
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (11): 1195-1201.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170027
• RESEARCH PAPER • Previous Articles Next Articles
CHEN Jian-Xun, WU Shu-Sen, ZHANG Ya-Nan, MAO You-Wu, LÜ Shu-Lin
Received:2017-01-13
Revised:2017-03-10
Published:2017-11-20
Online:2017-10-20
Supported by:CLC Number:
CHEN Jian-Xun, WU Shu-Sen, ZHANG Ya-Nan, MAO You-Wu, LÜ Shu-Lin. Reference Hydrogen Partial Pressure on Accurancy of Hydrogen Determination Utilizing Concentration Cell Type Sensor Based on Solid State Electrolyte[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(11): 1195-1201.
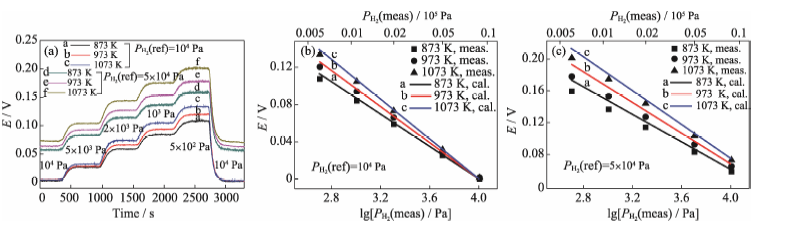
Fig. 6 Sensing results of type A sensor: (a) response curves, (b, c) stable electromotive forces vs reference hydrogen partial pressure of 104 Pa and 5×104 Pa, respectively (The solid straight lines represent the electromotive forces calculated according to function (6))
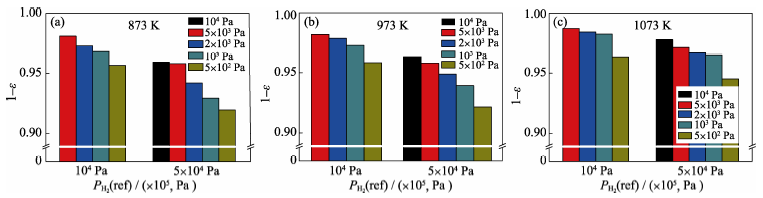
Fig. 7 Electromotive force ratios of measurement values to theory Nernst values for type A sensor with variable reference hydrogen partial pressure at temperatures of 873 K (a), 973 K (b) and 1073 K (c)
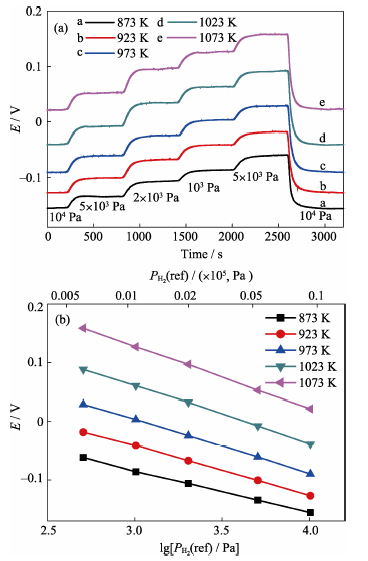
Fig. 8 Electromotive force response curves (a) and stable electromotive forces (b) of type B sensor towards variable reference hydrogen partial pressures
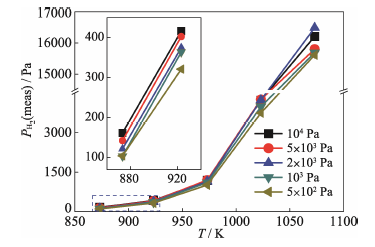
Fig. 9 Hydrogen pressures of (β+δ) ZrHx at temperatures ranging from 873 K to 1073 K calculated according to Equation (8) utilizing electromotive forces values in Fig. 8(b)
| In(Peq / Pa) | ΔHf/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔSf/(kJ·K-1·mol-1) | Temperature/K | Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -26119/T+34.1 | -217.2 | -0.284 | 823-1123 | Exp. | Ref. [20] |
| -28160/T+37 | -234.1 | -0.305 | 823-873 | Calc. | Ref. [21] |
| -25078/T+32.9 | -208.5 | -0.274 | 873-1073 | Exp. | This work |
Table 1 Comparisons of (β+δ) ZrHx hydrogen partial pressures, formation enthalpy and formation entropy obtained from different research methods
| In(Peq / Pa) | ΔHf/(kJ·mol-1) | ΔSf/(kJ·K-1·mol-1) | Temperature/K | Method | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| -26119/T+34.1 | -217.2 | -0.284 | 823-1123 | Exp. | Ref. [20] |
| -28160/T+37 | -234.1 | -0.305 | 823-873 | Calc. | Ref. [21] |
| -25078/T+32.9 | -208.5 | -0.274 | 873-1073 | Exp. | This work |
| [1] | SCHNELLER T, SCHOBER T. Chemical solution eposition prepared dense proton conducting Y-doped BaZrO3 thin films for SOFC and sensor devices. Solid State Ionics#/magtechI #, 2003, 3- 4: 131-136. |
| [2] | AZAD A, IRVINE J. Synthesis , chemical stability and proton conductivity of the perovksites Ba ( Ce , Zr ) 1-xScxO3-δ. Solid State Ionics , 2007, 7-10: 635-640. |
| [3] | SERRET P, COLOMINAS S, REYES G, et al. Characterization of ceramic materials for electrochemical hydrogen sensors. Fusion Engineering. Characterization of ceramic materials for electrochemical hydrogen sensors. Fusion Engineering and Design#/magtechI#, 2011, 9-11: 2446-2449. |
| [4] | LI Y, WANG C Z, ZHANG Z L,et al. A hydrogen sensor using SrCe0.95Yb0.05O3-α as proton conductor and YHx+YH2-z as reference electrode for determining hydrogen pressure in solid steel. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2010, 10: 957-960. |
| [5] | JEON S Y, LIM D K, CHOI M B,et al. Hydrogen separation by Pd-CaZr0.9Y0.1O3-δ cermet composite membranes. Separation and Purification Technology, 2011, 3: 337-341. |
| [6] | WANG D, LIU C M, LI S L,et al. Determination of hydrogen content and dehydrogenation in molten aluminum by concentration cell method. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(5): 505-509. |
| [7] | SOUZA E C, MUCCILLO R.Properties and applications of perovskite proton conductor.Materials Research, 2010, 13(3): 385-394. |
| [8] | HAN J D, WEN Z Y, ZHANG J C, et al. Electrical conductivity of fully densified nano CaZr0.90In0.10O3-δ ceramics prepared by a water- based gel precipitation method. Solid State Ionics#/magtechI#. Electrical conductivity of fully densified nano CaZr0.90In0.10O3-δ ceramics prepared by a water- based gel precipitation method. Solid State Ionics, 2009, 2-3: 154-159. |
| [9] | ZHOU M H, AHMAD A.Sol-Gel processing of In-doped CaZrO3 solid electrolyte and the impedimetric sensing characteristics of humidity and hydrogen.Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2008, 1: 285-291. |
| [10] | DAI L, WANG L, SHAO G J,et al. A novel amperometric hydrogen sensor based on nano-structured ZnO sensing electrode and CaZr0.9In0.1O3-δ electrolyte. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2012, 173: 85-92. |
| [11] | KURITA N, OOTAKE K, FUKATSU N.The electromotive force of a hydrogen and/or oxygen concentration cell using 10mol% In-doped CaZrO3 as the solid electrolyte.Journal of The Electrochemical Society, 2011, 158(6): B667-B674. |
| [12] | HAN J D, WEN Z Y, ZHANG J C,et al. CaZrO3 based high temperature proton conductors. Progress in Chemistry, 2012, 24(9): 1845-1856. |
| [13] | KURITA N, FUKATSU N, MIYAMOTO S,et al. The measurement of hydrogen activities in molten copper using an oxide protonic conductor. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions B, 1996, 27(12): 929-935. |
| [14] | SCHWANDT C.Solid state electrochemical hydrogen sensor for aluminium and aluminium alloy melts.Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical, 2013, 187: 227-233. |
| [15] | SCHWANDT C, FRAY D J.The titanium/hydrogen system as the solid-state reference in high-temperature proton conductor-based hydrogen sensors.Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2006, 5: 557-565. |
| [16] | HILLS M P, SCHWANDT C, KUMAR R V.The zirconium/hydrogen system as the solid-state reference of a high-temperature proton conductor-based hydrogen sensor.Journal of Applied Electrochemistry, 2011, 5: 499-506. |
| [17] | ZHANG J C, WEN Z Y, CHI X W,et al. Proton conducting CaZr0.9In0.1O3-δ ceramic membrane prepared by tape casting. Solid State Ionics, 2012, 225: 291-296. |
| [18] | LI Y, LU S L, WANG C Z,et al. Preparation and properties of CaZr1-xInxO3-α proton conductor. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(4): 427-432. |
| [19] | LEXCELLENT C, GONDOR G.Analysis of hydride formation for hydrogen storage: pressure-composition isotherm curves modeling.Intermetallics, 2007, 15(7): 934-944. |
| [20] | ZUZEK E, ABRIATA J P.The H-Zr (hydrogen-zirconium) system.Bulletin of Alloy Phase Diagrams, 1990, 11(4): 385-395. |
| KÖNIGSBERGERA E, ERIKSSONB G, OATESC W A. Optimisation of the thermodynamic properties of the Ti-H and Zr-H system.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2000, 299: 148-152. |
| [1] | LI Dong, LEI Chao, LAI Hua, LIU Xiao-Lin, YAO Wen-Li, LIANG Tong-Xiang, ZHONG Sheng-Wen. Recent Advancements in Interface between Cathode and Garnet Solid Electrolyte for All Solid State Li-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(7): 694-702. |
| [2] | ZHANG Zhi-Zhen, SHI Si-Qi, HU Yong-Sheng, CHEN Li-Quan. Sol-Gel Synthesis and Conductivity Properties of Sodium Ion Solid State Electrolytes Na3Zr2Si2PO12 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(11): 1255-1260. |
| [3] | SU Xin-Tai,LIU Rui-Quan,HU Yun-Xia,XIE Ya-Hong,WANG Ji-De. Preparation of Nanocrystalline Ba3(Ca1.18Nb1.82)O9-δ Powder by UsingCitrate Sol-Gel Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2004, 19(1): 229-233. |
| [4] | ZHANG Jian-Min,WANG Ji-De,WANG Jiang-Ying,YUE Fan. Electrochemical Research of Dense SrCe0.95Y0.05O3-δ under Atmosphere Contained Hydrogen [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2001, 16(3): 559-562. |
| [5] | ZHU Bin,Mellander B -E Mellander,LIU Wanyu,CHEN Shuyu,XIU Xiangqian,WANG Dazhi. A Novel Solid Electrolyte Material LiNaSO4-Al2O3 for Intermediate Temperature Fuel Cells [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 1997, 12(3): 412-414. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||