm的蓝光和620 nm附近的红光。蓝光发光强度随Ce3+浓度增加而增强, 当浓度为8.0at%时达到最强, 10.0at%时出现浓度淬灭, 发光减弱; 红光则随着Ce3+浓度的增加而持续增强。通过实验分析推测蓝光来源于Ce3+电子从激发态2D3/2到基态2F5/2的跃迁, 而红光则是由于V4+的电子能级跃迁而形成的。XPS测试显示部分Ce3+失去电子被氧化成为Ce4+, 失去的电子大部分被V5+捕获形成V4+。V4+的d轨道分裂为三个轨道单态2A1、2B1、2B2和一个轨道简并态2E等4个能级, 基态为2B2。V4+中电子通过能量传递、辐射跃迁和无辐射跃迁等过程, 可以实现波长在620 nm附近的红光发射以及在620 nm激发下的451 nm蓝光上转换发光。实验证实了上转换发光为双光子过程。研究结果对紫外激发下YVO4:Ce3+红、蓝光发光行为提供了理论支撑。
中图分类号:
杨广武, 杨瑞霞, 张守超, 朱 飞. Ce3+浓度对YVO4: Ce3+晶体发光性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(10): 1073-1080.
YANG Guang-Wu, YANG Rui-Xia, ZHANG Shou-Chao, ZHU Fei. Ce Doping Concentration on Luminescence Property of YVO4:Ce3+ Crystals[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(10): 1073-1080.
| Samples | Cell parameter/nm | Cell Volume/nm3 V=a2c | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a=b | c | ||
| YVO4 | 0.712140 | 0.629113 | 0.319050 |
| 1.0at% | 0.712641 | 0.630389 | 0.320148 |
| 2.0at% | 0.712730 | 0.630577 | 0.320323 |
| 3.0at% | 0.712782 | 0.630741 | 0.320453 |
| 5.0at% | 0.712823 | 0.63081 | 0.320525 |
| 8.0at% | 0.713023 | 0.630851 | 0.320725 |
| 10.0at% | 0.713103 | 0.631013 | 0.320880 |
表1 YVO4:Ce3+晶胞参数
Table 1 Cell parameters of YVO4:Ce3+ compound
| Samples | Cell parameter/nm | Cell Volume/nm3 V=a2c | |
|---|---|---|---|
| a=b | c | ||
| YVO4 | 0.712140 | 0.629113 | 0.319050 |
| 1.0at% | 0.712641 | 0.630389 | 0.320148 |
| 2.0at% | 0.712730 | 0.630577 | 0.320323 |
| 3.0at% | 0.712782 | 0.630741 | 0.320453 |
| 5.0at% | 0.712823 | 0.63081 | 0.320525 |
| 8.0at% | 0.713023 | 0.630851 | 0.320725 |
| 10.0at% | 0.713103 | 0.631013 | 0.320880 |
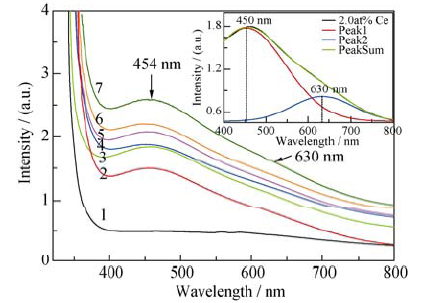
图3 YVO4和YVO4: Ce3+晶体吸收光谱及吸收峰Gauss拟合
Fig. 3 Absorption spectra and Gauss fitting of YVO4 and YVO4: Ce3+ crystals (line 1 to 7 represents absorption spectrum of YVO4 and 1.0at%, 2.0at%, 3.0at%, 5.0at%, 8.0at% and 10.0at% YVO4:Ce3+ crystals, respectively)
| Ce Concentration | Ce3+ Binding energy/eV | Ce4+ Binding energy/eV | Ce3+ Relative content/% | Ce4+ Relative content/% | Ce3+ Rela content/% | Ce4+ Rela content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0at% | 891.1,906.8 | 916.3 | 64.8 | 35.2 | 0.613% | 0.333% |
| 2.0at% | 884.2,904.3 | 898.1,916.2 | 75.0 | 25.0 | 1.426% | 0.476% |
| 3.0at% | 886.3,904.8 | 898.1,898.3,915.6 | 65.4 | 34.6 | 1.896% | 1.003% |
| 5.0at% | 885.4,904.6 | 882.5,899.3,916.7 | 69.0 | 31.0 | 3.284% | 1.45% |
| 8.0at% | 885.3,903.8 | 882.7,898.5,914.6 | 68.2 | 31.8 | 5.356% | 2.498% |
| 10.0at% | 884.5,903.1 | 882.6,899.2,915.7 | 71.4 | 28.6 | 6.877% | 2.755% |
表2 XPS分析YVO4:Ce3+晶体中Ce3+/Ce4+相对含量
Table 2 Ce3+/Ce4+ relative content in YVO4:Ce3+ crystals
| Ce Concentration | Ce3+ Binding energy/eV | Ce4+ Binding energy/eV | Ce3+ Relative content/% | Ce4+ Relative content/% | Ce3+ Rela content/% | Ce4+ Rela content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0at% | 891.1,906.8 | 916.3 | 64.8 | 35.2 | 0.613% | 0.333% |
| 2.0at% | 884.2,904.3 | 898.1,916.2 | 75.0 | 25.0 | 1.426% | 0.476% |
| 3.0at% | 886.3,904.8 | 898.1,898.3,915.6 | 65.4 | 34.6 | 1.896% | 1.003% |
| 5.0at% | 885.4,904.6 | 882.5,899.3,916.7 | 69.0 | 31.0 | 3.284% | 1.45% |
| 8.0at% | 885.3,903.8 | 882.7,898.5,914.6 | 68.2 | 31.8 | 5.356% | 2.498% |
| 10.0at% | 884.5,903.1 | 882.6,899.2,915.7 | 71.4 | 28.6 | 6.877% | 2.755% |
| Ce concentration | V4+ binding energy/eV | V5+ binding energy/eV | V4+ relative content/% | V5+ relative content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0at% | 515.5 | 517 | 0.24 | 99.76 |
| 2.0at% | 515.5 | 517 | 0.32 | 99.68 |
| 3.0at% | 515.5 | 517 | 0.58 | 99.42 |
| 5.0at% | 515.5 | 517 | 0.8 | 99.2 |
| 8.0at% | 515.5 | 517 | 1.37 | 98.63 |
| 10.0at% | 515.5 | 517 | 1.62 | 98.38 |
表3 XPS分析YVO4:Ce3+晶体中V4+/V5+相对含量
Table 3 V4+/V5+ relative content in YVO4:Ce3+ crystals
| Ce concentration | V4+ binding energy/eV | V5+ binding energy/eV | V4+ relative content/% | V5+ relative content/% |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.0at% | 515.5 | 517 | 0.24 | 99.76 |
| 2.0at% | 515.5 | 517 | 0.32 | 99.68 |
| 3.0at% | 515.5 | 517 | 0.58 | 99.42 |
| 5.0at% | 515.5 | 517 | 0.8 | 99.2 |
| 8.0at% | 515.5 | 517 | 1.37 | 98.63 |
| 10.0at% | 515.5 | 517 | 1.62 | 98.38 |
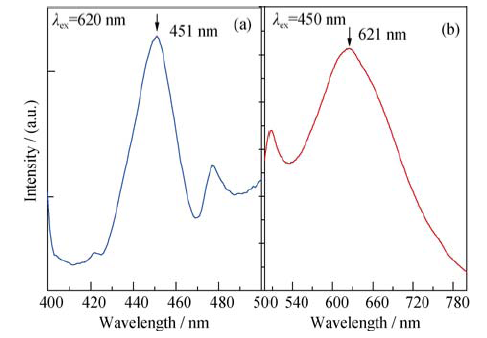
图10 YVO4:Ce3+晶体在620 nm激发下的上转换发光和450 nm激发下的红光发射
Fig. 10 Up-conversion luminescence (λex = 620 nm ) and red emission (λex = 450 nm ) of YVO4:Ce3+ crystal
| [1] | LI P L, WANG Y, GUO Q L.Research progress in single host white light emitting phosphor for white LEDs.Chinese Sci. Bull., 2011, 56(7): 488-503. |
| [2] | LI P L, WANG Z D, LUO Z Y, et al.Progress of phosphors for UV and near-UV based white LEDs. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2015, 44(11): 2954-2962. |
| [3] | ZHANG S H, ZHOU M B, HU J F, et al.Research progress in preparation of single phase silicate phosphor for nuv-white light emitting diodes.Materials Review, 2009, 23(5): 25-29. |
| [4] | WANG Z J, TIAN Z, YOU J Q, et al.Recent development on single-phase white emitting phosphors for white LEDs.Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2016, 44(1): 172-180. |
| [5] | RAUT S K, DHOBLE N S, DHOBLE S J.Optical properties of Eu, Dy, Mn activated M2SiO4,(M2=Ca, Sr, Zn) orthosilicate phosphors.Journal of Luminescence, 2013, 134: 325-332. |
| [6] | P S THAKER, S C GEDAM, S J DHOBLE, et al.Luminescence of KCaSO4Cl: X, Y (X=Eu or Ce; Y=Dy or Mn) halosulfate material.Journal of Luminescence, 2011, 131: 1612-1616. |
| [7] | RIWOTZKI K, HAASE M.Wet-chemical synthesis of doped colloidal nanoparticles: YVO4: Ln (Ln=Eu, Sm, Dy). The Journal of Physical Chemistry B, 1998, 102(50): 10129-10135. |
| [8] | SHEN L J, LI B, WANG Z Z, et al.Research development of rare earth vanadate liuminesence materials.Chinese Rare Earhts, 2015, 36(6): 129-137. |
| [9] | WITOLD R R, TOMASZ N, JAROS L K.Luminescence and energy transfer phenomena in YVO4 single crystal co-doped with Tm3+ and Eu3+.Journal of Luminescence, 2015, 162: 134-139. |
| [10] | BLASSE G.On the Eu3+ fluorescence of mixed metal oxides. IV. The photoluminescent efficiency of Eu3+-activated oxides.The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1966, 45(7): 2356-2360. |
| [11] | SHEN L J, LI B, WANG Z Z, et al.Vacuum ultraviolet spectra of YVO4:Tm3+.Chinese Journal of Luminescence, 2014, 35(9): 1034-1039. |
| [12] | DEVI C V, SINGH N R.Effect of annealing on the luminescence properties of YVO4: Dy phosphor on co-doping Pb2+ ions.Spectrochimica Acta Part A: Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy, 2015, 146: 331-341. |
| [13] | CHEN X B, ZHOU G, ZHOU Y F, et al.Near-Infrared quantum cutting downconversion luminescence of Yb3+ ion cooperative energy transferred from YVO4 matrix donor. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2015, 35(2): 315-319. |
| [14] | ZHANG S C, GU J X, JIA G Z, et al.Effect of annealing on the spectroscopy performance of YVO4: Ce3+ single crystal.Optical Materials, 2015, 39: 178-181. |
| [15] | ZHANG S C, RUAN R F, JIA G Z, et al.Blue-emitting properties of Ce3+ doped YVO4 under ultraviolet excitation.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10): 1067-1072. |
| [16] | PAN Y X, WANG W, LIU G K, et al.Correlation between structure variation and luminescence red shift in YAG:Ce.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 488: 638-642. |
| [17] | XIN J, YU Y C, LIU J J, et al.Synthesis of fluorescent YVO4: Eu nano-particle and its application in developing fingerprint.Chemical Research, 2010, 21(2): 1-6. |
| [18] | WANG Y F, WANG S, RUAN Y F, et al.Photoluminescence properties of Ce and Eu co-doped YVO4 crystals.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2013, 551: 262-266. |
| [19] | REN G H, PEI Y, WU Y T, et al. Influence of Ce doping concentration on the luminescence properties of LaCl3:Ce scintillation crystals. Acta Physica Sinica, 2014, 63(3): 037802-1-6. |
| [20] | WANG D J.Theoretical Calculation of Electronic Structures and 4f→5d Transitions of Lanthanide Ions Doped in Crystals. Anhui: University of Science and Technology of China A Dissertation for Doctor's Degree, 2009. |
| [21] | NINGTHOUJAM R S, SINGH L R, SUDARSAN V, et al.Energy transfer process and optimum emission studies in luminescence of core-shell nanoparticles: YVO4:Eu-YVO4 and surface state analysis.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2009, 484: 782-789. |
| [22] | P DORENBOS.5d-level energies of Ce3+ and the crystalline environment. IV. Aluminates and “simple” oxides.Journal of Luminescence, 2002, 99: 283-299. |
| [23] | DENG T G, XIA Z G, DING H.Effect of [PO4]3-/[VO4]3- substitution on the structure and luminescence properties of Ca5[(P,V)O4]]3F: Eu3+ phosphors.Chemical Physics Letters, 2015, 637: 67-70. |
| [24] | BLASSE G, A BRIL. Luminescence of phosphors based on host lattices ABO4 (A is Sc, In; B is P, V, Nb).The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1969, 50(7): 2974-2980. |
| [25] | SVITASHEVA S N, GILINSK A M.Influence of doping level on shift of the absorption edge of gallium nitride films (Burstein-Moss effect).Applied Surface Science, 2013, 281: 109-112. |
| [26] | DORENBOS P.The 5d level positions of the trivalent lanthanides in inorganic compounds.Journal of Luminescence, 2000, 91: 155-176. |
| [27] | ANANDAN C, BERA P.XPS studies on the interaction of CeO2 with silicon in magnetronsputtered CeO2 thin films on Si and Si3N4 substrates.Applied Surface Science, 2013, 283: 297-303. |
| [28] | HEIKKINEN H, JOHANSSON L S, NYKANEN E, et al.An XPS study of SrS:Ce thin films for electroluminescent devices.Applied Surface Science, 1998, 133: 205-212. |
| [29] | ZOU Y Q, LI X J, XU J, et al.Different chemical valence of V element in the YVO4 crystal.Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2003, 32(1): 27-30. |
| [30] | WANG Y F, WU Z L, RUAN Y F, et al. Spectroscopic properties of cerium doped YVO4 crystals and analysis on valence state of cerium ion. Acta Physica Sinica, 2012, 61(22): 228105(1)- 228105(8). |
| [31] | YANG Z Y, WEI Q, HAO Y.Investigations of lattice distortion and EPR parameters for YAG:V2+ laser crystal.Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2005, 34(3): 491-495. |
| [32] | HUANG Y P.Theoretical studies of optical spectra and EPR parameters for V4+ in ThSiO4 crystal.Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2008, 37(5): 1145-1147. |
| [33] | GREGORIO S D, GREENBLATT M, PIFER J H, et al.An ESR and optical study of V4+ in zircon-type crystals.The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1982, 76(6): 2931-2937. |
| [34] | TOMASZ G, ARTUR T.Up-conversion luminescence of GdOF: Yb3+, Ln3+ (Ln=Ho, Tm, Er) nanocrystals.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2016, 660: 235-243. |
| [1] | 彭跃红,任韦舟,邱建备,韩缙,杨正文,宋志国. 1550 nm激发层状BiOCl:Er3+上转换发光及温度传感特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(8): 902-908. |
| [2] | 张志洁,黄海瑞,程昆,郭少柯. 高效碳量子点/BiOCl纳米复合材料用于光催化污染物降解[J]. 无机材料学报, 2020, 35(4): 491-496. |
| [3] | 吕喜庆, 张环宇, 李瑞, 张梅, 郭敏. Nb2O5包覆对TiO2纳米阵列/上转换发光复合结构柔性染料敏化太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(6): 590-598. |
| [4] | 高东, 张煜亮, 孙静, 范宏筠. 一步法合成特异性pH响应碳量子点及其发光机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(12): 1309-1315. |
| [5] | 史忠祥, 王晶, 关昕. Er3+掺杂调控NaY(WO4)2: Dy3+的上转换发光性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2018, 33(5): 521-527. |
| [6] | 李永进, 刘群, 周玉婷, 邱建备, 宋志国. Yb3+-Tm3+共掺BiOBr纳米晶的近红外上转换发光特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(3): 279-284. |
| [7] | 周佳佳, 邱建荣. 单个纳米颗粒的上转换光谱现象研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(10): 1023-1030. |
| [8] | 朱美娟, 余建定, 张明辉, 谷彦静, 李 勤, 方必军, 赵洪阳, 沈 清. 无容器制备Er3+/Yb3+共掺La2O3-TiO2-ZrO2玻璃及其上转换发光研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(4): 391-396. |
| [9] | 彭 霞, 李淑星, 刘学建,黄毅华, 黄政仁, 李会利. Eu2+/Tb3+掺杂的Sr2Si5N8基荧光粉的制备与发光性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(4): 397-400. |
| [10] | 张继红, 陶海征, 顾少轩, 张高科, 刘 超, 赵修建. 面向太阳光全光谱应用铒掺杂硫卤玻璃上转换发光特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(3): 245-248. |
| [11] | 向军涛, 杜 鹏, 罗来慧, 方义权, 赵学洋, 胡旭波, 陈红兵. Er3+掺杂弛豫铁电材料PMNT的单晶生长与性能表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(2): 135-140. |
| [12] | 耿志明, 李 坤, 施东良, 施瑕玉, 黄海涛, 陈王丽华. 铌酸钾钠基透明上转换陶瓷材料制备及性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(12): 1265-1269. |
| [13] | 骆家亮, 吴云涛, 任国浩. Ce3+, Eu3+共掺Lu3Al5O12多晶的发光特性及能量传递研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(11): 1211-1217. |
| [14] | 傅鑫杰, 宋力昕, 李家成. 掺铈多组分硅酸盐玻璃电子辐照着色研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(10): 1018-1022. |
| [15] | 张守超, 阮永丰, 贾国治, 冯志辉, 刘枝朋, 裴利斌. 紫外光激发Ce3+掺YVO4蓝光发射性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(10): 1067-1072. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||