
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2018, Vol. 33 ›› Issue (6): 609-616.DOI: 10.15541/jim20170355
Special Issue: 陶瓷基复合材料
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
HUANG Xi-Peng1, WANG Bo2, YANG Cheng-Peng1, PAN Wen-Ge1, LIU Xiao-Ying3
Received:2017-08-07
Revised:2017-11-09
Published:2018-06-20
Online:2018-05-24
About author:HUANG Xi-Peng. E-mail: huangxp_nwpu@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
HUANG Xi-Peng, WANG Bo, YANG Cheng-Peng, PAN Wen-Ge, LIU Xiao-Ying. Evaluating Damage Evolution of Three-dimension Needled C/SiC Composite Based on Acoustic Emission Signal Analysis[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(6): 609-616.
| Modulus/ GPa | Strength/ MPa | Failure strain/% | Elastic limit/MPa | Poisson’s ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 104.29 | 115.06 | 0.3061 | 37.67 | 0.08 |
Table 1 Tensile mechanical properties of 3D-N C/SiC
| Modulus/ GPa | Strength/ MPa | Failure strain/% | Elastic limit/MPa | Poisson’s ratio |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 104.29 | 115.06 | 0.3061 | 37.67 | 0.08 |
| Cluster | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitude/mV | 226.4 | 1147.5 | 496.2 | 64.4 | 122.5 |
| Energy/(mV×ms) | 34.2 | 78.4 | 49.0 | 12.5 | 22.0 |
Table 2 Numerical value of the clustering center
| Cluster | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Amplitude/mV | 226.4 | 1147.5 | 496.2 | 64.4 | 122.5 |
| Energy/(mV×ms) | 34.2 | 78.4 | 49.0 | 12.5 | 22.0 |
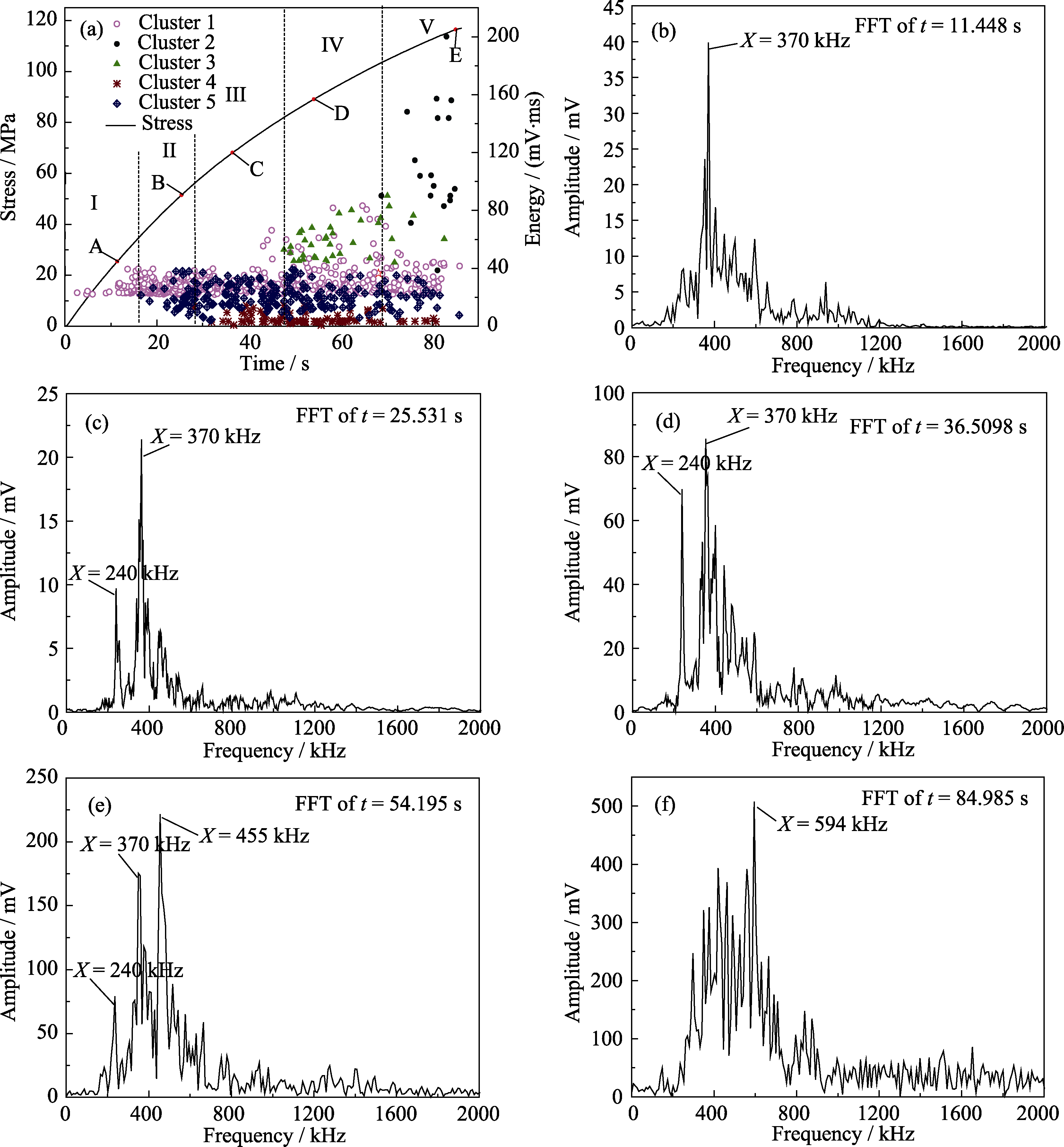
Fig. 8 Characteristics of acoustic emission events with stress distribution in 3D-N C/SiC (a) and spectral characteristics of the signal wave at point A (b), B (c), C (d), D (e) and E (f) in (a)
| Damage modes | Cluster | Energy/(mV·ms) | Frequency/kHz | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix cracking | 1 | 20-80 | 370 | When the load exceeds the proportional limit (37 MPa), crack begins to form and spreads until the sample fails. |
| Interface debonding | 5 | 10-40 | 240 | When crack extends to the fiber, it deflects and expands along the interface. |
| Interfacial slipping | 4 | 0-20 | ||
| Fiber breakage | 3 | 40-80 | 455 | As cracks become saturated, the fibers begin to break. |
| Fiber cluster failure | 2 | 70-260 | 594 | That cracks in the material expand rapidly to form macro-cracks attributes to fiber bundle breakage. |
Table 3 Characterization of acoustic emission signals and description of the damage modes
| Damage modes | Cluster | Energy/(mV·ms) | Frequency/kHz | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Matrix cracking | 1 | 20-80 | 370 | When the load exceeds the proportional limit (37 MPa), crack begins to form and spreads until the sample fails. |
| Interface debonding | 5 | 10-40 | 240 | When crack extends to the fiber, it deflects and expands along the interface. |
| Interfacial slipping | 4 | 0-20 | ||
| Fiber breakage | 3 | 40-80 | 455 | As cracks become saturated, the fibers begin to break. |
| Fiber cluster failure | 2 | 70-260 | 594 | That cracks in the material expand rapidly to form macro-cracks attributes to fiber bundle breakage. |
| [1] | CHEN XIAO-MING, CHEN LI, ZHANG CHUN-YAN,et al. Three-dimensional needle-punching for composites - a review. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2016, 85: 12-30. |
| [2] | KADIR BILISIK.Three-dimensional braiding for composites: a review.Textile Research Journal, 2012, 83(13): 1414-1436. |
| [3] | NIE JING-JIANG, XU YONG-DONG, ZHANG LI-TONG,et al. Microstructure and tensile behavior of multiply needled C/SiC composite fabricated by chemical vapor infiltration. Journal of Materials Processing Technology, 2009, 209(1): 572-576. |
| [4] | CHEN ZHEN, FANG GUO-DONG, XIE JUN-BO,et al. Experimental study of high-temperature tensile mechanical properties of 3D needled C/C-SiC composites. Materials Science & Engineering A, 2016, 654(10): 271-277. |
| [5] | XU HUA-JIE, ZHANG LI-TONG, CHENG LAI-FEI.The yarn size dependence of tensile and in-plane shear properties of three- dimensional needled textile reinforced ceramic matrix composites.Materials & Design, 2015, 67: 428-435. |
| [6] | XIE JUN-BO, FANG GUO-DONG, CHEN ZHEN, et al. An anisotropic elastoplastic damage constitutive model for 3D needled C/C-SiC composites. Composite Structures, 2017, 176: 164-177. |
| [7] | ZARIF KARIMI N, MINAK G, KIANFAR P.Analysis of damage mechanisms in drilling of composite materials by acoustic emission.Composite Structures, 2015, 131: 107-114. |
| [8] | MEI HUI, SUN YU-YAO, ZHANG LI-TONG,et al. Acoustic emission characterization of fracture toughness for fiber reinforced ceramic matrix composites. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2013, 560: 372-376. |
| [9] | MAILLET E, BAKER C, MORSCHER G N,et al. Feasibility and limitations of damage identification in composite materials using acoustic emission. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2015, 75: 77-83. |
| [10] | CHANG YAN-JUN, JIAO GUI-QIONG, ZHANG KE-SHI,et al. Investigation on tensile properties for 3D C/SiC composites by acoustic emission. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2010, 27(6): 82-87. |
| [11] | MOMON S, GODIN N, REYNAUD P,et al. Unsupervised and supervised classification of AE data collected during fatigue test on CMC at high temperature. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2012, 43(2): 254-260. |
| [12] | TONG XIAO-YAN, ZHANG JIA-LI, YAO LEI-JIANG, et al. Cluster analysis of acoustic emission signals of 2D-C/SiC under tensile loading. Chinese Journal of Solid Mechanics, 2014, 35(2): 109-114. |
| [13] | YAN LIAN-SHENG, CUI HONG, LI KE-ZHI, et al. Preparation and properties of carbon fiber needling preform reinforced silicon carbide composite. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2008, 23(2): 223-228. |
| [14] | JEONG H.Analysis of plate wave propagation in anisotropic laminates using a wavelet transform.NDT & E International, 2001, 34(3): 185-190. |
| [15] | MORIZET N, GODIN N, TAMG J, et al. Classification of acoustic emission signals using wavelets and random forests: application to localized corrosion. Mechanical Systems and Signal Processing, 2016, 70-71: 1026-1037. |
| [16] | SAIDANE E H, SCIDA D, ASSARAR M,et al. Damage mechanisms assessment of hybrid flax-glass fiber composites using acoustic emission. Composite Structures, 2017, 174(Supplement C): 1-11. |
| [17] | MORSCHER G, SINGH M, KISER J,et al. Modeling stress- dependent matrix cracking and stress-strain behavior in 2D woven SiC fiber reinforced CVI SiC composites. Composites Science and Technology, 2007, 67(6): 1009-1017. |
| [18] | BREEDE F, KOCH D, MAILLET E,et al. Modal acoustic emission of damage accumulation in C/C-SiC composites with different fiber architectures. Ceramic International, 2015, 41(9, Part B): 12087-12098. |
| [19] | LI PAN, WANG BO, ZHEN WEN-QIANG.Tensile constitutive model of 2D-SiC/SiC ceramic matrix composites.China Ceramic Industry, 2013, 20(5): 10-14. |
| [20] | LI LI, LOMOV S V, YAN X,et al. Cluster analysis of acoustic emission signals for 2D and 3D woven glass/epoxy composites. Composite Structures, 2014, 116(1): 286-299. |
| [21] | ECH-CHOUDARY Y, ASSARAR M, SCIDA D,et al. Unsupervised clustering for building a learning database of acoustic emission signals to identify damage mechanisms in unidirectional laminates. Applied Acoustics, 2017, 123: 123-132. |
| [22] | XU YONG-DONG, CHENG LAI-FEI, ZHANG LI-TONG.Carbon/ silicon carbide composites prepared by chemical vapor infiltration combined with silicon melt infiltration. Carbon, 1999, 37(8): 1179-1187. |
| [23] | SINGH Y P, MANSOUR R, MORSCHER G N.Combined acoustic emission and multiple lead potential drop measurements in detailed examination of crack initiation and growth during inter-laminar testing of ceramic matrix composites.Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2017, 97: 93-99. |
| [24] | SUN ZHI-GANG, SHAO HONG-YAN, NIU XU-MING,et al. Failure simulation of unidirectional fiber-reinforced ceramic matrix composites based on evolving compliant interfacial debonding model. Materials Science and Engineering: A, 2016, 663: 78-85. |
| [25] | MORSCHER G N, GORDON N A.Acoustic emission and electrical resistance in SiC-based laminate ceramic composites tested under tensile loading.Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2017, 37(13): 3861-3872. |
| [26] | GUTKIN R, GREEN C J, VANGRATTANACHAI S,et al. On acoustic emission for failure investigation in CFRP: pattern recognition and peak frequency analyses. Mechanical Systems & Signal Processing, 2011, 25(4): 1393-1407. |
| [1] | CHEN Yi, QIU Haipeng, CHEN Mingwei, XU Hao, CUI Heng. SiC/SiC Composite: Matrix Boron Modification and Mechanical Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(5): 504-510. |
| [2] | ZHANG Li, GUAN Haoyang, ZHENG Qining, HONG Zhiliang, WANG Jiaxuan, XING Ning, LI Mei, LIU Yongsheng, ZHANG Chengyu. Creep Properties and Damage Mechanisms of SiCf/SiC-SiYBC Prepared by Melt Infiltration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 23-30. |
| [3] | QUAN Wenxin, YU Yiping, FANG Bing, LI Wei, WANG Song. Oxidation Behavior and Meso-macro Model of Tubular C/SiC Composites in High-temperature Environment [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(8): 920-928. |
| [4] | WU Xiaochen, ZHENG Ruixiao, LI Lu, MA Haolin, ZHAO Peihang, MA Chaoli. Research Progress on In-situ Monitoring of Damage Behavior of SiCf/SiC Ceramic Matrix Composites at High Temperature Environments [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(6): 609-622. |
| [5] | SHEN Xuanyi, MA Qin, XUE Yudong, LIAO Chunjin, ZHU Min, ZHANG Xiangyu, YANG Jinshan, DONG Shaoming. Effects of Multilayered Interfaces on Mechanical Damage of SiCf/SiC Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(8): 917-922. |
| [6] | WANG Hongda, FENG Qian, YOU Xiao, ZHOU Haijun, HU Jianbao, KAN Yanmei, CHEN Xiaowu, DONG Shaoming. Microstructure and Corrosion Behavior of Brazed Joints of SiC/SiC Composites and Hastelloy N Alloy Using Cu-Ni Alloy [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(4): 452-458. |
| [7] | ZHANG Yachen, MENG Jia, CAI Kun, SHENG Xiaochen, LE Jun, SONG Lixin. Bending Failure Mechanism Study of Si-Cr-Ti High Temperature Oxidation Resistance Coating via Acoustic Emission Technique [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1185-1192. |
| [8] | LI Longbin, XUE Yudong, HU Jianbao, YANG Jinshan, ZHANG Xiangyu, DONG Shaoming. Influence of SiC Nanowires on the Damage Evolution of SiCf/SiC Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(10): 1111-1117. |
| [9] | ZHANG Bingyu,WANG ling,WANG Xiaomeng,QIU Haipeng. Effect of Precursors on Impregnation Behaviors of C/SiC Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(9): 1017-1022. |
| [10] | ZHANG Yongzhen, TONG Xiaoyan, YAO Leijiang, LI Bin, BAI Guodong. Acoustic Emission Pattern Recognition on Tensile Damage Process of C/SiC Composites Using an Improved Genetic Algorithm [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(5): 593-600. |
| [11] | ZHAO Shuang, YANG Zi-Chun, ZHOU Xin-Gui. Fracture Behavior of SiC/SiC Composites with Different Interfaces [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(1): 58-62. |
| [12] | WANG Hao, ZHOU Qing-Jun, JIAN Ke, SHAO Chang-Wei, ZHU Yi-Hua. Preparation of Ordered Porous Ceramic Joint on C/SiC Composites and Its Joining Technique [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(7): 763-768. |
| [13] | MA Qing-Song, LIU Hai-Tao, PAN Yu, LIU Wei-Dong, CHEN Zhao-Hui. Research Progress on the Application of C/SiC Composites in Scramjet [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2013, 28(3): 247-255. |
| [14] | DENG Qi-Huang, WANG Lian-Jun, XU Hong-Jie, WANG Hong-Zhi, JIANG Wan. Fatigue Life Investigation of PZT Ceramics by MSP Method [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2012, 27(10): 1047-1052. |
| [15] | ZHAO Dan, ZHANG Chang-Rui, ZHANG Yu-Di, CHEN Si-An, HU Hai-Feng. Reactive Preparation and Properties of ZrB2 Coating [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2011, 26(9): 902-906. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||