
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2017, Vol. 32 ›› Issue (7): 699-704.DOI: 10.15541/jim20160516
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
YANG Tao1,2, LI Xiao1,2, TIAN Xiao-Dong1,2, SONG Yan1, LIU Zhan-Jun1, GUO Quan-Gui1
Received:2016-09-18
Revised:2016-12-29
Published:2017-07-20
Online:2017-06-23
About author:YANG Tao. E-mail: taomung@126.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
YANG Tao, LI Xiao, TIAN Xiao-Dong, SONG Yan, LIU Zhan-Jun, GUO Quan-Gui. Preparation and Electrochemical Performance of Si@C/SiOx as Anode Material for Lithium-ion Batteries[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2017, 32(7): 699-704.
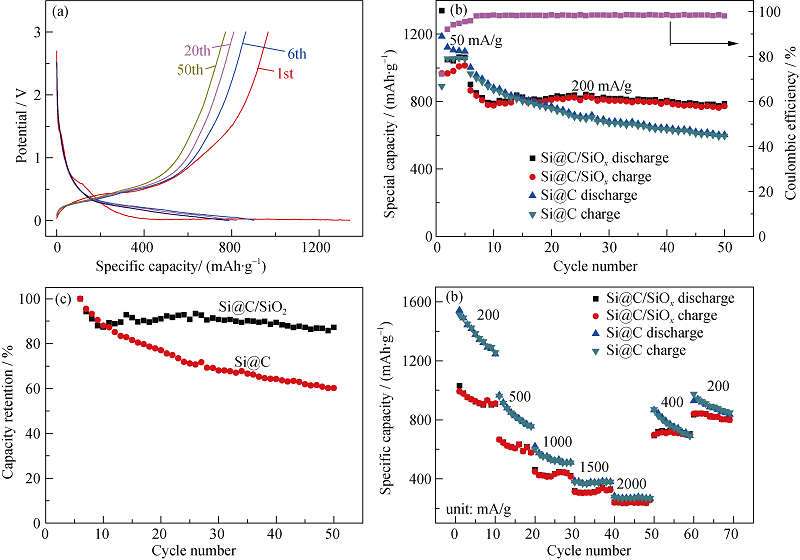
Fig. 6 (a) Galvanostatic charge-discharge profiles of Si@C/SiOx, (b) cycle performance of Si@C and Si@C/SiOx, (c) capacity retention of Si@C and Si@C/SiOx measured at 200 mA/g, and (d) rate capacity of Si@C and Si@C/SiOx nanocompositesAll electrochemical performance is measured at room temperature
| [1] | YAO Y, MCDOWELL M T, RYU I, et al.Interconnected silicon hollow nanospheres for lithium-ion battery anodes with long cycle life.Nano Lett., 2011, 7(11): 2949-2954. |
| [2] | CHEN T, HU Y, CHENG B, et al.Multi-yolk-shell copper oxide@carbon octahedra as high-stability anodes for lithium-ion batteries.Nano Energy, 2016, (20): 305-314. |
| [3] | YAN N, WANG F, ZHONG H, et al.Hollow porous SiO2 nanocubes towards high-performance anodes for lithium-ion batteries.Sci. Rep., 2013, 3: 1568-1574. |
| [4] | HUANG Y H, HAN X, CHEN H X, et al.Investigation of porous silicon/carbon composite as anodes for lithium ion batteries.J. Inorg. Mater., 2015, 4(30): 351-356. |
| [5] | JUNG Y S, LEE K T, OH S M.Si-carbon core-shell composite anode in lithium secondary batteries.Electrochim. Acta, 2007, 24(52): 7061-7067. |
| [6] | BRIDEL J S, AZAIS T, MORCRETTE M, et al.In situ observation and long-term reactivity of Si/C/CMC composites electrodes for Li-ion batteries.J. Electrochem. Soc., 2011, 6(158): A750-A759. |
| [7] | LEE J K, KUNG M C, TTAHEY L, et al.Nanocomposites derived from phenol-functionalized Si nanoparticles for high performance lithium Ion battery anodes.Chem.Mater., 2009, 1(21): 6-8. |
| [8] | LIU N, WU H, MCDOWELL M T, et al.A yolk-shell design for stabilized and scalable Li-ion battery alloy anodes.Nano Lett., 2012, 6(12): 3315-3321. |
| [9] | XU Y, YIN G, MA Y, et al.Nanosized core/shell silicon@carbon anode material for lithium ion batteries with polyvinylidene fluoride as carbon source.J. Mater. Chem., 2010, 16(20): 3216-3220. |
| [10] | DENG J, Ji H, YAN C, et al.Naturally rolled-up C/Si/C trilayer nanomembranes as stable anodes for lithium-ion batteries with remarkable cycling performance.Angew Chem Int Ed Engl, 2013, 8(52): 2326-2330. |
| [11] | CHEN S, GORDIN M L, YI R, et al.Silicon core-hollow carbon shell nanocomposites with tunable buffer voids for high capacity anodes of lithium-ion batteries.Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2012, 37(14): 12741-12745. |
| [12] | CHAE S, KO M, PARK S, et al.Micron-sized Fe-Cu-Si ternary composite anodes for high energy Li-ion batteries.Energy Environ. Sci., 2016, 4(9): 1251-1257. |
| [13] | FANG S, SHEN L, XU G, et al.Rational design of void-involved Si@TiO2 nanospheres as high-performance anode material for lithium-ion batteries.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2014, 9(6): 6497-6503. |
| [14] | GUO J, SUN A, WANG C.A porous silicon-carbon anode with high overall capacity on carbon fiber current collector.Electrochem. Commun., 2010, 7(12): 981-984. |
| [15] | LI H H, WANG J W, WU X L, et al.A novel approach to prepare Si/C nanocomposites with yolk-shell structures for lithium ion batteries.RSC Adv., 2014, 68(4): 36218-36225. |
| [16] | YOO H, LEE J I, KIM H, et al.Helical silicon/silicon oxide core-shell anodes grown onto the surface of bulk silicon.Nano Lett., 2011, 10(11): 4324-4328. |
| [17] | ZHANG C, GU L, KASKHEDIKAR N, et al.Preparation of silicon@silicon oxide core-shell nanowires from a silica precursor toward a high energy density Li-ion battery anode.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 23(5): 12340-12345. |
| [18] | WANG S, ZHANG M, ZHANG W.Yolk-shell catalyst of single Au nanoparticle encapsulated within hollow mesoporous Silica Microspheres.ACS Catal., 2011, 3(1): 207-211. |
| [19] | SU L, ZHOU Z, REN M.Core double-shell Si@SiO2@C nanocomposites as anode materials for Li-ion batteries.Chem. Commun., 2010, 15(46): 2590-2592. |
| [20] | TAO H C, YANG X L, ZHANG L L, et al.Double-walled core-shell structured Si@SiO2@C nanocomposite as anode for lithium-ion batteries.Ionics, 2014, 11(20): 1547-1552. |
| [21] | YANG L Y, LI H Z, LIU J, et al.Dual yolk-shell structure of carbon and silica-coated silicon for high-performance lithium-ion batteries.Sci. Rep., 2015, 5: 10908-10916. |
| [22] | JI L, ZHANG X.Electrospun carbon nanofibers containing silicon particles as an energy-storage medium.Carbon, 2009, 14(47): 3219-3226. |
| [23] | TAO H C, FAN L Z, SONG W L, et al.Hollow core-shell structured Si/C nanocomposites as high-performance anode materials for lithium-ion batteries.Nanoscale, 2014, 6(6): 3138-3142. |
| [24] | WANG J, ZHAO H, HE J, et al.Nano-sized SiOx/C composite anode for lithium ion batteries.J. Power Sources, 2011, 10(196): 4811-4815. |
| [1] | YANG Endong, LI Baole, ZHANG Ke, TAN Lu, LOU Yongbing. ZnCo2O4-ZnO@C@CoS Core-shell Composite: Preparation and Application in Supercapacitors [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(5): 485-493. |
| [2] | ZHANG Tingting, WANG Fangyuan, LIU Changyou, ZHANG Guorong, LÜ Jiahui, SONG Yuchen, JIE Wanqi. Hydrothermal-sintering Preparation of Cr2+:ZnSe/ZnSe Nanotwins with Core-shell Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(4): 409-415. |
| [3] | YUE Quanxin, GUO Ruihua, WANG Ruifen, AN Shengli, ZHANG Guofang, GUAN Lili. 3D Core-shell Structured NiMoO4@CoFe-LDH Nanorods: Performance of Efficient Oxygen Evolution Reaction and Overall Water Splitting [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1254-1264. |
| [4] | WU Rui, ZHANG Minhui, JIN Chenyun, LIN Jian, WANG Deping. Photothermal Core-Shell TiN@Borosilicate Bioglass Nanoparticles: Degradation and Mineralization [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(6): 708-716. |
| [5] | MA Xiaosen, ZHANG Lichen, LIU Yanchao, WANG Quanhua, ZHENG Jiajun, LI Ruifeng. 13X@SiO2: Synthesis and Toluene Adsorption [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2023, 38(5): 537-543. |
| [6] | CHI Congcong, QU Panpan, REN Chaonan, XU Xin, BAI Feifei, ZHANG Danjie. Preparation of SiO2@Ag@SiO2@TiO2 Core-shell Structure and Its Photocatalytic Degradation Property [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 750-756. |
| [7] | JIANG Yiyi, SHEN Min, SONG Banxia, LI Nan, DING Xianghuan, GUO Leyi, MA Guoqiang. Effect of Dual-functional Electrolyte Additive on High Temperature and High Voltage Performance of Li-ion Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(7): 710-716. |
| [8] | CHEN Xiaomei, CHEN Ying, YUAN Xia. Decomposition of Cyclohexyl Hydroperoxide Catalyzed by Core-shell Material Co3O4@SiO2 [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2022, 37(1): 65-71. |
| [9] | ZENG Fanxin, LIU Chuang, CAO Yuliang. Sodium Storage Behavior of Nanoporous Sb/MCNT Anode Material with High Cycle Stability by Dealloying Route [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2021, 36(11): 1137-1144. |
| [10] | GUO Si-Lin, KANG Shuai, LU Wen-Qiang. Ge Nanoparticles in MXene Sheets: One-step Synthesis and Highly Improved Electrochemical Property in Lithium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 105-111. |
| [11] | LI Meng-Xia, LU Yue, WANG Li-Bin, HU Xian-Luo. Controlled Synthesis of Core-shell Structured Mn3O4@ZnO Nanosheet Arrays for Aqueous Zinc-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2020, 35(1): 86-92. |
| [12] | Shi-Qiang LUO, Chun-Man ZHENG, Wei-Wei SUN, Wei XIE, Jian-Huang KE, Shuang-Ke LIU, Xiao-Bin HONG, Yu-Jie LI, Jing XU. Controllable Preparation of Co-NC Nanoporous Carbon Derived from ZIF-67 for Advanced Lithium-sulfur Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(5): 502-508. |
| [13] | Yi TAN, Kai WANG. Silicon-based Anode Materials Applied in High Specific Energy Lithium-ion Batteries: a Review [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(4): 349-357. |
| [14] | HU Xi, LIU Hong-Bo, XIA Xiao-Hong, GU Zhi-Qiang. Polyaniline-carbon Pillared Graphene Composite: Preparation and Electrochemical Performance [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2019, 34(2): 145-151. |
| [15] | LIU Huan-Long, ZHAO Wei, LI Rui-Zhe, HUANG Xie-Yi, TANG Yu-Feng, LI Dong-Mei, HUANG Fu-Qiang. Facile Synthesis of Reduced Graphene Oxide In-situ Wrapped MnTiO3 Nanoparticles for Excellent Lithium Storage [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2018, 33(9): 1022-1028. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||