无机材料学报 ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (4): 393-400.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150402
袁 钦, 宋永才
收稿日期:2015-08-27
修回日期:2015-11-16
出版日期:2016-04-20
网络出版日期:2016-03-25
作者简介:袁 钦(1983–), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: yinzi863@163.com
基金资助:YUAN Qin, SONG Yong-Cai
Received:2015-08-27
Revised:2015-11-16
Published:2016-04-20
Online:2016-03-25
About author:YUAN Qin. E-mail: yinzi863@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
采用不同Al含量的聚铝碳硅烷(PACS)为先驱体, 通过不同的PACS纤维不熔化方法调节O引入量, 制备了具有不同Al和O含量的连续SiAlCO纤维。研究了SiAlCO纤维经高温处理转变为Si(Al)C纤维过程中, Al、O含量对SiCxOy相分解、β-SiC结晶生长和微观形貌的影响。结果表明: 纤维中SiCxOy相的分解温度区间为1300~1700℃, 与Al、O含量基本无关; 提高Al含量可减少纤维在高温下表面形成粗大SiC结晶颗粒和相互连通的气孔, 并且对1700℃以上β-SiC结晶生长的抑制作用增强, 有利于烧结致密化; 利用纤维中O元素, 以放出CO或CO2方式脱除富余C, 但O含量过高导致气体逸出时产生较大孔洞, 不利于烧结致密化。当Al和O含量分别约为0.6wt%和9wt%时, SiAlCO纤维经高温处理后能得到具有较大β-SiC晶粒尺寸的致密化Si(Al)C纤维。
中图分类号:
袁 钦, 宋永才. Al、O含量对SiAlCO纤维高温转化为Si(Al)C纤维过程的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(4): 393-400.
YUAN Qin, SONG Yong-Cai. Effects of Al and O Content on Transformation from SiAlCO to Si(Al)C Fibers after High Temperature Treatment[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(4): 393-400.
| Sample | Oxidation temperature before EB/℃ | Si/wt% | C/wt% | Al/wt% | O/wt% | C/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiAlCO2-6 | - | 57.27 | 36.71 | 0.24 | 5.78 | 1.496 |
| SiAlCO2-9 | 160 | 55.88 | 35.08 | 0.20 | 8.84 | 1.465 |
| SiAlCO2-13 | 190 | 54.16 | 32.21 | 0.22 | 13.41 | 1.388 |
| SiAlCO3-6 | - | 55.20 | 36.93 | 0.33 | 7.54 | 1.561 |
| SiAlCO3-9 | 160 | 54.77 | 35.42 | 0.33 | 9.48 | 1.509 |
| SiAlCO3-13 | 190 | 53.63 | 33.02 | 0.36 | 12.94 | 1.437 |
| SiAlCO6-6 | - | 55.77 | 36.27 | 0.62 | 7.36 | 1.517 |
| SiAlCO6-9 | 160 | 54.69 | 35.03 | 0.57 | 9.71 | 1.495 |
| SiAlCO6-13 | 190 | 54.10 | 32.69 | 0.53 | 12.68 | 1.410 |
表1 SiAlCO纤维的元素组成
Table1 Chemical compositions of SiAlCO fibers
| Sample | Oxidation temperature before EB/℃ | Si/wt% | C/wt% | Al/wt% | O/wt% | C/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiAlCO2-6 | - | 57.27 | 36.71 | 0.24 | 5.78 | 1.496 |
| SiAlCO2-9 | 160 | 55.88 | 35.08 | 0.20 | 8.84 | 1.465 |
| SiAlCO2-13 | 190 | 54.16 | 32.21 | 0.22 | 13.41 | 1.388 |
| SiAlCO3-6 | - | 55.20 | 36.93 | 0.33 | 7.54 | 1.561 |
| SiAlCO3-9 | 160 | 54.77 | 35.42 | 0.33 | 9.48 | 1.509 |
| SiAlCO3-13 | 190 | 53.63 | 33.02 | 0.36 | 12.94 | 1.437 |
| SiAlCO6-6 | - | 55.77 | 36.27 | 0.62 | 7.36 | 1.517 |
| SiAlCO6-9 | 160 | 54.69 | 35.03 | 0.57 | 9.71 | 1.495 |
| SiAlCO6-13 | 190 | 54.10 | 32.69 | 0.53 | 12.68 | 1.410 |
| Sample | Si/wt% | C/wt% | O/wt% | Al/wt% | C/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiAlCO2-6 | 62.53 | 37.27 | 0.06 | 0.39 | 1.396 |
| SiAlCO2-9 | 65.72 | 33.80 | 0.04 | 0.44 | 1.200 |
| SiAlCO2-13 | 68.73 | 31.07 | 0.02 | 0.48 | 1.060 |
| SiAlCO3-6 | 62.31 | 37.36 | 0.15 | 0.47 | 1.406 |
| SiAlCO3-9 | 63.33 | 36.34 | 0.04 | 0.57 | 1.345 |
| SiAlCO3-13 | 66.97 | 32.70 | 0.03 | 0.64 | 1.145 |
| SiAlCO6-6 | 62.03 | 37.11 | 0.11 | 0.75 | 1.396 |
| SiAlCO6-9 | 63.02 | 36.06 | 0.08 | 0.84 | 1.335 |
| SiAlCO6-13 | 65.55 | 33.50 | 0.04 | 0.91 | 1.222 |
| Tyranno SA(edge)[ | 68.00 | 31.30 | - | 0.50 | 1.080 |
| Tyranno SA(core)[ | 62.90 | 36.10 | 0.40 | 0.60 | 1.340 |
表2 1700℃处理后SiAlCO纤维的元素组成
Table2 Chemical compositions of SiAlCO fibers after heat-treatment at 1700℃
| Sample | Si/wt% | C/wt% | O/wt% | Al/wt% | C/Si |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiAlCO2-6 | 62.53 | 37.27 | 0.06 | 0.39 | 1.396 |
| SiAlCO2-9 | 65.72 | 33.80 | 0.04 | 0.44 | 1.200 |
| SiAlCO2-13 | 68.73 | 31.07 | 0.02 | 0.48 | 1.060 |
| SiAlCO3-6 | 62.31 | 37.36 | 0.15 | 0.47 | 1.406 |
| SiAlCO3-9 | 63.33 | 36.34 | 0.04 | 0.57 | 1.345 |
| SiAlCO3-13 | 66.97 | 32.70 | 0.03 | 0.64 | 1.145 |
| SiAlCO6-6 | 62.03 | 37.11 | 0.11 | 0.75 | 1.396 |
| SiAlCO6-9 | 63.02 | 36.06 | 0.08 | 0.84 | 1.335 |
| SiAlCO6-13 | 65.55 | 33.50 | 0.04 | 0.91 | 1.222 |
| Tyranno SA(edge)[ | 68.00 | 31.30 | - | 0.50 | 1.080 |
| Tyranno SA(core)[ | 62.90 | 36.10 | 0.40 | 0.60 | 1.340 |
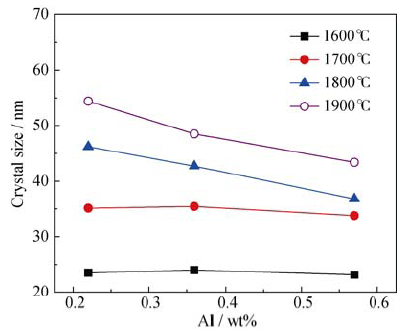
图6 不同温度热处理后β-SiC晶粒尺寸随Al含量的变化
Fig. 6 β-SiC crystallite size varied with Al content for the SiAlCO fibers after heat-treatment at different temperatures
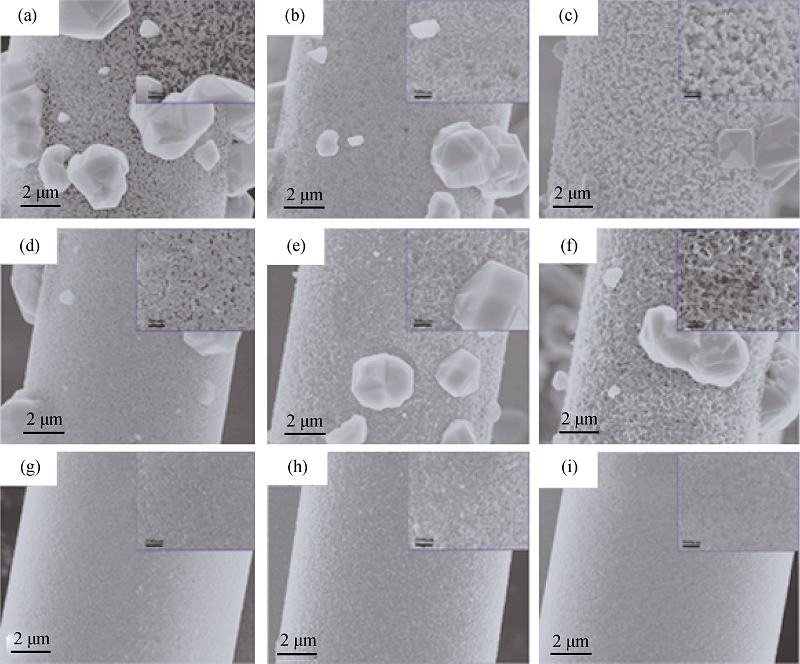
图7 1700℃处理后SiAlCO纤维表面SEM照片
Fig. 7 Surface morphologies of SiAlCO fibers after heat-treatment at 1700℃ (a)-(c) SiAlCO2-6~SiAlCO2-13, (d)-(f) SiAlCO3-6~SiAlCO3-13, (g)-(i) SiAlCO6-6~SiAlCO6-13
| [1] | DONG S, KATOH Y, KOHYAMA A.Preparation of SiC/SiC composites by hot-pressing, using Tyranno-SA fiber as reinforcement. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2003, 86(1): 26-32. |
| [2] | WANG DE-YIN,MAO XIAN-HE,SONG YONG-CAI, et al.Preparation and properties of SiC fiber with a stable excess carbon layer on the surface.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(6): 1209-1213. |
| [3] | KATOH Y, OZAWA K, SHIH C, et al.Continuous SiC fiber, CVI SiC matrix composites for nuclear applications: properties and irradiation effects. J. Nucl. Mater., 2014, 448(1/2/3): 448-476. |
| [4] | ABE T, KISHIMOTO H, NAKAZATO N, et al.SiC/SiC composite heater for IFMIF.Fusion. Eng. Des., 2012, 87(7/8): 1258-1260. |
| [5] | WANG DE-YIN,MAO XIAN-HE,SONG YONG-CAI, et al.Preparation and properties of SiC fiber with a stable excess carbon layer on the surface.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(6): 1209-1213. |
| [6] | WANG DE-YIN, SONG YONG-CAI, JIAN KE.Effect of structure and composition on the specific resistivity of continuous silicon carbide fibers.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(2): 162-168. |
| [7] | BUNSELL A, PIANT A.A review of the development of the three generations of small diameter silicon carbide fibers.J. Mater. Sci., 2006, 41(3): 823-839. |
| [8] | ISHIKAWA T.Advances in inorganic fibers.Adv. Polym. Sci., 2005, 178: 109-144. |
| [9] | ZHAO DA-FANG,WANG HAI-ZHE,LI XIAO-DONG.Development of polymer-derived SiC fiber.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2009, 24(6): 1097-1104. |
| [10] | ISHIKAWA T, KOHTOKU Y, KUMAGAWA K, et al.High-strength alkali-resistant sintered SiC fibre stable to 2200℃.Nature, 1998, 391(6669): 773-775. |
| [11] | ISHIKAWA T, KAJII S, MATSUNAGA K, et al.A tough, thermally conductive silicon carbide composite with high strength up to 1600℃ in air. Science, 1998, 282(5392): 1295-1297. |
| [12] | DONG S M, CHOLLON G, LABRUGERE C, et al.Characterizaiton of nearly stoichiometric SiC ceramic fibres.J. Mater. Sci., 2001, 36(10): 2371-2381. |
| [13] | CAO F, KIM D P, LI X D, et al.Synthesis of polyaluminocarbosilane and reaction mechanism study.J. Appl. Polym. Sci., 2002, 85(13): 2787-2792. |
| [14] | YU Y, TAI J, TANG X, et al.Continuous Si-C-O-Al fiber derived from aluminum-containing polycarbosilane precursor.Compos. Part A-Appl. S., 2008, 39(7): 1101-1105. |
| [15] | MORISHITA K, OCHIAI S, OKUDA H, et al.Fracture toughness of a crystalline silicon carbide fiber Tyranno-SA3. J. Am Ceram. Soc., 2006, 89(8): 2571-2576. |
| [16] | CHEN L, ZHANG L, CAI Z, et al, Effects of oxidation curing and sintering additives on the formation of polymer-derived near-stoichiometric silicon carbide fibers.J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 2008, 9(2): 428-436. |
| [17] | TAKEDA M, IMAI Y, ICHIKAWA H, et al.Thermal stability of SiC fiber prepared by an irradiation-curing process.Compos. Sci. Technol., 1999, 59(6): 793-799. |
| [18] | SUGIMOTO M, SHIMOO T, OKAMURA K, et al.Reaction mechanisms of silicon carbide fiber synthesis by heat treatment of polycarbosilane fibers cured by radiation: I, Evolved gas analysis. J. Am. Ceram. Soc., 1995, 78(8): 1013-1017. |
| [19] | CHOLLON G, PAILLER R, NASLAIN R, et al.Thermal stability of a PCS-derived SiC fibre with a low oxygen content (Hi-Nicalon). J. Mater. Sci., 1997, 32(2): 327-347. |
| [20] | LY H Q, TAYLOR R, DAY J, et al.Conversion of polycarbosilane (PCS) to SiC-based ceramic Part Ⅱ pyrolysis and characterisation.J. Mater. Sci., 2001, 36(16): 4045-4057. |
| [21] | PORTE L, SARTRE A.Evidence for a silicon oxycarbide phase in the Nicalon silicon carbide fibre.J. Mater. Sci., 1989, 24(1): 271-275. |
| [22] | LAFFON C, FLANK A M, LAGARDE P, et al.Study of Nicalon-based ceramic fibres and powders by EXAFS spectrometry, X-ray diffractometry and some additional methods.J. Mater. Sci., 1989, 24(4): 1503-1512. |
| [23] | COUSTUMER L P, MONTHIOUX M, OBERLIN A.Understanding Nicalon fiber.J. Eur. Ceram. Soc., 1993, 11(2): 95-103. |
| [24] | SHIMOO T, CHEN H, OKAMURA K.High-temperature stability of Nicalon under Ar or O2 atmosphere.J. Mater. Sci., 1994, 29(2): 456-463. |
| [25] | ORTIZ A L, SANCHEZ B F, CUMBRERA F L, et al.X-ray powder diffraction analysis of a silicon carbide-based ceramic.Mater. Lett., 2001, 49(2): 137-145. |
| [26] | JACOBSON N S, KLINE S E.A thermoanalytical study of the conversion of amorphous Si-Ti-C-O fibers to SiC.Int. J. Appl. Ceram. Technol., 2012, 9(4): 816-822. |
| [27] | SHIMOO T, OKAMURA K, TSUKADA I, et al.Thermal stability of low-oxygen SiC fibers fired under different conditions.J. Mater. Sci., 1999, 34(22): 5623-5631. |
| [28] | RAHAMAN M N.Ceramic Processing and Sintering, 2nd edition. New York: Marcel Dekker Inc, 2003: 591-592. |
| [1] | 杨勇, 郭啸天, 唐杰, 常浩天, 黄政仁, 胡秀兰. 非氧化物陶瓷光固化增材制造研究进展及展望[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(3): 267-277. |
| [2] | 王椎, 韩建军, 李建强, 李晓禹, 李江涛, 贺刚, 谢俊. 大尺寸La2O3-TiO2-ZrO2非晶塑性烧结行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(4): 433-438. |
| [3] | 聂兰舰, 顾真安, 王玉芬, 向在奎, 张辰阳, 饶传东. SiO2疏松体真空烧结致密化与透明化机理研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(10): 1060-1066. |
| [4] | 郭胜强, 王皓, 涂兵田, 王斌, 徐鹏宇, 王为民, 傅正义. 细晶MgO·1.44Al2O3透明陶瓷的制备及其性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2019, 34(10): 1067-1071. |
| [5] | 王军凯, 张远卓, 李俊怡, 张海军, 李发亮, 韩 磊, 宋述鹏. 微波加热催化反应低温制备β-SiC粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(7): 725-730. |
| [6] | 袁 钦, 宋永才. SiCxOy相分解方式对SiCO(Al)纤维烧结致密化的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(12): 1320-1326. |
| [7] | 李海涛, 李 谦, 闫焉服, 许荣辉. ZnO掺杂对Ca0.25(Li0.43Sm0.57)0.75TiO3陶瓷烧结性能和微波介电性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(4): 369-373. |
| [8] | 杜贤武, 张志晓, 王为民, 傅正义, 王 皓. 粉末粒径对热压烧结碳化硼致密化及力学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(10): 1062-1066. |
| [9] | 卢振亚,黄 欢,吴建青. SnO2-Sb2O3基压敏陶瓷致密化及脉冲电流耐受特性[J]. 无机材料学报, 2009, 24(4): 841-844. |
| [10] | 李小雷,马红安,左桂鸿,郑友进,李吉刚,贾晓鹏. AlN陶瓷的高压烧结研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2008, 23(1): 104-108. |
| [11] | 林 枞,徐 政,彭 虎,孙丹峰. 微波烧结氧化锌压敏电阻的致密化和晶粒生长[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(5): 917-921. |
| [12] | 邹继兆,曾燮榕,熊信柏,谢盛辉,唐汉玲,李 龙. 气体滞留时间对微波热解CVI工艺制备C/C复合材料性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2007, 22(4): 677-680. |
| [13] | 张明瑜,黄启忠,苏哲安,谢志勇,朱建军. 多元耦合场 CVI法炭/炭复合材料制备及结构分析[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(6): 1373-1377. |
| [14] | 徐国忠,李贺军,白瑞成,陈拂晓,胡志彪. 新技术制备 C/C复合材料及特性研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2006, 21(6): 1385-1390. |
| [15] | 孙万昌,李贺军,卢锦花,白瑞成,黄勇. 不同层次界面对C/C复合材料断裂行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2005, 20(6): 1257-1462. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||