
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2016, Vol. 31 ›› Issue (8): 869-875.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150633
• Orginal Article • Previous Articles Next Articles
ZOU Yang, ZHAO Li-Li, YOU Li-Jun, CHEN Xiao-Ying, SONG Li-Xin
Received:2015-12-16
Published:2016-08-20
Online:2016-07-20
About author:ZOU Yang(1989–), male, candidate of master degree. E-mail: zouyang@student.sic.ac.cn
CLC Number:
ZOU Yang, ZHAO Li-Li, YOU Li-Jun, CHEN Xiao-Ying, SONG Li-Xin. Preparation and Numerical Simulation Investigation of High Reflectance Anti-laser-ablation Coating[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2016, 31(8): 869-875.
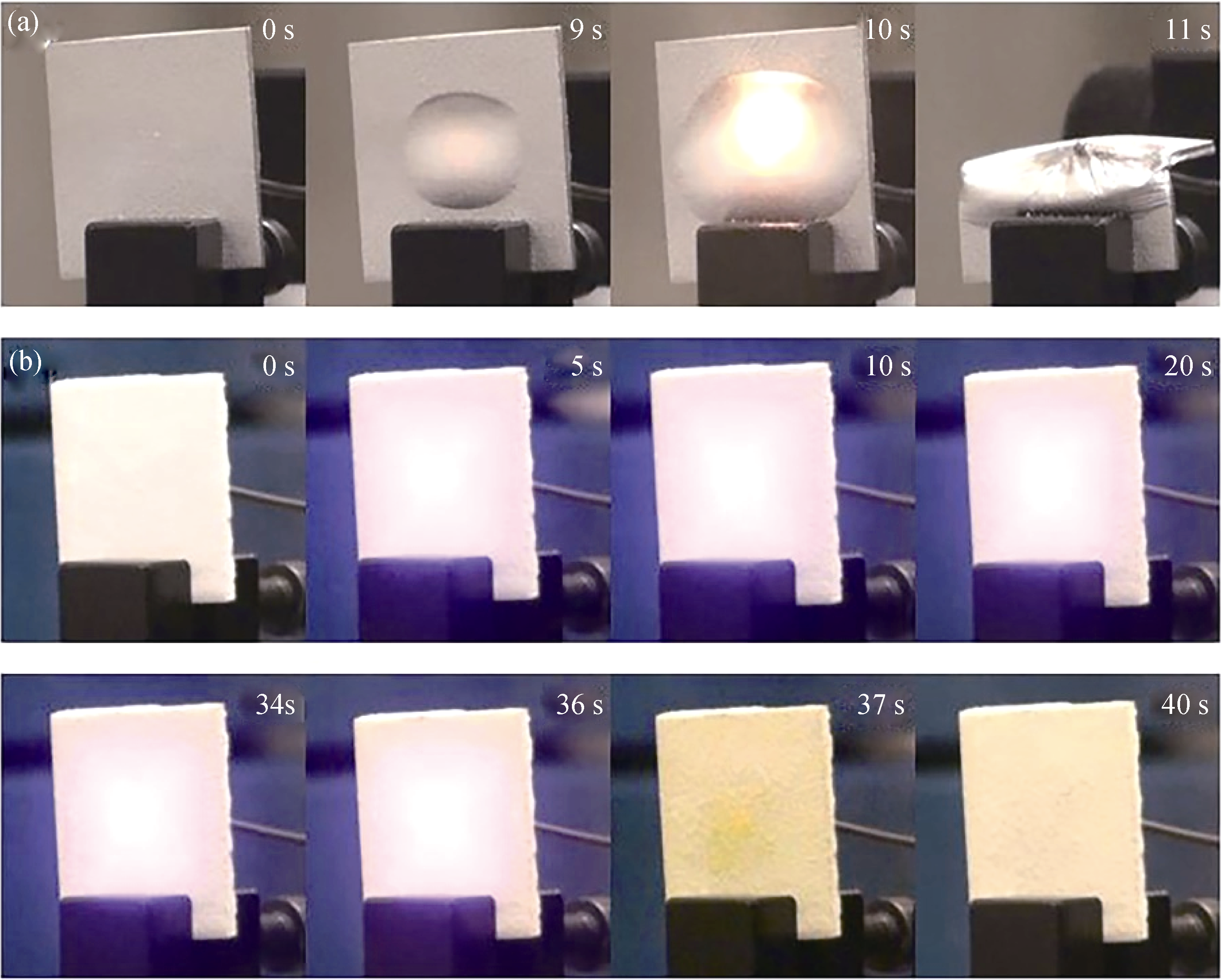
Fig. 4 Images of samples irradiated by 1064-nm CW laserUncoated sample (laser switched off at 11 s); (b) Coated 200 µm KS-T coating (laser switched off at 36 s)
| T / ℃ | 25 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k/(W·m-1·K-1) | 1.145 | 0.943 | 0.883 | 0.805 | 0.790 | 0.746 | 0.727 | 0.727 |
| Cp/(J·kg-1·K-1) | 699 | 772 | 844 | 881 | 907 | 937 | 967 | 978 |
Table 1 Temperature-dependent parameters of KS-T coating
| T / ℃ | 25 | 100 | 200 | 300 | 400 | 500 | 600 | 700 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| k/(W·m-1·K-1) | 1.145 | 0.943 | 0.883 | 0.805 | 0.790 | 0.746 | 0.727 | 0.727 |
| Cp/(J·kg-1·K-1) | 699 | 772 | 844 | 881 | 907 | 937 | 967 | 978 |
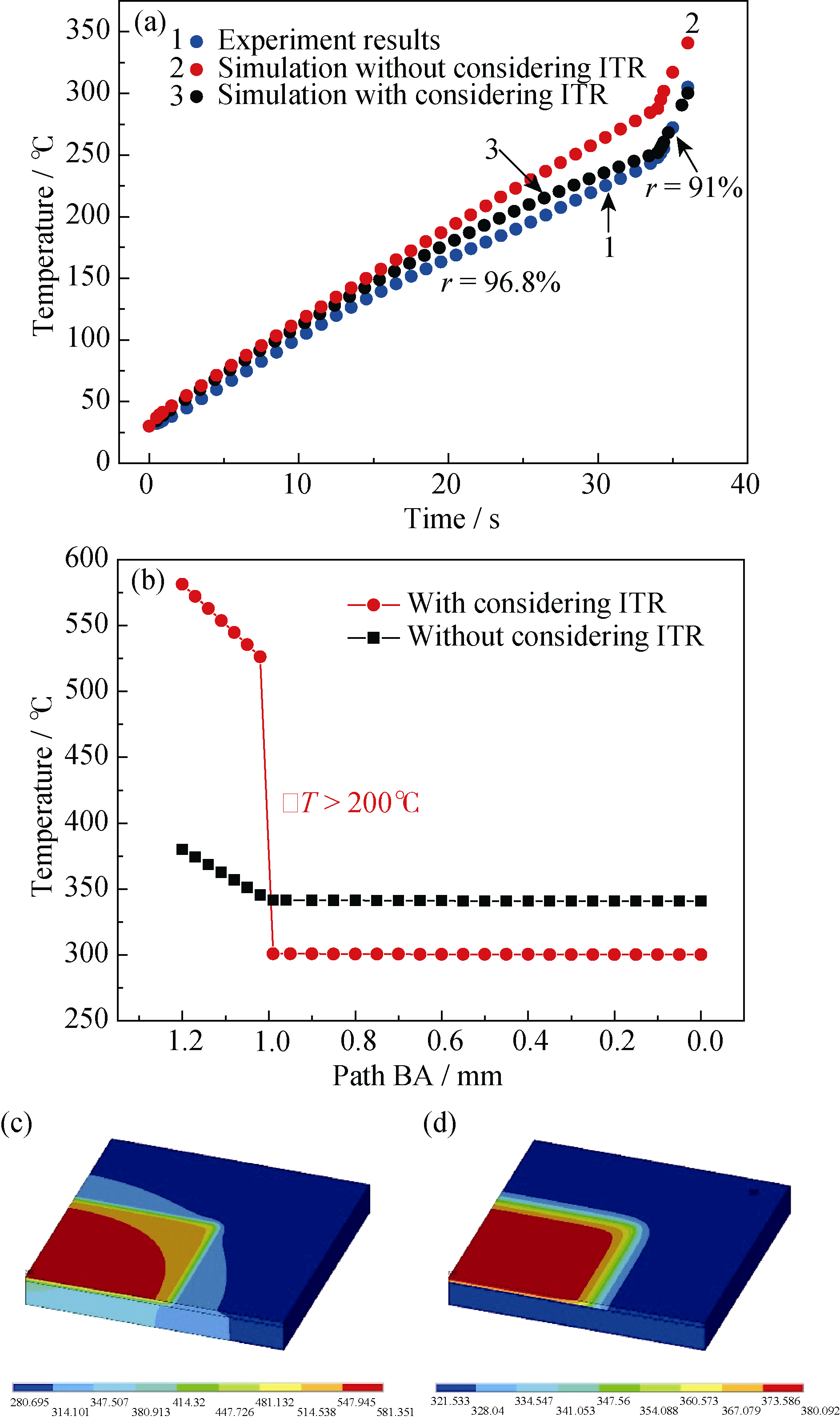
Fig. 7 The simulation results(a) Backside center temperature of the sample coated by KS-T coating; (b) Temperature along the path B; (c) Temperature distribution plot without considering interface thermal resistance; (d) Temperature distribution plot with considering interface thermal resistance. ((b)-(d) are at the ending time of laser irradiation)
| [1] | LI X F, WINFIELD R J, O’BRIEN S, et al. Application of Bessel beams to 2D microfabrication.Applied Surface Science, 2009, 255(10): 5146-5149. |
| [2] | SROKA R, STEPP H, HENNIG G, et al.Medical laser application: translation into the clinics.Journal of Biomedical Optics, 2015, 20(6): 061110. |
| [3] | ESKELINEN J, HÆGGSTRÖM E, DELIKARIS-MANIAS S, et al. Beamforming with a volumetric array of massless laser spark sources—Application in reflection tracking. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2015, 137(6): EL389-EL395. |
| [4] | ANDRE B, POUPINET L, RAVEL G.Evaporation and ion assisted deposition of HfO2 coatings: some key points for high power laser applications.Journal of Vacuum Science & Technology A, 2000, 18(5): 2372-2377. |
| [5] | WANG W, LUO Y, ZHANG D, et al.Dynamic optical limiting experiments on vanadium dioxide and vanadium pentoxide thin films irradiated by a laser beam.Applied Optics, 2006, 45(14): 3378-3381. |
| [6] | YUAN L, ZHAO Y, SHANG G, et al.Comparison of femtosecond and nanosecond laser-induced damage in HfO2 single-layer film and HfO2-SiO2 high reflector.JOSA B, 2007, 24(3): 538-543. |
| [7] | CHEN X, SONG L, YOU L, et al.Incorporation effect of Y2O3 on the structure and optical properties of HfO2 thin films.Applied Surface Science, 2013, 271: 248-252. |
| [8] | LIU N, WANG Y J, ZHOU M, et al.Laser resistance of Ta2O5/SiO2 and ZrO2/SiO2 optical coatings under 2 µm femtosecond pulsed irradiation.Chinese Physics Letters, 2010, 27(7): 074215. |
| [9] | SHEN J, ZHANG Q, WANG J, et al.Sol-Gel processing of zirconia coating for HR mirrors with high laser damage threshold.Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology, 2000, 19(1/2/3): 271-274. |
| [10] | STOLZ C J, GÉNIN F Y. Laser Resistant Coatings. Springer Berlin Heidelberg, 2003: 309-333. |
| [11] | KUMAR S, VERMA N K, SINGLA M L.Study on reflectivity and photostability of Al-doped TiO2 nanoparticles and their reflectors.Journal of Materials Research, 2013, 28(03): 521-528. |
| [12] | ZHANG L, YAN C W, QU Q, et al.Study on the protection of TiO2-K2SiO3 inorganic coatings for Ag used in space.Acta Chimica Sinica-Chinese Edition, 2003, 61(9): 1369-1374. |
| [13] | KUMAR S, VERMA N K, SINGLA M L.Size dependent reflective properties of TiO2 nanoparticles and reflectors made thereof.Digest Journal of Nanomaterials and Biostructures, 2012, 7(2): 607-619. |
| [14] | MIKHAILOV M M, SOKOLOVSKII A N.Photostability of coatings based on TiO2 (rutile) doped with potassium peroxoborate.Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2006, 43(2): 451-455. |
| [15] | FAROOQ W A, ATIF M, ALI S M, et al.Effects of 1064 nm laser on the structural and optical properties of nanostructured TiO2 thin film.Optics and Spectroscopy, 2014, 117(3): 386-391. |
| [16] | OLIVEIRA V, VILAR R.Finite element simulation of pulsed laser ablation of titanium carbide.Applied Surface Science, 2007, 253(19): 7810-7814. |
| [17] | WANG L, ZHONG X H, ZHAO Y X, et al.Effect of interface on the thermal conductivity of thermal barrier coatings: a numerical simulation study.International Journal of Heat and Mass Transfer, 2014, 79: 954-967. |
| [18] | MADENCI E, GUVEN I.The Finite Element Method and Applications in Engineering Using ANSYS®. Springer, 2015. |
| [19] | PAEK U C, KESTENBAUM A.Thermal analysis of thin-film micromachining with lasers.Journal of Applied Physics, 1973, 44(5): 2260-2268. |
| [20] | MARIMUTHU S, MHICH A, MOLCHAN I S, et al.Numerical simulation of excimer laser cleaning of film and particle contaminants.Journal of Heat Transfer, 2013, 135(12): 121301. |
| [21] | SWARTZ E T, POHL R O.Thermal resistance at interfaces.Applied Physics Letters, 1987, 51(26): 2200-2202. |
| [22] | JENG Y R, CHEN J T, CHENG C Y.Thermal contact conductance of coated surfaces.Wear, 2006, 260(1): 159-167. |
| [23] | BRADY R F, WAKE L V.Principles and formulations for organic coatings with tailored infrared properties.Progress in Organic Coatings, 1992, 20(1): 1-25. |
| [24] | UJIHARA K.Reflectivity of metals at high temperatures.Journal of Applied Physics, 1972, 43(5): 2376-2383. |
| [25] | WOODCRAFT A L.Predicting the thermal conductivity of aluminium alloys in the cryogenic to room temperature range.Cryogenics, 2005, 45(6): 421-431. |
| [26] | HO K C, LIN J, DEAN T A.Modelling of springback in creep forming thick aluminum sheets.International Journal of Plasticity, 2004, 20(4): 733-751. |
| [27] | PAN X, YANG M Q, FU X, et al.Defective TiO2 with oxygen vacancies: synthesis, properties and photocatalytic applications.Nanoscale, 2013, 5(9): 3601-3614. |
| [1] | CHAO Shaofei, XUE Yanhui, WU Qiong, WU Fufa, MUHAMMAD Sufyan Javed, ZHANG Wei. Efficient Potassium Storage through Ti-O-H-O Electron Fast Track of MXene Heterojunction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1212-1220. |
| [2] | REN Guanyuan, LI Yiguan, DING Donghai, LIANG Ruihong, ZHOU Zhiyong. CaBi2Nb2O9 Ferroelectric Thin Films: Modulation of Growth Orientation and Properties [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1228-1234. |
| [3] | XIE Tian, SONG Erhong. Effect of Elastic Strains on Adsorption Energies of C, H and O on Transition Metal Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1292-1300. |
| [4] | ZHANG Zhe, SUN Tingting, WANG Lianjun, JIANG Wan. Flexible Thermoelectric Films with Different Ag2Se Dimensions: Performance Optimization and Device Integration [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(11): 1221-1227. |
| [5] | TAO Shunyan, YANG Jiasheng, SHAO Fang, WU Yingchen, ZHAO Huayu, DONG Shaoming, ZHANG Xiangyu, XIONG Ying. Thermal Spray Coatings for Aircraft CMC Hot-end Components: Opportunities and Challenges [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1077-1083. |
| [6] | JIANG Qiang, SHI Lizhi, CHEN Zhengran, ZHOU Zhiyong, LIANG Ruihong. Preparation and Properties of Hard PZT Piezoelectric Ceramics Poled above Curie Temperature and Multilayer Actuators [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1091-1099. |
| [7] | PENG Ping, TAN Litao. Structure and Piezoelectric Properties of CuO-doped (Ba,Ca)(Ti,Sn)O3 Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1100-1106. |
| [8] | WANG Bo, CAI Delong, ZHU Qishuai, LI Daxin, YANG Zhihua, DUAN Xiaoming, LI Yanan, WANG Xuan, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Mechanical Properties and Thermal Shock Resistance of SrAl2Si2O8 Reinforced BN Ceramic Composites [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1182-1188. |
| [9] | SHI Rui, LIU Wei, LI Lin, LI Huan, ZHANG Zhijun, RAO Guanghui, ZHAO Jingtai. Preparation and Properties of BaSrGa4O8: Tb3+ Mechanoluminescent Materials [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1107-1113. |
| [10] | CHEN Mengjie, WANG Qianqian, WU Chengtie, HUANG Jian. Predicting the Degradability of Bioceramics through a DFT-based Descriptor [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(10): 1175-1181. |
| [11] | QU Mujing, ZHANG Shulan, ZHU Mengmeng, DING Haojie, DUAN Jiaxin, DAI Henglong, ZHOU Guohong, LI Huili. CsPbBr3@MIL-53 Nanocomposite Phosphors: Synthesis, Properties and Applications in White LEDs [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1035-1043. |
| [12] | YANG Jialin, WANG Liangjun, RUAN Siyuan, JIANG Xiulin, YANG Chang. Highly Weak-light Sensitive and Dual-band Switchable Photodetector Based on CuI/Si Unilateral Heterojunction [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1063-1069. |
| [13] | WANG Xu, LI Xiang, KOU Huamin, FANG Wei, WU Qinghui, SU Liangbi. Effect of Doping with Different Concentrations of Y3+ Ions on the Properties of CaF2 Crystals [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1029-1034. |
| [14] | XUN Daoxiang, LUO Xuwei, ZHOU Mingran, HE Jiale, RAN Maojin, HU Zhiyi, LI Yu. ZIF-L Derived Nitrogen-doped Carbon Nanosheets/Carbon Cloth Self-supported Electrode for Lithium-selenium Battery [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1013-1021. |
| [15] | CHEN Jia, FAN Yiran, YAN Wenxin, HAN Yingchao. Polyacrylate-calcium (cerium) Nanocluster Fluorescent Probes for Quantitative Detection of Inorganic Phosphorus [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2024, 39(9): 1053-1062. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||