
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2021, Vol. 36 ›› Issue (9): 901-918.DOI: 10.15541/jim20200703
Special Issue: 【虚拟专辑】新型材料表征技术(2020~2021)
• INVITED REVIEW • Next Articles
LIU Yunpeng1( ), SHENG Weifan1,2, WU Zhonghua1,2(
), SHENG Weifan1,2, WU Zhonghua1,2( )
)
Received:2020-12-08
Revised:2021-01-29
Published:2021-09-20
Online:2021-04-05
Contact:
WU Zhonghua, professor. E-mail: wuzh@ihep.ac.cn
About author:LIU Yunpeng (1990-), male, PhD. E-mail: liuyunpeng@ihep.ac.cn
Supported by:CLC Number:
LIU Yunpeng, SHENG Weifan, WU Zhonghua. Synchrotron Radiation and Its Applications Progress in Inorganic Materials[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(9): 901-918.

Fig. 1 In situ high pressure XRD patterns of (BA)4AgBiBr8 and schematic illustration of crystal structure changes[33] (a) Representative XRD patterns of (BA)4AgBiBr8 at selected pressures up to 25.0βGPa. The magnification factor of the peak intensities in the left panel is two times that of the right panel; (b) Crystal structure of (BA)4AgBiBr8 perpendicular to the c axis (perpendicular to a axis, phase II). Pink and green octahedra represent [AgBr6]5- and [BiBr6]3- octahedra, respectively; (c) Crystal structures of (BA)4AgBiBr8 along (100) ((001), Phase II) with increasing pressure. Ag-Br octahedra are shown in pink. Bi-Br octahedral are shown in green; (d)βIllustrations of Bi-Br1-Ag bond angle within the inorganic layers framework before and after the phase transition. (1 atm=1.01×105 Pa)
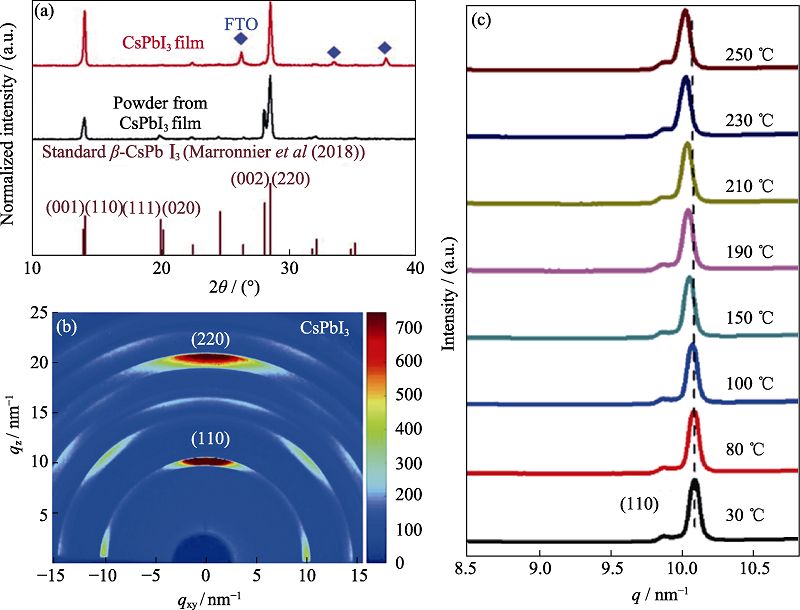
Fig. 2 Relevant SR-XRD patterns of β-CsPbI3[11] (a) XRD patterns acquired from a CsPbI3 thin film and powders scratched from its films. Brown lines indicate the standard β-CsPbI3 XRD pattern calculated for Cu Kα1 radiation for the tetragonal perovskite structure at 518 K; (b) GIWAXS data from β-CsPbI3 films; (c) Azimuthally integrated intensity profiles for the β-CsPbI3 perovskite films annealed at different temperatures (30, 80, 100, 150, 190, 210, 230, 250 ℃)
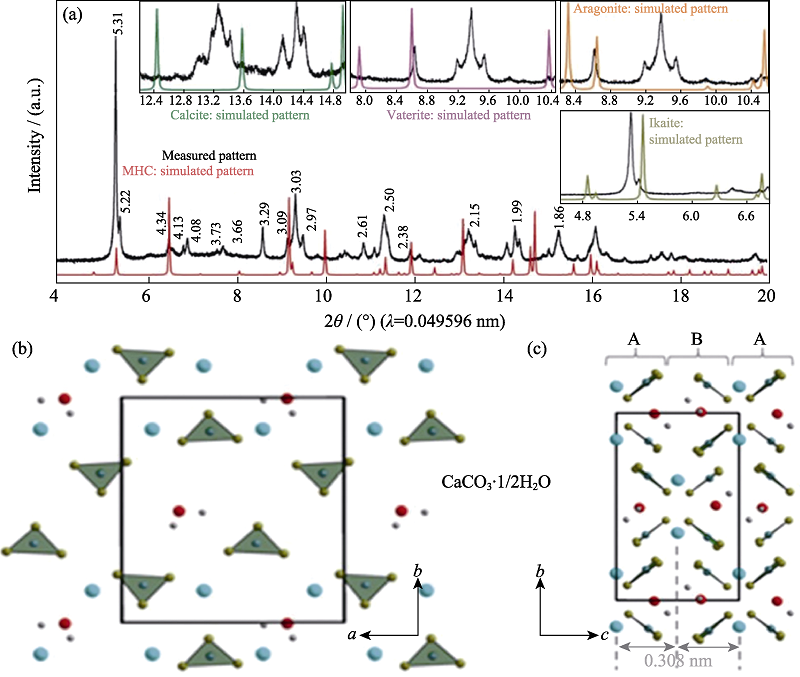
Fig. 4 High-resolution SR-XRD pattern of CaCO3·1/2H2O and its crystal structure model[9] (a) Synchrotron HRXRPD pattern of CaCO3·1/2H2O using a wavelength of 0.049596 nm; (b) The layers of CaCO3·1/2H2O consist of Ca(μ2-CO3)2/5(μ1-CO3)3/5(H2O)1/2 double zigzag chains running along the a axis, here, differently oriented (up and down) carbonate groups are indicated by indices μ2 and μ1; (c) Stacking in the c direction occurs in a conventional ABAB fashion with an interlayer spacing (the distance between Ca planes) equal to 0.308 nm. The insets in (a) show comparisons of the measured HRXRPD pattern of CaCO3·1/2H2O with simulated patterns of other calcium carbonate phases. Different types of atoms are colored as follows: Ca, blue; carbonate group, green; oxygen from water, red; and hydrogen, gray
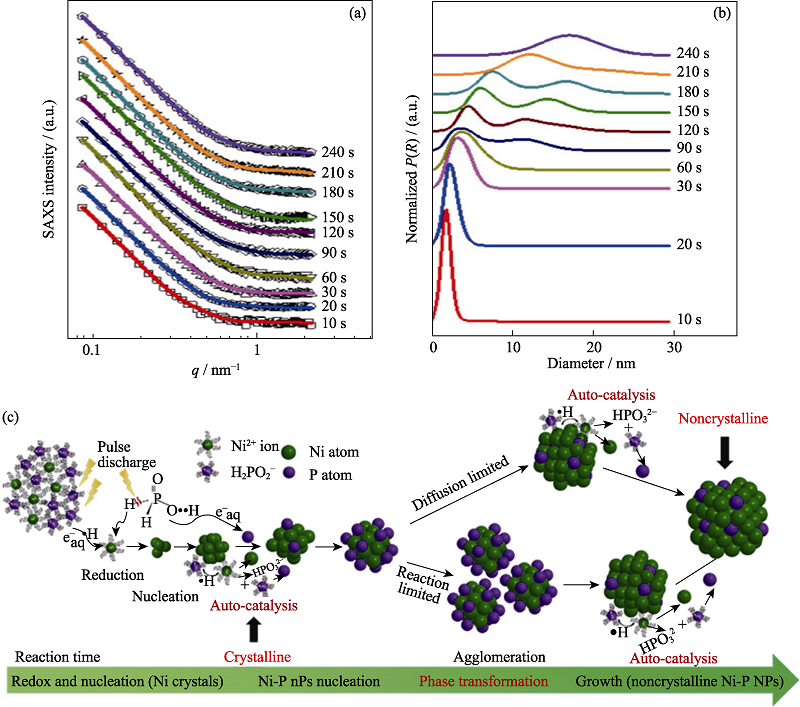
Fig. 7 Time-resolved SAXS results and schematic illustration of the formation mechanism for NiP[46] (a) Comparison between the experimental SAXS intensities (symbols) and the simulated ones (solid lines); (b) Normalized particle-volume distribution P(R) extracted from the SAXS data; (c) Schematic map of the formation mechanism of noncrystalline Ni-P nanoparticles
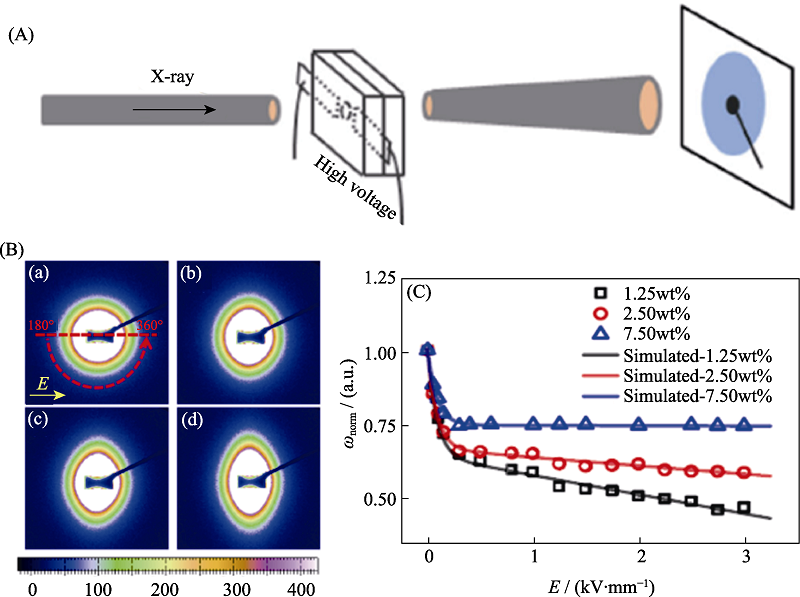
Fig. 8 In-situ SAXS technique applied on the study for the orientation of suspended Na2Ti3O7 nanofiber induced by applied electric field[47] (A) Sketch map of in-situ SAXS measurements; (B) SAXS patterns of the silicone oil suspension with 1.25wt% of Na2Ti3O7 nanofibers under the DC electric-field strength: 0 kV/mm (a), 0.5 kV/mm (b), 1.5 kV/mm (c), and 2.5 kV/mm (d); (C) Electric-field strength dependence of normalized orientation distribution width, the solid lines represent the simulation
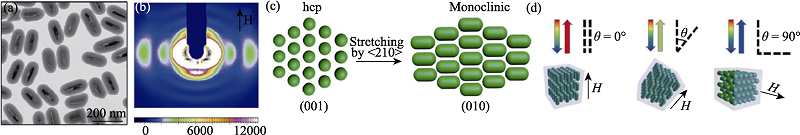
Fig. 9 Structural evolution of Fe3O4@SiO2 nanorods under magnetic field studied by SAXS[48] (a) TEM image of the Fe3O4@SiO2 nanorods; (b) Small-angle X-ray diffraction pattern of an aqueous suspension of Fe3O4@SiO2 nanorods (volume fraction ϕ=21%) in the presence of a 200-Gauss external magnetic field, the color bar on the bottom shows the relative diffraction intensity; (c) Schematic illustration of the stretching of the hcp lattice along the <210> direction. The (001) facet of the original hcp lattice was transformed into the (010) facet of the new monoclinic structure. The main axis of nanorods is aligned along the <201> direction of the monoclinic lattice, which is parallel to external magnetic fields; (d) Schematic illustration of magnetically tuning the Bragg diffractions from crystalline colloidal array by changing the angle (θ) between the magnetic field and the incident light
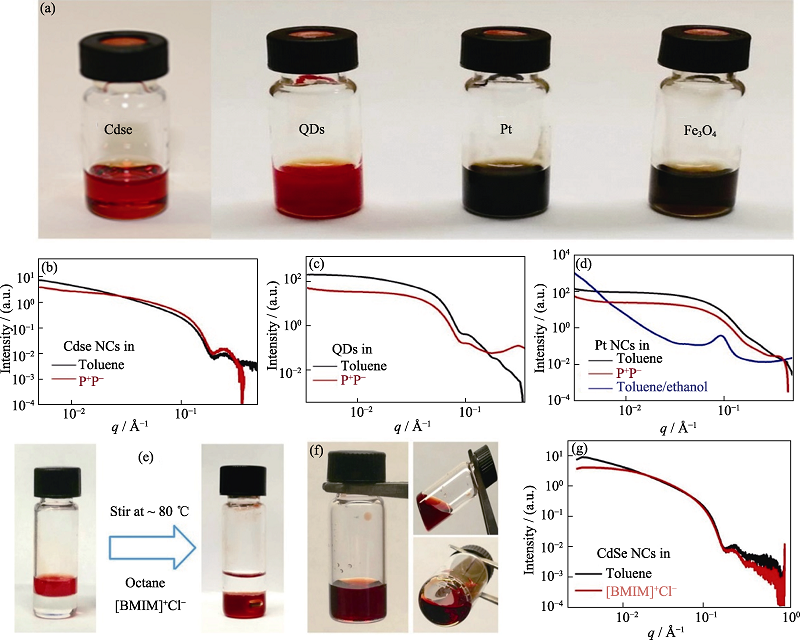
Fig. 10 Experimental evidence for the stable presence of nanoparticles in molten inorganic salts provided by SAXS technique[49] (a) Photographs of stable nanocrystals (NC) colloids in P+P-; (b-d) Small-angle X-ray scattering (SAXS) patterns of CdSe (b), quantum dots (QDs) (c) and Pt NCs (d) in toluene and P+P-. The SAXS patterns of NCs in P+P- resemble those of NCs in toluene, indicating high NC colloidal stability; (e) Photographs showing the phase transfer of CdSe NCs from octane to [BMIM]+Cl- without additional ligands; (f) Photographs of stable CdSe NC colloids in [BMIM]+Cl-; (g) SAXS patterns of CdSe NCs in toluene (with OA/TOP/TOPO) and [BMIM]+Cl-. All samples were gently heated to keep [BMIM]+Cl- in the molten state (1 Å=0.1 nm)
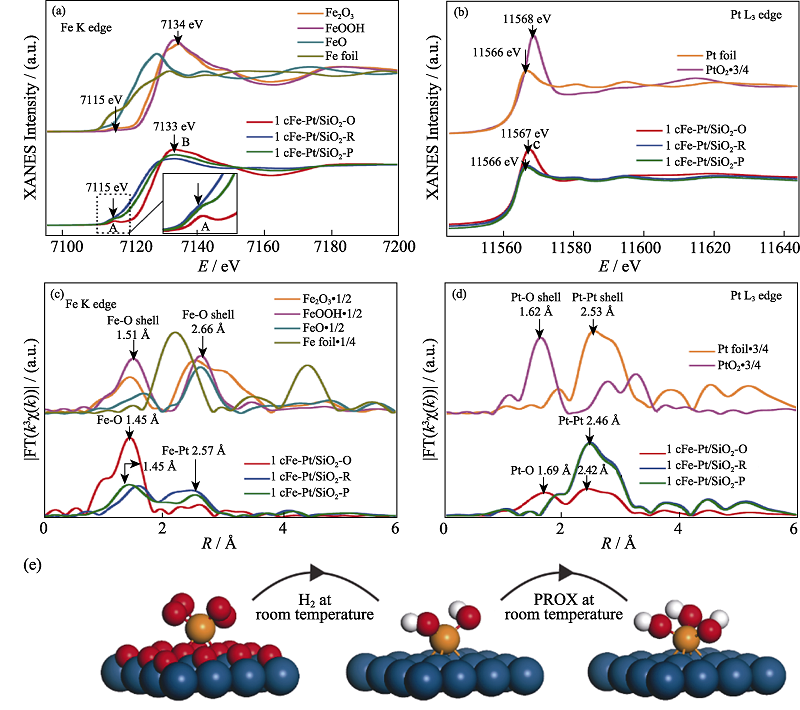
Fig. 11 In situ XAFS measurements of the 1cFe-Pt/SiO2 catalyst and its schematic illustration of catalytic mechanism[54] (a-d) XANES spectra at Fe K edge (a) and Pt L3 edge (b), detailed structural information shown in the k3-weighted FT spectra in R-space at the Fe K edge (c) and the Pt L3 edge (d) (E: energy, R: distance between absorbing atom and neighbouring scatterer atoms, without correcting for scattering phase shift, and χ(k): the amplitude of the EXAFS oscillations as a function of photoelectron wavenumber k (a.u., arbitrary units). The inset in (a) shows a magnified view of the pre-edge peak A. The energy positions of Fe pre-edge peak A, Fe white-line peak B and Pt white-line peak C, as well as R-space peak positions of the shells of Fe-O, Fe-Fe, Fe-Pt, Pt-O and Pt-Pt, are also shown; (e) Schematic models of 1cFe-Pt/SiO2-O (left), 1cFe-Pt/SiO2-R (middle) and 1cFe-Pt/SiO2-P (right), Fe, O, H and Pt atoms are shown in orange, red, white, and blue, respectively. (1 Å=0.1 nm) (colorful figures are available on website)
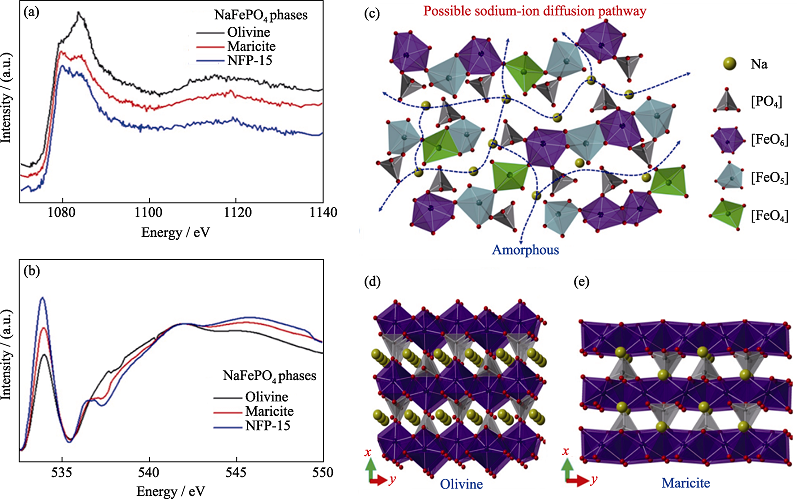
Fig. 12 XAFS spectra of NaFePO4 and schematic illustrations for Na diffusive mechanism[55] X-ray absorption near edge structure spectra of Na K-edge (a), O K-edge (b) for olivine-type, maricite-type and polymorphic composites obtained by milling for 15 h (NFP-15); Schematic illustrations for Na diffusive mechanism: possible sodium-ion diffusive pathways and atomistic structure for amorphous NaFePO4 (c), structural sketching diagrams of olivine-type NaFePO4 (d), and maricite-type NaFePO4 (e) Colorful figures are available on website
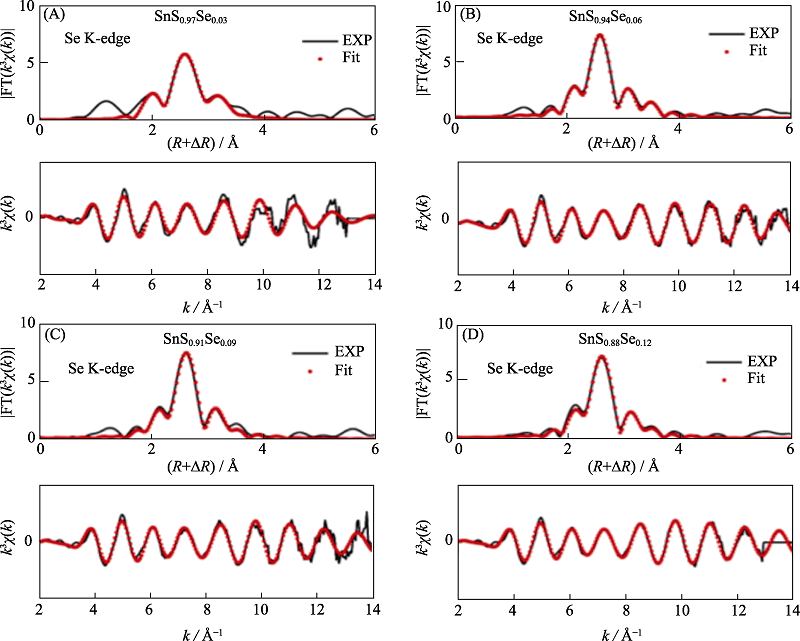
Fig. 13 Fitting of the Fourier transforms of k3 weighted EXAFS oscillations at Se K-edge of SnS1-xSex[57] (A) x=0.03; (B) x=0.06; (C) x=0.09; (D) x=0.12 (1 Å=0.1 nm) (colorful figures are available on website)
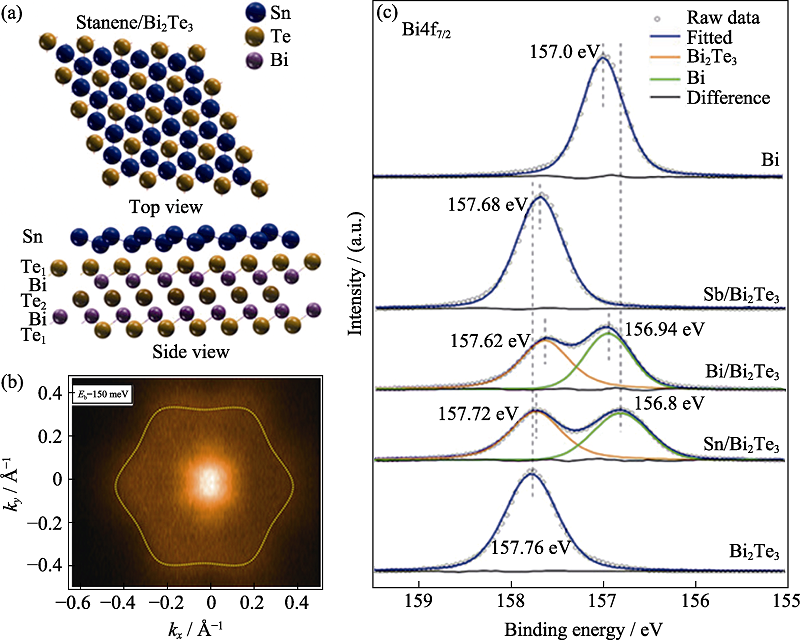
Fig. 14 Electronic structure and interfacial interaction of 2D Sn/Bi2Te3 material studied by SR-XRS[59] (a) Perspective top and side views of atomic structure of stanene/Bi2Te3; (b) ARPES intensity evolution of CE contours in the 2D Brillouin zone at the specified binding energies; (c) XPS results of Bi4f7/2 core levels. The Bi4f7/2 spectra are measured at 500 eV under room temperature (1 Å=0.1 nm) (colorful figures are available on website)
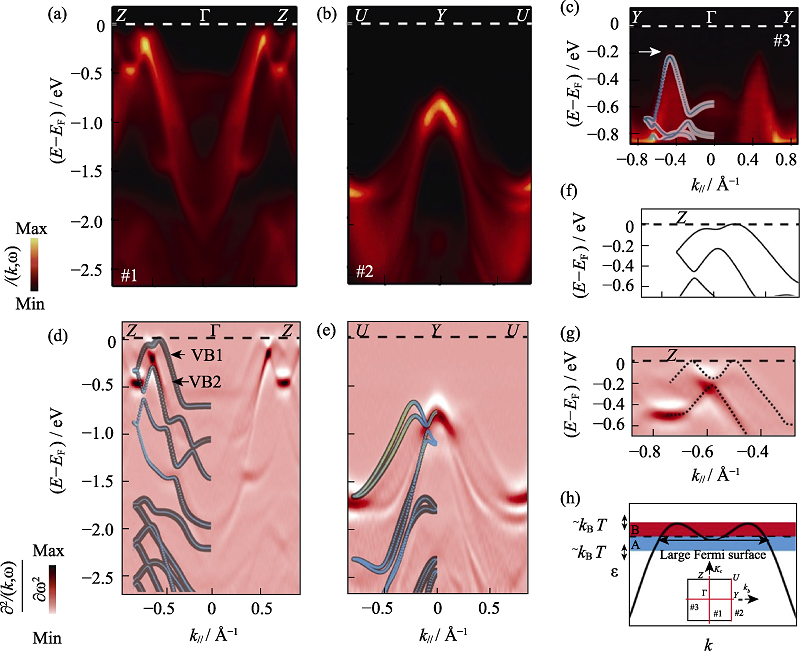
Fig. 15 Electronic structure of p-SnSe resolved by ARPES[60] ARPES measures band dispersions along high-symmetry directions of Z-Γ-Z (a), U-Y-U (b), and Y-Γ-Y (c), taken with 50 eV photon energy. The second derivative plots (d) and (e), corresponding to (a) and (b), respectively, directly compared with the DFT calculations, in which the weight of Sn5s and Se4p orbitals are represented by light blue and yellow, respectively; Close-up of the top VBs along Γ-Z reveals pronounced differences between the theoretical band dispersion (f) and the ARPES measured results (g), as highlighted by the X-shaped dashed lines; (h) Schematic plot of a pudding-moul shaped VB with corrugations, which leads to giant S due to the band geometry effect with inset showing the ARPES cut directions in the projected two-dimensional first Brillouin zone (BZ) (1 Å=0.1 nm)
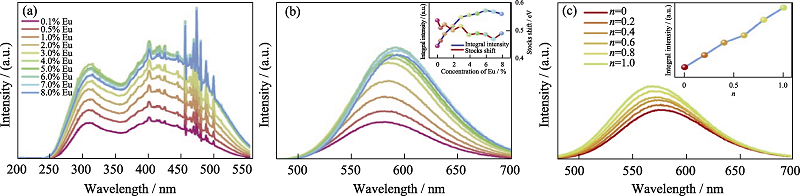
Fig. 16 Persistent luminescence properties of CaSi10-nAl2+nOnN16-n:xEu2+ material studied by VUV-UV spectra[61] (a) Excitation and (b) emission spectra of CaSi10Al2N16: xEu (x = 0.1%-8%) samples with inset showing the integral intensity (blue curve) and the Stokes shift (red curve) of those samples against Eu concentration (the sharp peaks in the range of 400-500 nm being caused by the Xe lamp equipped in the FLS 920 spectrophotometer); (c) Emission spectra of CaSi10-nAl2+nOnN16-n: 0.5%Eu (n=0-1) samples with inset showing the integral intensity versus n values (colorful figures are avaailable on websites)
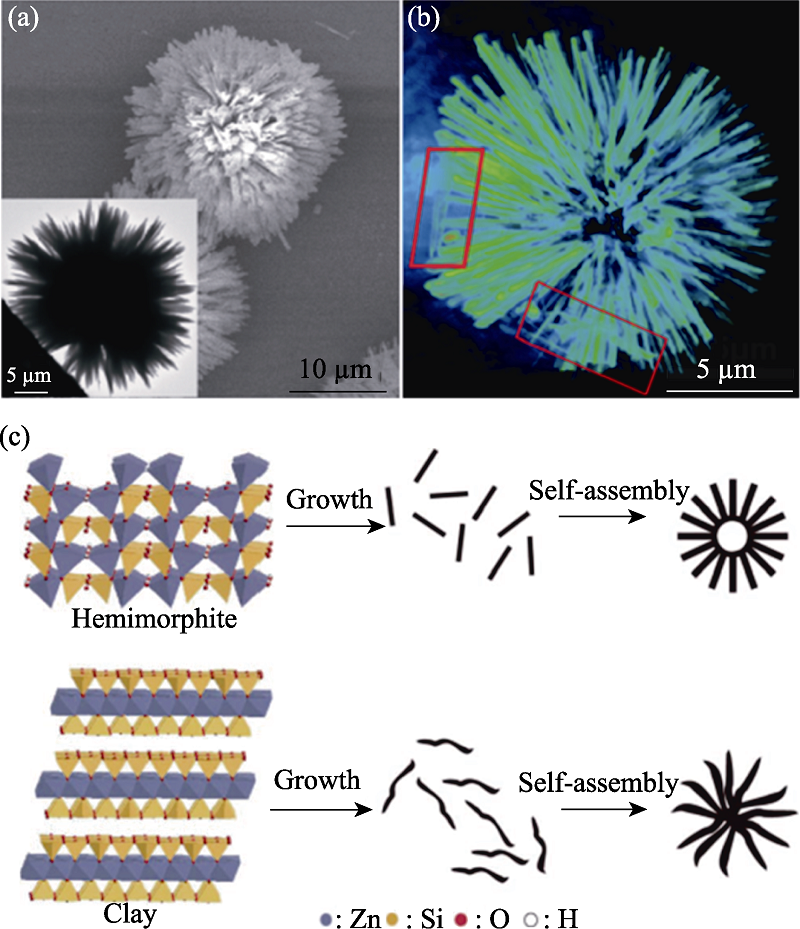
Fig. 17 Structural defects and formation process of Zn4Si2O7(OH)2·H2O particles studied by SR-XRI[66] (a) SEM image (inset: TEM image); (b) Reconstructed three dimensional rendering view of the urchin-like zinc silicate; (c) Schematic illustration of the preparation of the zinc silicate nanomaterials
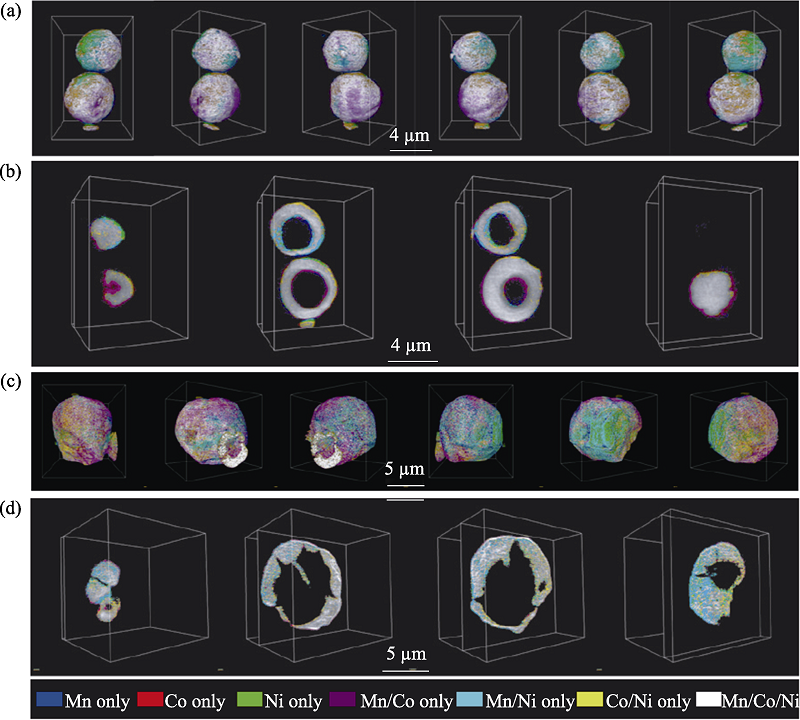
Fig. 18 3D element distribution of particles analyzed by X-ray tomography technique[67] Elemental association maps of the as-made NMC precursor after spray pyrolysis (a,b) and the powder after annealing at 850 ℃ (c,d); 3D rendering of the elemental associations viewing the particles at different angles (a,c); 2D slices of the elemental associations cut through at different depths of the imaged particles (b,d). The colours representing the elemental associations are shown at the bottom
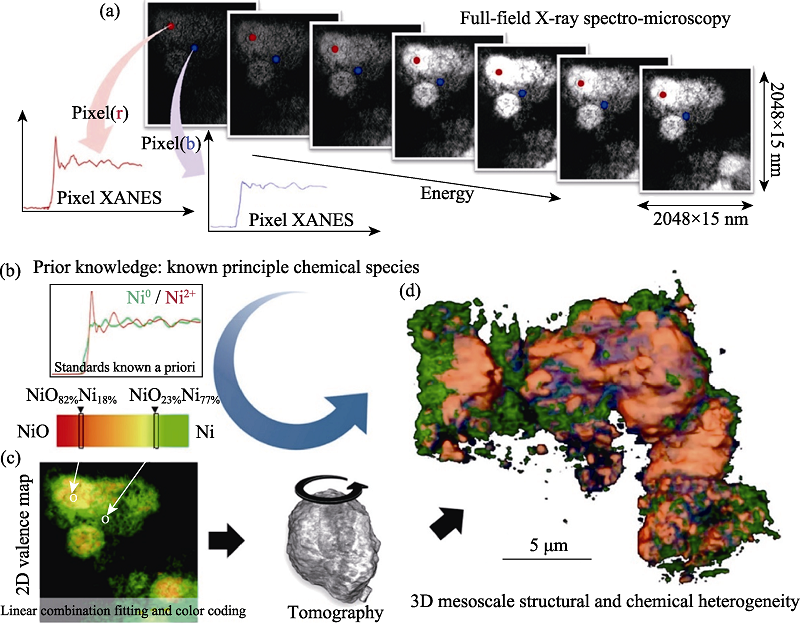
Fig. 19 3D distributions of chemical components and valence states of LiNi0.4Mn0.4Co0.2O2 battery particles studied by X-ray spectro-microscopy[68] (a) Panel illustrating the data structure; (b) Panel showing the prior knowledge of a list of anticipated principal chemical species in the sample, which is indispensable for the chemical mapping in this approach. Panel (c) illustrates the quantification procedures including the linear combination fitting, the color coding, and the tomographic reconstruction. Panel (d) shows the 3D mesoscale structural and chemical heterogeneity of a cluster of partially reduced NiO electrode particles
| [1] | 郑昌琼, 冉均国. 新型无机材料. 北京: 科学出版社, 2003. |
| [2] | ZHANG L L, JIANG H L, CHEN M Q, et al. Nanotechnology and nanomaterial-application of inorganic nano-materials in traditional industry sectors. China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics, 2004, 34(2):123-126. |
| [3] | KUMAR N, FOSSO-KANKEU E, RAY S S. Achieving controllable MoS2 nanostructures with increased interlayer spacing for efficient removal of Pb (II) from aquatic systems. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(21):19141-19155. |
| [4] |
LIU Y P, WANG H, QIAN L X, et al. Bismuth-iron-based precursor: preparation, phase composition, and its thermal treatment in two way. RSC Advances, 2020, 10(35):20713-20723.
DOI URL |
| [5] |
LIU Y P, QIAN L X, ZHAO X Y, et al. Synthesis and formation mechanism of self-assembled 3D flower-like Bi/γ-Fe2O3 composite particles. CrystEngComm, 2019, 21(17):2799-2808.
DOI URL |
| [6] |
WANG L, ZHOU H, HU J, et al. A Eu3+-Eu2+ ion redox shuttle imparts operational durability to Pb-I perovskite solar cells. Science, 2019, 363(6424):265-270.
DOI URL |
| [7] |
ZHAO X Y, LIU Y P, WANG J Y, et al. Modulating the hydrothermal synthesis of Co3O4 and CoOOH nanoparticles by H2O2concentration. Inorganic Chemistry, 2019, 58(10):7054-7061.
DOI URL |
| [8] |
LIU X J, HE J, ZHAO S Z, et al. Self-powered H2 production with bifunctional hydrazine as sole consumable. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1):1-10.
DOI URL |
| [9] | ZOU Z Y, HABRAKEN W J E M, MATVEEVA G, et al. A hydrated crystalline calcium carbonate phase: calcium carbonate hemihydrate. Science, 2019, 363(6425):396-400. |
| [10] |
HE W K, WANG D Y, WU H J, et al. High thermoelectric performance in low-cost SnS0.91Se0.09 crystals. Science, 2019, 365(6460):1418-1424.
DOI URL |
| [11] |
WANG Y, DAR M I, ONO L K, et al. Thermodynamically stabilized β-CsPbI3-based perovskite solar cells with efficiencies> 18%. Science, 2019, 365(6453):591-595.
DOI URL |
| [12] |
SURYANARAYANA C. Structure and properties of nanocrystalline materials. Bulletin of Materials Science, 1994, 17(4):307-346.
DOI URL |
| [13] | KENDALL K. Materials Science and Technology, Volume 11: Structure and Properties of Ceramics. VCH, Weinheim, Germany: MV Swain, 1994: 841. |
| [14] | WEN W, ZHANG L J, FU Y N, et al. Application of Shanghai light source in material science. Modern Physics, 2019, 31(5):9-26. |
| [15] | 冼鼎昌. 神奇的光: 同步辐射. 长沙: 湖南教育出版社, 1994. |
| [16] | ELDER F R, GUREWITSCH A M, LANGMUIR R V, et al. Radiation from electrons in a synchrotron. Physical Review, 1947, 71(11):829. |
| [17] | WINICK H, BIENENSTOCK A. Synchrotron radiation research. Annual Review of Nuclear and Particle Science, 1978, 28(1):33-113. |
| [18] | JACKSON J D. 经典电动力学. (下册). 北京: 人民教育出版社, 1980. |
| [19] | 刘祖平. 同步辐射光源物理引论. 合肥: 中国科学技术大学出版社, 2009. |
| [20] |
WINICK H, DONIACH S. Synchrotron radiation research. Journal of Vacuum Science and Technology, 1981, 19(1):126.
DOI URL |
| [21] | BROWN G S, MONCTON D E. Handbook on Synchrotron Radiation. North-Holland, 1991. |
| [22] | 马礼敦, 杨福家. 同步辐射应用概论. 上海: 复旦大学出版社, 2001. |
| [23] | 姜晓明, 修立松. 同步辐射及其应用. 北京: 北京科学技术出版社, 1996. |
| [24] | MAI Z H. Development history and current situation of synchrotron radiation-introduction to the new book “synchrotron radiation source and its application”. Modern Physics, 2014, 26(2):65-71. |
| [25] | 北京同步辐射装置[EB/OL]. [2020-12-07]. http://www.ihep.cas.cn/dkxzz/bsrf/. |
| [26] | 上海光源[EB/OL]. [2020-12-07]. http://ssrf.sinap.ac.cn/. |
| [27] | 国家同步辐射实验室[EB/OL]. [2020-12-07]. http://www.nsrl.ustc.edu.cn/. |
| [28] |
MCCUSKER L B, VON DREELE R B, COX D E, et al. Rietveld refinement guidelines. Journal of Applied Crystallography, 1999, 32(1):36-50.
DOI URL |
| [29] |
ZHAO H F, TAN D Y, TIAN Y, et al. Studies on Im-3-type KSbO3 using high pressure X-ray diffraction and Raman spectroscopy. High Pressure Research, 2018, 38(3):232-242.
DOI URL |
| [30] |
YAN Z P, YIN K T, YU Z H, et al. Pressure-induced band-gap closure and metallization in two-dimensional transition metal halide CdI2. Applied Materials Today, 2020, 18:100532.
DOI URL |
| [31] |
FENG G Q, ZHANG W X, DONG L Y, et al. Negative area compressibility of a hydrogen-bonded two-dimensional material. Chemical Science, 2019, 10(5):1309-1315.
DOI URL |
| [32] |
MAO H K, HEMLEY R J, WU Y, et al. High-pressure phase diagram and equation of state of solid helium from single-crystal X-ray diffraction to 23.3 GPa. Physical Review Letters, 1988, 60(25):2649.
DOI URL |
| [33] | FANG Y Y, ZHANG L, WU L W, et al. Pressure-induced emission (PIE) and phase transition of a two-dimensional halide double perovskite (BA)4AgBiBr8 (BA=CH3(CH2)3NH3+). Angewandte Chemie International Edition, 2019, 131(43):15393-15397. |
| [34] |
ZUO Y X, LI B, JIANG N, et al. A high-capacity O2-type Li-rich cathode material with a single-layer Li2MnO3 superstructure. Advanced Materials, 2018, 30(16):1707255.
DOI URL |
| [35] |
WANG J K, GAO R, ZHOU D, et al. Boosting the electrocatalytic activity of Co3O4 nanosheets for a Li-O2 battery through modulating inner oxygen vacancy and exterior Co3+/Co2+ ratio. ACS Catalysis, 2017, 7(10):6533-6541.
DOI URL |
| [36] |
WANG J K, GAO R, ZHENG L R, et al. CoO/CoP heterostructured nanosheets with an O-P interpenetrated interface as a bifunctional electrocatalyst for Na-O2 battery. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(9):8953-8960.
DOI URL |
| [37] | DU R, CHEN, Z J, CAI Q, et al. Application of Mythen detector: in-situ XRD study on the thermal expansion behavior of metal indium. Science China-Physics Mechanics & Astronomy, 2016, 59(7):677011. |
| [38] | DU R, CAI Q, CHEN Z J, et al. Mythen detector for X-ray diffraction at the Beijing synchrotron radiation facility. Instrumentation Science & Technology, 2016, 44(1):1-11. |
| [39] |
CHANG C, WU M H, HE D S, et al. 3D charge and 2D phonon transportsleading to high out-of-plane ZT in n-type SnSe crystals. Science, 2018, 360(6390):778-783.
DOI URL |
| [40] | KRISHNAMURTI P. Studies in X-ray diffraction. Part I: the structure of amorphous scattering. Part II: colloidal solutions and liquid mixtures. Indian Journal of Physics, 1930, 5:473-500. |
| [41] |
WARREN B E. X-ray diffraction study of carbon black. The Journal of Chemical Physics, 1934, 2(9):551-555.
DOI URL |
| [42] | ANDRÉ G, GÉRARD F, WALKER C B, et al. Small-angle scattering of X-rays. Physics Today, 1956, 9(8):38. |
| [43] |
YAN S, WU Z H, YU H Y, et al. Time-resolved small-angle X-ray scattering study on the growth behavior of silver nanoparticles. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2014, 118(21):11454-11463.
DOI URL |
| [44] |
YAN S, SUN D B, TAN Y Y, et al. Synthesis and formation mechanism of Ag-Ni alloy nanoparticles at room temperature. Journal of Physics and Chemistry of Solids, 2016, 98:107-114.
DOI URL |
| [45] |
YAN S, SUN D B, GONG Y, et al. Temperature-driven directional coalescence of silver nanoparticles. Journal of Synchrotron Radiation, 2016, 23(3):718-728.
DOI URL |
| [46] |
TAN Y Y, SUN D B, YU H Y, et al. In-situ time-resolved X-ray absorption fine structure and small angle X-ray scattering revealed an unexpected phase structure transformation during the growth of nickel phosphide nanoparticles. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2018, 122(28):16397-16405.
DOI URL |
| [47] |
WANG J Y, ZHAO X Y, LIU Y P, et al. Small-angle X-ray scattering study on the orientation of suspended sodium titanate nanofiber induced by applied electric field. Radiation Detection Technology and Methods, 2019, 3(3):1-7.
DOI URL |
| [48] |
LI H, LI C R, SUN W, et al. Single-stimulus-induced modulation of multiple optical properties. Advanced Materials, 2019, 31(23):1900388.
DOI URL |
| [49] |
ZHANG H, DASBISWAS K, LUDWIG N B, et al. Stable colloids in molten inorganic salts. Nature, 2017, 542(7641):328-331.
DOI URL |
| [50] |
YAO T, LIU S J, SUN Z H, et al. Probing nucleation pathways for morphological manipulation of platinum nanocrystals. Journal of the American Chemical Society, 2012, 134(22):9410-9416.
DOI URL |
| [51] |
QIAO B T, WANG A Q, YANG X F, et al. Single-atom catalysis of CO oxidation using Pt1/FeOx. Nature Chemistry, 2011, 3(8):634-641.
DOI URL |
| [52] |
WANG X J, WANG H Y, LIU Y C, et al. A direct sulfation method for introducing the transition metal cation Co2+ into ZrO2 with little change in the Brønsted acid sites. Journal of Catalysis, 2011, 279(2):301-309.
DOI URL |
| [53] |
XIN Y, LI H, ZHANG N N, et al. Molecular-level insight into selective catalytic reduction of NOx with NH3 to N2 over a highly efficient bifunctional Va-MnOx catalyst at low temperature. ACS Catalysis, 2018, 8(6):4937-4949.
DOI URL |
| [54] |
CAO L N, LIU W, LUO Q Q, et al. Atomically dispersed iron hydroxide anchored on Pt for preferential oxidation of CO in H2. Nature, 2019, 565(7741):631-635.
DOI URL |
| [55] |
XIONG F Y, AN Q Y, XIA L X, et al. Revealing the atomistic origin of the disorder-enhanced Na-storage performance in NaFePO4 battery cathode. Nano Energy, 2019, 57:608-615.
DOI URL |
| [56] |
LI B, JIANG N, HUANG W F, et al. Thermodynamic activation of charge transfer in anionic redox process for Li-ion batteries. Advanced Functional Materials, 2018, 28(4):1704864.
DOI URL |
| [57] |
HE W, WANG D, WU H, et al. High thermoelectric performance in low-cost SnS0.91Se0.09 crystals. Science, 2019, 365(6460):1418-1424.
DOI URL |
| [58] | HUMMEL R E. Electronic Properties of Materials. Springer Science & Business Media, 2011. |
| [59] |
LI J M, LEI T, WANG J O, et al. Anisotropic electronic structure and interfacial chemical reaction of stanene/Bi2Te3. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2020, 124(8):4917-4924.
DOI URL |
| [60] |
WANG Z, FAN C C, SHEN Z X, et al. Defects controlled hole doping and multivalley transport in SnSe single crystals. Nature Communications, 2018, 9(1):1-9.
DOI URL |
| [61] |
WANG F X, GUO J Z, WANG S X, et al. Yellow persistent luminescence and electronic structure of Ca-α-Sialon: Eu2+. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2020, 821:153482.
DOI URL |
| [62] | ZHOU X J, ZHONG J J, DONG J M, et al. Applications of NFPS/SSRF BL01B1 Synchrotron Infrared Beamline Station. Spectroscopy and Spectral Analysis, 2018, 38(10):29-30. |
| [63] | YUAN Q X, DENG B, GUAN Y, et al. Novel developments and applications of nanoscale synchrotron radiation microscopy. Physics, 2019, 48(4):205-218. |
| [64] |
CHEN J, WU C Y, TIAN J P, et al. Three-dimensional imaging of a complex concaved cuboctahedron copper sulfide crystal by X-ray nanotomography. Applied Physics Letters, 2008, 92(23):233104.
DOI URL |
| [65] |
CAO C, TONEY M F, SHAM T K, et al. Emerging X-ray imaging technologies for energy materials. Materials Today, 2020, 34:132-147.
DOI URL |
| [66] |
QU J, CAO C Y, HONG Y L, et al. New hierarchical zinc silicate nanostructures and their application in lead ion adsorption. Journal of Materials Chemistry, 2012, 22(8):3562-3567.
DOI URL |
| [67] | LIN F, NORDLUND D, LI Y Y, et al. Metal segregation in hierarchically structured cathode materials for high-energy lithium batteries. Nature Energy, 2016, 1(1):1-8. |
| [68] |
WEI C X, XIA S H, HUANG H, et al. Mesoscale battery science: the behavior of electrode particles caught on a multispectral X-ray camera. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2018, 51(10):2484-2492.
DOI URL |
| [69] | LIU Z J, LUO Z L. Simultaneous quick measurements of combined synchrotron EDXAFS and EDXRD. Nuclear Techniques, 2019, 42(12):8-12. |
| [70] | WU Z H, HUANG Y Y, ZHANG J L, et al. Real-time tracking research on the formation of new materials in complex fluids. China Basic Science, 2018, 20:17-22. |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | ZHANG Jiguo, WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien. Improvement of Cycling Stability of Cathode Materials and Industrialization Process for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | FAN Xiaobo, ZU Mei, YANG Xiangfei, SONG Ce, CHEN Chen, WANG Zi, LUO Wenhua, CHENG Haifeng. Research Progress on Proton-regulated Electrochemical Ionic Synapses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | HAIREGU Tuxun, GUO Le, DING Jiayi, ZHOU Jiaqi, ZHANG Xueliang, NUERNISHA Alifu. Research Progress of Optical Bioimaging Technology Assisted by Upconversion Fluorescence Probes in Tumor Imaging [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | SUN Shujuan, ZHENG Nannan, PAN Haokun, MA Meng, CHEN Jun, HUANG Xiubing. Research Progress on Preparation Methods of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | TAO Guilong, ZHI Guowei, LUO Tianyou, OUYANG Peidong, YI Xinyan, LI Guoqiang. Progress on Key Technologies of Cavity-structured Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Wave Filter [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | ZHOU Fan, TIAN Zhilin, LI Bin. Research Progress on Carbide Ultra-high Temperature Ceramic Anti-ablation Coatings for Thermal Protection System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||