|
|
Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect
CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu
2025 Vol. 40 (3): 225–244
 Abstract
Abstract(
435 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(3321KB)(
255
)
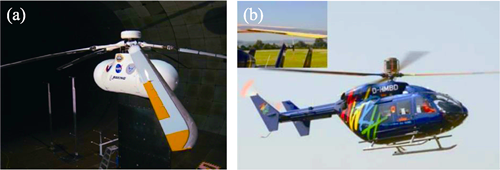
To further expand the application of advanced ceramic materials in helicopters, this paper reviews their application in helicopter structures both domestically and internationally. It emphasizes the technical maturity and development trends of various ceramic materials in helicopter specific structural applications, such as energy impact protection parts, energy conversion components, and corrosion protection areas. By comparing the gaps between domestic and international use of advanced ceramic materials in helicopter specific structures, the paper provides suggestions for the future development. Recommendations include the use of reaction-sintered contoured integrated opaque armor ceramics and polycrystalline transparent armor ceramics for the high-speed dynamic impact energy protection parts, cermet composite coatings compatible with epoxy resin composite substrates for the low-energy impact protection parts, and hybrid ceramic matrix composite/polymer matrix composite (HCMC-PMC) materials for the thermal shock protection parts. Additionally, multifunctional composite materials, such as high-performance miniature piezoelectric ceramic thin film functional devices and flexible hybrid electronic structures based on micro-piezoelectric ceramic materials, should be developed for the mechanical and electrical energy conversion components. Microwave-absorbing ceramic composites derived from polymer-derived ceramics that are compatible with epoxy resin composite substrates are recommended for the electromagnetic and thermal energy conversion components. Furthermore, high-performance abrasion-resistant and corrosion-resistant Sol-Gel coatings are suggested for the corrosion protection areas. It is also essential to establish a high-speed dynamic energy impact protection mechanism for helicopters, optimize the ballistic performance of protective materials, and develop advanced ceramic materials digital testing and verification technologies, represented by multi-functional composite materials for helicopter specific structures. These efforts will greatly shorten the application cycle of advanced ceramic materials and reduce the verification cost.
|
|
|
Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics
YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren
2025 Vol. 40 (3): 245–255
 Abstract
Abstract(
365 )
 HTML
HTML(
8)
 PDF
PDF(4237KB)(
492
)
SiC ceramics exhibit high strength and thermal stability, rendering them highly suitable for applications in space and thermal components. However, the growing demand for large-sized and complex-shaped SiC ceramics necessitates advanced manufacturing techniques. In comparison to traditional reduction and equal material manufacturing methods, 3D printing technology offers significant advantages in various aspects, such as manufacturing cycle, effective cost, and reliability. There are many 3D printing methods, each with distinct characteristics. Stereolithography (SLA) is capable of achieving high precision and superior surface quality. However, its practical applications often necessitate special design of support structures. Additionally, issues such as residual stress and low solid content significantly hinder its further development. Selective laser sintering (SLS) exhibits strong material compatibility, which is suitable for a wide range of materials, including polymers, metals and ceramics. This technology enables large-scale rapid prototyping at low manufacturing costs. But its surface quality of the formed billet is typically insufficient, which needs additional post-processing. Fused deposition modeling (FDM) though facilitates the preparation of SiC ceramics via reaction sintering, proves unsuitable for constructing large components which restricts its applicability in actual production contexts, due to its inadequate interlayer bonding strength coupled with pronounced surface striations and slower forming speeds. This paper reviews the latest research progresses of 3D-printed SiC ceramics and analyzes the subsequent high-temperature densification treatments of green bodies, along with their fundamental physical properties. Finally, it proposes some prospects of 3D printing of SiC ceramic materials, and strengthens integration of new 3D printing technologies and various printing methods for fine regulation of ceramics’ macro- and micro-structures.

|
|
|
Research Progress on Proton-regulated Electrochemical Ionic Synapses
FAN Xiaobo, ZU Mei, YANG Xiangfei, SONG Ce, CHEN Chen, WANG Zi, LUO Wenhua, CHENG Haifeng
2025 Vol. 40 (3): 256–270
 Abstract
Abstract(
268 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(11674KB)(
174
)
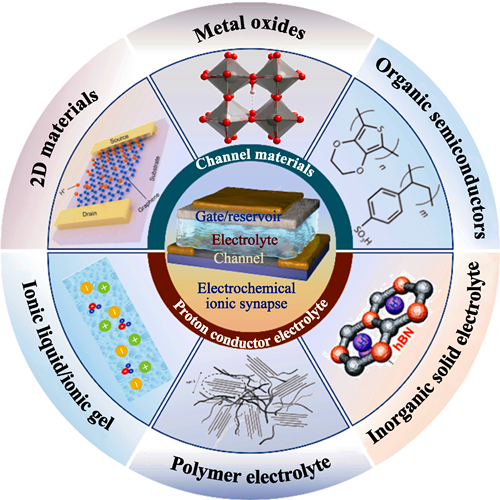
Development of novel artificial synaptic devices, which make up the majority of neural networks, has emerged as a pivotal path to hardware realization of neuromorphic computing. An electrochemical ion synapse, also known as a three-terminal synaptic device based on electrochemical transistors, is a device that may efficiently use ions in the electrolyte layer to modify channel conductivity. By electrochemical doping and recovering ions in channel materials exhibiting redox activity, this device mimics biological synaptic properties. The advantages of the electrochemical ion synapse, which uses proton (H+) as the doping particle, are lower energy consumption, faster operation, and a longer cycle life among the ions that alter the channel material's conductance. This article reviews the recent research progress on proton-regulated electrochemical ion synapses, summarizes the material systems used for the channel layer and electrolyte layer of proton-regulated electrochemical ion synapses, analyzes the challenges faced by proton-regulated electrochemical ion synapses, and points out directions on their future development.
|
|
|
(Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiC Composite Ceramics: Preparation via Precursor Route and Properties
LI Ziwei, GONG Weilu, CUI Haifeng, YE Li, HAN Weijian, ZHAO Tong
2025 Vol. 40 (3): 271–280
 Abstract
Abstract(
277 )
 HTML
HTML(
13)
 PDF
PDF(10286KB)(
183
)
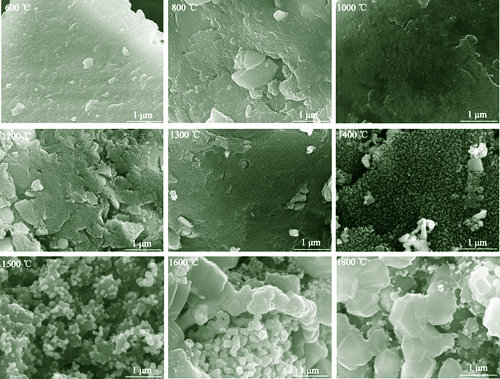
High-entropy carbide (HEC) ceramics are distinguished by their high hardness, oxidation resistance, corrosion resistance, wear resistance, and high thermal conductivity, positioning them as promising candidates for application in extreme environments. However, inherent brittleness of these high-entropy ceramics limits their further application. In order to enhance the toughness of HEC ceramics, polycarbosilane (PCS), a precursor of silicon carbide (SiC), was added into the precursor of (Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C high-entropy ceramic. The in-situ formed SiC (SiCi) by pyrolysis of PCS can serve as reinforcement for HEC ceramics. The results demonstrate that the volume fraction of SiC in the ceramics obtained from the pyrolysis of PCS is 23.38%. The SiC phases, with an average grain size of 1.19 μm, are evenly distributed in the high-entropy ceramic matrix. The pyrolysis process of ceramic precursors was investigated, revealing that the pyrolysis products of PCS exit as amorphous Ox-Si-Cy at low pyrolysis temperature, while a crystalline SiC phase emerges when the pyrolysis temperature exceeds 1500 ℃. Bulk (Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiCi ceramic was prepared by hot-pressing of precursor-derived ceramic powders obtained through pyrolysis at 1600 ℃. Mechanical properties of (Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiCi ceramic bulk were investigated, and composite ceramic bulks toughened by commercial silicon carbide nanopowders or silicon carbide whiskers were also prepared for comparison. Compared with (Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C ceramic, all composite ceramic bulks exhibit enhanced flexural strength and toughness. Notably, the in-situ generated SiCi via precursor-derived method shows the most significant toughening effect. Flexural strength and fracture toughness of (Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C-SiCi ceramic are (698±9) MPa and (7.9±0.6) MPa·m1/2, respectively, representing improvements of 17.71% and 41.07% compared to that of (Zr, Hf, Nb, Ta, W)C ceramic bulk. Taking all above data into comprehensive account, the improvement is mainly due to the small grain size and uniform distribution of SiC in the composite ceramics prepared via precursor-derived method, which enhance energy consumption and hinder crack propagation under external stress.
|
|
|
Preparation and Properties of ZrO2 Doped Y2O3-MgO Nanocomposite Ceramics
MU Haojie, ZHANG Yuanjiang, YU Bin, FU Xiumei, ZHOU Shibin, LI Xiaodong
2025 Vol. 40 (3): 281–289
 Abstract
Abstract(
186 )
 HTML
HTML(
12)
 PDF
PDF(13750KB)(
154
)
Compared with single-phase Y2O3 ceramics, Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics exhibit superior mechanical strength, hardness, thermal conductivity, and excellent infrared band transparency, endowing them a good infrared window material. However, harsh mechanical and thermal operating conditions impose stringent requirements on the optical and mechanical properties of infrared window materials. In this study, high-purity Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite powder was used as raw material, and Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite powders with different ZrO2 contents, in which Zr4+ ions accounted for the percentage of Y3+ ions at 1%, 3% and 5%, were prepared by adding zirconium nitrate aqueous solution during ball milling. ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics were fabricated by hot pressing sintering at 1350 ℃ and 35 MPa for 30 min. The influence of ZrO2 content on the phase, microstructure, infrared transmittance, hardness, and bending strength of nanocomposite ceramics was systematically studied. The results showed that doping ZrO2 dissolved and uniformly distributed in the Y2O3 lattice changed microstructure of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics and caused lattice distortion, which had a significant impact on the optical and mechanical properties of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics. The microstructures of ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics reveal that increasing ZrO2 content can hinder ceramic densification, resulting in obvious pores in 5%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramic. Meanwhile, doping ZrO2 can enhance the hardness and bending strength of Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramics, which can be attributed to lattice distortion suppressing the dislocations’ motion. 3%ZrO2:Y2O3-MgO nanocomposite ceramic has a dense microstructure, with a transmittance of ~82% in the range of 3-5 μm, while exhibiting a hardness of 11.43 GPa and a bending strength of 276.67 MPa.

|
|
|
SiBCN-rGO Ceramic Fibers Based on Wet Spinning Technology: Microstructure, Mechanical and Microwave-absorbing Properties
GAO Chenguang, SUN Xiaoliang, CHEN Jun, LI Daxin, CHEN Qingqing, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu
2025 Vol. 40 (3): 290–296
 Abstract
Abstract(
254 )
 HTML
HTML(
4)
 PDF
PDF(1543KB)(
148
)
With the rapid development of new aerospace vehicles, there are increasing demands for higher structural reliability and wideband microwave stealth requirements for the components operating under high-temperature condition. SiBCN based metastable ceramics exhibit good resistance to high temperature, thermal shock, ablation, long-term oxidation, and creep, showcasing great potential in the field of high-temperature structural microwave absorption. However, their ability to absorb electromagnetic waves is limited by low dielectric loss. In this study, the SiBCN-rGO ceramic fibers with good mechanical and microwave-absorbing properties were prepared using the wet spinning technology. Results showed that the as-prepared SiBCN-rGO ceramic fibers possessed porous structure, with porosity increasing with the increase of reduced graphene oxide (rGO) content. Additionally, both high rGO content and high fiber specific surface area promoted the crystallization of SiC within the amorphous matrix. The introduction of rGO significantly enhanced the tensile properties of the resulting ceramic fibers. As the mass fraction of rGO increased from 0 to 4%, the fibers’ elongation at break increased from 8.05% to 18.05%, and the tensile strength increased from 1.62 cN/dtex (0.324 GPa) to 2.32 cN/dtex (0.464 GPa). The increase of rGO content also reduced the electrical resistivity of the ceramic fibers. Moreover, as the rGO mass fraction increased from 0 to 4%, both the real and imaginary parts of the fibers’ dielectric constant decreased, while the loss tangent gradually increased. The SiBCN-rGO ceramic fibers with those containing 6% (mass fraction) rGO exhibited excellent wave-absorption performance, showing the minimum reflection coefficient of -50.90 dB at 9.20 GHz and an effective absorption bandwidth of 2.3 GHz, indicating promising applications in wave-absorbing ceramic matrix composites.

|
|
|
K0.5Na0.5NbO3-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Excellent Temperature Stability and Application in Type 1-3 Transducer
GAO Tianyu, LIU Dong, ZHAO Sixue, DENG Wei, ZHANG Boping, ZHU Lifeng
2025 Vol. 40 (3): 297–304
 Abstract
Abstract(
180 )
 HTML
HTML(
5)
 PDF
PDF(5123KB)(
129
)
Potassium-sodium niobate (K0.5Na0.5NbO3) based piezoelectric ceramics are considered the most potential lead-free piezoelectric ceramics due to their excellent piezoelectric coefficient (d33) and high Curie temperature (TC). However, the temperature stability of its d33 is poor in comparison with the Pb-based piezoelectric ceramics. To solve this problem, (K0.5Na0.5)0.96Li0.04(Nb0.95Sb0.05)O3-(Bi0.5Na0.5)ZrO3 (KNLNS-BNZ) piezoelectric ceramic with a single tetragonal phase (T phase) was designed and prepared by the conventional solid-state sintering method and texture engineering. It was found that KNLNS-BNZ-based textured ceramic with T phase at room temperature not only possessed a good piezoelectric coefficient (d33=256 pC∙N-1) and a longitudinal electromechanical coupling coefficient (k33=34%), but also exhibited excellent temperature stability of d33 and k33 in comparison to the non-textured ceramics. The change rates of d33 and k33 for KNLNS-BNZ-based textured ceramics were 12% and 4% with the measured temperature of 25-250 ℃, respectively. In addition, the 1-3 type transducer composed of KNLNS-BNZ-based textured ceramics and epoxy resin was also prepared and investigated. This 1-3 type transducer not only exhibited a large bandwidth (BW=61.2%) and excellent signal strength (fc=1 MHz), but also showed excellent temperature stability. As the measured temperature increased to 100 ℃, its bandwidth BW and center frequency fc were 58.7% and 0.94 MHz, whose rates of change were 4% and 6% in comparison to the results measured at room temperature, respectively. All these results show that KNLNS-BNZ lead-free piezoelectric ceramics have good piezoelectric properties and excellent temperature stability, and the 1-3 type transducer prepared by KNLNS-BNZ can provide reference for the practical application of new lead-free piezoelectric ceramics.

|
|
|
Room-temperature Ferromagnetic All-carbon Films Based on Reduced Graphene Oxide
WANG Yue, WANG Xin, YU Xianli
2025 Vol. 40 (3): 305–313
 Abstract
Abstract(
175 )
 HTML
HTML(
9)
 PDF
PDF(1547KB)(
117
)
Nano carbon materials with ferromagnetism have significant application value in fields such as spintronics, biomedical imaging, electrodes, and dye adsorption. Graphene derivatives graphene oxide (GO) and reduced graphene oxide (rGO) exhibit excellent physical and chemical properties, presenting a room temperature ferromagnetic ordered structure. In order to achieve large-scale, low-cost, and stable performance of all-carbon films, a dual dimensional carbon composite strategy combining thermal reduction was adopted to prepare composite films of micro reduced graphene oxide fibers (rGOFs) and nano scale rGO sheets, and the ferromagnetic mechanism of all-carbon films was explained partially. This work prepared rGO-rGOFs all-carbon composite films with different masses of rGOFs, focusing on the ferromagnetic mechanism and magnetoresistance effect of the materials. The research results find that introducing a certain amount of rGOFs can increase the room temperature saturation magnetization of rGO films from 0.0083 to 0.0960 A·m2·kg-1. Enhancement of the ferromagnetism is achieved through combined effect of vacancy type defects and sp3(C-C) states in carbon film. Interference of metal impurities in the sample, which may affect the saturation magnetization, is eliminated by inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry. In addition, at room temperature and ±1 T magnetic field, the magnetoresistance (MR) curve shows MR value of sample is negative. By regulating the surface topology and sp3(C-C)/sp2(C=C) ratio of the material, the room temperature saturation magnetization has been improved to a higher extent. In short, this new type of all-carbon thin film is expected to be applied to spintronic devices and biomedical fields in the near future.

|
|
|
Stability of Phosphors for White LED Excitable by Violet Light
PAN Zesheng, YOU Yaping, ZHENG Ya, CHEN Haijie, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan
2025 Vol. 40 (3): 314–322
 Abstract
Abstract(
172 )
 HTML
HTML(
2)
 PDF
PDF(5321KB)(
106
)
Violet light excited white light emitting diodes (LEDs) have attracted widespread attention due to their advantages of tunable color temperature and visual comfort. However, high-performance phosphors suitable for violet light excitation (400-420 nm) have not yet been widely applied on a large scale. One of the key factors regarding the commercial utilizations is the stability. Unfortunately, there still lacks research on this issue. In this study, three rare-earth phosphors suitable for violet light excitation in LEDs were synthesized via a solid-state reaction method, namely K2CaPO4F:Eu2+, K1.3Al11O17+δ:Eu2+ and Ca2YHf2Al3O12:Ce3+,Tb3+. The stability experiments were then conducted under conditions of high temperature and humidity, water immersion, and long-term violet light irradiation from LED chips. The luminescent properties, failure mechanisms, and environmental stability were analyzed. Finally, a white LED device was prepared by combining the as-synthesized three phosphors onto a 400 nm violet light chip. Results demonstrate that the as-synthesized phosphors exhibit not only optimized luminescence performance compared to phosphors prepared in former works, but also a more comprehensive evaluation of environmental stability across different conditions. The white LED device achieves a color rendering index of 93.6, a correlated color temperature of 5151 K and a color coordinate of (0.34, 0.36), showcasing excellent white light illumination performance. Furthermore, the environmental stability of the white LED device is improved compared to individual phosphors. By taking lead in investigating the environmental stability of violet light excited LED phosphors, this work provides valuable insights and guidance for advancing their applications.

|
|
|
Oxidation Behavior of Yb2Si2O7 Modified SiC/SiC Mini-composites
MU Shuang, MA Qin, ZHANG Yu, SHEN Xu, YANG Jinshan, DONG Shaoming
2025 Vol. 40 (3): 323–328
 Abstract
Abstract(
236 )
 HTML
HTML(
3)
 PDF
PDF(5404KB)(
189
)
Silicon-carbide-fiber-reinforced silicon-carbide-ceramic-based matrix (SiC/SiC) composites possess excellent properties such as low density, high strength and high temperature resistance, showing a potential application for structural components in the aerospace field, but their oxidation behavior remains largely unknown. In this study, Yb2Si2O7 modified SiC/SiC (SiC/SiC-Yb2Si2O7) mini-composites were prepared by introducing Yb2Si2O7 as anti-oxidation phase into SiC fiber bundles via Sol-Gel and depositing SiC matrix by chemical vapor deposition (CVD). Influence of Yb2Si2O7 on microstructure, mechanical property and oxidation behavior of SiC/SiC mini-composites was investigated. The results showed that after oxidation in air at 1200 and 1400 ℃ for 50 h, the tensile strength retentions of SiC/SiC mini-composites were 77% and 69%, respectively, and the fracture morphology exhibited flat. The Yb2Si2O7 introduced by Sol-Gel partially distributed in layers, contributing to the toughening of the material. On the fracture surface, there was interlayer debonding, which extended energy dissipation mechanism of SiC/SiC mini-composites. Tensile strength of SiC/SiC-Yb2Si2O7 mini-composites at room temperature was 484 MPa. After oxidation in air at 1200 and 1400 ℃ for 50 h, the tensile strengths decreased to 425 and 374 MPa, resulting in retention rates of 88% and 77%, respectively. It displayed typical non-brittle fracture characteristics. The interface oxygen content of SiC/SiC mini-composites at the fracture surface was higher than that of SiC/SiC-Yb2Si2O7 mini-composites, indicating that introduction of Yb2Si2O7 could alleviate oxygen diffusion towards the interface, and therefore improve the oxidation resistance of SiC/SiC-Yb2Si2O7 mini-composites.

|
|
|
GeP3/Ketjen Black Composite: Preparation via Ball Milling and Performance as Anode Material for Sodium-ion Batteries
YANG Shuqi, YANG Cunguo, NIU Huizhu, SHI Weiyi, SHU Kewei
2025 Vol. 40 (3): 329–336
 Abstract
Abstract(
231 )
 HTML
HTML(
11)
 PDF
PDF(9548KB)(
196
)
Metal phosphides have been studied as prospective anode materials for sodium-ion batteries (SIBs) due to their higher specific capacity compared to other anode materials. However, rapid capacity decay and limited cycle life caused by volume expansion and low electrical conductivity of phosphides in SIBs remain still unsolved. To address these issues, GeP3 was first prepared by high-energy ball milling, and then Ketjen black (KB) was introduced to synthesize composite GeP3/KB anode materials under controlled milling speed and time by a secondary ball milling process. During the ball milling process, GeP3 and KB form strong chemical bonds, resulting in a closely bonded composite. Consequently, the GeP3/KB anodes was demonstrated excellent sodium storage performance, achieving a high reversible capacity of 933.41 mAh·g-1 at a current density of 0.05 A·g-1 for a special formula of GeP3/KB-600-40 sample prepared at ball milling speed of 600 r/min for 40 h. Even at a high current density of 2 A·g-1 over 200 cycles, the capacity remains 314.52 mAh·g-1 with a retention rate of 66.6%. In conclusion, this work successfully prepares GeP3/KB anode-carbon composite for electrodes by high-energy ball milling, which can restrict electrode volume expansion, enhance capacity, and improve cycle stability of SIBs.

|
|
