无机材料学报 ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (10): 1055-1060.DOI: 10.15541/jim20140008
李小艳1,2, 阎建辉1,2, 张 丽1,2, 周民杰2, 刘又年1
收稿日期:2014-01-06
修回日期:2014-03-14
出版日期:2014-10-20
网络出版日期:2014-09-22
作者简介:李小艳(1989–), 女, 硕士研究生. E-mail: yuyicaocao@163.com
基金资助:LI Xiao-Yan1,2, YAN Jian-Hui1,2, ZHANG Li1,2, ZHOU Ming-Jie2, LIU You-Nian1
Received:2014-01-06
Revised:2014-03-14
Published:2014-10-20
Online:2014-09-22
About author:LI Xiao-Yan. E-mail: yuyicaocao@163.com
Supported by:摘要:
以葡萄糖为模板, 硝酸锌、硝酸铜和硝酸铝为原料, 采用水热法制备高比表面Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4复合空心球。采用XRD、SEM、HRTEM、BET、DRS和PL等手段对样品进行表征, 结果表明: 在600℃下焙烧的Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4复合物呈空心球状, 球体直径约为2 μm, 比表面积高达214.97 m2/g。引入Zn有助于提高样品对紫外和可见光的吸收能力, 减少光生电子空穴对的复合, 光催化活性显著提高。在模拟太阳光照下, 以甲基橙溶液为目标降解物, 考察样品的煅烧温度和Zn加入量对光催化活性的影响。当Zn加入量为0.5wt%, 煅烧温度为600℃时, 样品的光催化活性最佳。光照60 min, 0.5 g/L光催化剂用量对25 mg/L甲基橙溶液的脱色率高达97%。
中图分类号:
李小艳, 阎建辉, 张 丽, 周民杰, 刘又年. Zn掺杂CuO/CuAl2O4复合空心球的制备及光催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2014, 29(10): 1055-1060.
LI Xiao-Yan, YAN Jian-Hui, ZHANG Li, ZHOU Ming-Jie, LIU You-Nian. Preparation and Photocatalytic Properties of Hollow Spheres-like Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 Composite Photocatalysts[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(10): 1055-1060.
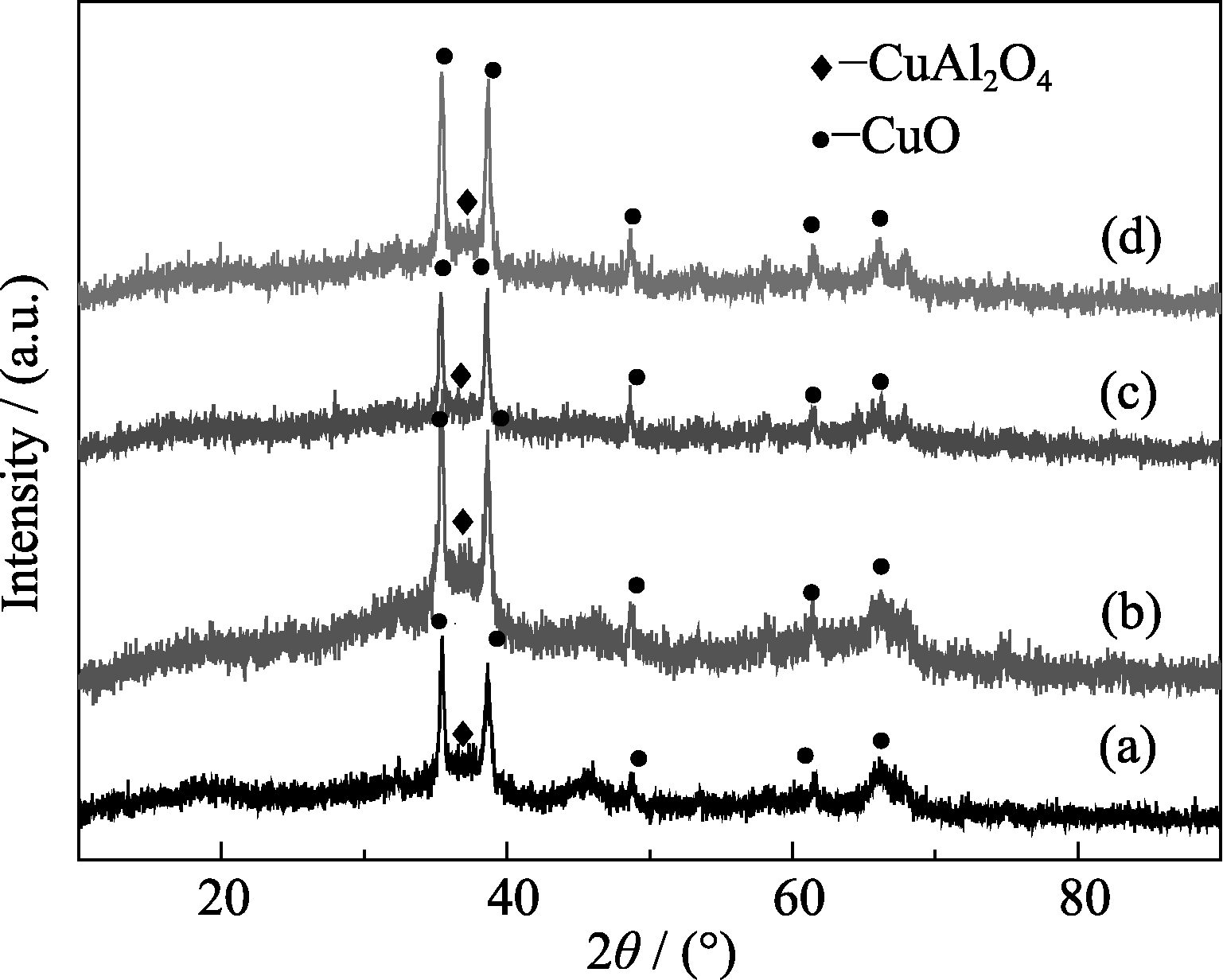
图2 600℃煅烧Zn掺杂CuO/CuAl2O4样品的XRD图谱
Fig. 2 XRD patterns of Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 samples calcined at 600℃ (a) 0wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (b) 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (c) 1wt% Zn- CuO/CuAl2O4; (d) 2wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4
| Element | Area 1 | Area 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | at% | wt% | at% | |
| O | 32.00 | 52.78 | 30.99 | 51.06 |
| Al | 33.76 | 33.01 | 36.15 | 35.32 |
| Cu | 33.30 | 13.83 | 32.03 | 13.29 |
| Zn | 0.94 | 0.38 | 0.83 | 0.34 |
表1 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4样品的EDS分析结果
Table 1 EDS analyses of 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 samples
| Element | Area 1 | Area 2 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| wt% | at% | wt% | at% | |
| O | 32.00 | 52.78 | 30.99 | 51.06 |
| Al | 33.76 | 33.01 | 36.15 | 35.32 |
| Cu | 33.30 | 13.83 | 32.03 | 13.29 |
| Zn | 0.94 | 0.38 | 0.83 | 0.34 |

图3 Zn微球(a, b), 500℃煅烧Zn微球(c)和0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4样品(d, e)的SEM照片, 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4样品(f)的HRTEM照片
Fig. 3 SEM images of Zn microspheres (a, b), Zn microspheres calcined at 500℃(c), 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 samples (d, e) and HRTEM images of 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 samples (f)
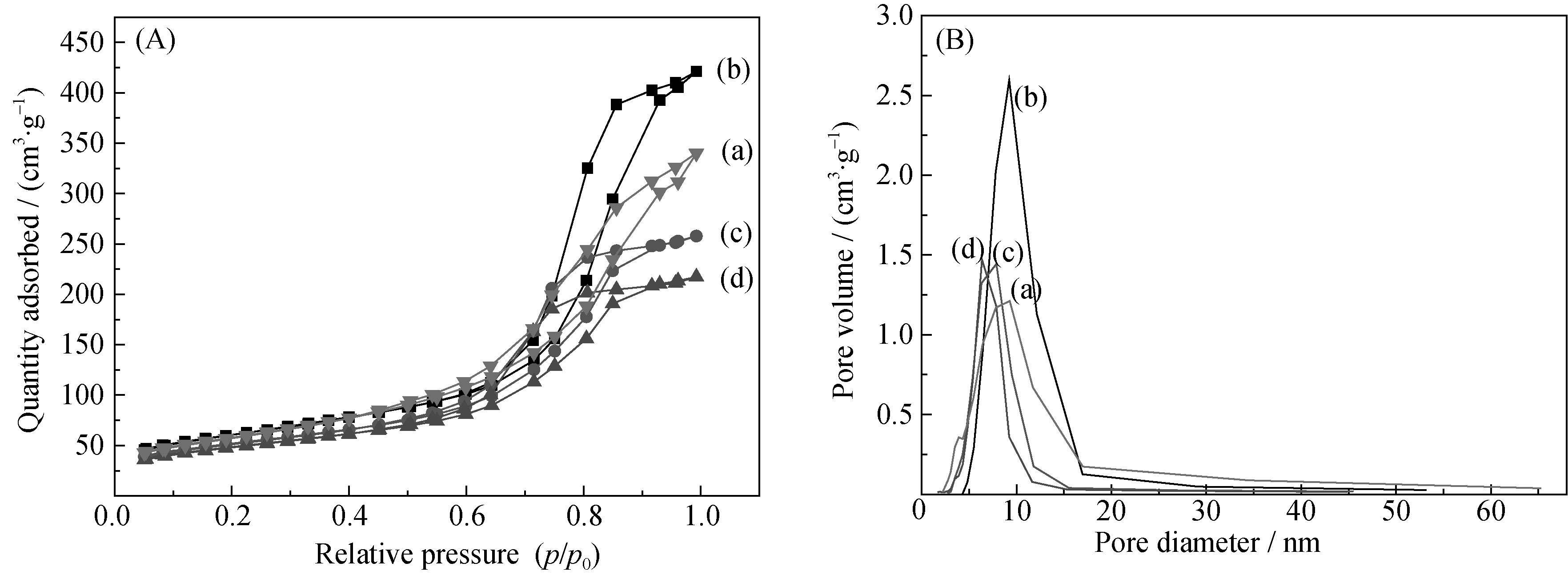
图4 Zn掺杂CuO/CuAl2O4样品的(a)N2吸附-脱附等温线和(b)孔径分布图
Fig. 4 (A) N2 adsorption-desorption isotherms and (B) pore size distribution curves of Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 samples (a) 0wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (b) 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (c) 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (d) 2wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4
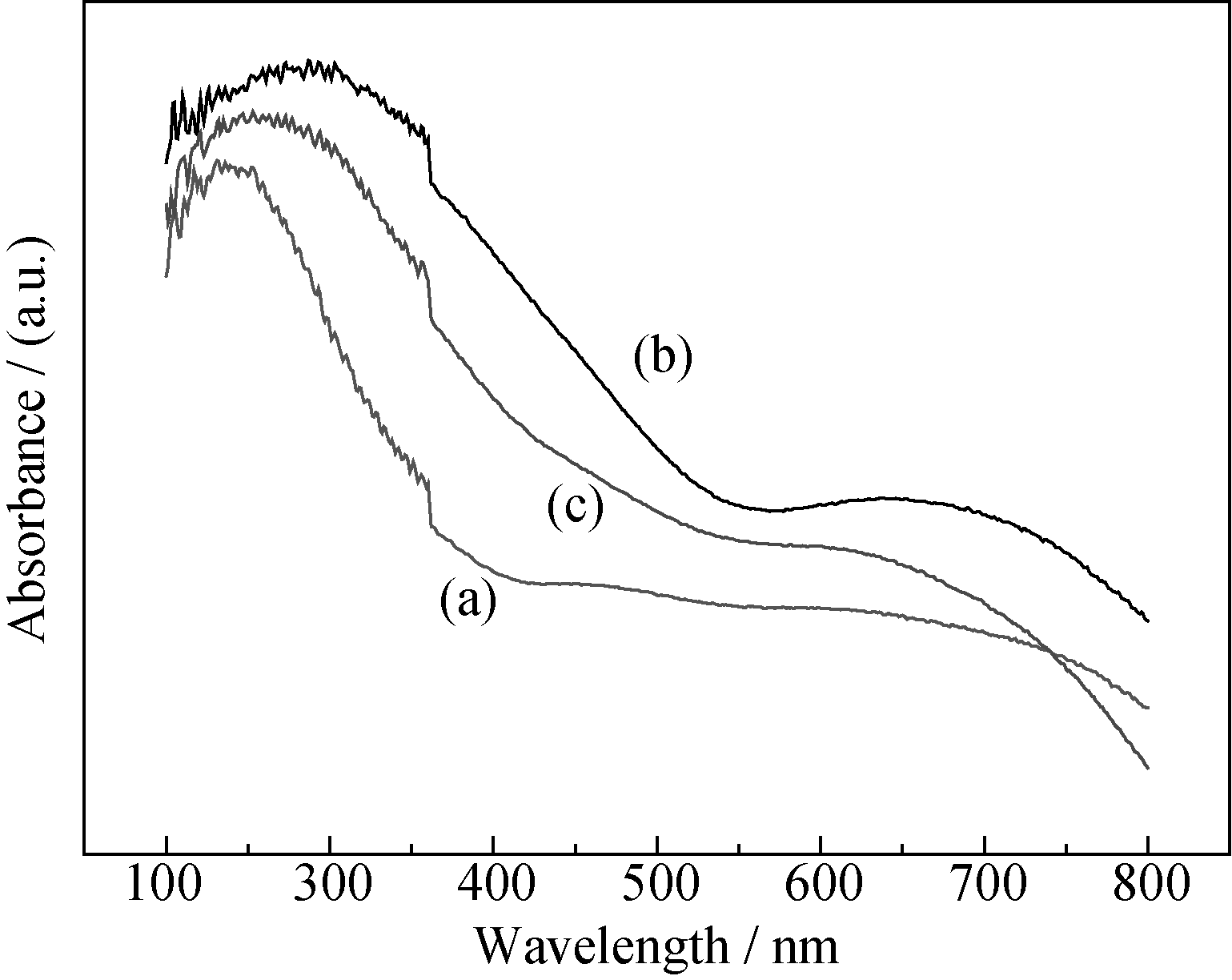
图5 Zn掺杂CuO/CuAl2O4样品的UV-Vis DRS图谱
Fig. 5 UV-Vis DRS spectra of Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 samples (a) 0wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (b) 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (c) 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 calcined at 600℃
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Adsorption average pore width / nm | Pore volume /(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 208.25 | 7.7 | 0.59 |
| 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 214.97 | 9.2 | 0.71 |
| 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 182.92 | 7.0 | 0.45 |
| 2wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 171.42 | 6.5 | 0.37 |
表2 Zn掺杂CuO/CuAl2O4样品的物理性质
Table 2 Physical property of Zn-doped CuO/CuAl2O4 samples
| Sample | SBET/(m2·g-1) | Adsorption average pore width / nm | Pore volume /(cm3·g-1) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0.3wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 208.25 | 7.7 | 0.59 |
| 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 214.97 | 9.2 | 0.71 |
| 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 182.92 | 7.0 | 0.45 |
| 2wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 | 171.42 | 6.5 | 0.37 |
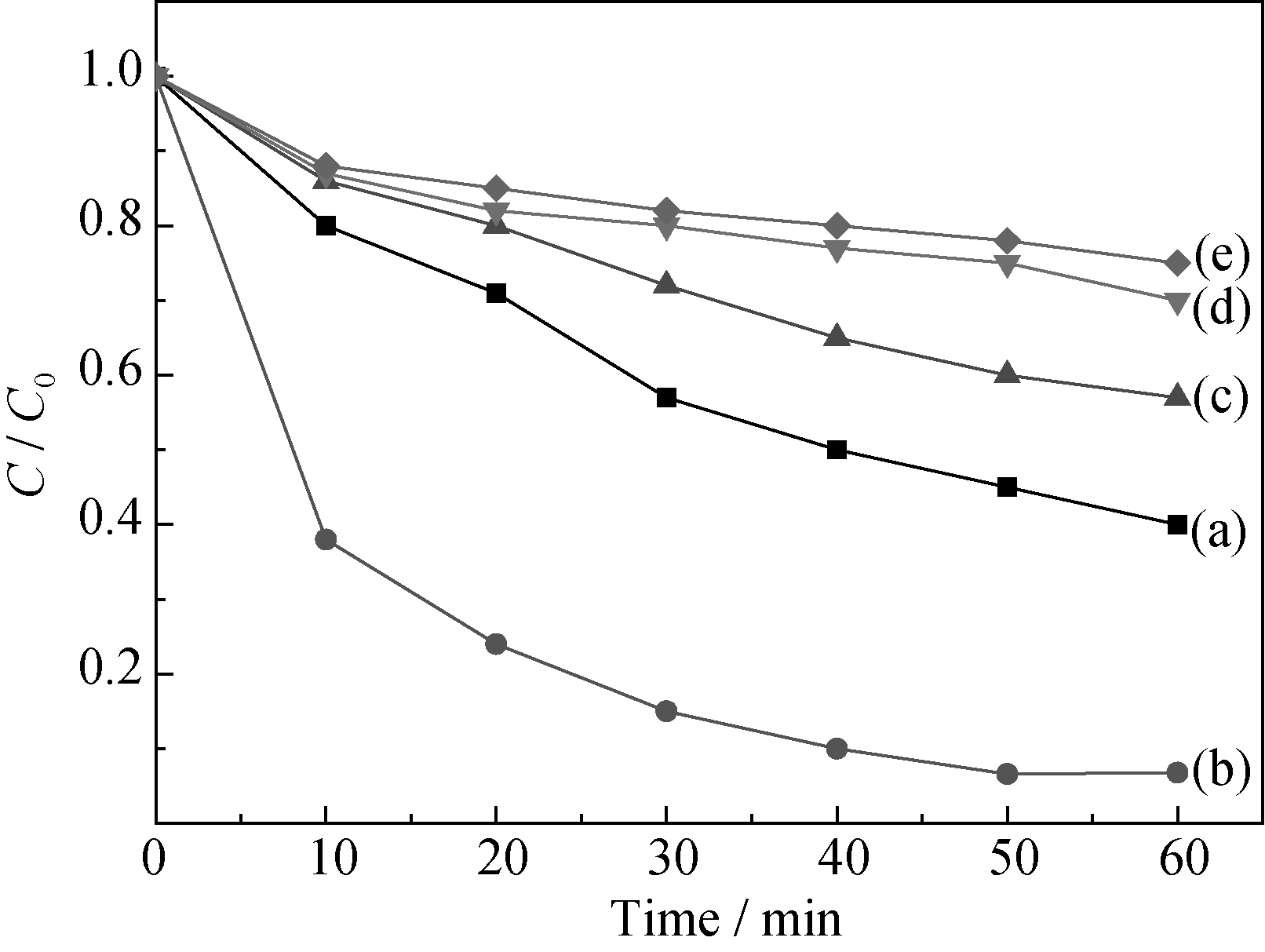
图7 煅烧温度对0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4样品降解甲基橙的影响
Fig. 7 Effect of calcination temperatures on methyl orange degradation of 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 samples (a) 500℃; (b) 600℃; (c) 700℃; (d) 800℃; (e) 900℃
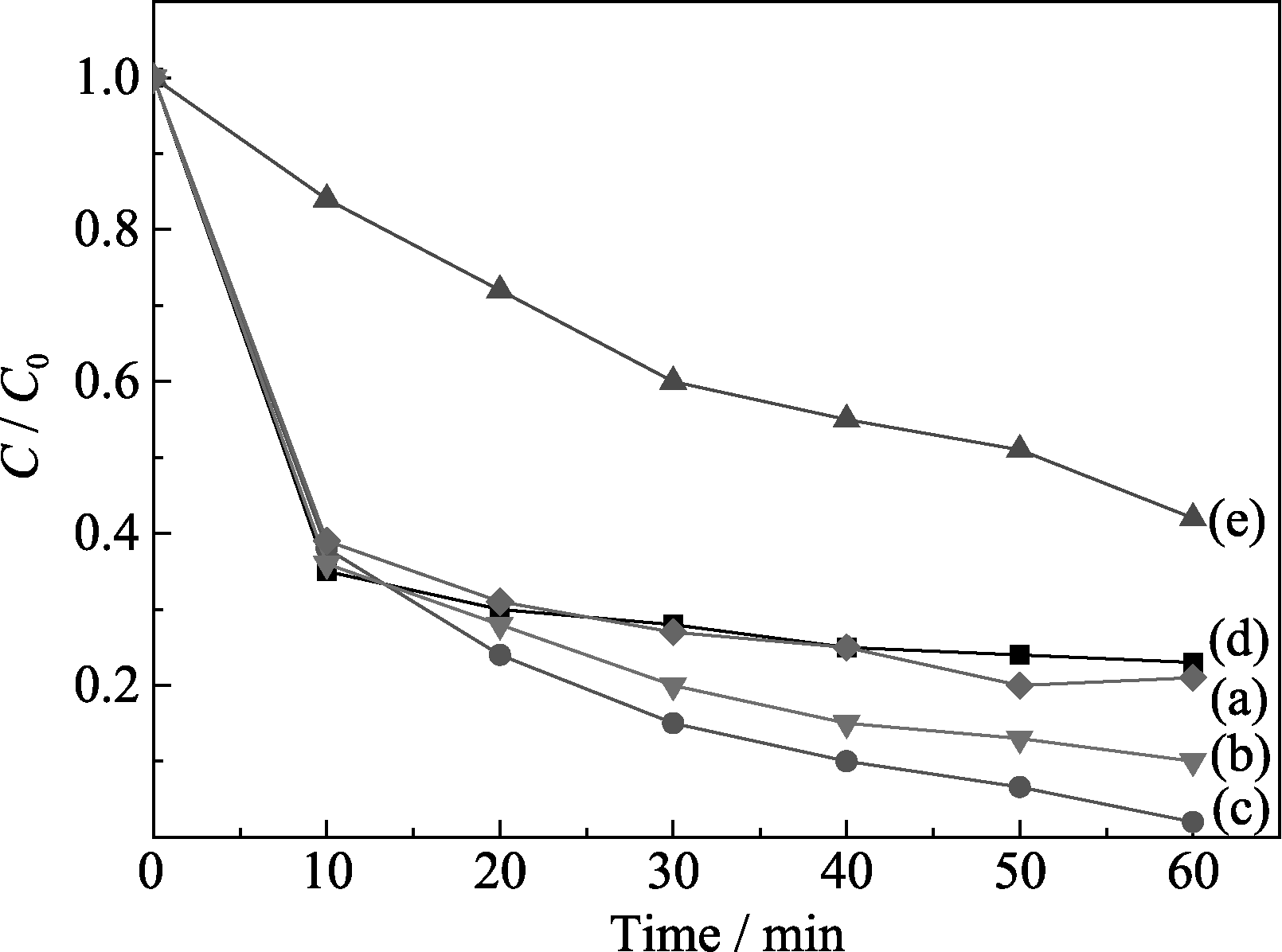
图 8 Zn加入量对CuO/CuAl2O4样品降解甲基橙的影响
Fig. 8 Effect of Zn doped content on methyl orange degradation of Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4 samples (a) 0wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (b) 0.3wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (c) 0.5wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (d) 1wt% Zn-CuO/CuAl2O4; (e) 2wt% Zn-CuO/ CuAl2O4 calcined at 600℃
| [1] | LI F H, LIN H, LI J F, et al. Influence of LiF on the infrared transmissivity of magnesia alumina spinel transparent ceramics. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(4): 417-421. |
| [2] | TORKIAN L, AMINI M M, BAHRAMI Z. Synthesis of nano crystalline MgAl2O4 spinel powder by microwave assisted combustion. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(5): 550-554. |
| [3] | BAYAL N, JEEVANANDAM P. Synthesis of metal aluminate nanoparticles by Sol-Gel method and studies on their reactivity. J. Alloys Compd., 2012, 516: 27-32. |
| [4] | NADERI M, SHAMIRIAN A, EDRISI M. Synthesis, characterization and photocatalytic properties of nanoparticles CuAl2O4 by pechini method using taguchi statistical design. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 2011, 58(2): 557-563. |
| [5] | EDRISI M, TAJIK S, SOLEYMANI M. Synthesis of CuAl2O4 nanoparticles by mixed chelates thermolysis and homogeneous precipitation using solubility difference reactions; taguchi optimization and photocatalytic application. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics, 2013, 24(10): 3914-3920. |
| [6] | LIANG C X, LI X Y, QU Z P, et al. The role of copper species on Cu/γ-Al2O3 catalysts for NH3-SCO reaction. Applied Surface Science, 2012, 258(8): 3738-3743. |
| [7] | SHANG H X, TIAN Y, WANG X T, et al. Photocatalytic H2 evolution from glycerol solution over Bi3+-doped TiO2 nanoparti-cles. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(12): 1283-1288. |
| [8] | YIN J, ZANG Y S, YUE C, et al. Ag nanoparticle/ZnO hollow nanosphere arrays: large scale synthesis and surface plasmon resonance effect induced Raman scattering enhancement. J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(16): 7902-7909. |
| [9] | ZHAO G, LIU S W, LU Q F. Synthesis of TiO2/Bi2WO6 nanofibers with electrospinning technique for photocatalytic methyl blue degradation. J. Sol-Gel Sci. Technol., 2013, 66(3): 406-412. |
| [10] | LI Z Q, CHEN X T, XUE Z L. Microwave-assisted synthesis and photocatalytic properties of flower-like Bi2WO6 and Bi2O3-Bi2WO6 composite. J. Colloid Interface sci., 2013, 394: 69-77. |
| [11] | TIAN G H, CHEN Y J, MENG X Y, et al. Hierarchical composite of Ag/AgBr nanoparticles supported on Bi2MoO6 hollow spheres for enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performance. ChemPlusChem, 2013, 78(1): 117-123. |
| [12] | BAO Y, YANG Y Q, MA J Z. Research progress of hollow structural materials prepared via templating method. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(5): 459-468. |
| [13] | ZHAO B, LIN L, CHEN C, et al. Research progress on crystal growth mechanism of titania/titanate nano-powder materials. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(7): 683-690. |
| [14] | MENG H X, WANG B B, LIU S, et al. Hydrothermal preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity of TiO2/Fe-TiO2 composite catalysts. Ceram. Int., 2013, 39(5): 5785-5793. |
| [15] | YIN B, WANG J T, XU W, et al. Preparation of TiO2/mesoporous carbon composites and their photocatalytic performance for methyl orange degradation. New Carbon Materials, 2013, 28(1): 47-54. |
| [16] | ZHANG L, YAN J H, ZHOU M J, et al. Fabrication and photocatalytic properties of spheres-in-spheres ZnO/ZnAl2O4 composite hollow microspheres. Appl. Surf. Sci., 2013, 268: 237-245. |
| [17] | ZHANG L, YAN J H, ZHOU M J, et al. Preparation and photocatalytic property of hollow sphere-like ZnO/ZnAl2O4 composite photocatalysts with high specific surface area. Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2012, 28(9): 1827-1834. |
| [18] | LV K, YU J, DENG K, et al. Synergistic effects of hollow structure and surface fluorination on the photocatalytic activity of titania. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2010, 173(1): 539-543. |
| [19] | ZHANG Y J, XU Y, LI T, et al. Preparation of ternary Cr2O3-SiC-TiO2 composites for the photocatalytic production of hydrogen. Particuology, 2012, 10(1): 46-50. |
| [20] | DONG F, SUN Y J, FU M, et al. Room temperature synthesis and highly enhanced visible light photocatalytic activity of porous BiOI/BiOCl composites nanoplates microflowers. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 219: 26-34. |
| [21] | LEE S S, BAI H W, LIU Z Y, et al. Novel-structured electrospun TiO2/CuO composite nanofibers for high efficient photocatalytic cogeneration of clean water and energy from dye wastewater. Water Research, 2013, 47(12): 4059-4073. |
| [1] | 伍林, 胡明蕾, 王丽萍, 黄少萌, 周湘远. TiHAP@g-C3N4异质结的制备及光催化降解甲基橙[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(5): 503-510. |
| [2] | 王磊, 李建军, 宁军, 胡天玉, 王洪阳, 张占群, 武琳馨. CoFe2O4@Zeolite催化剂活化过一硫酸盐对甲基橙的强化降解: 性能与机理[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(4): 469-476. |
| [3] | 马心全, 李喜宝, 陈智, 冯志军, 黄军同. S型异质结BiOBr/ZnMoO4的构建及光催化降解性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 62-70. |
| [4] | 姚仪帅, 郭瑞华, 安胜利, 张捷宇, 周国治, 张国芳, 黄雅荣, 潘高飞. 原位负载Pt-Co高指数晶面催化剂的制备及其电催化性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2023, 38(1): 71-78. |
| [5] | 陈瀚翔, 周敏, 莫曌, 宜坚坚, 李华明, 许晖. CoN/g-C3N4 0D/2D复合结构及其光催化制氢性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 1001-1008. |
| [6] | 王红宁, 黄丽, 清江, 马腾洲, 黄维秋, 陈若愚. 有机-无机氧化硅空心球的合成及VOCs吸附应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [7] | 薛虹云, 王聪宇, MAHMOOD Asad, 于佳君, 王焱, 谢晓峰, 孙静. 二维g-C3N4与Ag-TiO2复合光催化剂降解气态乙醛抗失活研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(8): 865-872. |
| [8] | 洪佳辉, 马冉, 仵云超, 文涛, 艾玥洁. MOFs自牺牲模板法制备CoNx/g-C3N4纳米材料用作高效光催化还原U(VI)[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 741-749. |
| [9] | 迟聪聪, 屈盼盼, 任超男, 许馨, 白飞飞, 张丹洁. SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2核壳结构的制备及其光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [10] | 王晓俊, 许文, 刘润路, 潘辉, 朱申敏. 水凝胶负载的纳米银/氮化碳光催化剂的制备及性能研究[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(7): 731-740. |
| [11] | 安琳, 吴淏, 韩鑫, 李耀刚, 王宏志, 张青红. 非贵金属Co5.47N/N-rGO助催化剂增强TiO2光催化制氢性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 534-540. |
| [12] | 张叶, 姚冬旭, 左开慧, 夏咏锋, 尹金伟, 曾宇平. 原位引入BN-SiC燃烧合成Si3N4-BN-SiC复合材料[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(5): 574-578. |
| [13] | 陈士昆, 王楚楚, 陈晔, 李莉, 潘路, 文桂林. 磁性Ag2S/Ag/CoFe1.95Sm0.05O4 Z型异质结的制备及光催化降解性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(12): 1329-1336. |
| [14] | 刘彭, 吴仕淼, 吴昀峰, 张宁. Zn0.4(CuGa)0.3Ga2S4/CdS光催化材料的制备及其CO2还原性能[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 15-21. |
| [15] | 刘雪晨, 曾滴, 周沅逸, 王海鹏, 张玲, 王文中. 改性氮化碳光催化剂在生物质氧化反应中的应用[J]. 无机材料学报, 2022, 37(1): 38-44. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||