
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2014, Vol. 29 ›› Issue (3): 284-288.DOI: 10.3724/SP.J.1077.2014.13271
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
MA Yi-Juan1, 2, HAO Li-Jing1, 2, DU Shao-Long2, ZHAO Na-Ru1, 2
Received:2013-05-16
Revised:2013-07-02
Published:2014-03-20
Online:2014-02-18
About author:MA Yi-Juan. E-mail: yijuanma@126.com
CLC Number:
MA Yi-Juan, HAO Li-Jing, DU Shao-Long, ZHAO Na-Ru. Synthesis of Hydroxyapatite Microspheres by Hydro-thermal Method under the Control of Sodium Citrate[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2014, 29(3): 284-288.
Add to citation manager EndNote|Ris|BibTeX
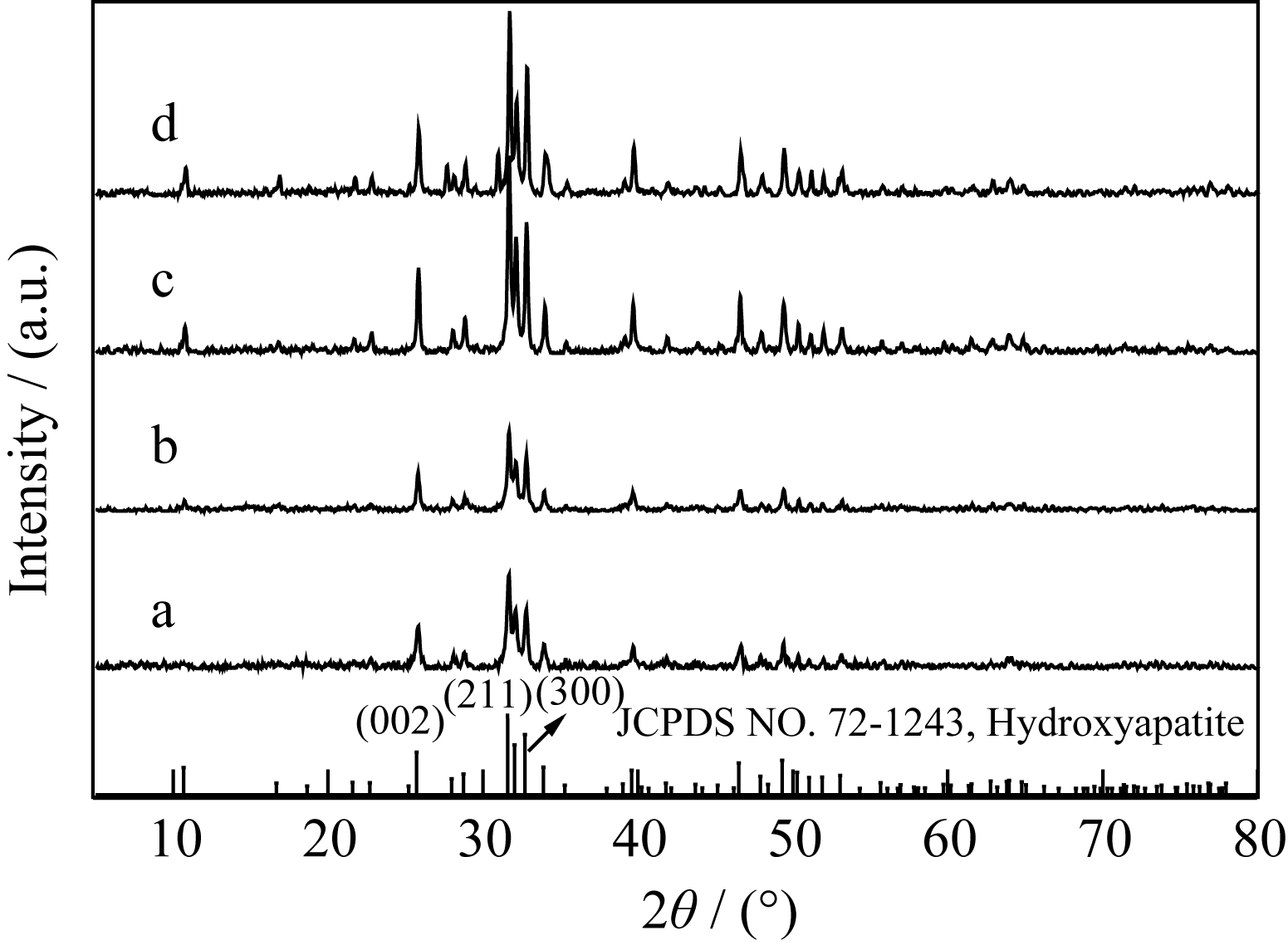
Fig. 1 XRD patterns of products under varied initial pH values (a) pH=2; (b) pH=3; (c) pH =4; ( d) pH=5 Tick marks below the patterns corresponding to the position of the Bragg reflections of the HA (JCPDS 72-1243)
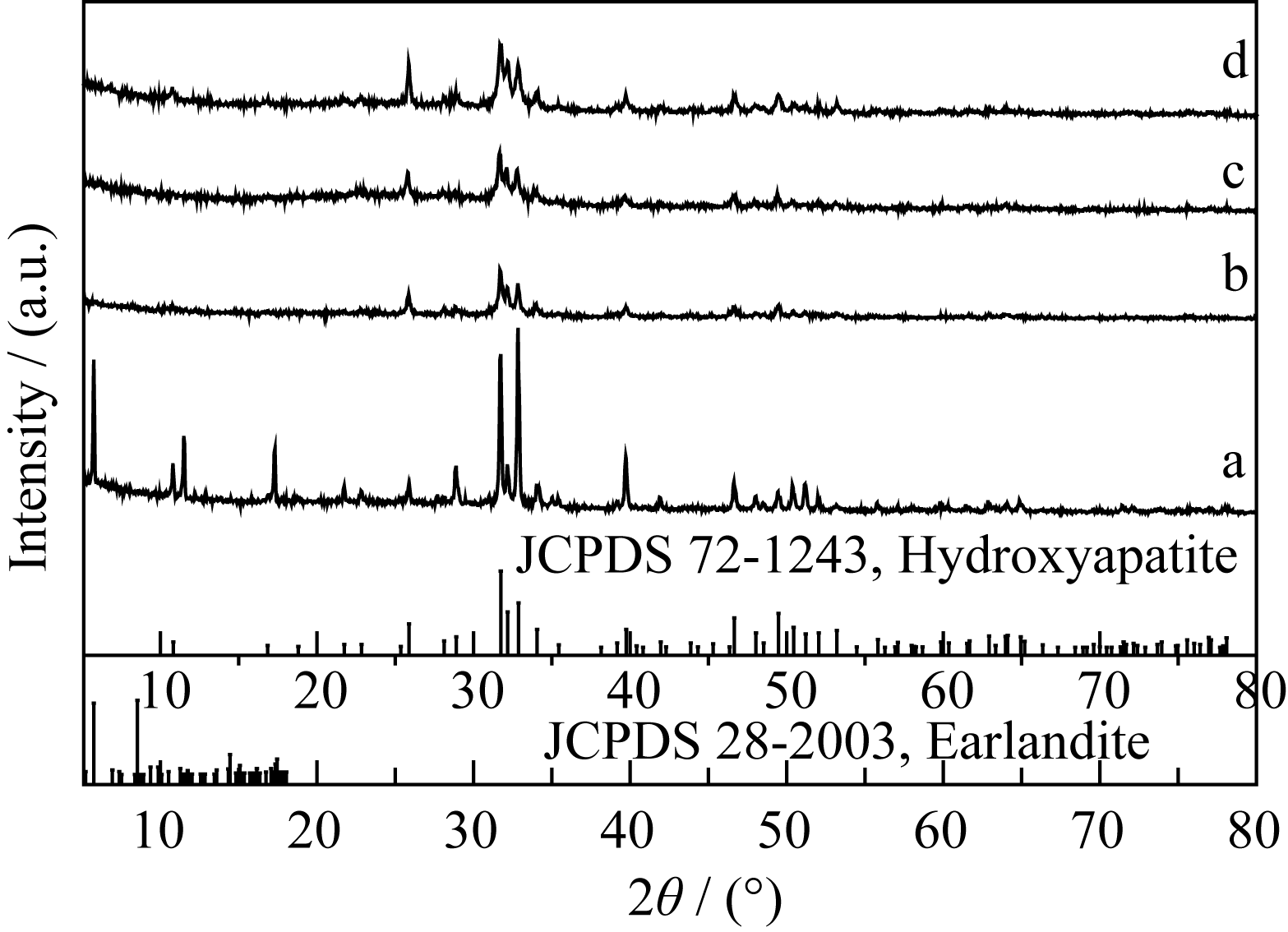
Fig. 4 XRD patterns of the products synthesized with varied molar ratios of sodium citrate to calcium source (a) TSC/Ca=1:0.5; (b) TSC/Ca =1:1; (c) TSC/Ca =1:1.5; (d) TSC/Ca =1:3 Tick marks below the patterns correspond to the position of the Bragg reflections of the Earlandite (JCPDS 28-2003) and the hexagonal HA (JCPDS 72-1243)
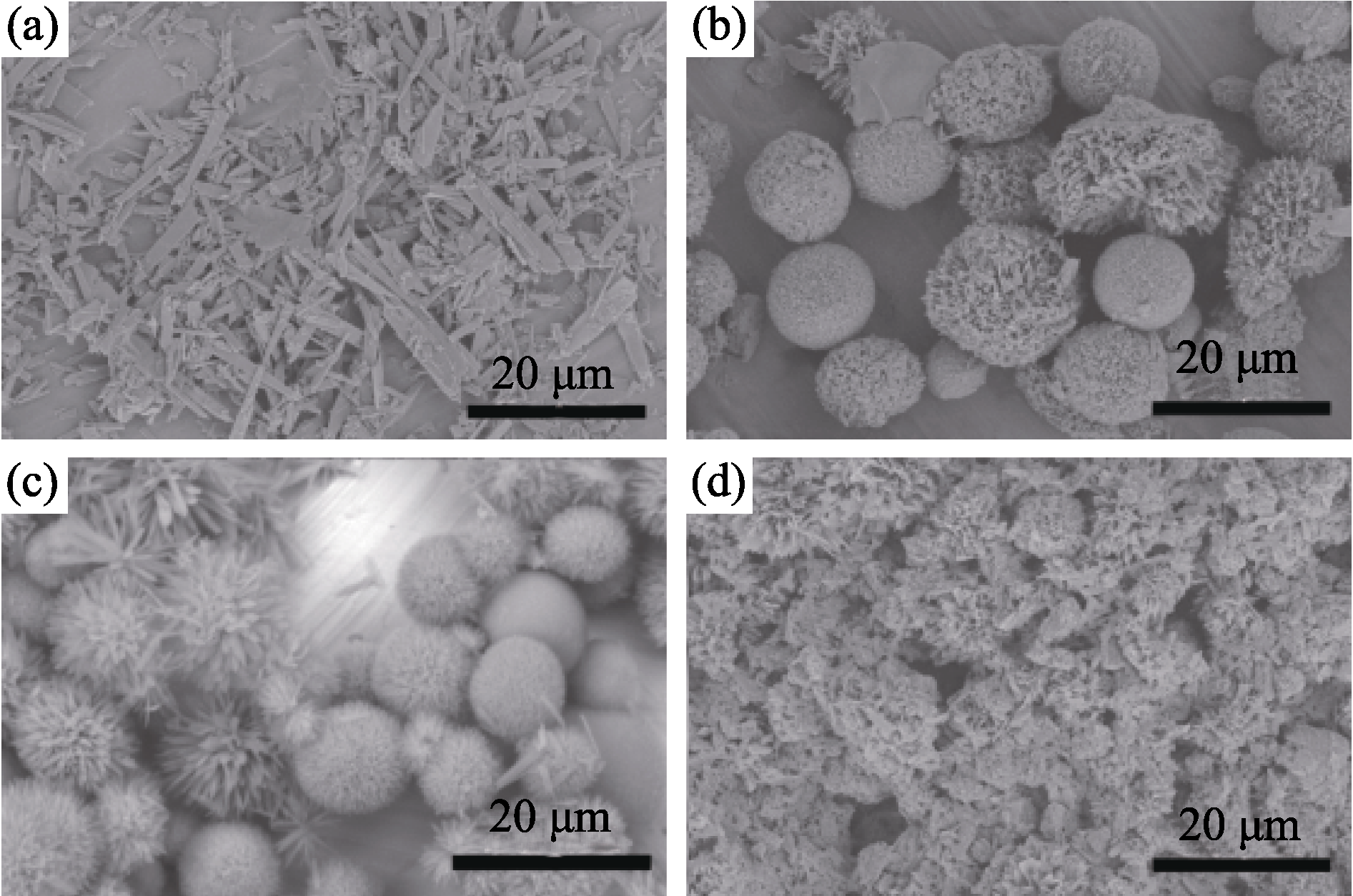
Fig. 5 SEM images of the products synthesized with varied molar ratios of sodium citrate to calcium source (a) TSC/Ca =1:0.5; (b) TSC/Ca =1:1; (c) TSC/Ca =1:1.5; (d) TSC/Ca =1:3
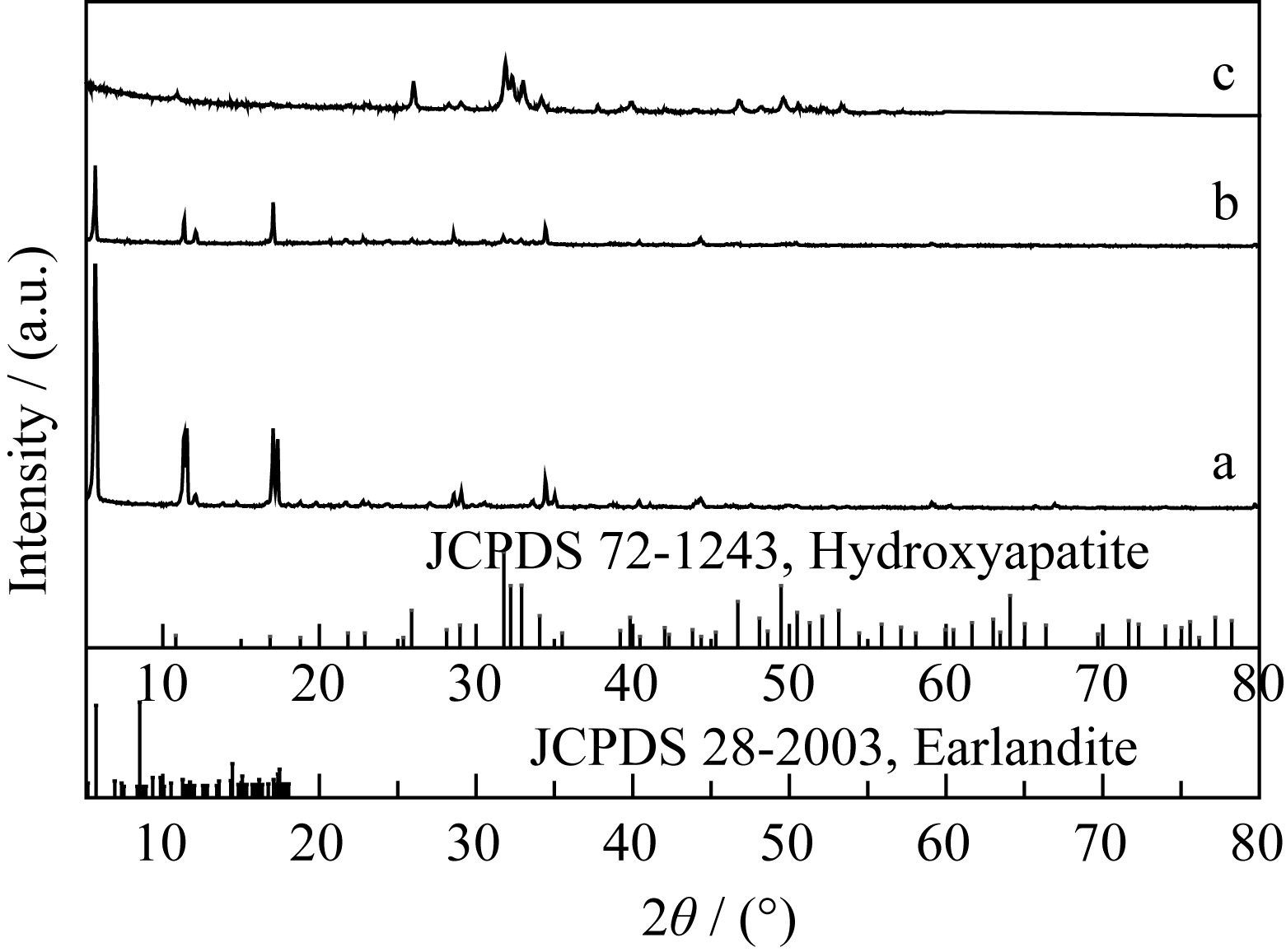
Fig. 6 XRD patterns of the products synthesized under varied hydrothermal temperatures (a) T=120℃; (b) T =150℃; (c) T =180℃ Tick marks below the patterns correspond to the position of the Bragg reflections of the Earlandite (JCPDS 28-2003) and the hexagonal HA (JCPDS 72-1243)
| [1] | FATHI M H, HANIFI A. Evaluation and characterization of nanostructure hydroxyapatite powder prepared by simple Sol-Gel method. Materials Letters, 2007, 61(18):3978-3983. |
| [2] | FATHI M H, HANIFI A, MORTAZAVI V. Preparation and bioactivity evaluation of bone-like hydroxyapatite nanopowder. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2008, 202(1/2/3):536-542. |
| [3] | TANG Y J, TANG Y F, LV C T, et al. Preparation of uniform porous hydroxyapatite biomaterials by a new method. Applied Surface Science, 2008, 254(17):5359-5362. |
| [4] | HAYATI A N, REZAIE H R, HOSSEINALIPOUR S M. Preparation of poly(3-hydroxybutyrate)/nano-hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering. Materials Letters, 2011, 65(4):736-739. |
| [5] | RAHIMI F, MAURER B T, ENZWEILER M G. Coralline hydroxyapatite: a bone graft alternative in foot and ankle surgery. The Journal of Foot and Ankle Surgery: Official Publication of the American College of Foot and Ankle Surgeons, 1997, 36(3):192-203. |
| [6] | MA M Y, ZHU Y J, LI L, et al. Nanostructured porous hollow ellipsoidal capsules of hydroxyapatite and calcium silicate: preparation and application in drug delivery. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2008, 18(23):2722-2727. |
| [7] | SUGANTHI R V, ELAYARAJA K, JOSHY M I A, et al. Fibrous growth of strontium substituted hydroxyapatite and its drug release. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications, 2011, 31(3): 593-599. |
| [8] | TENG S H, LEE E J, WANG P, et al. Functionally gradient chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for controlled drug release. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part B-Applied Biomaterials, 2009, 90B(1):275-282. |
| [9] | KRUSE A, JUNG R E, NICHOLLS F. Bone regeneration in the presence of a synthetic hydroxyapatite/silica oxide-based and a xenogenic hydroxyapatite-based bone substitute material. Clinical Oral Implants Research, 2011, 22(5):506-511. |
| [10] | WANG A J, MA X L, LV Y P. Preparation and characterization and chromatographic property of hydroxyapatite microspheres,Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2010, 38(3):468-471. |
| [11] | CHO J S, KANG Y C. Nano-sized hydroxyapatite powders prepared by flame spray pyrolysis. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2008, 464(1/2):282-287. |
| [12] | MIZUSHIMA Y, IKOMA T, TANAKA J, et al. Injectable porous hydroxyapatite microparticles as a new carrier for protein and lipophilic drugs. Journal of Controlled Release, 2006, 110(2):260-265. |
| [13] | BENSON R S, HUTCHENS S A, EVANS B R, et al. Biomimetic synthesis of calcium-deficient hydroxyapatite in a natural hydrogel. Biomaterials, 2006, 27(26):4661-4670. |
| [14] | ZHANG H, ZHOU K, LI Z, et al. Synthesis of hollow hybrid hydroxyapatite microspheres based on chitosan-poly (acrylic acid) microparticles. Biomedical Materials, 2009, 4(3): 31002. |
| [15] | TAKAI C, HOTTA T, SHIOZAKI S, et al. Unique porous microspheres with dense core and a porous layer prepared by a novel S/O/W emulsion technique. Chemical Communications, 2009(37): 5533-5535. |
| [16] | YANG L X, YIN J J, WANG L L. Hydrothermal synthesis of hierarchical hydroxyapatite: preparation, growth mechanism and drug release property. Ceramics International, 2012, 38:495-502. |
| [17] | SADAT-SHOJAI M, KHORASANI M T, JAMSHIDI A. Hydrothermal processing of hydroxyapatite nanoparticles: a taguchi experimental design approach. Journal of Crystal Growth, 2012, 361:73-84. |
| [18] | 王迎军, 杨 辉, 杜 昶, 等. 一种中空分级结构羟基磷灰石微球及其制备方法和应用. 中国, A61K 9/19. CN 103058159 A. 2013.04.24 |
| [19] | HAO L J, YANG H, ZHAO N R, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of hydroxyapatite fibers precipitated by propionmide. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(1):63-68. |
| [20] | AIZAWA M, PORTER A E, BEST S M, et al. Synthesis and characterization of hydroxyapatite crystals: a review study on the analytical methods. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research, 2002, 62(4): 600-612. |
| [21] | 李世普,王友法. 磷灰石纳米粒子的制备改性及其生物安全. 北京: 科学出版社, 2010: 146-149. |
| [22] | ZHANG Y, ZHOU C M. Preparation and application of sodiumcitrate. Liaoning Chemical Industry, 2007, 36(5):350-352. |
| [1] | AN Ran, LIN Si, GUO Shigang, ZHANG Chong, ZHU Shun, HAN Yingchao. Iron-doped Nano-hydroxyapatite: Preparation and Ultraviolet Absorption Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 457-465. |
| [2] | LI Chengyu, DING Ziyou, HAN Yingchao. In vitro Antibacterial and Osteogenic Properties of Manganese Doped Nano Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(3): 313-320. |
| [3] | LI Yuejun, CAO Tieping, SUN Dawei. Bi4O5Br2/CeO2 Composite with S-scheme Heterojunction: Construction and CO2 Reduction Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 963-970. |
| [4] | NIU Haibin, HUANG Jiahui, LI Qianwen, MA Dongyun, WANG Jinmin. Directly Hydrothermal Growth and Electrochromic Properties of Porous NiMoO4 Nanosheet Films [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(12): 1427-1433. |
| [5] | LIU Yan, ZHANG Yufan, WANG Ximan, LI Ting, MA Wenting, YANG Fuwei, CHEN Liang, ZHAO Dongyue, YAN Xiaoqin. Consolidation of Fragile Weathered Bone Relics Using Hydroxyapatite Material as Consolidant [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(11): 1345-1354. |
| [6] | YAO Yishuai, GUO Ruihua, AN Shengli, ZHANG Jieyu, CHOU Kuochih, ZHANG Guofang, HUANG Yarong, PAN Gaofei. In-situ Loaded Pt-Co High Index Facets Catalysts: Preparation and Electrocatalytic Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(1): 71-78. |
| [7] | CHEN Yaling, SHU Song, WANG Shaoxin, LI Jianjun. Mn-HAP SCR Catalyst: Preparation and Sulfur Resistance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(10): 1065-1072. |
| [8] | ZHANG Xian, ZHANG Ce, JIANG Wenjun, FENG Deqiang, YAO Wei. Synthesis, Electronic Structure and Visible Light Photocatalytic Performance of Quaternary BiMnVO5 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 58-64. |
| [9] | ZHU Yutong, TAN Peijie, LIN Hai, ZHU Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingdong. Injectable Hyaluronan/Hydroxyapatite Composite: Preparation, Physicochemical Property and Biocompatibility [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 981-990. |
| [10] | LIN Ziyang, CHANG Yuchen, WU Zhangfan, BAO Rong, LIN Wenqing, WANG Deping. Different Simulated Body Fluid on Mineralization of Borosilicate Bioactive Glass-based Bone Cement [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(7): 745-752. |
| [11] | WU Zhongcao, HUAN Zhiguang, ZHU Yufang, WU Chengtie. 3D Printing and Characterization of Microsphere Hydroxyapatite Scaffolds [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(6): 601-607. |
| [12] | WU Yonghao, LI Xiangfeng, ZHU Xiangdong, ZHANG Xingdong. Construction of Hydroxyapatite Nanoceramics with High Mechanical Strength and Efficiency in Promoting the Spreading and Viability of Osteoblasts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(5): 552-560. |
| [13] | SONG Keke, HUANG Hao, LU Mengjie, YANG Anchun, WENG Jie, DUAN Ke. Hydrothermal Preparation and Characterization of Zn, Si, Mg, Fe Doped Hydroxyapatite [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1091-1096. |
| [14] | SHAO Yueting, ZHU Yingjie, DONG Liying, CAI Anyong. Nanocomposite “Xuan Paper” Made from Ultralong Hydroxyapatite Nanowires and Cellulose Fibers and Its Anti-mildew Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 107-112. |
| [15] | XIAO Yumin, Li Bin, QIN Lizhao, LIN Hua, LI Qing, LIAO Bin. Efficient Preparation of CuGeO3 with Controllable Morphology Using CuCl2 as Copper Source [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(1): 69-74. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||