无机材料学报 ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (4): 432-438.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140618
黄 萍, 李 鹏, 赵军胜, 屈树新, 冯 波, 翁 杰
收稿日期:2014-11-27
修回日期:2015-01-08
出版日期:2015-04-29
网络出版日期:2015-03-26
作者简介:黄 萍(1989–), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: huangping135515@163.com
基金资助:HUANG Ping, LI Peng, ZHAO Jun-Sheng, QU Shu-Xin, FENG Bo, WENG Jie
Received:2014-11-27
Revised:2015-01-08
Published:2015-04-29
Online:2015-03-26
About author:HUANG Ping. E-mail: huangping135515@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
本研究采用球磨对磷酸钙骨水泥(CPC)起始粉末进行机械活化处理, 以期改善CPC力学性能, 并探讨了其影响机理。采用激光粒度仪、比表面积测量仪和X射线衍射仪(XRD)表征球磨后的CPC粉末(Ball milling CPC, BCPC)。利用发泡法制备多孔BCPC支架, 采用万能力学试验机、XRD和扫描电子显微镜(SEM)表征多孔BCPC支架。结果显示, 球磨后的BCPC粉末平均粒径减小, 比表面积增大, 表观密度、堆积密度及紧密密度减小。BCPC支架孔隙率为(77.98 ± 0.58)%, 抗压强度为(4.11 ± 0.46) MPa, 相比CPC支架的(64.23 ± 2.32)%和(1.99 ± 0.43) MPa有显著提高。SEM结果显示BCPC支架具有数微米和数百微米的两种孔隙结构。XRD结果表明机械活化作用降低了DCPD、α-TCP、CaCO3和HA的晶粒尺寸和结晶度, 促使DCPD向DCPA转化, 促进了各相磷酸钙盐的水化和HA的沉积, 提高了BCPC支架的力学性能, 为增强CaP基多孔材料的力学性能和扩展其临床应用提供了新途径。
中图分类号:
黄 萍, 李 鹏, 赵军胜, 屈树新, 冯 波, 翁 杰. 机械活化增强多孔磷酸钙骨水泥支架的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(4): 432-438.
HUANG Ping, LI Peng, ZHAO Jun-Sheng, QU Shu-Xin, FENG Bo, WENG Jie. Mechanical Activation Reinforced Porous Calcium Phosphate Cement[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(4): 432-438.
| Samples | (L/P ratio)/ (mL·g-1) | CH2O2/% | pH | T/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCPC-S | 1.0 | 25 | 8.0 | 60 |
| CPC-S | 0.4 | 25 | 8.0 | 60 |
| Control-S | 1.0 | 0 | 8.0 | 60 |
表1 BCPC-S、CPC-S和Control-S的最优参数组合
Table 1 The optimal parameter combinations of orthogonal test for CPC-S, BCPC-S and Control-S
| Samples | (L/P ratio)/ (mL·g-1) | CH2O2/% | pH | T/℃ |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCPC-S | 1.0 | 25 | 8.0 | 60 |
| CPC-S | 0.4 | 25 | 8.0 | 60 |
| Control-S | 1.0 | 0 | 8.0 | 60 |
| Samples | d/(g·cm-3) | dB/(g·cm-3) | dC/(g·cm-3) | SSA/(m2·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCPC | 2.430 ± 0.138a | 0.498 ± 0.098b | 1.937 ± 0.106c | 15.100 |
| CPC | 2.871 ± 0.112a | 0.891 ± 0.127b | 2.135 ± 0.114c | 8.616 |
表 2 BCPC-P和CPC-P的表观密度d、堆积密度dB、紧密密度dC和比表面积SSA (n=6)
Table. 2 Apparent densities, bulk densities, compact densities and specific surface areas of BCPC-P and CPC-P(n=6)
| Samples | d/(g·cm-3) | dB/(g·cm-3) | dC/(g·cm-3) | SSA/(m2·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCPC | 2.430 ± 0.138a | 0.498 ± 0.098b | 1.937 ± 0.106c | 15.100 |
| CPC | 2.871 ± 0.112a | 0.891 ± 0.127b | 2.135 ± 0.114c | 8.616 |
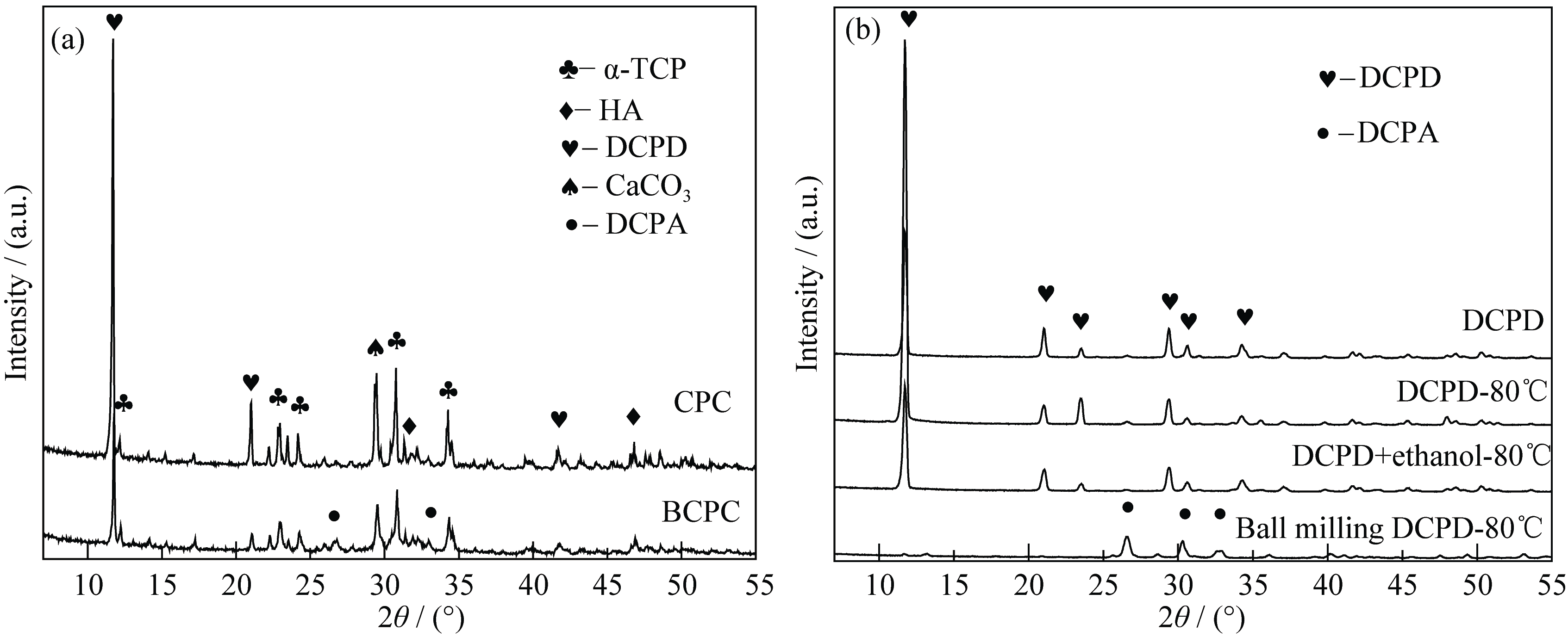
图2 BCPC-P和CPC-P的XRD图谱(a)和不同处理条件下DCPD的XRD图谱(b)
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of BCPC-P and CPC-P (a) and XRD patterns of DCPD with different treatments (b) DCPD: Drying at 37℃; DCPD-80℃: Drying at 80℃; DCPD + ethanol - 80℃: Drying at 80℃ after adding 50 mL ethanol; Ball milling DCPD-80℃: Drying at 80℃ after ball milling
| Grain size/nm | DCPD | α-TCP | CaCO3 | HA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCPC-P | 59.42 | 29.48 | 33.16 | 42.59 |
| CPC-P | 74.26 | 51.65 | 51.85 | 47.15 |
表3 BCPC-P和CPC-P中不同磷酸钙的晶粒尺寸
Table 3 Grain sizes of different calcium phosphates of BCPC-P and CPC-P
| Grain size/nm | DCPD | α-TCP | CaCO3 | HA |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| BCPC-P | 59.42 | 29.48 | 33.16 | 42.59 |
| CPC-P | 74.26 | 51.65 | 51.85 | 47.15 |
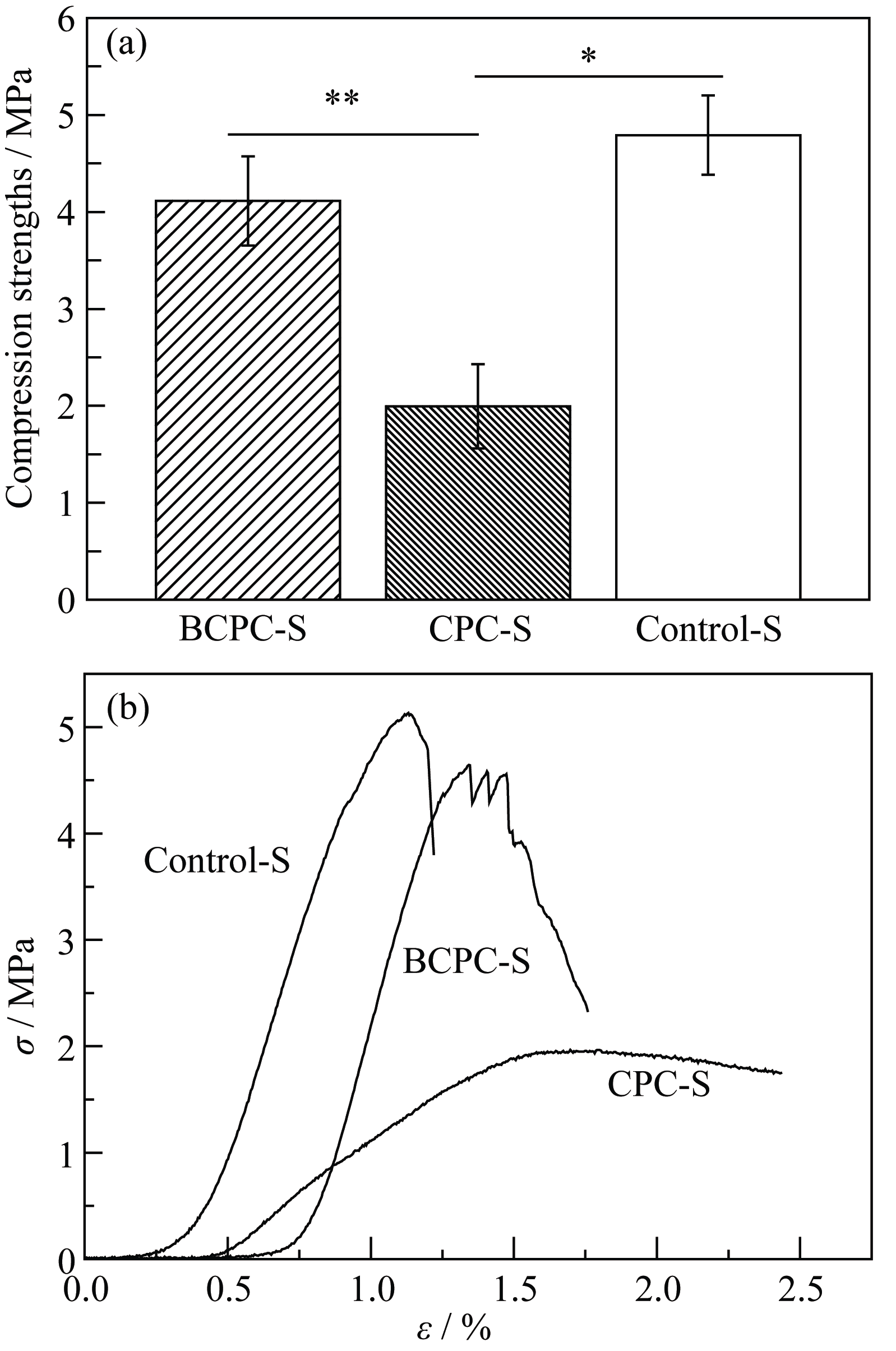
图3 BCPC-S、CPC-S和Control-S的抗压强度(a)和典型应力应变曲线(b)
Fig. 3 Compression strengths of the CPC-S, BCPC-S and Control-S (a), and typical stress-strain curves (b)
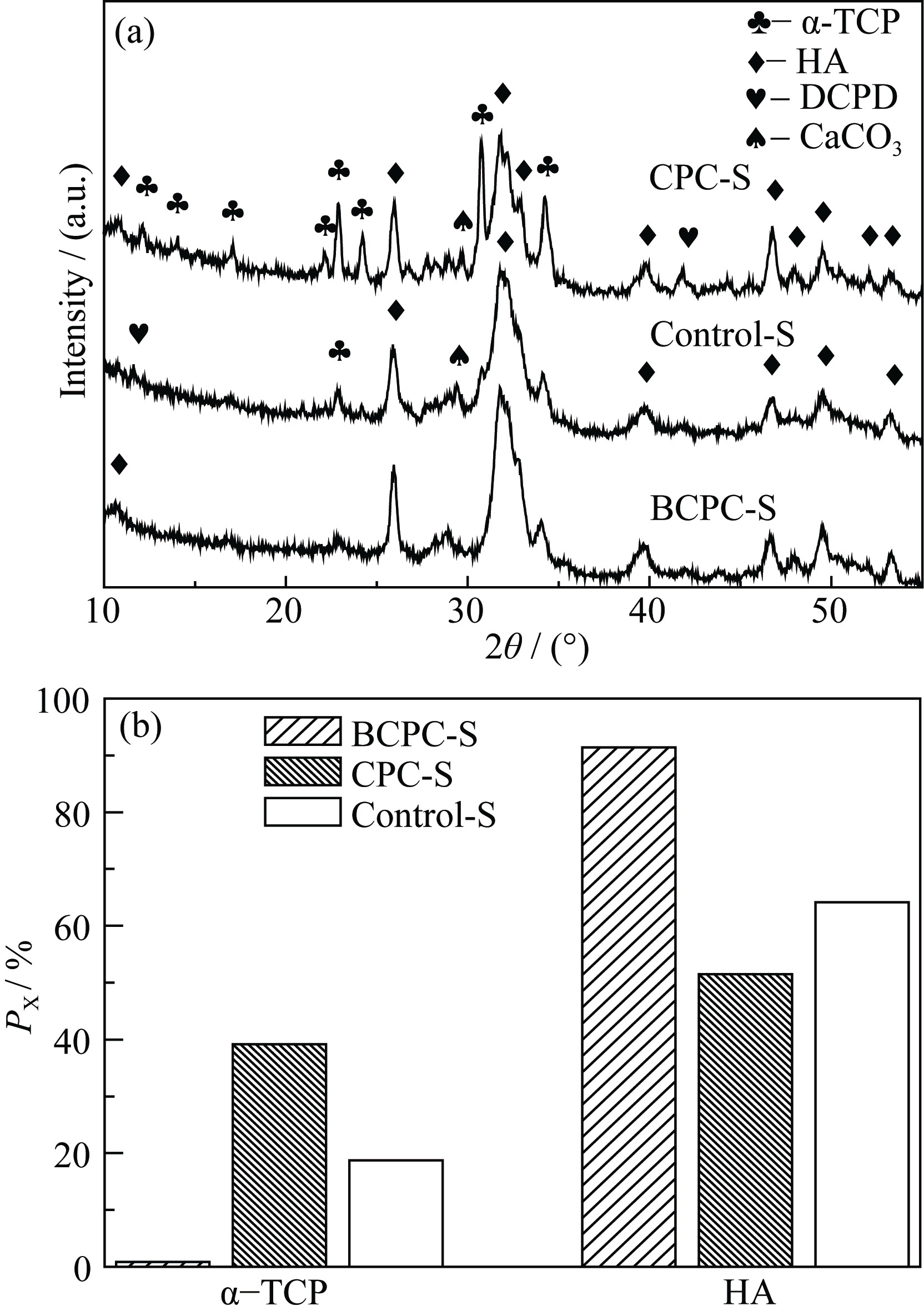
图4 BCPC-S、CPC-S和Control-S水化后的XRD图谱(a)和BCPC-S、CPC-S和Control-S中α-TCP和HA的相对含量(b)
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of CPC-S, BCPC-S and Control-S after hydration for 24 h (a) and relative quantity of α-TCP and HA in BCPC-S, CPC-S and Control-S (b)
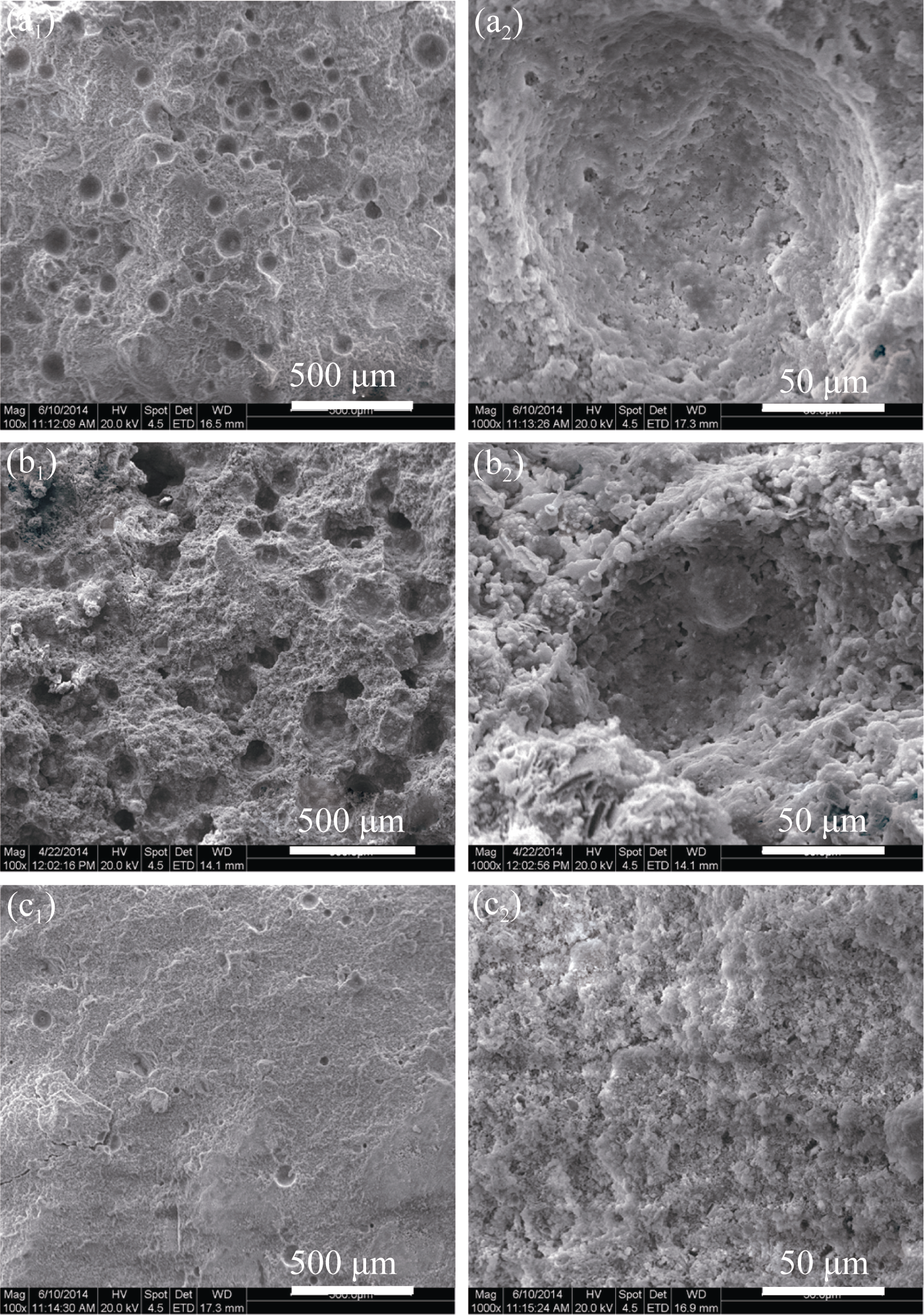
图6 BCPC-S(a1, a2)、CPC-S(b1, b2)与Control-S(c1, c2)的自然断面的SEM照片
Fig. 6 SEM images of cross-section of BCPC-S (a1, a2), CPC-S (b1, b2) and Control-S (c1, c2)
| [1] | DOROZHKIN S V, EPPLE M.Biological and medical significance of calcium phosphates.Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2002, 41(17): 3130-3146. |
| [2] | NANDI S K, ROY S, MUKHERJEE P, et al.Orthopaedic applications of bone graft and graft substitutes: a review.Indian Journal of Medical Research, 2010, 132: 15-30. |
| [3] | FELIX LANAO R P, HOEKSTRA J W, WOLKE J G, et al. Porous calcium phosphate cement for alveolar bone regeneration.Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, 2014, 8: 473-482. |
| [4] | DALL'OCA C, MALUTA T, CAVANI F, et al. The biocompatibility of porous vs non-porous bone cements: a new methodological approach.European Journal of Histochemistry, 2014, 58(2): 95-102. |
| [5] | DONG H, YE J D, WANG X P, et al.Preparation of calcium phosphate cement tissue engineering scaffold reinforced with chitin fiber.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2007, 22(5): 1007-1010. |
| [6] | THEIN-HAN W, XU H H.Collagen-calcium phosphate cement scaffolds seeded with umbilical cord stem cells for bone tissue engineering.Tissue Engineering Part A, 2011, 17(23/24): 2943-2954. |
| [7] | QI X P, YE JIAN-DONG, WANG YING-JING.Alginate/poly (lactic- co-glycolic acid)/calcium phosphate cement scaffold with oriented pore structure for bone tissue engineering.Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2009, 89(4): 980-987. |
| [8] | LODE A, MEISSNER K, LUO Y, et al.Fabrication of porous scaffolds by three-dimensional plotting of a pasty calcium phosphate bone cement under mild conditions.Journal of Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine, 2014, 8(9): 682-693. |
| [9] | CHEN W, ZHOU H, TANG M, et al.Gas-foaming calcium phosphate cement scaffold encapsulating human umbilical cord stem cells. Tissue Engineering Part A, 2012, 18(7/8): 816-827. |
| [10] | ALMIRALL A, LARRECQ G, DELGADO J A, et al.Fabrication of low temperature macroporous hydroxyapatite scaffolds by foaming and hydrolysis of an alpha-TCP paste.Biomaterials, 2004, 25(17): 3671-3680. |
| [11] | ZHANG J, LIU W, SCHNITZLER V, et al.Calcium phosphate cements for bone substitution: chemistry, handling and mechanical properties. Acta Biomaterialia, 2014, 10(3): 1035-1049. |
| [12] | LIU W, ZHANG J, RETHORE G, et al.A novel injectable, cohesive and toughened Si-HPMC (silanized-hydroxypropyl methylcellulose) composite calcium phosphate cement for bone substitution. Acta Biomaterialia, 2014, 10(7): 3335-3345. |
| [13] | DAI H L, LI S P, HE J H, et al.Carbon fiber reinforced α-TCP/ TTCP bone cement.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2004, 19(5): 1025-1030. |
| [14] | SCHUMACHER M, HENSS A, ROHNKE M, et al.A novel and easy-to-prepare strontium(II) modified calcium phosphate bone cement with enhanced mechanical properties. Acta Biomaterialia, 2013, 9(7): 7536-7544. |
| [15] | RENNO A C, NEJADNIK M R, VAN DE WATERING F C, et al. Incorporation of bioactive glass in calcium phosphate cement: material characterization and in vitro degradation. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A, 2013, 101(8): 2365-2373. |
| [16] | MULAK W, BALAŽ P, CHOJNACKA M.Chemical and morphological changes of millerite by mechanical activation. International Journal of Mineral Processing, 2002, 66(1/2/3/4): 233-240. |
| [17] | NEIRA I S, KOLEN'KO Y V, KOMMAREDDY K P, et al. Reinforcing of a calcium phosphate cement with hydroxyapatite crystals of various morphologies. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2010, 2(11): 3276-3284. |
| [18] | JIANG X X, QU S X, LIN S Z, et al. Influence of drynaria on physicochemical and in vitro biological properties of calcium phosphate cement. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(1): 29-37. |
| [19] | JGJ 52-2006. 普通混凝土用砂、石质量及检验方法标准. |
| [20] | ASTM C29/C29M-97. Standard Test Method for Bulk Density (Unit Weight) and Voids in Aggregate. |
| [21] | GIROD FULLANA S, TERNET H, FRECHE M, et al.Controlled release properties and final macroporosity of a pectin microspheres-calcium phosphate composite bone cement. Acta Biomaterialia, 2010, 6(6): 2294-2300. |
| [22] | MOHAMMADI M, HESARAKI S, HAFEZI-ARDAKANI M.Investigation of biocompatible nanosized materials for development of strong calcium phosphate bone cement: comparison of nano-titania, nano-silicon carbide and amorphous nano-silica. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(6): 8377-8387. |
| [23] | LIU C S, CHEN F Y, HUANG Y, et al.Effects of particles size of the starting materials on hydration and hardening progress of calcium phosphate cement. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 1999, 27(2): 139-147. |
| [24] | YANG J J, YE J D.Effects of particle size on the rheological properties and injectability of a calcium phosphate cement.Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2008, 27(2): 213-219. |
| [25] | LEWIS G.Viscoelastic properties of injectable bone cements for orthopaedic applications: state-of-the-art review.Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B: Applied Biomaterials, 2011, 98(1): 171-191. |
| [26] | HUANG Z L, LIU Y, WANG D W, et al.Properties of crystallizing and absorbing F- ion of HAP synthesized by Sol-Gel process. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2001, 16(4): 661-666. |
| [27] | NASIRI-TABRIZI B, FAHAMI A.Mechanochemical synthesis and structural characterization of nano-sized amorphous tricalcium phosphate.Ceramics International, 2013, 39(8): 8657-8666. |
| [28] | KO C L, CHEN J C, HUNG C C, et al.Biphasic products of dicalcium phosphate-rich cement with injectability and nondispersibility.Materials Science and Engineering C, Materials for Biological Applications, 2014, 39: 40-46. |
| [29] | TAMIMI F, LE NIHOUANNEN D, EIMAR H, et al.The effect of autoclaving on the physical and biological properties of dicalcium phosphate dihydrate bioceramics: brushite vs monetite. Acta Biomaterialia, 2012, 8(8): 3161-3169. |
| [30] | BOHNER M.Calcium orthophosphates in medicine: from ceramics to calcium phosphate cements.Injury, 2000, 31: D37-D47. |
| [31] | BOANINI E, GAZZANO M, BIGI A.Ionic substitutions in calcium phosphates synthesized at low temperature.Acta biomaterialia, 2010, 6(6): 1882-1894. |
| [32] | WEI J, JIA J, WU F, et al.Hierarchically microporous/macroporous scaffold of magnesium-calcium phosphate for bone tissue regeneration.Biomaterials, 2010, 31(6): 1260-1269. |
| [1] | 张航, 韩坤原, 董兰兰, 李祥. DLP打印β-磷酸三钙/纳米黏土复合支架的制备与表征[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(10): 1116-1122. |
| [2] | 张丰年, 郭猛, 苗洋, 高峰, 成楚飞, 程富豪, 刘宇峰. 高熵陶瓷(Zr1/7Hf1/7Ce1/7Y2/7La2/7)O2-δ的制备及烧结行为[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(4): 372-378. |
| [3] | 曾凡鑫, 刘创, 曹余良. 去合金化制备具有高循环稳定性的纳米多孔Sb/MCNT储钠负极材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2021, 36(11): 1137-1144. |
| [4] | 孙丹丹, 张家良, 武燕庆, 张仲秋, 刘大康. 原料预处理对BaTiO3压电陶瓷的物性影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2017, 32(6): 615-620. |
| [5] | 孟方礼, 章冬云, 常程康, 徐家跃, KAMZIN A S. 基于铁粉还原的LiFePO4/C合成路径及其电化学性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(8): 802-806. |
| [6] | 刘战强, 唐宇峰, 林天全, 毕 辉, 于刘涛, 黄富强. 石墨烯-二硫化钼复合负极材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2016, 31(4): 345-350. |
| [7] | 刘 婧, 刘 军, 李 江, 林 丽, 潘裕柏, 程晓农, 郭景坤. 球磨转速对Nd:YAG透明陶瓷的显微结构及光学性能的影响[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(6): 581-587. |
| [8] | 赵军胜, 屈树新, 黄 萍, 刘宗光, 王铈汶, 翁 杰. 纳米晶体纤维素增强磷酸钙骨水泥的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2015, 30(3): 318-324. |
| [9] | 戴红莲, 胡付俭, 方彩萍, 李世普. 可注射镁基磷酸钙骨水泥的研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(9): 991-996. |
| [10] | 巩梦安, 饶群力, 王鸿烈. 造孔剂和发泡剂结合法制备氟化羟基磷灰石多孔支架研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(3): 289-293. |
| [11] | 张国芳, 张羊换, 刘卓承, 许剑轶, 张 胤. CeO2基固溶体对Mg2Ni合金储氢动力学性能的影响研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(12): 1241-1245. |
| [12] | 胡冬力, 邢娟娟, 郑 强, 顾 辉, 倪德伟, 张国军. HfB2-SiC-HfC陶瓷相组成与相成分定量分析的对比研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(10): 1105-1109. |
| [13] | 罗会涛, 郭泰林, 朱德贵, 智 伟, 段 可, 张成栋, 屈树新, 翁 杰. 溶胶–凝胶法制备不同形态的半透明羟基磷灰石陶瓷[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(8): 804-810. |
| [14] | 吴小贤, 李红霞, 刘国齐, 牛冲冲, 王 刚, 孙加林. 高能球磨合成纳米碳包覆α-Al2O3复合粉体[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(3): 261-266. |
| [15] | 赵 婧, 李金雨, 智 伟, 鲁 雄, 贾治彬, 翁 杰. 蜡球造孔法制备多孔HA陶瓷支架及其性能优化[J]. 无机材料学报, 2013, 28(1): 74-78. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||