
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (5): 557-564.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170308
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
DU Yu-Cheng1, WANG Xue-Kai1, HOU Rui-Qin2, WU Jun-Shu1, ZHANG Shi-Hao1, QI Chao1
Received:2017-06-21
Revised:2017-09-28
Published:2018-05-20
Online:2018-04-26
Supported by:CLC Number:
DU Yu-Cheng, WANG Xue-Kai, HOU Rui-Qin, WU Jun-Shu, ZHANG Shi-Hao, QI Chao. In-situ Growth of Nb2O5 Nanorods on Diatomite and Highly Effective Removal of Cr(VI)[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(5): 557-564.
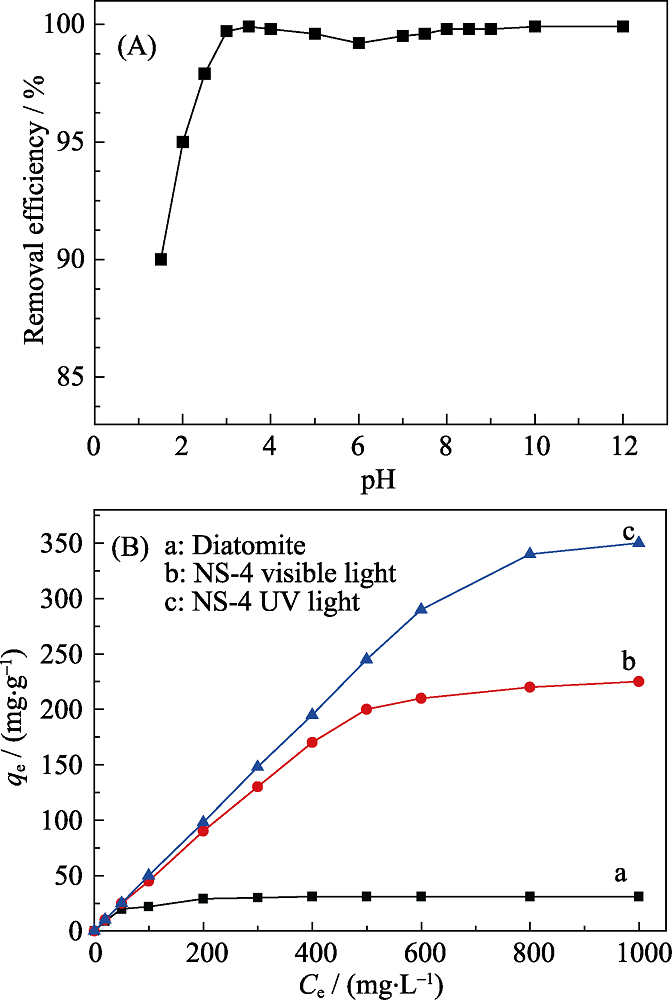
Fig. 5 (A) Effect of the solution pH on the efficiency of Cr(VI) adsorption, and (B) effect of the initial Cr (Ⅵ) concentrations on the efficiency of Cr(Ⅵ) adsorption under UV and visible light irradiation
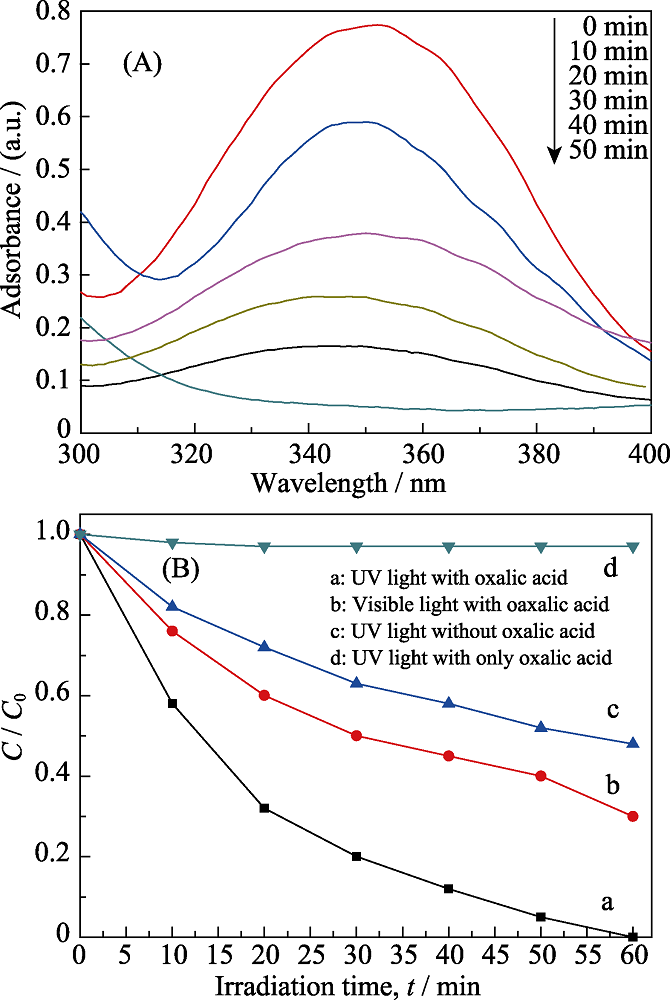
Fig. 6 (A) Time-dependent ultraviolet-visible (UV) absorption spectrum of the Cr(Ⅵ) reduction by the sample NS-4 and (B) the time-dependent photoreduction rate under different conditions
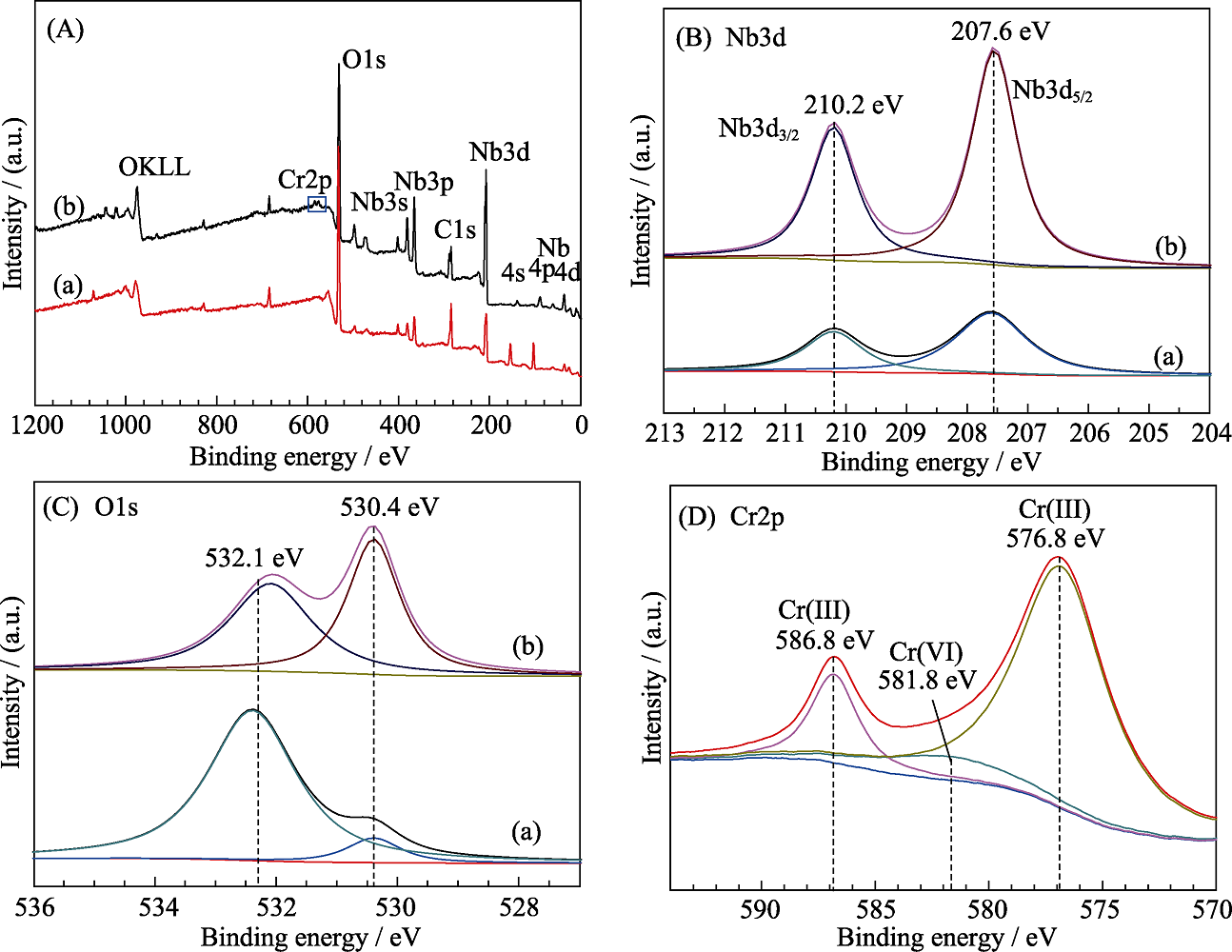
Fig. 9 (A) Full-scan XPS spectra, (B) Nb3d XPS spectra, and (C) O 1s XPS spectra of NS-4 (a) before and (b) after the photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ), and (D) Cr2p XPS spectrum of NS-4 sample after the photocatalytic reduction of Cr(Ⅵ)
| [1] | METIN G, DUYGU V, AYSE M.Removal of trivalent chromium from water using low-cost natural diatomite.J. Hazard. Mater., 2008, 160(2/3): 318-323. |
| [2] | JIANG BO, XIN SHUAI-SHUAI, GAO LI,et al. Dramatically enhanced aerobic Cr(VI) reduction with scrap zero-valent aluminum induced by oxalate. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2016, 308: 588-596. |
| [3] | HANS R, SENANAYAKE G, DHARMASIRI L C S,et al. A preliminary batch study of sorption kinetics of Cr(VI) ions from aqueous solutions by a magnetic ion exchange (MIEX®;) resin and determination of film/pore diffusivity. Hydrometallurgy, 2016, 164: 208-218. |
| [4] | FU XIAO-FEI, YANG HAN-PEI, LU GUANG-HUA,et al. Improved performance of surface functionalized TiO2/activated carbon for adsorption-photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI) in aqueous solution. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing, 2015, 39: 362-370. |
| [5] | DINDA D, KUMAR S S.Sulfuric acid doped poly diaminopyridine/ graphene composite to remove high concentration of toxic Cr(VI). Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2015, 291: 93-101. |
| [6] | GUAN XIAO-HONG, DU JUAN-SHAN, MENG XIAO-GUANG,et al. Application of titanium dioxide in arsenic removal from water: a review. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 215-216(10): 1-16. |
| [7] | LI HUI, LI WEI, ZHANG YAN-JUN,et al. Chrysanthemum-like a-FeOOH microspheres produced by a simple green method and their outstanding ability in heavy metal ion removal . J. Mater. Chem., 2011, 21: 7878-7881. |
| [8] | MISHRA S, BHARAGAVA R N.Toxic and genotoxic effects of hexavalent chromium in environment and its bioremediation strategies. Journal of Environmental Science & Health Part C Environmental Carcinogenesis & Ecotoxicology Reviews, 2016, 34(1): 1-32. |
| [9] | YAO HUA, GUO LAN, JIANG BING-HUA,et al. Oxidative stress and chromium(VI) carcinogenesis. Journal of Environmental Pathology Toxicology & Oncology Official Organ of the International Society for Environmental Toxicology & Cancer, 2008, 27(2): 77-88. |
| [10] | WISE S S, HOLMES A L, SR J P W. Particulate and soluble hexavalent chromium are cytotoxic and genotoxic to human lung epithelial cells. Mutation Research/genetic Toxicology & Environmental Mutagenesis, 2006, 610(1/2): 2-7. |
| [11] | MYROSLAV SPRYNSKYY.The separation of uranium ions by natural and modified diatomite from aqueous solution. Hazard. Mater. , 2010, 181: 700-707. |
| [12] | LI CONG-JU, LI YONG-JIAN, WANG JIAO-NA,et al. PA6@FexOy nanofibrous membrane preparation and its strong Cr (VI)- removal performance. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 220: 294-301. |
| [13] | LOPES O F, PARIS E C, RIBERIRO C.Synthesis of Nb2O5, nanoparticles through the oxidant peroxide method applied to organic pollutant photodegradation: a mechanistic study. Applied Catalysis B Environmental, 2014, 144(2): 800-808. |
| [14] | ZHAO YUN, ELEY CLIVE, HU JING-PING,et al. Shape- dependent acidity and photocatalytic activity of Nb2O5 nanocrystals with an active TT (001) surface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 51(16): 3846-3849. |
| ZHAO YUN, ELEY CLIVE, HU JING-PING,et al. Shape- dependent acidity and photocatalytic activity of Nb2O5 nanocrystals with an active TT (001) surface. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 51(16): 3846-3849. | |
| [15] | GAO BAO-JIAO, JIANG PENG-FEI, AN FU-QIANG,et al. Studies on the surface modification of diatomite with polyethyleneimine and trapping effect of the modified diatomite for phenol. Applied Surface Science, 2005, 250(1-4): 273-279. |
| [16] | ONOZATO T, KATASE T, YAMAMOTO A,et al. Optoelectronic properties of valence-state-controlled amorphous niobium oxide. Journal of Physics Condensed Matter An Institute of Physics Journal, 2016, 28(25): 1-8. |
| [17] | HUO QI-SHENG, MARGOLESE DAVID I, CIESLA U LRIKE,et al. Organization of organic molecules with inorganic molecular species into nanocomposite biphase arrays. Chemistry of Materials, 1994, 6(8): 1176-1191. |
| [18] | YAN CHENG-LIN, XUE DONG-FENG.Formation of Nb2O5 nanotube arrays through phase transformation. Advanced Materials, 2010, 20(5): 1055-1058. |
| [19] | DU YU-CHENG, YAN JING, MENG QI,et al. Fabrication and excellent conductive performance of antimony-doped tin oxide- coated diatomite with porous structure. Materials Chemistry & Physics, 2012, 133(2/3): 907-912. |
| [20] | SHENG GUO-DONG, WANG SUO-WEI, HU JUN,et al. Adsorption of Pb(II) on diatomite as affected via aqueous solution chemistry and temperature. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects, 2009, 339(1/2/3): 159-166. |
| [21] | KHRAISHEH M A, AL-GHOUTI M A, ALLEN S J,et al. Effect of OH and silanol groups in the removal of dyes from aqueous solution using diatomite. Water Research, 2005, 39(5): 922-932. |
| [22] | HADJAR H, HAMDI B, JABER M,et al. Elaboration and characterization of new mesoporous materials from diatomite and charcoal. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials, 2007, 107(3): 219-226. |
| [23] | CHENG YUE-HONG, JIANG HENG, GONG HONG,et al. Synthesis and characterization of niobic acid. Industrial Catalysis, 2011,19(1): 50-52. |
| [24] | JULIEN C M, MASSOT M.Spectroscopic studies of the structural transitions in positive electrodes for lithium batteries. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics, 2002, 4(17): 4226-4235. |
| [1] | WEI Jianwen, ZHANG Lijuan, GENG Linlin, LI Yu, LIAO Lei, WANG Dunqiu. Novel CO2 Adsorbent Prepared with ZSM-5/MCM-48 as Support: High Adsorption Property and Its Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 833-839. |
| [2] | JIANG Zongyu, HUANG Honghua, QING Jiang, WANG Hongning, YAO Chao, CHEN Ruoyu. Aluminum Ion Doped MIL-101(Cr): Preparation and VOCs Adsorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 747-753. |
| [3] | HONG Peiping, LIANG Long, WU Lian, MA Yingkang, PANG Hao. Structure Regulation of ZIF-67 and Adsorption Properties for Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 388-396. |
| [4] | WU Guangyu, SHU Song, ZHANG Hongwei, LI Jianjun. Enhanced Styrene Adsorption by Grafted Lactone-based Activated Carbon [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 390-398. |
| [5] | XIE Tian, SONG Erhong. Effect of Elastic Strains on Adsorption Energies of C, H and O on Transition Metal Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1292-1300. |
| [6] | CHAO Shaofei, XUE Yanhui, WU Qiong, WU Fufa, MUHAMMAD Sufyan Javed, ZHANG Wei. Efficient Potassium Storage through Ti-O-H-O Electron Fast Track of MXene Heterojunction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1212-1220. |
| [7] | MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [8] | GUO Chunxia, CHEN Weidong, YAN Shufang, ZHAO Xueping, YANG Ao, MA Wen. Adsorption of Arsenate in Water by Zirconia-halloysite Nanotube Material [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 529-536. |
| [9] | WANG Shiyi, FENG Aihu, LI Xiaoyan, YU Yun. Pb (II) Adsorption Process of Fe3O4 Supported Ti3C2Tx [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 521-528. |
| [10] | YU Yefan, XU Ling, NI Zhongbing, SHI Dongjian, CHEN Mingqing. Prussian Blue Modified Biochar: Preparation and Adsorption of Ammonia Nitrogen from Sewage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 205-212. |
| [11] | LING Jie, ZHOU Anning, WANG Wenzhen, JIA Xinyu, MA Mengdan. Effect of Cu/Mg Ratio on CO2 Adsorption Performance of Cu/Mg-MOF-74 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1379-1386. |
| [12] | TANG Ya, SUN Shengrui, FAN Jia, YANG Qingfeng, DONG Manjiang, KOU Jiahui, LIU Yangqiao. PEI Modified Hydrated Calcium Silicate Derived from Fly Ash and Its adsorption for Removal of Cu (II) and Catalytic Degradation of Organic Pollutants [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1281-1291. |
| [13] | DAI Jieyan, FENG Aihu, MI Le, YU Yang, CUI Yuanyuan, YU Yun. Adsorption Mechanism of NaY Zeolite Molecular Adsorber Coating on Typical Space Contaminations [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(10): 1237-1244. |
| [14] | WANG Hongning, HUANG Li, QING Jiang, MA Tengzhou, HUANG Weiqiu, CHEN Ruoyu. Mesoporous Organic-inorganic Hybrid Siliceous Hollow Spheres: Synthesis and VOCs Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(9): 991-1000. |
| [15] | LIU Cheng, ZHAO Qian, MOU Zhiwei, LEI Jiehong, DUAN Tao. Adsorption Properties of Novel Bismuth-based SiOCNF Composite Membrane for Radioactive Gaseous Iodine [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1043-1050. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||