
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (6): 643-648.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160509
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
WANG Mi-Tang, FANG Long, LI Mei, LIU Zhao-Gang, HU Yan-Hong, ZHANG Xiao-Wei
Received:2016-09-12
Revised:2016-12-05
Published:2017-06-20
Online:2017-05-27
About author:WANG Mi-Tang. E-mail: btwmt@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
WANG Mi-Tang, FANG Long, LI Mei, LIU Zhao-Gang, HU Yan-Hong, ZHANG Xiao-Wei. Effect of Rare Earth Dopant on Thermal Stability and Structure of ZnO-B2O3-SiO2 Glass[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(6): 643-648.
| Glass | Tg /℃ | Tc /℃ | Tp /℃ | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 570 | 699 | 727 | 6.3 |
| L1 | 568 | 701 | 734 | 7.7 |
| L2 | 565 | 692 | 728 | 8.1 |
| L3 | 565 | 689 | 724 | 7.7 |
| L4 | 565 | 695 | 728 | 7.6 |
| Y1 | 573 | 708 | 739 | 7.3 |
| Y2 | 575 | 715 | 744 | 7.1 |
| Y3 | 576 | 724 | 750 | 6.7 |
Table 1 Characteristic temperature of glasses doped with REO
| Glass | Tg /℃ | Tc /℃ | Tp /℃ | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| B0 | 570 | 699 | 727 | 6.3 |
| L1 | 568 | 701 | 734 | 7.7 |
| L2 | 565 | 692 | 728 | 8.1 |
| L3 | 565 | 689 | 724 | 7.7 |
| L4 | 565 | 695 | 728 | 7.6 |
| Y1 | 573 | 708 | 739 | 7.3 |
| Y2 | 575 | 715 | 744 | 7.1 |
| Y3 | 576 | 724 | 750 | 6.7 |
| Glass | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P7 | P8 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | C | A | C | A | C | A | C | A | C | A | |
| B0 | 580.4 | 693.2 | 21.9 | 837.3 | 6.1 | 914.6 | 30.4 | 1328.4 | 89.6 | 1464.8 | 25.0 |
| L1 | 581.4 | 692.4 | 14.3 | 886.3 | 21.1 | 997.1 | 39.4 | 1343.3 | 36.6 | 1445.2 | 43.2 |
| L2 | 581.8 | 695.8 | 15.0 | 870.0 | 13.8 | 965.5 | 41.3 | 1337.4 | 16.4 | 1431.7 | 56.1 |
| L3 | 587.8 | 702.8 | 19.8 | 862.2 | 14.2 | 956.8 | 54.3 | 1331.2 | 33.8 | 1429.8 | 58.9 |
| L4 | 584.9 | 704.3 | 18.9 | 851.4 | 10.0 | 943.2 | 50.1 | 1332.7 | 32.3 | 1430.2 | 49.5 |
| Y1 | 585.3 | 692.3 | 9.9 | 883.3 | 17.2 | 988.3 | 33.1 | 1370.8 | 27.2 | 1473 | 43.1 |
| Y2 | 585.9 | 696.7 | 18.5 | 871.9 | 15.4 | 965.4 | 41.2 | 1351.7 | 30.3 | 1450.2 | 43.0 |
| Y3 | 588.3 | 700.4 | 15.2 | 867.7 | 12.4 | 958.7 | 37.2 | 1337.6 | 15.7 | 1433.4 | 59.1 |
Table 2 Deconvoluted parameters of the FT-IR spectra of the glasses (the band centers C and the relative area A)
| Glass | P1 | P2 | P3 | P4 | P7 | P8 | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| C | C | A | C | A | C | A | C | A | C | A | |
| B0 | 580.4 | 693.2 | 21.9 | 837.3 | 6.1 | 914.6 | 30.4 | 1328.4 | 89.6 | 1464.8 | 25.0 |
| L1 | 581.4 | 692.4 | 14.3 | 886.3 | 21.1 | 997.1 | 39.4 | 1343.3 | 36.6 | 1445.2 | 43.2 |
| L2 | 581.8 | 695.8 | 15.0 | 870.0 | 13.8 | 965.5 | 41.3 | 1337.4 | 16.4 | 1431.7 | 56.1 |
| L3 | 587.8 | 702.8 | 19.8 | 862.2 | 14.2 | 956.8 | 54.3 | 1331.2 | 33.8 | 1429.8 | 58.9 |
| L4 | 584.9 | 704.3 | 18.9 | 851.4 | 10.0 | 943.2 | 50.1 | 1332.7 | 32.3 | 1430.2 | 49.5 |
| Y1 | 585.3 | 692.3 | 9.9 | 883.3 | 17.2 | 988.3 | 33.1 | 1370.8 | 27.2 | 1473 | 43.1 |
| Y2 | 585.9 | 696.7 | 18.5 | 871.9 | 15.4 | 965.4 | 41.2 | 1351.7 | 30.3 | 1450.2 | 43.0 |
| Y3 | 588.3 | 700.4 | 15.2 | 867.7 | 12.4 | 958.7 | 37.2 | 1337.6 | 15.7 | 1433.4 | 59.1 |
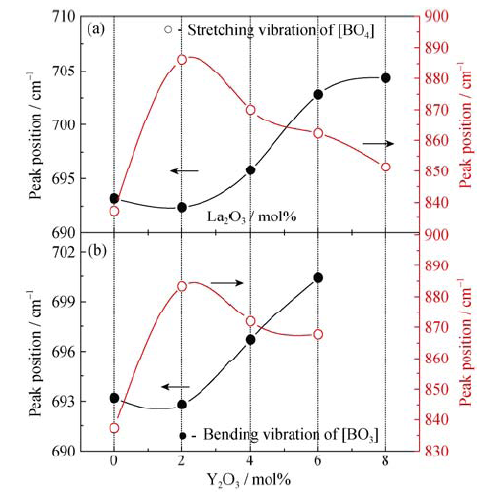
Fig. 7 (a) Peak position of bending vibration of [BO3] P2 and stretching vibration of [BO4] P3 vs content of La2O3; (b) Peakposition of bending vibration of [BO3] P2 and stretching vibration of [BO4] P3 vs content of Y2O3.
| [1] | KHALKHALI Z, HAMNABARD Z, QAZVINI S S A, et al. Preparation, phase formation and photoluminescence properties of ZnO-SiO2-B2O3 glasses with different ZnO/B2O3 ratios.Optical Materials, 2012, 34(5): 850-855. |
| [2] | SHEN Y, HOU L Y, ZUO G F, et al.Preparation of ZnO-B2O3-SiO2: Mn2+ optical-storage glass-ceramics with different ZnF2 dopant by Sol-Gel method.Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2015, 73(1): 192-198. |
| [3] | ANNAPURNA K, KUMAR A, DWIVEDI R N, et al.Fluorescence spectra of Cu+: ZnO-B2O3-SiO2 glass.Materials Letters, 2000, 45(1): 23-26. |
| [4] | ANNAPURNA K, DWIVEDI R N, KUNDU P, et al.Blue emission spectrum of Ce3+: ZnO-B2O3-SiO2 optical glass.Materials Letters, 2004, 58(5): 787-789. |
| [5] | ANNAPURNA K, DWIVEDI R D, KUNDU P, et al.Emission properties of Mn2+: ZnO-B2O3-SiO2 glass.Journal of Materials Science Letters, 2003, 22(12): 873-875. |
| [6] | ZHANG B, CHEN Q, SONG L, et al.Fabrication and properties of novel low-melting glasses in the ternary system ZnO-Sb2O3-P2O5.Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2008, 354(18): 1948-1954. |
| [7] | ZHENG W H, CHENG J S, TANG L Y, et al.Effect of Y2O3 addition on viscosity and crystallization of the lithium aluminosilicate glasses.Thermochimica Acta, 2007, 456(1): 69-74. |
| [8] | XIAO L Y, XIAO Q, LIU Y L, et al.A transparent surface-crystallized Eu2+, Dy3+ co-doped strontium aluminate long-lasting phosphorescent glass-ceramic.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2010, 495(1): 72-75. |
| [9] | XU X H, YAN X, YU X, et al.Concentration-dependent effects of optical storage properties in CSSO: Dy.Materials Letters, 2013, 99: 158-160. |
| [10] | WANG M T, FANG L, LI M, et al.Dependence of Gd2O3 containing silicate glass workability and fragility on structure.Materials Chemistry and Physics, 2016, 179: 304-309. |
| [11] | QIAN B, LIANG X F, YANG S Y, et al.Raman spectra study on the structure of lanthanum-iron phosphate glasses.Chinese Journal of Inorganic Chemistry, 2013, 29(2): 314-318. |
| [12] | LU P, ZHENG Y, CHENG J S, et al.Effect of La2O3 addition on crystallization and properties of Li2O-Al2O3-SiO2 glass-ceramics.Ceramics International, 2013, 39(7): 8207-8212. |
| [13] | WANG J, LIU C, ZHANG G K, et al.Crystallization properties of magnesium aluminosilicate glass-ceramics with and without rare-earth oxides. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids, 2015, 419: 1-5. |
| [14] | SINGH K, GUPTA N, PANDEY O P.Effect of Y2O3 on the crystallization behavior of SiO2-MgO-B2O3-Al2O3 glasses.Journal of Materials Science, 2007, 42(15): 6426-6432. |
| [15] | COSTANTINI A, FRESA R, BURI A, et al.Effect of the substitution of Y2O3 for CaO on the bioactivity of 2.5CaO-2SiO2 glass.Biomaterials, 1997, 18(6): 453-458. |
| [16] | WANG M T, LI X W, LI M, et al.Corrosion behavior of ZnO-B2O3-SiO2 glass doped with rare earth oxides.Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2015, 43(4): 504-510. |
| [17] | LI X W, LI M, WANG M T, et al.Effects of neodymium and gadolinium on weathering resistance of ZnO-B2O3-SiO2 glass.Journal of Rare Earths, 2014, 32(9): 874-878. |
| [18] | ZHANG Y Q, WANG M T, LI M, et al.The effect of Sm2O3 on the chemical stability of borosilicate glass and glass ceramics.Journal of Wuhan University of Technology-Mater. Sci. Ed., 2014, 29(4): 692-697. |
| [19] | 西北轻工业学院. 玻璃工艺学. 北京: 中国轻工业出版社, 2006: 66-74. |
| [20] | SHANNON R D.Revised effective ionic radii and systematic studies of interatomie distances in halides and chaleogenides.Acta Crystallographica Section A, 1976, 32(5): 751-767. |
| [21] | 刘光华. 稀土材料学. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2007: 19-34. |
| [22] | W· 福格尔. 玻璃化学. 北京: 轻工业出版社, 1988: 22-25. |
| [23] | LAFI O A, IMRAN M M A. Compositional dependence of thermal stability, glass-forming ability and fragility index in some Se-Te-Sn glasses.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2011, 509(16): 5090-5094. |
| [24] | SAAD M, POULAIN M. Glass forming ability criteria. Materials Science Forum, 1987, 19-20(September): 11-18. |
| [25] | NOVATSKI A, STEIMACHER A, MEDINA A N, et al.Relations among nonbridging oxygen, optical properties, optical basicity, and color center formation in CaO-MgO aluminosilicate glasses.Journal of Applied physics, 2008, 104(9): 1-7. |
| [26] | HOU L Y, ZUO G F, SHEN Y, et al.Effects of the replacing content of ZnBr2 on the properties of ZnO-B2O3-SiO2: Mn2+ glass-ceramics. Ceramics International, 2014, 40(8): 13097-13103. |
| [27] | MANAL A B, FOUAD E D.Role of oxygen on the optical properties of borate glass doped with ZnO. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2011, 184(10): 2762-2769. |
| [28] | RANI S, SANGHI S, AHLAWAT N, et al.Influence of Bi2O3 on thermal, structural and dielectric properties of lithium zinc bismuth borate glasses.Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2014, 597(10): 110-118. |
| [29] | MOTKE S G, YAWALE S P, YAWALE S S.Infrared spectra of zinc doped lead borate glasses.Bulletin of Materials Science, 2002, 25(1): 75-78. |
| [30] | EL-EGILI K.Infrared studies of Na2O-B2O3-SiO2 and Al2O3-Na2O-B2O3-SiO2 glasses.Physica B, 2003, 325(1-4): 340-348. |
| [31] | SAMEE M A, EDUKONDALU A, AHMMAD S K, et al.Mixed-Alkali Effect in Li2O-Na2O-K2O-B2O3 Glasses: Infrared and Optical Absorption Studies.Journal of Electronic Materials, 2013, 42(8): 2516-2524. |
| [32] | 干福熹. 光学玻璃. 北京:科学出版社, 1982: 370-376. |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | WEI Zhifan, CHEN Guoqing, ZU Yufei, LIU Yuan, LI Minghao, FU Xuesong, ZHOU Wenlong. ZrB2-HfSi2 Ceramics: Microstructure and Formation Mechanism of Core-rim Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 817-825. |
| [3] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [4] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | ZHOU Yangyang, ZHANG Yanyan, YU Ziyi, FU Zhengqian, XU Fangfang, LIANG Ruihong, ZHOU Zhiyong. Enhancement of Piezoelectric Properties in CaBi4Ti4O15-based Ceramics through Bi3+ Self-doping Strategy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 719-728. |
| [6] | HUANG Zipeng, JIA Wenxiao, LI Lingxia. Crystal Structure and Terahertz Dielectric Properties of (Ti0.5W0.5)5+ Doped MgNb2O6 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 647-655. |
| [7] | ZHAO Kaixuan, LIU Wenpeng, DING Shoujun, DOU Renqin, LUO Jianqiao, GAO Jinyun, SUN Guihua, REN Hao, ZHANG Qingli. Nd:YLF Crystal Growth: Raw Materials Preparation by Melting Method and Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 529-535. |
| [8] | GUO Ziyu, ZHU Yunzhou, WANG Li, CHEN Jian, LI Hong, HUANG Zhengren. Effect of Zn2+ Catalyst on Microporous Structure of Porous Carbon Prepared from Phenolic Resin/Ethylene Glycol [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 466-472. |
| [9] | HONG Peiping, LIANG Long, WU Lian, MA Yingkang, PANG Hao. Structure Regulation of ZIF-67 and Adsorption Properties for Chlortetracycline Hydrochloride [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 388-396. |
| [10] | CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | MU Haojie, ZHANG Yuanjiang, YU Bin, FU Xiumei, ZHOU Shibin, LI Xiaodong. Preparation and Properties of ZrO2 Doped Y2O3-MgO Nanocomposite Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 281-289. |
| [12] | BAO Weichao, GUO Xiaojie, XIN Xiaoting, PENG Pai, WANG Xingang, LIU Jixuan, ZHANG Guojun, XU Fangfang. Establishment of Symbiotic Structure with Metal Atomic-layer Phase-separation in Carbide Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 17-22. |
| [13] | ZHOU Fan, TIAN Zhilin, LI Bin. Research Progress on Carbide Ultra-high Temperature Ceramic Anti-ablation Coatings for Thermal Protection System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| [14] | WEI Xiangxia, ZHANG Xiaofei, XU Kailong, CHEN Zhangwei. Current Status and Prospects of Additive Manufacturing of Flexible Piezoelectric Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 965-978. |
| [15] | WANG Xu, LI Xiang, KOU Huamin, FANG Wei, WU Qinghui, SU Liangbi. Effect of Doping with Different Concentrations of Y3+ Ions on the Properties of CaF2 Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1029-1034. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||