
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (5): 466-472.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150469
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
SHI Zhen-Wu1,2, GUO Shao-Bo3, XUE Qun-Hu1
Received:2015-09-28
Revised:2015-12-11
Published:2016-05-20
Online:2016-04-25
About author:SHI Zhen-Wu. E-mail: 545366954@qq.com
CLC Number:
SHI Zhen-Wu, GUO Shao-Bo, XUE Qun-Hu. Preparation, Photocatalytic Property and Antibacterial Property of Ag@TiO2@SiO2 Composite Nanomaterials[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(5): 466-472.
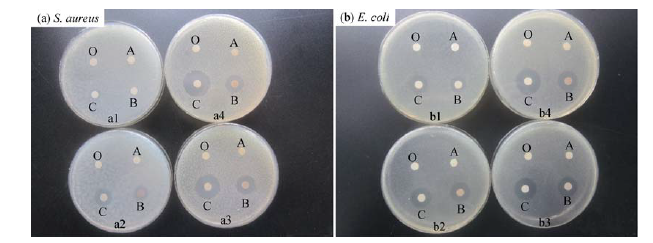
Fig. 6 Inhibition zones of the as-synthesized SiO2 spheres, TiO2@SiO2 composites, Ag, and Ag@TiO2@SiO2 composites against S. aureus (a) and E. coli (b)a1,b1: 0.2 mg/mL; a2,b2: 0.4 mg/mL; a3,b3: 0.6 mg/mL; a4,b4: 0. mg/mL
| Concentration /(mg·mL-1) | B. subtilis -inhibition zones/cm | E.coli-inhibition zones /cm |
|---|---|---|
| Ag Ag@TiO2@SiO2 | Ag Ag@TiO2@SiO2 | |
| 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 | 0.2 0.1 0.5 0.3 1.1 0.7 1.2 0.8 | 0.5 0.3 0.7 0.5 1.1 0.8 1.3 1.0 |
Table 1 Inhibition zone diameters of the Ag and Ag@TiO2@SiO2 against B. subtilis and E. coli.
| Concentration /(mg·mL-1) | B. subtilis -inhibition zones/cm | E.coli-inhibition zones /cm |
|---|---|---|
| Ag Ag@TiO2@SiO2 | Ag Ag@TiO2@SiO2 | |
| 0.2 0.4 0.6 0.8 | 0.2 0.1 0.5 0.3 1.1 0.7 1.2 0.8 | 0.5 0.3 0.7 0.5 1.1 0.8 1.3 1.0 |
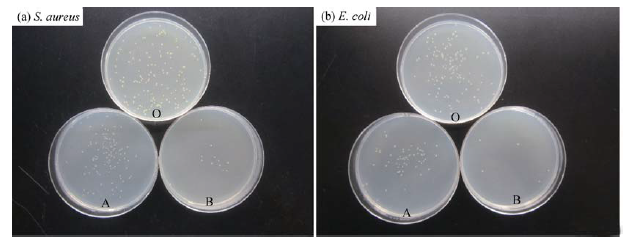
Fig. 7 Spread-plate test results using 0.6 mg/mL of Ag and Ag@TiO2@SiO2 composites against S. aureus (a) and E. coli (b)O: control; A: 0.6 mg/mL commercial Ag; B: 0.6 mg/mL Ag@TiO2@SiO2
| [1] | PARIDA K M, SAHU N.Visible light induced photocatalytic activity of rare earth titania nanocomposites.Journal of Molecular Catalysis A: Chemical, 2008, 287(1/2): 151-158. |
| [2] | FAZIO E, CALANDRA P, LIVERI V T, et al.Synthesis and physico- chemical characterization of Au/TiO2 nanostructures formed by novel “cold” and “hot” nanosoldering of Au and TiO2 nanoparticles dispersed in water.Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochem. Eng. Aspects, 2011, 392(1): 171-177. |
| [3] | KEBIR M, TRARI M, MAACHI R, et al. Relevance of a hybrid process coupling adsorption and visible light photocatalysis involving a new hetero-system CuCo2O4/TiO2 for the removal of hexavalent chromium.Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering, 2015(3): 548-559. |
| [4] | CHI Y, YUAN Q, LI Y, et al.Magnetically separable Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2-Ag microspheres with well-designed nanostructure and enhanced photocatalytic activity.Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 262: 404-411. |
| [5] | XU M W, BAO S J, ZHANG X G.Enhanced photocatalytic activity of magnetic TiO2 photocatalyst by silver deposition.Materials Letters, 2005, 59(17): 2194-2198. |
| [6] | GAO L, NG K, SUN D D.Sulfonated graphene oxide-ZnO-Ag photocatalyst for fast photodegradation and disinfection under visible light. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 262: 826-835. |
| [7] | CHEN H W, KU Y, KUO Y L.Effect of Pt/TiO2 characteristics on temporal behavior of o-cresol decomposition by visible light-induced photocatalysis.Water Research, 2007, 41(10): 2069-2078. |
| [8] | PANDIKUMAR A, RAMARAJ R.Photocatalytic reduction of hexavalent chromium at gold nanoparticles modified titania nanotubes.Materials Chemistry and Physics 2013, 141(2/3): 629-635. |
| [9] | MICHAL M, MALGORZATA G.The newest achievements in synthesis, immobilization and practical applications of antibacterial nanoparticles.Chemical Engineering Journal. 2013, 228: 596-613. |
| [10] | ZHAO W, FENG L, YANG R, ZHENG J, et al.Synthesis, characterization, and photocatalytic properties of Ag modified hollow SiO2/TiO2 hybrid microspheres.Applied Catalysis B: Environmental, 2011, 103(1/2): 181-189. |
| [11] | PANDIKUMAR A, RAMARAJ R. Titanium dioxide-gold nanocomposite materials embedded in silicate Sol-Gel film catalyst for simultaneous photodegradation of hexavalent chromium and methylene blue. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2012, 203-204: 244-250. |
| [12] | CHEN Y H, CHENG H D, CHOU S N.Efficient mineralization of dimethyl phthalate by catalytic ozonation using TiO2/Al2O3 catalyst.Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2011, 192(3): 1017-1025. |
| [13] | SHANMUGAM S, GABASHVILI A, JACOB D S, et al.Synthesis and characterization of TiO2@C core-shell composite nanoparticles and ealuation of their photocatalytic activities.Materials Chemistry, 2006, 18(9): 2275-2282. |
| [14] | CHEN X Y, LU D F, LIN S F.Preparation and properties of sulfur- doped visible-light response S-TiO2/SiO2 photocatalystChinese Journal of Catalysis, 2012, 33(6): 993-999. |
| [15] | ZHOU M J, ZHANG N, HOU C H.Preparation and photocatalytic activity for hydrogen evolution of graphene-ZnIn2S4 nanocomposite spheres.Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 7: 713-718. |
| [16] | GUO S B, MA J Q, CHEN W Q, et al.Study on the antibacterial activity of Ag/TiO2.Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2015, 7: 1946-1950. |
| [17] | Su J W, ZHANG Y X, XU S C, et al.Highly efficient and recyclable triple-shelled Ag@Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2 photocatalysts for degradation of organic pollutants and reduction of hexavalent chromium ions.Nanoscale, 2014, 6(10): 5181-5192. |
| [18] | MA J Q, GUO S B, GUO X H, et al.Study on the antibacterial activity of Ag/TiO2.Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2015, 7: 1946-1950. |
| [19] | MA J Q, GUO S B, GUO X H, et al.A mild synthetic route to Fe3O4@TiO2-Au composites: preparation, characterization and photocatalytic activity.Applied Surface Science, 2015, 353: 1117-1125. |
| [20] | MA J Q, GUO S B, GUO X H, et al.Modified photodeposition of uniform Ag nanoparticles on TiO2 with superior catalytic and antibacterial activities.Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2015, 75: 366-373. |
| [21] | CHIA Y, YUAN Q, LI Y J, et al.Magnetically separable Fe3O4@SiO2@TiO2-Ag microspheres with well-designed nanostructure and enhanced photocatalytic activity.Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2013, 262: 404-411. |
| [22] | DENG Z W, CHEN M, WU L M.Novel method to fabricate SiO2/Ag composite spheres and their catalytic, surface-enhanced raman scattering properties.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2007, 111(31): 11692-11698. |
| [23] | LIU S X, QU Z P, HAN X W, et al.Effect of silver deposition on photocatalytic activity of TiO2.Chinese Journal of Catalysis, 2002, 4(25): 133-137. |
| [24] | MORIT M, MALGORZAZT G.The newest achievements in synthesis, immobilization and practical applications of antibacterial nanoparticles.Chemical Engineering Journal, 2013, 228: 596-613. |
| [25] | ANTOLY I S, SUSUMU K, KEIJIRO K.Chemical composition of Eubacterium nodatum cell wall peptidoglycan.Archives of Microbiology, 1989, 151(4): 353-358. |
| [1] | TUERHONG Munire, ZHAO Honggang, MA Yuhua, QI Xianhui, LI Yuchen, YAN Chenxiang, LI Jiawen, CHEN Ping. Construction and Photocatalytic Activity of Monoclinic Tungsten Oxide/Red Phosphorus Step-scheme Heterojunction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 701-707. |
| [2] | KONG Guoqiang, LENG Mingzhe, ZHOU Zhanrong, XIA Chi, SHEN Xiaofang. Sb Doped O3 Type Na0.9Ni0.5Mn0.3Ti0.2O2 Cathode Material for Na-ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 656-662. |
| [3] | DING Ling, JIANG Rui, TANG Zilong, YANG Yunqiong. MXene: Nanoengineering and Application as Electrode Materials for Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 619-633. |
| [4] | JIN Sai, LIU Xiaogen, QI Shuang, ZHAO Runchang, LI Zhijun. Fused Silica Glass: Laser-induced Damage on Bending Strength Weakening and Safety Design [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 671-677. |
| [5] | WANG Bo, YU Jian, LI Cuncheng, NIE Xiaolei, ZHU Wanting, WEI Ping, ZHAO Wenyu, ZHANG Qingjie. Service Stability of Gd/Bi0.5Sb1.5Te3 Thermo-electro-magnetic Gradient Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 663-670. |
| [6] | CHEN Qiang, BAI Shuxin, YE Yicong. Highly Thermal Conductive Silicon Carbide Ceramics Matrix Composites for Thermal Management: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 634-646. |
| [7] | ZHANG Xiangsong, LIU Yetong, WANG Yongying, WU Zirui, LIU Zhenzhong, LI Yi, YANG Juan. Self-assembled Platinum-iridium Alloy Aerogels and Their Efficient Electrocatalytic Ammonia Oxidation Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 511-520. |
| [8] | LIU Wenlong, ZHAO Jin, LIU Juan, MAO Xiaojian, ZHANG Jian, WANG Shiwei. Microwave Drying of Spontaneous-Coagulation-Cast Wet Alumina Green Body [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 461-468. |
| [9] | WANG Lei, LI Jianjun, NING Jun, HU Tianyu, WANG Hongyang, ZHANG Zhanqun, WU Linxin. Enhanced Degradation of Methyl Orange with CoFe2O4@Zeolite Catalyst as Peroxymonosulfate Activator: Performance and Mechanism [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(4): 469-476. |
| [10] | WU Zhen, LI Huifang, ZHANG Zhonghan, ZHANG Zhen, LI Yang, LAN Jianghe, SU Liangbi, WU Anhua. Growth and Characterization of CeF3 Crystals for Magneto-optical Application [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 296-302. |
| [11] | SHI Xiaotu, ZHANG Qingli, SUN Guihua, LUO Jianqiao, DOU Renqin, WANG Xiaofei, GAO Jinyun, ZHNAG Deming, LIU Jiandang, YE Bangjiao. Positron Annihilation Study of Yb:YAG Single Crystal Defects under Czochralski Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 316-321. |
| [12] | YANG Jiaxue, LI Wen, WANG Yan, ZHU Zhaojie, YOU Zhenyu, LI Jianfu, TU Chaoyang. Spectroscopic and Yellow Laser Features of Dy3+: Y3Al5O12 Single Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 350-356. |
| [13] | YANG Xiaoming, LAN Jianghe, WEI Zhantao, SU Rongbing, LI Yang, WANG Zujian, LIU Ying, HE Chao, LONG Xifa. High Quality and Large Size Yttrium Iron Garnet Crystal Grown by Top Seeded Solution Growth Technique [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 322-328. |
| [14] | WANG Zhiqiang, WU Ji’an, CHEN Kunfeng, XUE Dongfeng. Large-size Er,Yb:YAG Single Crystal: Growth and Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(3): 329-334. |
| [15] | XIE Bing, CAI Jinxia, WANG Tongtong, LIU Zhiyong, JIANG Shenglin, ZHANG Haibo. Research Progress of Polymer-based Multilayer Composite Dielectrics with High Energy Storage Density [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(2): 137-147. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||