无机材料学报 ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (6): 571-575.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140565
陈子琪1, 朱 松1, 林秀娟1,2, 熊 威3,4, 周科朝1, 张 斗1
收稿日期:2014-11-06
修回日期:2015-01-05
出版日期:2015-06-04
网络出版日期:2015-05-22
作者简介:陈子琪(1990–), 男, 硕士研究生. E-mail: chenziqiqi@126.com
基金资助:CHEN Zi-Qi1, ZHU Song1, LIN Xiu-Juan1,2, XIONG Wei3,4, ZHOU Ke-Chao1, ZHANG Dou1
Received:2014-11-06
Revised:2015-01-05
Published:2015-06-04
Online:2015-05-22
About author:CHEN Zi-Qi. E-mail: chenziqiqi@126.com
Supported by:摘要:
实验制备了不同纤维厚度和体积分数的压电纤维复合物, 并在0.1 Hz的激励电压下测试了压电纤维复合物的自由应变性能和驱动性能, 研究复合物典型结构参数对其性能的影响。实验发现, 随着压电纤维厚度增加, 复合物自由应变和顶端位移下降, 1000 V激励电压下, 纤维厚度为200 μm样品纵向自由应变为665 με, 驱动Mylar膜产生的顶端位移为1.9 mm, 而纤维厚度为300 μm和400 μm样品的纵向自由应变仅为纤维厚度为200 μm样品的23.2%和11.7%, 顶端位移为纤维厚度为200 μm样品的45.8%和19.0%。压电纤维复合物具有驱动正交异性, 横向自由应变、纵向自由应变以及横向效应系数随着纤维体积分数的降低而减小, 纤维体积分数为74%的复合物其横向自由应变和纵向自由应变分别为体积分数为59%样品的2.04倍和1.72倍, 横向效应系数也从0.519减小到0.451。
中图分类号:
陈子琪, 朱 松, 林秀娟, 熊 威, 周科朝, 张 斗. 纤维厚度和体积分数对压电纤维复合物应变性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(6): 571-575.
CHEN Zi-Qi, ZHU Song, LIN Xiu-Juan, XIONG Wei, ZHOU Ke-Chao, ZHANG Dou. Effects of Fiber Thickness and Volume Fraction on the Strain Performance of Piezoelectric Fiber Composites[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(6): 571-575.
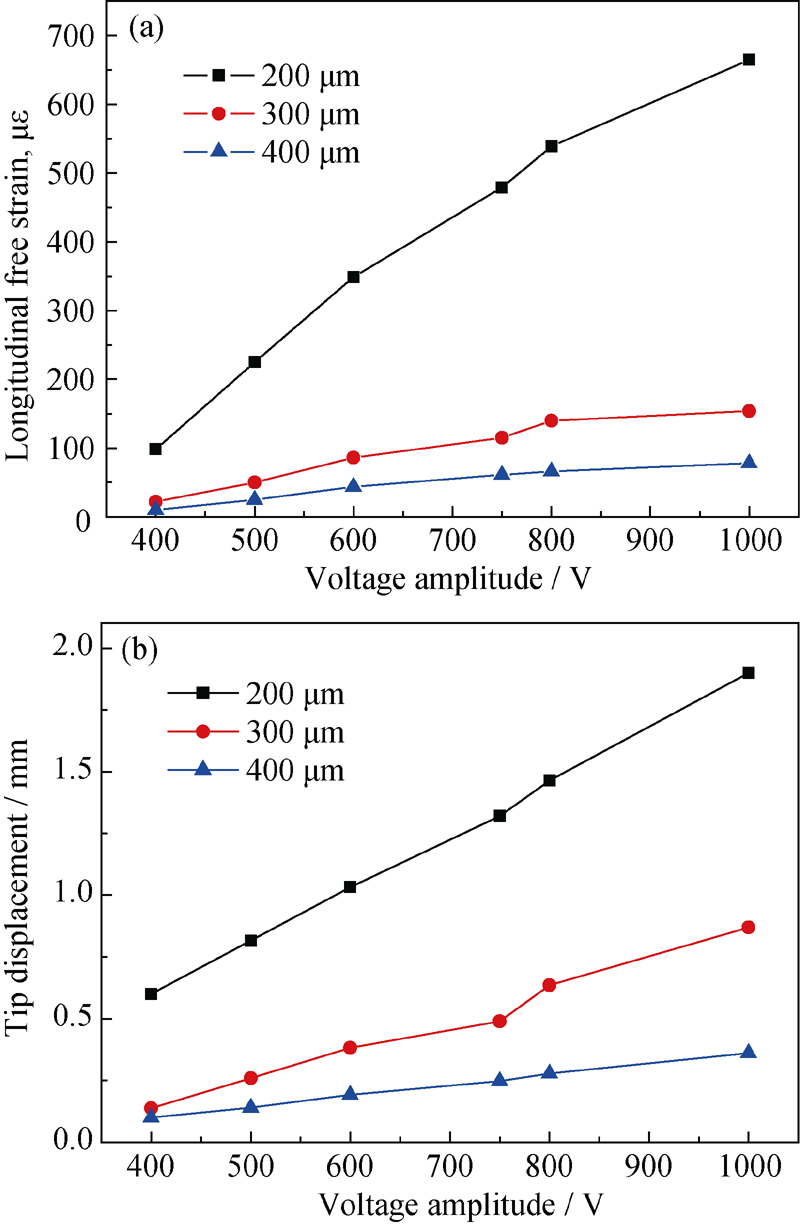
图3 不同压电纤维厚度的样品纵向自由应变(a)和顶端位移(b)随激励电压的变化
Fig. 3 Voltage amplitude dependence of (a) longitudinal free strain and (b) tip displacement for sample with different thickness of piezoelectric fiber
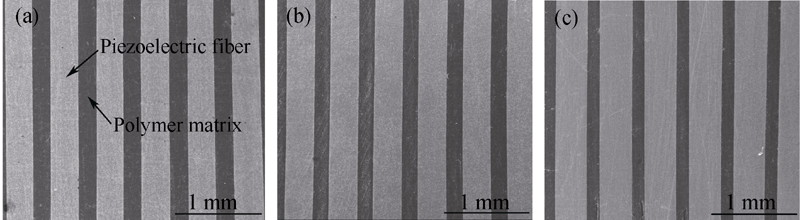
图4 不同纤维体积分数的压电纤维复合物SEM照片
Fig. 4 SEM micrographs of piezoelectric fiber composites with different volume fractions of piezoelectric fiber (a) 59%; (b) 65%; (c) 74%
| [1] | BENT A A, HAGOOD N W.Piezoelectric fiber composites with interdigitated electrodes.Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 1997, 8(11): 903-919. |
| [2] | BENT A A.Active Fiber Composite Material Systems for Structural Control Application. Newport Beach: Smart Structures and Materials 1999: Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies, 1999: 166-177. |
| [3] | HAGOOD N, KINDEL R, GHANDI K, et al.Improving Transverse Actuation of Piezoceramics Using Interdigitated Surface Electrodes. Albuquerque: Smart Structures and Materials 1993: Smart Structures and Intelligent Systems, 1993: 341-352. |
| [4] | WILKIE W K, BRYANT R G, HIGH J W, et al.Low-cost Piezocomposite Actuator for Structural Control Applications. Newport Beach: Smart Structures and Materials 2000: Industrial and Commercial Applications of Smart Structures Technologies, 2000: 323-324. |
| [5] | CHEN Y, VIRESH W, ZIMCIK D.Development and Verification of Real-time Controllers for F/A-18 Vertical Fin Buffet Load Alleviation. San Diego: Smart Structures and Materials 2006:Smart Structures and Integrated Systems, 2006: 6173101-61731012. |
| [6] | TUNGPIMOLRUT K, HATTI N, PHONTIP J, et al.Design of Energy Harvester Circuit for a MFC Piezoelectric Based on Electrical Circuit Modeling. Piscataway: IEEE International Symposium on Applications of Ferroelectrics, 2011: 1-4. |
| [7] | TARAZAGA P A, PEAIRS D M, WILKIE W K, et al.Structural Health Monitoring of an Inflatable Boom Subjected to Simulated Micrometeoroid/orbital Debris Damage. San Diego: Proceedings of SPIE, Nondestructive Evaluation and Health Monitoring of Aerospace Materials, Composites, and Civil Infrastructure, 2006: 617601-617609. |
| [8] | ERIC J, RUGGIERO, DANIEL J, et al. Gossamer spacecraft recent trends in design, analysis, experimentation, and control. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2006(43): 10-24. |
| [9] | PARADIES R, CIRESA P.Active wing design with integrated flight control using piezoelectric macro fiber composites.Smart Materials and Structures, 2009, 18(3): 1-9. |
| [10] | WILKIE W K, INMAN D J, LLOYD J M, et al.Anisotropic Piezocomposite Actuator Incorporating Machined PMN-PT Single Crystal Fibers. Palm Springs, California: SDM 12th AIAA/ASME/ AHS Adaptive Structures Conference, 2004: 19-22. |
| [11] | BOWEN C R, NELSON L J, STEVENS R, et al.Optimisation of interdigitated electrodes for piezoelectric actuators and active fiber composites. Journal of Electroceramics, 2006, 16(4): 263-269. |
| [12] | WILLIAMS R B, INMAN D J, WILKIE W K.Nonlinear Actuation Properties of Macro Fiber Composite Actuators. Washington, DC: ASME 2003 International Mechanical Engineering Congress and Exposition, 2003: 11-17. |
| [13] | LIN X, ZHOU K, BUTTON T W, et al.Fabrication, characterization, and modeling of piezoelectric fiber composites.Journal of Applied Physics, 2013, 114(2): 0270151-0270156. |
| [14] | LIN X, ZHANG D, ZHANG X, et al.Modeling and optimization of piezoelectric fiber composites based on finite element method.The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals, 2012, 22(6): 1748-1753. |
| [15] | JAHNSON T J, YANG C, ADAMS D E, et al.Embedded sensitivity functions for characterizing structural damage.Smart Materials and Structures, 2005, 14(1): 155-169. |
| [16] | DERAEMAEKER A, NASSER N, BENJEDDOU A, et al.Mixing rules for the piezoelectric properties of macro fiber composites.Journal of Intelligent Material Systems and Structures, 2009, 20(12): 1475-1482. |
| [1] | 顾薛苏, 殷杰, 王康龙, 崔崇, 梅辉, 陈忠明, 刘学建, 黄政仁. 颗粒级配对黏结剂喷射打印碳化硅陶瓷性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 216-. |
| [2] | 陈雨, 林埔安, 蔡冰, 张文华. 钙钛矿太阳能电池无机空穴传输材料的研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 105-. |
| [3] | 田煜彬, 田超凡, 李森, 赵永鑫, 邢涛, 李智, 陈萧如, 向帅蓉, 代鹏程. 高导电性生物质碳布的制备及其燃料电池气体扩散层性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 127-. |
| [4] | 江润璐, 吴鑫, 郭昊骋, 郑琦, 王连军, 江莞. UiO-67基导电复合材料的制备及其热电性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 197-. |
| [5] | 李海燕, 旷峰华, 吴昊龙, 刘小根, 包亦望, 万德田. 残余拉应力的温度依赖性及其对裂纹扩展行为的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 214-. |
| [6] | 方万丽, 沈黎丽, 李海燕, 陈薪羽, 陈宗琦, 寿春晖, 赵斌, 杨松旺. NiOx介孔层的成膜过程对碳电极钙钛矿太阳能电池性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 2-. |
| [7] | 丁统顺, 丰平, 孙学文, 单沪生, 李琪, 宋健. Fmoc-FF-OH钝化钙钛矿薄膜及其太阳能电池性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 50-. |
| [8] | 徐昊, 钱伟, 花银群, 叶云霞, 戴峰泽, 蔡杰. 皮秒激光加工的微织构对碳化硅润湿性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 0, (): 73-. |
| [9] | 邱海洋, 苗广潭, 李辉, 栾奇, 刘国侠, 单福凯. 等离子体处理对突触晶体管长程塑性的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 406-412. |
| [10] | 杜剑宇, 葛琛. 光电人工突触研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 378-386. |
| [11] | 杨洋, 崔航源, 祝影, 万昌锦, 万青. 柔性神经形态晶体管研究进展[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 367-377. |
| [12] | 吴俊林, 丁继扬, 黄新友, 朱丹阳, 黄东, 代正发, 杨文钦, 蒋兴奋, 周健荣, 孙志嘉, 李江. Gd2O2S:Tb闪烁陶瓷的制备与结构: 水浴合成中H2SO4/Gd2O3摩尔比的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 452-460. |
| [13] | 陈鑫力, 李岩, 王伟胜, 石智文, 竺立强. 明胶/羧化壳聚糖栅控氧化物神经形态晶体管[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 421-428. |
| [14] | 游钧淇, 李策, 杨栋梁, 孙林锋. 氧化物双介质层忆阻器的设计及应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 387-398. |
| [15] | 方仁瑞, 任宽, 郭泽钰, 徐晗, 张握瑜, 王菲, 张培文, 李悦, 尚大山. 基于氧化物基电解质栅控晶体管突触的关联学习[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 399-405. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||