无机材料学报 ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 1121-1130.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150182
• • 下一篇
韩 成1, 雷永鹏2, 王应德1
收稿日期:2015-04-14
修回日期:2015-06-25
出版日期:2015-11-20
网络出版日期:2015-10-20
作者简介:韩 成(1991–), 男, 博士研究生. E-mail: hancheng.com@163.com
基金资助:HAN Cheng1, LEI Yong-Peng2, WANG Ying-De1
Received:2015-04-14
Revised:2015-06-25
Published:2015-11-20
Online:2015-10-20
About author:HAN Cheng. E-mail: hancheng.com@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
光催化制取太阳能燃料主要包括光催化分解H2O制取H2及光催化还原CO2制取碳氢化合物, 是应对能源危机最具前景的方法之一。目前, 太阳能燃料的最高转化效率为5%, 无法满足商业化要求(≥10%)。纳米异质结由于能展现出单组分纳米材料或体相异质结所不具备的独特性质, 更能促进光生电子和空穴快速转移, 提供更多的光生电子或使光生电子具有更强的还原性, 因而能显著提高光催化活性。本文主要综述了几种纳米异质结(I-型、II-型、p-n型及Z-型)的光催化原理及其在制取太阳能燃料方面的研究进展, 并展望了研究发展方向。
中图分类号:
韩 成, 雷永鹏, 王应德. 纳米异质结光催化材料制取太阳能燃料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(11): 1121-1130.
HAN Cheng, LEI Yong-Peng, WANG Ying-De. Recent Progress on Nano-heterostructure Photocatalysts for Solar Fuels Generation[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(11): 1121-1130.
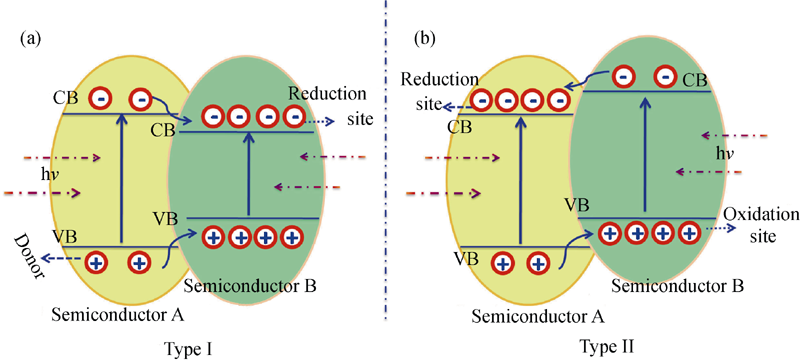
图2 I-型(a)和II-型(b)纳米异质结中半导体能级分布及光生载流子的转移途径[23]
Fig. 2 Band alignment and transportation of the charge carries in type I (a) and type II (b) nano-heterostructures[23]
| Nano-heterostructure photocatalysts | Production of H2 from water splitting | Generation of CxHyOz from CO2 reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | TiO2/CuO[ | Bi2S3/CdS[ |
| Type II | g-C3N4-N-TiO2[ | g-C3N4-N-TiO2[ |
| p-n type | Cu2S/CdS[ | |
| Z-scheme | TiO2/RGO/Metal sulfide[ WO3/g-C3N4[ | Ag3PO4/Ag/g-C3N4[ TaON/Ag/RuBLRu′[ |
表1 用于制取太阳能燃料的纳米异质结光催化材料
Table 1 Nano-heterostructure photocatalysts for solar fuels generation
| Nano-heterostructure photocatalysts | Production of H2 from water splitting | Generation of CxHyOz from CO2 reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | TiO2/CuO[ | Bi2S3/CdS[ |
| Type II | g-C3N4-N-TiO2[ | g-C3N4-N-TiO2[ |
| p-n type | Cu2S/CdS[ | |
| Z-scheme | TiO2/RGO/Metal sulfide[ WO3/g-C3N4[ | Ag3PO4/Ag/g-C3N4[ TaON/Ag/RuBLRu′[ |
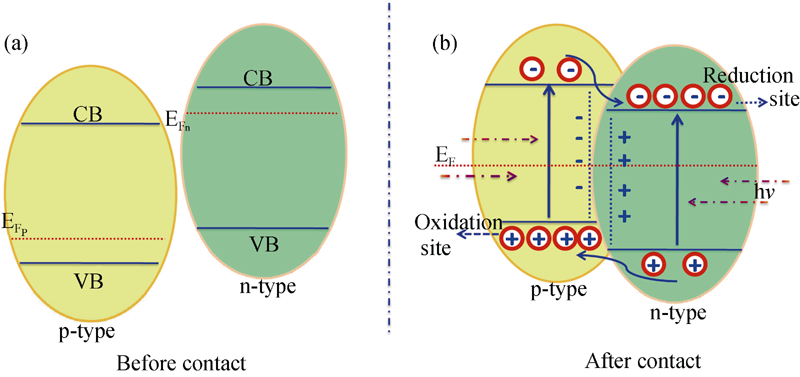
图3 (a) p-型、n-型半导体接触前能级分布和(b) p-n型纳米异质结中光生载流子的转移途径[27]
Fig. 3 (a) Band alignment of p-type and n-type semiconductors before contact and (b) transportation of the charge carries in p-n type nano-heterostructure[27]
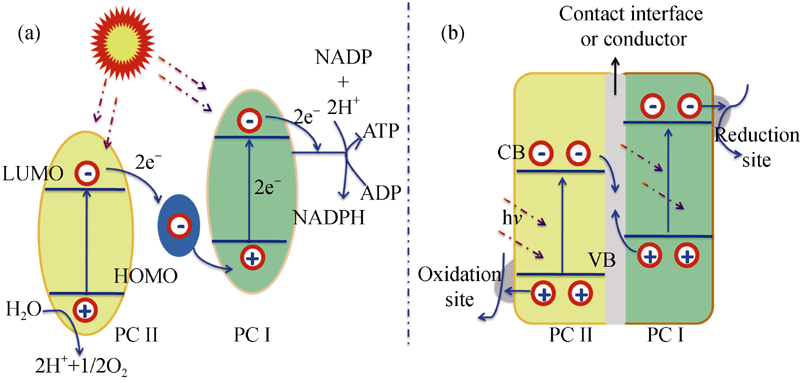
图4 绿色植物光合作用系统(a)和全固态Z-型纳米异质结(b)中电子转移途径[24]
Fig. 4 Transportation of the electrons in (a) photosynthesis system and (b) all-solid-state Z-scheme nano-heterostructure[24]
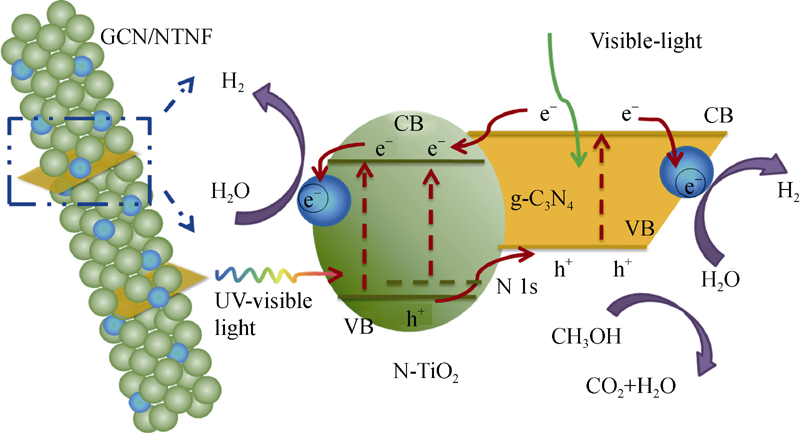
图5 基于II-型异质结的g-C3N4/TiO2纳米纤维光催化制H2机理示意图[22]
Fig. 5 Schematic illustration of the mechanism for photocatalytic H2 production in the type II nano-heterostructure of g-C3N4/TiO2 nanofiber[22]
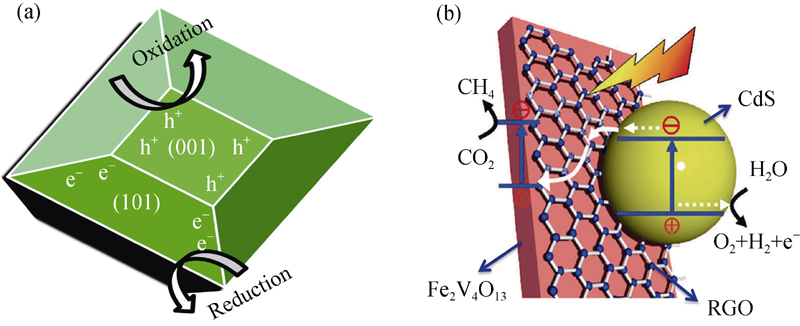
图6 (a) TiO2 {001}/{101}晶面异质结中氧化还原反应位点的空间分离[49]和(b) Fe2V4O13/RGO/CdS Z-型纳米异质结光催化还原CO2制取CH4[58]
Fig. 6 Schematic illustration of (a) the spatial separation of redox sites in TiO2 {001}/{101} surface heterojunction[49] and (b) conversion of CO2 into CH4 over Fe2V4O13/RGO/CdS Z-scheme nano-heterostructure photocatalyst[58]
| [1] | MA Y, WANG X, JIA Y, et al.Titanium dioxide-based nanomaterials for photocatalytic fuel generations.Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(19): 9987-10043. |
| [2] | ZHANG Q H.Progress on TiO2-based nanomaterials and its utilization in the clean energy technology.J. Inor. Mater., 2012, 27(1): 1-10. |
| [3] | HE Y, ZHANG L, TENG B, et al.New application of Z-scheme Ag3PO4/g-C3N4 composite in converting CO2 to fuel.Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49(1): 649-656. |
| [4] | CAO S, YUAN Y, FANG J, et al.In-situ growth of CdS quantum dots on g-C3N4 nanosheets for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen generation under visible light irradiation.Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38: 1258-1266. |
| [5] | LIU G, NIU P, YIN L, et al.α-sulfur crystals as a visible- light-active photocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(22): 9070-9073. |
| [6] | ZHANG Y, XIA T, WALLENMEYER P, et al.Photocatalytic hydrogen generation from pure water using silicon carbide nanoparticles.Energy Technol., 2014, 2(2): 183-187. |
| [7] | CHU Z Y, YUAN B, YAN T N.Recent progress in photocatalysis of g-C3N4.J. Inor. Mater., 2014, 29(8): 785-794. |
| [8] | ZHANG J, WANG X.Solar water splitting at λ=600 nm: a step coser to sustainable hydrogen production.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(25): 7230-7232. |
| [9] | XIANG Q, CHENG B, YU J.Graphene-based photocatalysts for solar-fuel generation.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, DOI: 10.1002/ anie.201411096. |
| [10] | MARTIN D J, QIU K, SHEVLIN S D, et al.Highly efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution from water using visible light and structure-controlled graphitic carbon nitride.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(35): 9240-9245. |
| [11] | WU N, WANG Y, LEI Y, et al.Preparation and photocatalytic activity of N-Ag co-doped TiO2/C porous ultrafine fibers mat.Ceram. Int., 2014, 40(1): 2017-2022. |
| [12] | LIU C, JING L, HE L, et al.Phosphate-modified graphitic C3N4 as efficient photocatalysts for degrading colorless pollutants by promoting O2 adsorption.Chem. Commun., 2014, 50(16): 1999-2001. |
| [13] | TAKANABE K, KAMATA K, WANG X, et al.Photocatalytic hydrogen evolution on dye-sensitized mesoporous carbon nitride photocatalyst with magnesium phthalocyanine.Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12(40): 13020-13025. |
| [14] | WANG H, ZHANG L, CHEN Z, et al.Semiconductor heterojunction photocatalysts: design, construction, and photocatalytic performances.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43(15): 5234-5244. |
| [15] | WITHERS F, POZO-ZAMUDIO O D, MISHCHENKO A, et al. Light-emitting diodes by band-structure engineering in van der Waals heterostructures.Nat. Mater., 2015, 14: 301-306. |
| [16] | WANG X, XIA F.Van der Waals heterostructures: stacked 2D materials shed light.Nat. Mater., 2015, 14: 264-265. |
| [17] | YU H, QUAN X.Nano-heterojunction photocatalytic materials in environmental pollution controlling.Progress in Chemistry, 2009, 21(2/3): 406-419. |
| [18] | ZHENG H, LI Y, LIU H, et al.Construction of heterostructure materials toward functionality.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40(9): 4506-4524. |
| [19] | LI X H, ANTONIETTI M.Metal nanoparticles at mesoporous N-doped carbons and carbon nitrides: functional Mott-Schottky heterojunctions for catalysis.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42(16): 6593-6604. |
| [20] | LI H, ZHOU Y, TU W, et al.State-of-the-art progress in diverse heterostructured photocatalysts toward promoting photocatalytic performance.Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25(7): 998-1013. |
| [21] | WU N, WANG Y, LEI Y, et al.Flexible N-doped TiO2/C ultrafine fiber mat and its photocatalytic activity under simulated sunlight.Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 319: 136-142. |
| [22] | HAN C, WANG Y, LEI Y, et al.In situ synthesis of graphitic-C3N4 nanosheet hybridized N-doped TiO2 nanofiber for efficient photocatalytic H2 production and degradation.Nano Res., 2015, 8(4): 1199-1209. |
| [23] | MARSCHALL R.Semiconductor composites: strategies for enhancing charge carrier separation to improve photocatalytic activity.Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24(17): 2421-2440. |
| [24] | ZHOU P, YU J, JARONIEC M.All-solid-state Z-scheme photocatalytic systems.Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(29): 4920-4935. |
| [25] | HUSNG L, WANG X, YANG J, et al.Dual cocatalysts loaded type I CdS/ZnS core/shell nanocrystals as effective and stable photocatalysts for H2 evolution.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(22): 11584-11591. |
| [26] | WANG Y, WANG Q, ZHAN X, et al.Visible light driven type II heterostructures and their enhanced photocatalysis properties: a review.Nanoscale, 2013, 5(18): 8326-8339. |
| [27] | JIANG D, CHRN L, ZHU J, et al.Novel p-n heterojunction photocatalyst constructed by porous graphite-like C3N4 and nanostructured BiOI: facile synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic activity.Dalton Trans., 2013, 42(44): 15726-15734. |
| [28] | KIM D, SAKIMOTO K K, HONG D, et al.Artificial photosynthesis for sustainable fuel and chemical production.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(11): 3259-3266. |
| [29] | MAEDA K.Z-scheme water splitting using two different semiconductor photocatalysts.ACS Catal., 2013, 3(7): 1486-1503. |
| [30] | IWASHINA K, IWASE A, NG Y H, et al.Z-schematic water splitting into H2 and O2 using metal sulfide as a hydrogen-evolving photocatalyst and reduced graphene oxide as a solid-state electron mediator.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(2): 604-607. |
| [31] | WANG W, CHEN J, LI C, et al.Achieving solar overall water splitting with hybrid photosystems of photosystem II and artificial photocatalysts.Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 4647. |
| [32] | TU W, ZHOU Y, ZOU Z.Photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into renewable hydrocarbon fuels: state-of-the-art accomplishment, challenges, and prospects.Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(27): 4607-4626. |
| [33] | FUJISHIMA A, HONDA K.Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode.Nature, 1972, 238(5358): 37-38. |
| [34] | INOUE T, FUJISHIMA A, KONISHI S, et al.Photo- electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide in aqueous suspensions of semiconductor powders.Nature, 1979, 277(5698): 637-638. |
| [35] | LEE S S, BAI H, LIU Z, et al.Optimization and an insightful properties-activity study of electrospun TiO2/CuO composite nanofibers for efficient photocatalytic H2 generation.Appl. Catal., B, 2013, 140: 68-81. |
| [36] | THIBERT A, FRAME F A, BUSBY E, et al.Sequestering high-energy electrons to facilitate photocatalytic hydrogen generation in CdSe/CdS nanocrystals.J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2011, 2(21): 2688-2694. |
| [37] | YANG X, XU J, WONG T, et al.Synthesis of In2O3-In2S3 core-shell nanorods with inverted type-I structure for photocatalytic H2 generation.Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15(30): 12688-12693. |
| [38] | XIE Y P, YU Z B, LIU G, et al.CdS-mesoporous ZnS core-shell particles for efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light.Energy Environ. Sci., 2015, 7(6): 1895-1901. |
| [39] | HOU Y, LAURSEN A B, ZHANG J, et al.Layered nanojunctions for hydrogen-evolution catalysis.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(13): 3621-3625. |
| [40] | LI X, CHEN J T, LI H L, et al.Photoreduction of CO2 to methanol over Bi2S3/CdS photocatalyst under visible light irradiation.J. Nat. Gas. Chem., 2011, 20(4): 413-417. |
| [41] | ZHANG J, ZHANG M, SUN R Q, et al.A facile band alignment of polymeric carbon nitride semiconductors to construct isotype heterojunctions.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 124(40): 10292-10296. |
| [42] | SUI Y, LIU J, ZHANG Y, et al.Dispersed conductive polymer nanoparticles on graphitic carbon nitride for enhanced solar-driven hydrogen evolution from pure water.Nanoscale, 2013, 5(19): 9150-9155. |
| [43] | XU X, LIU G, RANDOM C, et al.g-C3N4 coated SrTiO3 as an efficient photocatalyst for H2 production in aqueous solution under visible light irradiation.Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36: 13501-13507. |
| [44] | ZHANG J, WANG Y, JIN J, et al.Efficient visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and enhanced photostability of core/shell CdS/g-C3N4 nanowires.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5(20): 10317-10324. |
| [45] | YAN Z, WU H, HAN A, et al.Noble metal-free cobalt oxide (CoOx) nanoparticles loaded on titanium dioxide/cadmium sulfide composite for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production from water.Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39: 13353-13360. |
| [46] | ZHOU S, LIU Y, LI J M, et al.Facile in situ synthesis of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-N-TiO2 heterojunction as an efficient photocatalyst for the selective photoreduction of CO2 to CO.Appl. Catal. B, 2014, 158: 20-29. |
| [47] | HE Y, WANG Y, ZHANG L, et al.High-efficiency conversion of CO2 to fuel over ZnO/g-C3N4 photocatalyst.Appl. Catal. B, 2015, 168: 1-8. |
| [48] | WANG J, JI G, LIU Y, et al.Cu2O/TiO2 heterostructure nanotube arrays prepared by an electrodeposition method exhibiting enhanced photocatalytic activity for CO2 reduction to methanol.Catal. Commun., 2014, 46: 17-21. |
| [49] | YU J, LOW J, XIAO W, et al.Enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction activity of anatase TiO2 by coexposed {001} and {101} facets.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(25): 8839-8842. |
| [50] | CHEN Y, QIN Z, WANG X, et al.Noble-metal-free Cu2S-modified photocatalysts for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production by forming nanoscale p-n junction structure.RSC Adv., 2015, 5(23): 18159-18166. |
| [51] | ZONG X, YAN H, WU G, et al.Enhancement of photocatalytic H2 evolution on CdS by loading MoS2 as cocatalyst under visible light irradiation.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130(23): 7176-7177. |
| [52] | SIMON Q, BARRECA D, GASPAROTTO A, et al.Vertically oriented CuO/ZnO nanorod arrays: from plasma-assisted synthesis to photocatalytic H2 production.J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(23): 11739-11747. |
| [53] | KATSUMATA H, TACHI Y, SUZUKI T, et al.Z-scheme photocatalytic hydrogen production over WO3/g-C3N4 composite photocatalysts.RSC Adv., 2014, 4(41): 21405-21409. |
| [54] | WANG X, LIU G, WANG L, et al.ZnO-CdS@Cd heterostructure for effective photocatalytic hydrogen generation.Adv. Energy Mater., 2012, 2(1): 42-46. |
| [55] | LI W, FENG C, DAI S, et al.Fabrication of sulfur-doped g-C3N4/Au/CdS Z-scheme photocatalyst to improve the photocatalytic performance under visible light.Appl. Catal. B, 2015, 168: 465-471. |
| [56] | LIU C, TANG J, CHEN H M, et al.A fully integrated nanosystem of semiconductor nanowires for direct solar water splitting.Nano Lett., 2013, 13(6): 2989-2992. |
| [57] | PENG Y, GUO Z, YANG J, et al.Enhanced photocatalytic H2 evolution over micro-SiC by coupling with CdS under visible light irradiation.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(18): 6296-6300. |
| [58] | LI P, ZHOU Y, LI H, et al.All-solid-state Z-scheme system arrays of Fe2V4O13/RGO/CdS for visible light-driving photocatalytic CO2 reduction into renewable hydrocarbon fuel.Chem. Commun., 2015, 51(4): 800-803. |
| [59] | HE Y, ZHANG L, FAN M, et al.Z-scheme SnO2-x/g-C3N4 composite as an efficient photocatalyst for dye degradation and photocatalytic CO2 reduction.Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. C, 2015, 137: 175-184. |
| [60] | SEKIZAWA K, MAEDA K, DOMEN K, et al.Artificial Z-scheme constructed with a supramolecular metal complex and semiconductor for the photocatalytic reduction of CO2.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(12): 4596-4599. |
| [61] | LIU J, LIU Y, LIU N, et al.Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting via a two-electron pathway.Science, 2015, 347(6225): 970-974. |
| [62] | WANG X, MAEDA K, THOMAS A, et al.A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light.Nat. Mater., 2009, 8(1): 76-79. |
| [63] | GONG Y, LI M, WANG Y.Carbon nitride in energy conversion and storage: recent advances and future prospects.ChemSusChem, 2015, 8(6): 931-946. |
| [64] | CAO S, LOW J, YU J, et al.Polymeric photocatalysts based on graphitic carbon nitride.Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(13): 2150-2176. |
| [65] | SUNG S K, Sang S K, PARK H.Photocatalytic comparison of TiO2 nanoparticles and electrospun TiO2 nanofibers: effects of mesoporosity and interparticle charge transfer.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114(39): 16475-16480. |
| [66] | XIE Y, ZHANG X, MA P, et al.Hierarchical TiO2 photocatalysts with one-dimensional heterojunction for improved photocatalytic activities.Nano Res., 2015, DOI: 10.1007/s12274-015-0720-3. |
| [67] | RAN J, ZHANG J, YU J, et al.Earth-abundant cocatalysts for semiconductor-based photocatalytic water splitting.Chem. Sov. Rev., 2014, 43(22): 7787-7812. |
| [68] | BAIS, WANG L, CHEN X, et al.Chemically exfoliated metallic MoS2 nanosheets: A promising supporting co-catalyst for enhancing the photocatalytic performance of TiO2 nanocrystals.Nano Res., 2015, 8(1): 175-183. |
| [69] | ZHAO H, DONG Y, JIANG P, et al.In situ light-assisted preparation of MoS2 on graphitic-C3N4 nanosheets for enhanced photocatalytic H2 production from water.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(14): 7375-7381. |
| [70] | YIN L, YUAN Y P, CAO S W, et al.Enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen generation over g-C3N4 through loading the noble metal-free NiS2 cocatalyst.RSC Adv., 2014, 4(12): 6127-6132. |
| [71] | HONG J, WANG Y, WANG Y, et al.Noble-metal-free NiS/C3N4 for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from water.ChemSusChem, 2013, 6(12): 2263-2268. |
| [72] | LI X, WEN J, LOW J, et al.Design and fabrication of semiconductor photocatalyst for photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to solar fuel.Sci. China Mater., 2014, 57(1): 70-100. |
| [73] | MARSZEWSKI M, CAO S, YU J, et al.Semiconductor-based photocatalytic CO2 conversion.Mater. Horiz., 2015, 2(3): 261-278. |
| [74] | LI R, ZHANG F, WANG D, et al.Spatial separation of photogenerated electrons and holes among {010} and {110} crystal facets of BiVO4.Nat. Commun., 2013, 4: 1432. |
| [75] | MAO J, PENG T, ZHANG X, et al.Effect of graphitic carbon nitride microstructures on the activity and selectivity of photocatalytic CO2 reduction under visible light.Catal. Sci. Technol., 2013, 3(5): 1253-1260. |
| [76] | MATSUBU J C, YANG V N, CHRISTOPHER P.Isolated metal active site concentration and stability control catalytic CO2 reduction selectivity.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(8): 3076-3084. |
| [77] | NEATU S, MACIA-AGULLO J A, CONCEPCION P, et al. Gold-copper nanoalloys supported on TiO2 as photocatalysts for CO2 reduction by water.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(45): 15969-15976. |
| [1] | 丁玲, 蒋瑞, 唐子龙, 杨运琼. MXene材料的纳米工程及其作为超级电容器电极材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [2] | 杨卓, 卢勇, 赵庆, 陈军. X射线衍射Rietveld精修及其在锂离子电池正极材料中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 589-605. |
| [3] | 陈强, 白书欣, 叶益聪. 热管理用高导热碳化硅陶瓷基复合材料研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [4] | 林俊良, 王占杰. 铁电超晶格的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(6): 606-618. |
| [5] | 牛嘉雪, 孙思, 柳鹏飞, 张晓东, 穆晓宇. 铜基纳米酶的特性及其生物医学应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 489-502. |
| [6] | 苑景坤, 熊书锋, 陈张伟. 聚合物前驱体转化陶瓷增材制造技术研究趋势与挑战[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 477-488. |
| [7] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [8] | 杨洋, 崔航源, 祝影, 万昌锦, 万青. 柔性神经形态晶体管研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [9] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [10] | 陈昆峰, 胡乾宇, 刘锋, 薛冬峰. 多尺度晶体材料的原位表征技术与计算模拟研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 256-269. |
| [11] | 张超逸, 唐慧丽, 李宪珂, 王庆国, 罗平, 吴锋, 张晨波, 薛艳艳, 徐军, 韩建峰, 逯占文. 新型GaN与ZnO衬底ScAlMgO4晶体的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 228-242. |
| [12] | 齐占国, 刘磊, 王守志, 王国栋, 俞娇仙, 王忠新, 段秀兰, 徐现刚, 张雷. GaN单晶的HVPE生长与掺杂进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 243-255. |
| [13] | 林思琪, 李艾燃, 付晨光, 李荣斌, 金敏. Zintl相Mg3X2(X=Sb, Bi)基晶体生长及热电性能研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(3): 270-279. |
| [14] | 刘岩, 张珂颖, 李天宇, 周菠, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 陶瓷材料电场辅助连接技术研究现状及发展趋势[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 113-124. |
| [15] | 谢兵, 蔡金峡, 王铜铜, 刘智勇, 姜胜林, 张海波. 高储能密度聚合物基多层复合电介质的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||