
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2019, Vol. 34 ›› Issue (10): 1109-1114.DOI: 10.15541/jim20190067
Previous Articles Next Articles
XIA Tian1,2,MENG Xie1,LUO Ting1,ZHAN Zhong-Liang1( )
)
Received:2019-02-13
Published:2019-09-23
Online:2019-05-29
Supported by:CLC Number:
XIA Tian, MENG Xie, LUO Ting, ZHAN Zhong-Liang. Synthesis and Evaluation of Ca-doped Sr2Fe1.5Mo0.5O6-δ as Symmetrical Electrodes for High Performance Solid Oxide Fuel Cells[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(10): 1109-1114.
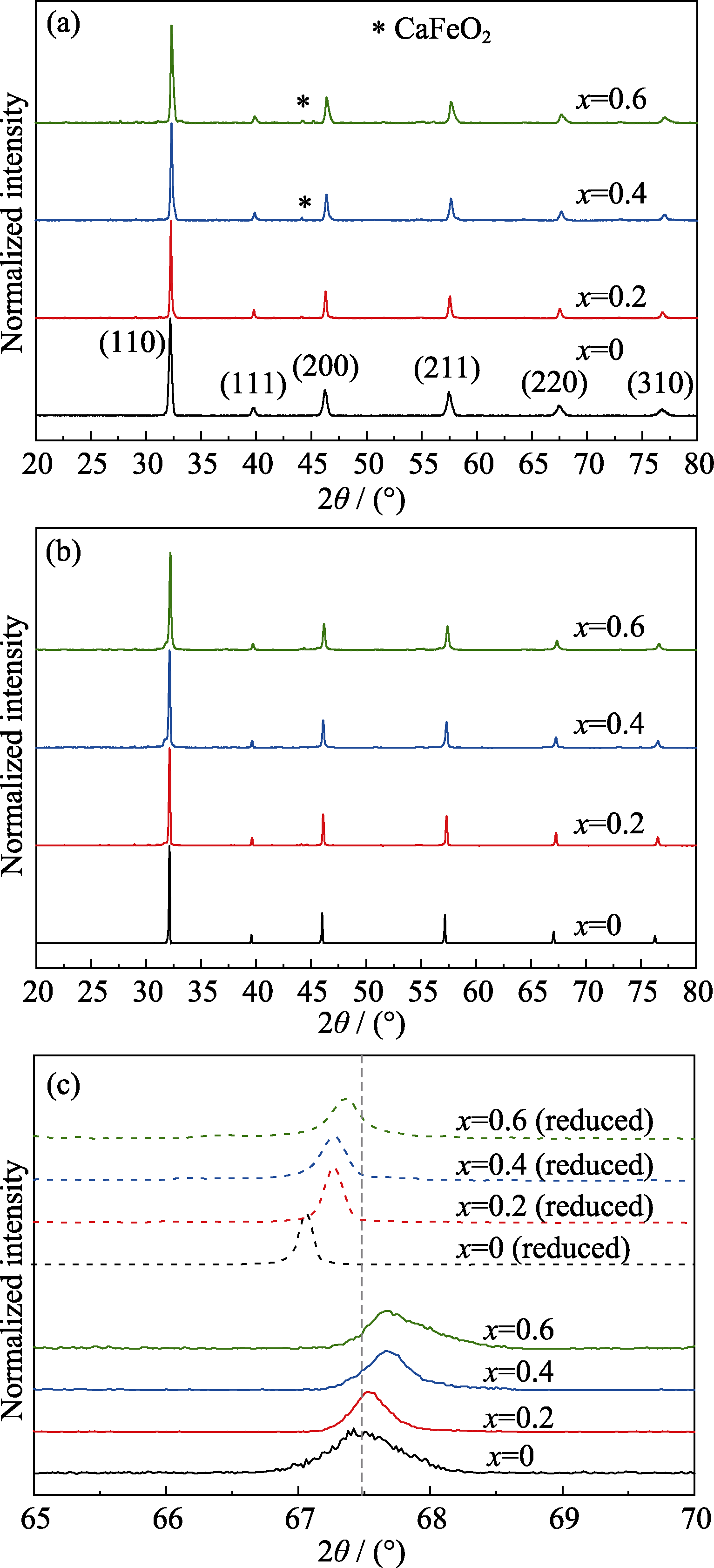
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of Sr2-xCaxFe1.5Mo0.5O6-δ powders synthetized in air (a) and reduced in humidified hydrogen (b) at 800 ℃ for 4 h; (c) Magnified view of the diffraction peak at 67.5°
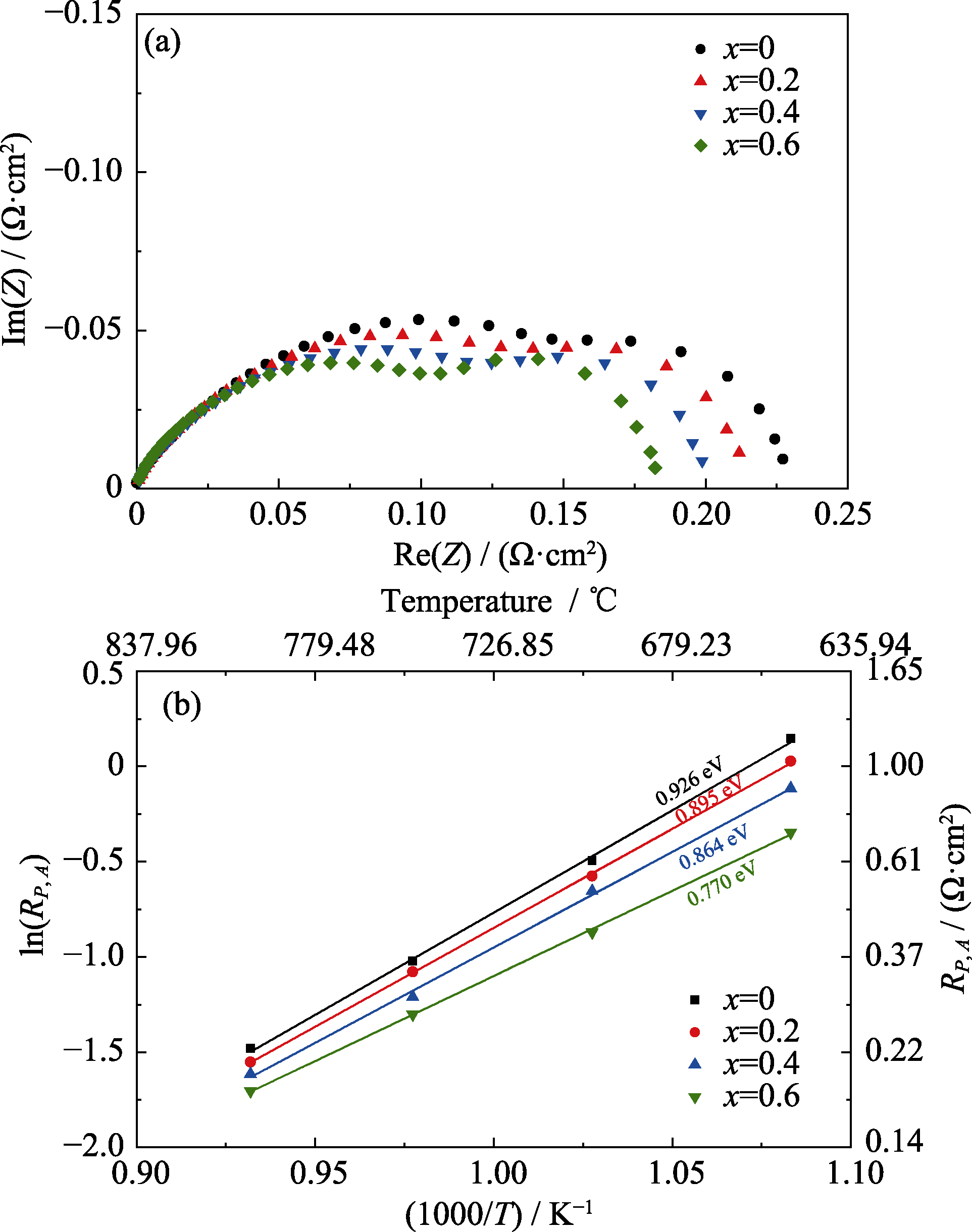
Fig. 4 (a) EIS plots of the Sr2-xCaxFe1.5Mo0.5O6-δ symmetrical cells measured in humidified hydrogen at 800 ℃, and (b) Arrhenius plots of the anode polarization resistances over the temperature range of 650-800 ℃
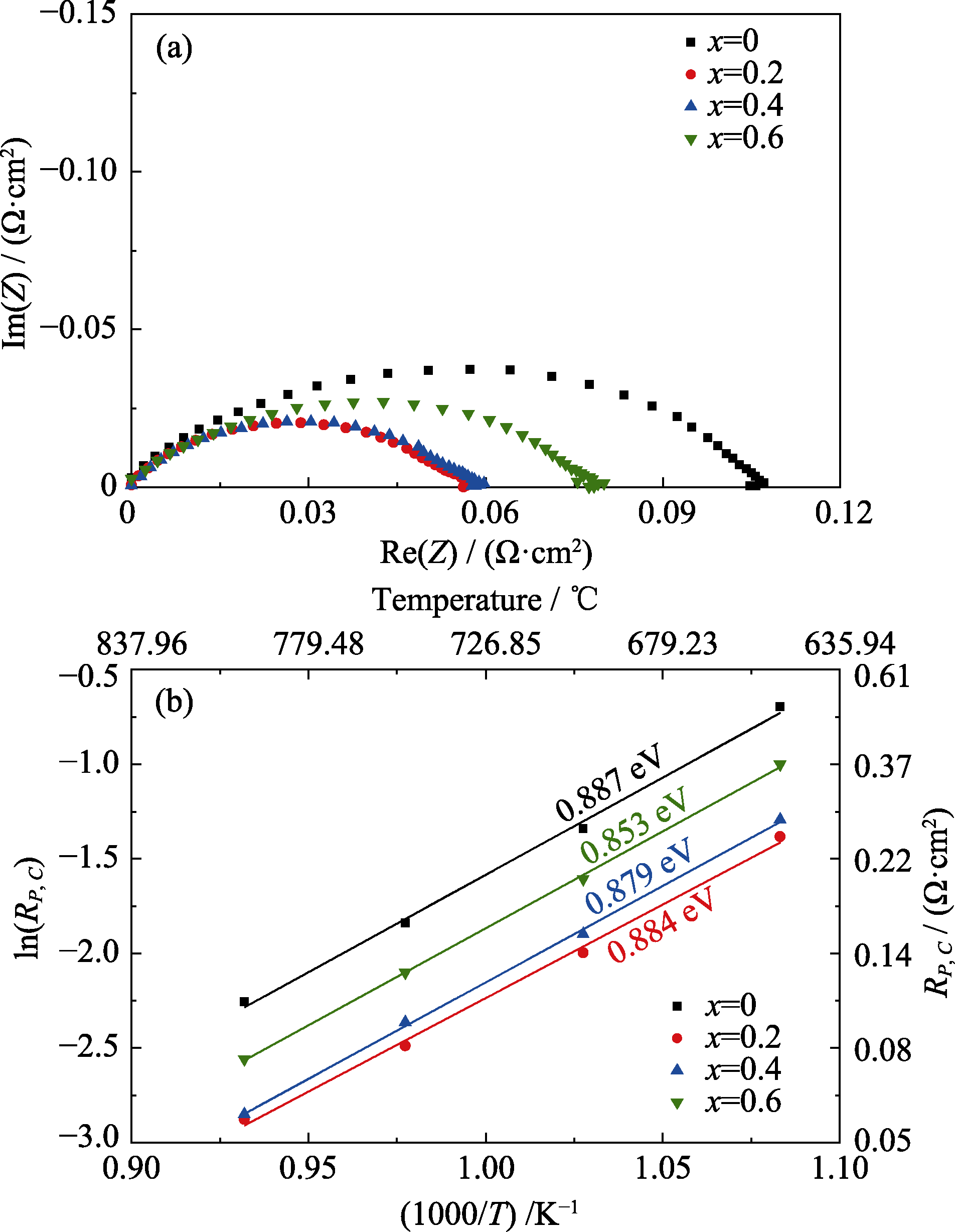
Fig. 5 (a) EIS plots of the Sr2-xCaxFe1.5Mo0.5O6-δ symmetrical cells measured in air at 800 ℃, and (b) Arrhenius plots of the cathode polarization resistances over the temperature range of 650-800 ℃
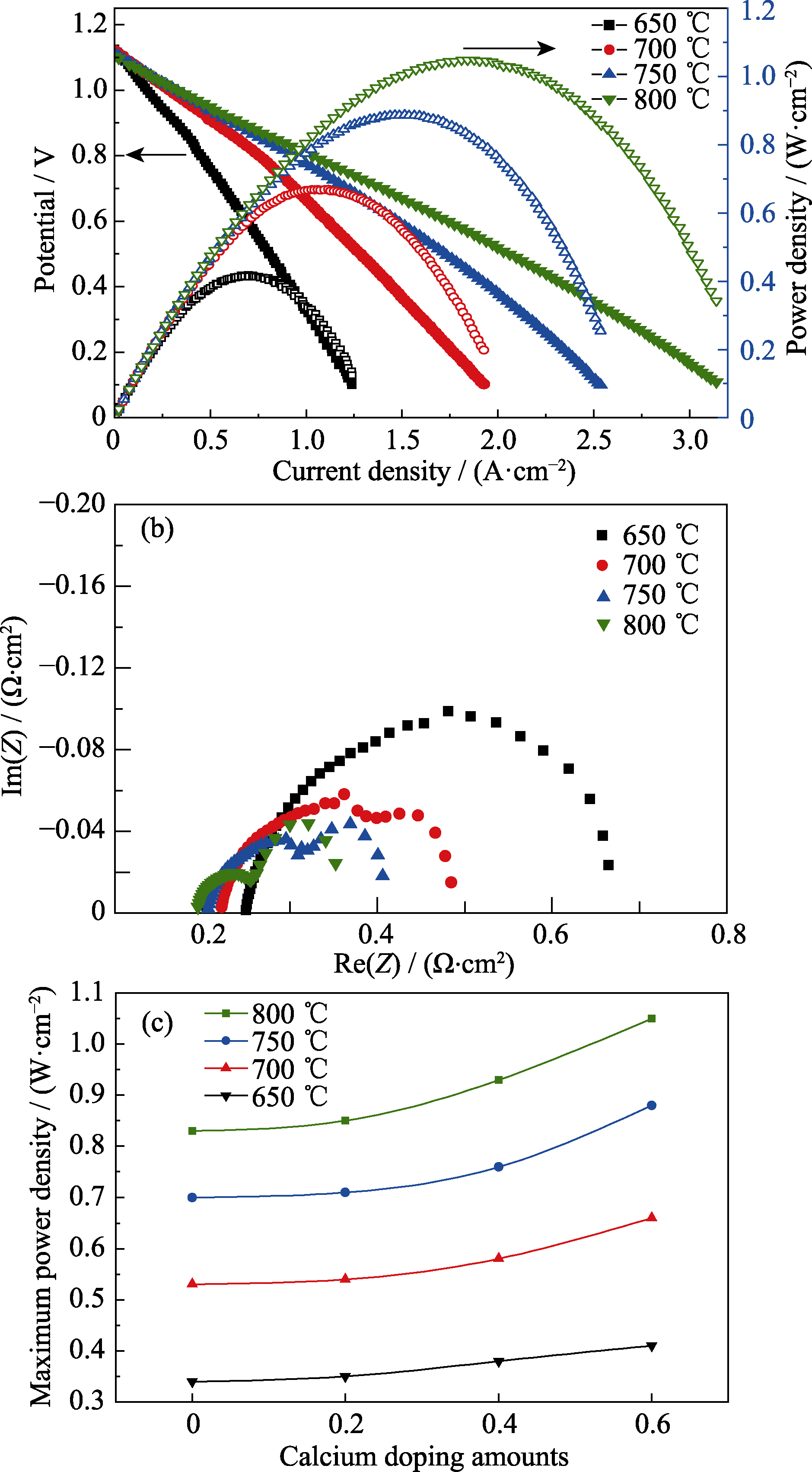
Fig. 6 (a) Voltage and power density versus current density for a symmetrical fuel cell with Sr2-xCaxFe1.5Mo0.5O6-δ(x=0.6) electrode measured in humidified hydrogen fuel and dry air over the temperature range of 650-800 ℃; (b) Nyquist plots of impedance data measured at open circuits; (c) Maximum power densities of the symmetrical SCFMO electrode cells at different Ca2+ substitutions over the temperature range of 650-800 ℃
| [1] | ORMEROD R M . Solid oxide fuel cells. Chemical Society Reviews, 2003,32(1):17-28. |
| [2] | MINH N Q . Solid oxide fuel cell technology—features and applications. Solid State Ionics, 2004,174(1):271-277. |
| [3] | IRVINE J T S, CONNOR P . SOFC Facts and Figures: Past Present and Future Perspectives for SOFC Technologies. London: Springer London, 2013. |
| [4] | STEELE B C H, HEINZEL A . Materials for fuel-cell technologies. Nature, 2001,414:345-352. |
| [5] | CARLOS RUIZ-MORALES J, MARRERO-LOPEZ D, CANALES-VAZQUEZ J , et al. Symmetric and reversible solid oxide fuel cells.RSC Adv., 2011,1(8):1403-1414. |
| [6] | SU C, WANG W, LIU M , et al. Progress and prospects in symmetrical solid oxide fuel cells with two identical electrodes.Advanced Energy Materials, 2015,5(14):1500188. |
| [7] | DOS SANTOS-GÓMEZ L, PORRAS-VÁZQUEZ J M, LOSILLA E R , et al. Ti-doped SrFeO3 nanostructured electrodes for symmetric solid oxide fuel cells.RSC Adv., 2015,5(130):107889-107895. |
| [8] | BIAN L, DUAN C, WANG L , et al. Ce-doped La0.7Sr0.3Fe0.9Ni0.1O3-δ as symmetrical electrodes for high performance direct hydrocarbon solid oxide fuel cells.Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2017,5(29):15253-15259. |
| [9] | LIN B, WANG S, LIU X , et al. Simple solid oxide fuel cells.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010,490(1):214-222. |
| [10] | BASTIDAS D M, TAO S ,IRVINE J T S. A symmetrical solid oxide fuel cell demonstrating redox stable perovskite electrodes. J. Mater. Chem., 2006,16(17):1603-1605. |
| [11] | CHEN M, PAULSON S, THANGADURAI V , et al. Sr-rich chromium ferrites as symmetrical solid oxide fuel cell electrodes.Journal of Power Sources, 2013,236:68-79. |
| [12] | CANALES-VÁZQUEZ J, RUIZ-MORALES J C, MARRERO-LÓPEZ D , et al. Fe-substituted (La,Sr)TiO3 as potential electrodes for symmetrical fuel cells (SFCs).Journal of Power Sources, 2007,171(2):552-557. |
| [13] | MARTíNEZ-CORONADO R, AGUADERO A, PÉREZ-COLL D , et al. Characterization of La0.5Sr0.5Co0.5Ti0.5O3-δ as symmetrical electrode material for intermediate-temperature solid-oxide fuel cells.International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2012,37(23):18310-18318. |
| [14] | FERNANDEZ-ROPERO A J, PORRAS-VAZQUEZ J M, CABEZA A , et al. High valence transition metal doped strontium ferrites for electrode materials in symmetrical SOFCs.J. Power Sources, 2014,249:405-413. |
| [15] | LIU Q, DONG X, XIAO G , et al. A novel electrode material for symmetrical SOFCs.Advanced Materials, 2010,22(48):5478-5482. |
| [16] | MENG X, LIU X J, DA H , et al. Symmetrical solid oxide fuel cells with impregnated SrFe0.75Mo0.25O3-δ electrodes.J. Power Sources, 2014,252:58-63. |
| [17] | GAO J, MENG X, LUO T , et al. Symmetrical solid oxide fuel cells fabricated by phase inversion tape casting with impregnated SrFe0.75Mo0.25O3-δ(SFMO) electrodes.International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, 2017,42(29):18499-18503. |
| [18] | LIU F, ZHANG L, HUANG G , et al. High performance ferrite-based anode La0.5Sr0.5Fe0.9Mo0.1O3-δ for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cell.Electrochimica Acta, 2017,255:118-126. |
| [19] | QIAO J, CHEN W, WANG W , et al. The Ca element effect on the enhancement performance of Sr2Fe1.5Mo0.5O6-δ perovskite as cathode for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells.J. Power Sources, 2016. 331:400-407. |
| [20] | MENG X, HAN D, WU H , et al. Characterization of SrFe0.75Mo0.25O3-δ-La0.9Sr0.1Ga0.8Mg0.2O3-δ composite cathodes prepared by infiltration.Journal of Power Sources, 2014,246(Supplement C):906-911. |
| [21] | MUÑOZ-GARCÍA A B, BUGARIS D E, PAVONE M , et al. Unveiling structure-property relationships in Sr2Fe1.5Mo0.5O6-δ, an electrode material for symmetric solid oxide fuel cells.Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012,134(15):6826-6833. |
| [22] | XIAO G L, CHAO J, QING L , et al.. Ni modified ceramic anodes for solid oxide fuel cells.Journal of Power Sources, 2012,201:43-48. |
| [23] | WANG Y, LIU T, LI M , et al. Exsolved Fe-Ni nano-particles from Sr2Fe1.3Ni0.2Mo0.5O6 perovskite oxide as a cathode for solid oxide steam electrolysis cells.Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2016,4(37):14163-14169. |
| [24] | KUBO J, UEDA W . Catalytic behavior of AMoO x(A=Ba, Sr) in oxidation of 2-propanol.Materials Research Bulletin, 2009,44(4):906-912. |
| [25] | HE B, ZHAO L, SONG S , et al. Sr2Fe1.5Mo0.5O6-δ-Sm0.2Ce0.8O1.9 composite anodes for intermediate-temperature solid oxide fuel cells.Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2012,159(5):B619-B626. |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [3] | QU Jifa, WANG Xu, ZHANG Weixuan, ZHANG Kangzhe, XIONG Yongheng, TAN Wenyi. Enhanced Sulfur-resistance for Solid Oxide Fuel Cells Anode via Doping Modification of NaYTiO4 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 489-496. |
| [4] | LÜ Xinyi, XIANG Hengyang, ZENG Haibo. Long-range Ordered Films Boost Efficient Perovskite Quantum Dot Light-emitting Devices [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 111-112. |
| [5] | QU Mujing, ZHANG Shulan, ZHU Mengmeng, DING Haojie, DUAN Jiaxin, DAI Henglong, ZHOU Guohong, LI Huili. CsPbBr3@MIL-53 Nanocomposite Phosphors: Synthesis, Properties and Applications in White LEDs [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1035-1043. |
| [6] | XIAO Zichen, HE Shihao, QIU Chengyuan, DENG Pan, ZHANG Wei, DAI Weideren, GOU Yanzhuo, LI Jinhua, YOU Jun, WANG Xianbao, LIN Liangyou. Nanofiber-modified Electron Transport Layer for Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(7): 828-834. |
| [7] | ZHANG Hui, XU Zhipeng, ZHU Congtan, GUO Xueyi, YANG Ying. Progress on Large-area Organic-inorganic Hybrid Perovskite Films and Its Photovoltaic Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 457-466. |
| [8] | CHEN Tian, LUO Yuan, ZHU Liu, GUO Xueyi, YANG Ying. Organic-inorganic Co-addition to Improve Mechanical Bending and Environmental Stability of Flexible Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 477-484. |
| [9] | YU Man, GAO Rongyao, QIN Yujun, AI Xicheng. Influence of Upconversion Luminescent Nanoparticles on Hysteresis Effect and Ion Migration Kinetics in Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 359-366. |
| [10] | CHEN Zhengpeng, JIN Fangjun, LI Mingfei, DONG Jiangbo, XU Renci, XU Hanzhao, XIONG Kai, RAO Muming, CHEN Chuangting, LI Xiaowei, LING Yihan. Double Perovskite Sr2CoFeO5+δ: Preparation and Performance as Cathode Material for Intermediate-temperature Solid Oxide Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 337-344. |
| [11] | LIU Suolan, LUAN Fuyuan, WU Zihua, SHOU Chunhui, XIE Huaqing, YANG Songwang. In-situ Growth of Conformal SnO2 Layers for Efficient Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1397-1403. |
| [12] | WANG Yu, XIONG Hao, HUANG Xiaokun, JIANG Linqin, WU Bo, LI Jiansheng, YANG Aijun. Regulation of Low-dose Stannous Iso-octanoate for Two-step Prepared Sn-Pb Alloyed Perovskite Solar Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(12): 1339-1347. |
| [13] | ZHOU Zezhu, LIANG Zihui, LI Jing, WU Congcong. Preparation of MAPbI3 Perovskite Solar Cells/Module via Volatile Solvents [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1197-1204. |
| [14] | LI Qianyuan, LI Jiwei, ZHANG Yuhan, LIU Yankang, MENG Yang, CHU Yu, ZHU Yijia, XU Nuoyan, ZHU Liang, ZHANG Chuanxiang, TAO Haijun. Enhanced Photovoltaic Performance of Perovskite Solar Cells by PbTiO3 Modification and Polarization Treatment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1205-1211. |
| [15] | DAI Xiaodong, ZHANG Luwei, QIAN Yicheng, REN Zhixin, CAO Huanqi, YIN Shougen. Controlling Vertical Composition Gradients in Sn-Pb Mixed Perovskite Solar Cells via Solvent Engineering [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(9): 1089-1096. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||