
Journal of Inorganic Materials ›› 2015, Vol. 30 ›› Issue (11): 1121-1130.DOI: 10.15541/jim20150182
• Orginal Article • Next Articles
HAN Cheng1, LEI Yong-Peng2, WANG Ying-De1
Received:2015-04-14
Revised:2015-06-25
Published:2015-11-20
Online:2015-10-20
About author:HAN Cheng. E-mail: hancheng.com@163.com
Supported by:CLC Number:
HAN Cheng, LEI Yong-Peng, WANG Ying-De. Recent Progress on Nano-heterostructure Photocatalysts for Solar Fuels Generation[J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2015, 30(11): 1121-1130.
| Nano-heterostructure photocatalysts | Production of H2 from water splitting | Generation of CxHyOz from CO2 reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | TiO2/CuO[ | Bi2S3/CdS[ |
| Type II | g-C3N4-N-TiO2[ | g-C3N4-N-TiO2[ |
| p-n type | Cu2S/CdS[ | |
| Z-scheme | TiO2/RGO/Metal sulfide[ WO3/g-C3N4[ | Ag3PO4/Ag/g-C3N4[ TaON/Ag/RuBLRu′[ |
Table 1 Nano-heterostructure photocatalysts for solar fuels generation
| Nano-heterostructure photocatalysts | Production of H2 from water splitting | Generation of CxHyOz from CO2 reduction |
|---|---|---|
| Type I | TiO2/CuO[ | Bi2S3/CdS[ |
| Type II | g-C3N4-N-TiO2[ | g-C3N4-N-TiO2[ |
| p-n type | Cu2S/CdS[ | |
| Z-scheme | TiO2/RGO/Metal sulfide[ WO3/g-C3N4[ | Ag3PO4/Ag/g-C3N4[ TaON/Ag/RuBLRu′[ |
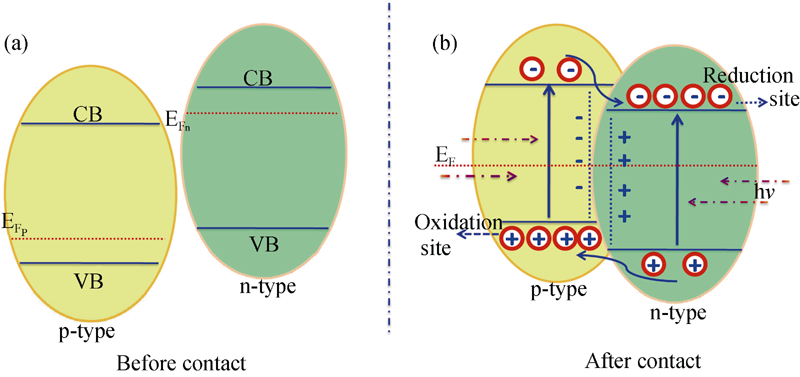
Fig. 3 (a) Band alignment of p-type and n-type semiconductors before contact and (b) transportation of the charge carries in p-n type nano-heterostructure[27]
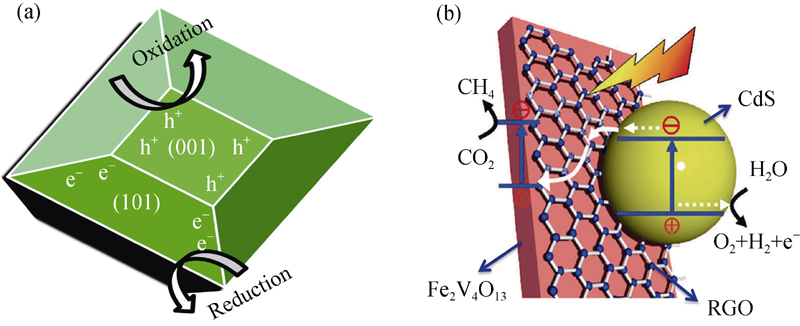
Fig. 6 Schematic illustration of (a) the spatial separation of redox sites in TiO2 {001}/{101} surface heterojunction[49] and (b) conversion of CO2 into CH4 over Fe2V4O13/RGO/CdS Z-scheme nano-heterostructure photocatalyst[58]
| [1] | MA Y, WANG X, JIA Y, et al.Titanium dioxide-based nanomaterials for photocatalytic fuel generations.Chem. Rev., 2014, 114(19): 9987-10043. |
| [2] | ZHANG Q H.Progress on TiO2-based nanomaterials and its utilization in the clean energy technology.J. Inor. Mater., 2012, 27(1): 1-10. |
| [3] | HE Y, ZHANG L, TENG B, et al.New application of Z-scheme Ag3PO4/g-C3N4 composite in converting CO2 to fuel.Environ. Sci. Technol., 2015, 49(1): 649-656. |
| [4] | CAO S, YUAN Y, FANG J, et al.In-situ growth of CdS quantum dots on g-C3N4 nanosheets for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen generation under visible light irradiation.Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2013, 38: 1258-1266. |
| [5] | LIU G, NIU P, YIN L, et al.α-sulfur crystals as a visible- light-active photocatalyst. J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2012, 134(22): 9070-9073. |
| [6] | ZHANG Y, XIA T, WALLENMEYER P, et al.Photocatalytic hydrogen generation from pure water using silicon carbide nanoparticles.Energy Technol., 2014, 2(2): 183-187. |
| [7] | CHU Z Y, YUAN B, YAN T N.Recent progress in photocatalysis of g-C3N4.J. Inor. Mater., 2014, 29(8): 785-794. |
| [8] | ZHANG J, WANG X.Solar water splitting at λ=600 nm: a step coser to sustainable hydrogen production.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(25): 7230-7232. |
| [9] | XIANG Q, CHENG B, YU J.Graphene-based photocatalysts for solar-fuel generation.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, DOI: 10.1002/ anie.201411096. |
| [10] | MARTIN D J, QIU K, SHEVLIN S D, et al.Highly efficient photocatalytic H2 evolution from water using visible light and structure-controlled graphitic carbon nitride.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2014, 53(35): 9240-9245. |
| [11] | WU N, WANG Y, LEI Y, et al.Preparation and photocatalytic activity of N-Ag co-doped TiO2/C porous ultrafine fibers mat.Ceram. Int., 2014, 40(1): 2017-2022. |
| [12] | LIU C, JING L, HE L, et al.Phosphate-modified graphitic C3N4 as efficient photocatalysts for degrading colorless pollutants by promoting O2 adsorption.Chem. Commun., 2014, 50(16): 1999-2001. |
| [13] | TAKANABE K, KAMATA K, WANG X, et al.Photocatalytic hydrogen evolution on dye-sensitized mesoporous carbon nitride photocatalyst with magnesium phthalocyanine.Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2010, 12(40): 13020-13025. |
| [14] | WANG H, ZHANG L, CHEN Z, et al.Semiconductor heterojunction photocatalysts: design, construction, and photocatalytic performances.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2014, 43(15): 5234-5244. |
| [15] | WITHERS F, POZO-ZAMUDIO O D, MISHCHENKO A, et al. Light-emitting diodes by band-structure engineering in van der Waals heterostructures.Nat. Mater., 2015, 14: 301-306. |
| [16] | WANG X, XIA F.Van der Waals heterostructures: stacked 2D materials shed light.Nat. Mater., 2015, 14: 264-265. |
| [17] | YU H, QUAN X.Nano-heterojunction photocatalytic materials in environmental pollution controlling.Progress in Chemistry, 2009, 21(2/3): 406-419. |
| [18] | ZHENG H, LI Y, LIU H, et al.Construction of heterostructure materials toward functionality.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2011, 40(9): 4506-4524. |
| [19] | LI X H, ANTONIETTI M.Metal nanoparticles at mesoporous N-doped carbons and carbon nitrides: functional Mott-Schottky heterojunctions for catalysis.Chem. Soc. Rev., 2013, 42(16): 6593-6604. |
| [20] | LI H, ZHOU Y, TU W, et al.State-of-the-art progress in diverse heterostructured photocatalysts toward promoting photocatalytic performance.Adv. Funct. Mater., 2015, 25(7): 998-1013. |
| [21] | WU N, WANG Y, LEI Y, et al.Flexible N-doped TiO2/C ultrafine fiber mat and its photocatalytic activity under simulated sunlight.Appl. Surf. Sci., 2014, 319: 136-142. |
| [22] | HAN C, WANG Y, LEI Y, et al.In situ synthesis of graphitic-C3N4 nanosheet hybridized N-doped TiO2 nanofiber for efficient photocatalytic H2 production and degradation.Nano Res., 2015, 8(4): 1199-1209. |
| [23] | MARSCHALL R.Semiconductor composites: strategies for enhancing charge carrier separation to improve photocatalytic activity.Adv. Funct. Mater., 2014, 24(17): 2421-2440. |
| [24] | ZHOU P, YU J, JARONIEC M.All-solid-state Z-scheme photocatalytic systems.Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(29): 4920-4935. |
| [25] | HUSNG L, WANG X, YANG J, et al.Dual cocatalysts loaded type I CdS/ZnS core/shell nanocrystals as effective and stable photocatalysts for H2 evolution.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2013, 117(22): 11584-11591. |
| [26] | WANG Y, WANG Q, ZHAN X, et al.Visible light driven type II heterostructures and their enhanced photocatalysis properties: a review.Nanoscale, 2013, 5(18): 8326-8339. |
| [27] | JIANG D, CHRN L, ZHU J, et al.Novel p-n heterojunction photocatalyst constructed by porous graphite-like C3N4 and nanostructured BiOI: facile synthesis and enhanced photocatalytic activity.Dalton Trans., 2013, 42(44): 15726-15734. |
| [28] | KIM D, SAKIMOTO K K, HONG D, et al.Artificial photosynthesis for sustainable fuel and chemical production.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2015, 54(11): 3259-3266. |
| [29] | MAEDA K.Z-scheme water splitting using two different semiconductor photocatalysts.ACS Catal., 2013, 3(7): 1486-1503. |
| [30] | IWASHINA K, IWASE A, NG Y H, et al.Z-schematic water splitting into H2 and O2 using metal sulfide as a hydrogen-evolving photocatalyst and reduced graphene oxide as a solid-state electron mediator.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(2): 604-607. |
| [31] | WANG W, CHEN J, LI C, et al.Achieving solar overall water splitting with hybrid photosystems of photosystem II and artificial photocatalysts.Nat. Commun., 2014, 5: 4647. |
| [32] | TU W, ZHOU Y, ZOU Z.Photocatalytic conversion of CO2 into renewable hydrocarbon fuels: state-of-the-art accomplishment, challenges, and prospects.Adv. Mater., 2014, 26(27): 4607-4626. |
| [33] | FUJISHIMA A, HONDA K.Electrochemical photolysis of water at a semiconductor electrode.Nature, 1972, 238(5358): 37-38. |
| [34] | INOUE T, FUJISHIMA A, KONISHI S, et al.Photo- electrocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide in aqueous suspensions of semiconductor powders.Nature, 1979, 277(5698): 637-638. |
| [35] | LEE S S, BAI H, LIU Z, et al.Optimization and an insightful properties-activity study of electrospun TiO2/CuO composite nanofibers for efficient photocatalytic H2 generation.Appl. Catal., B, 2013, 140: 68-81. |
| [36] | THIBERT A, FRAME F A, BUSBY E, et al.Sequestering high-energy electrons to facilitate photocatalytic hydrogen generation in CdSe/CdS nanocrystals.J. Phys. Chem. Lett., 2011, 2(21): 2688-2694. |
| [37] | YANG X, XU J, WONG T, et al.Synthesis of In2O3-In2S3 core-shell nanorods with inverted type-I structure for photocatalytic H2 generation.Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys., 2013, 15(30): 12688-12693. |
| [38] | XIE Y P, YU Z B, LIU G, et al.CdS-mesoporous ZnS core-shell particles for efficient and stable photocatalytic hydrogen evolution under visible light.Energy Environ. Sci., 2015, 7(6): 1895-1901. |
| [39] | HOU Y, LAURSEN A B, ZHANG J, et al.Layered nanojunctions for hydrogen-evolution catalysis.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2013, 52(13): 3621-3625. |
| [40] | LI X, CHEN J T, LI H L, et al.Photoreduction of CO2 to methanol over Bi2S3/CdS photocatalyst under visible light irradiation.J. Nat. Gas. Chem., 2011, 20(4): 413-417. |
| [41] | ZHANG J, ZHANG M, SUN R Q, et al.A facile band alignment of polymeric carbon nitride semiconductors to construct isotype heterojunctions.Angew. Chem. Int. Ed., 2012, 124(40): 10292-10296. |
| [42] | SUI Y, LIU J, ZHANG Y, et al.Dispersed conductive polymer nanoparticles on graphitic carbon nitride for enhanced solar-driven hydrogen evolution from pure water.Nanoscale, 2013, 5(19): 9150-9155. |
| [43] | XU X, LIU G, RANDOM C, et al.g-C3N4 coated SrTiO3 as an efficient photocatalyst for H2 production in aqueous solution under visible light irradiation.Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2011, 36: 13501-13507. |
| [44] | ZHANG J, WANG Y, JIN J, et al.Efficient visible-light photocatalytic hydrogen evolution and enhanced photostability of core/shell CdS/g-C3N4 nanowires.ACS Appl. Mater. Interfaces, 2013, 5(20): 10317-10324. |
| [45] | YAN Z, WU H, HAN A, et al.Noble metal-free cobalt oxide (CoOx) nanoparticles loaded on titanium dioxide/cadmium sulfide composite for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production from water.Int. J. Hydrogen Energy, 2014, 39: 13353-13360. |
| [46] | ZHOU S, LIU Y, LI J M, et al.Facile in situ synthesis of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-N-TiO2 heterojunction as an efficient photocatalyst for the selective photoreduction of CO2 to CO.Appl. Catal. B, 2014, 158: 20-29. |
| [47] | HE Y, WANG Y, ZHANG L, et al.High-efficiency conversion of CO2 to fuel over ZnO/g-C3N4 photocatalyst.Appl. Catal. B, 2015, 168: 1-8. |
| [48] | WANG J, JI G, LIU Y, et al.Cu2O/TiO2 heterostructure nanotube arrays prepared by an electrodeposition method exhibiting enhanced photocatalytic activity for CO2 reduction to methanol.Catal. Commun., 2014, 46: 17-21. |
| [49] | YU J, LOW J, XIAO W, et al.Enhanced photocatalytic CO2 reduction activity of anatase TiO2 by coexposed {001} and {101} facets.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(25): 8839-8842. |
| [50] | CHEN Y, QIN Z, WANG X, et al.Noble-metal-free Cu2S-modified photocatalysts for enhanced photocatalytic hydrogen production by forming nanoscale p-n junction structure.RSC Adv., 2015, 5(23): 18159-18166. |
| [51] | ZONG X, YAN H, WU G, et al.Enhancement of photocatalytic H2 evolution on CdS by loading MoS2 as cocatalyst under visible light irradiation.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2008, 130(23): 7176-7177. |
| [52] | SIMON Q, BARRECA D, GASPAROTTO A, et al.Vertically oriented CuO/ZnO nanorod arrays: from plasma-assisted synthesis to photocatalytic H2 production.J. Mater. Chem., 2012, 22(23): 11739-11747. |
| [53] | KATSUMATA H, TACHI Y, SUZUKI T, et al.Z-scheme photocatalytic hydrogen production over WO3/g-C3N4 composite photocatalysts.RSC Adv., 2014, 4(41): 21405-21409. |
| [54] | WANG X, LIU G, WANG L, et al.ZnO-CdS@Cd heterostructure for effective photocatalytic hydrogen generation.Adv. Energy Mater., 2012, 2(1): 42-46. |
| [55] | LI W, FENG C, DAI S, et al.Fabrication of sulfur-doped g-C3N4/Au/CdS Z-scheme photocatalyst to improve the photocatalytic performance under visible light.Appl. Catal. B, 2015, 168: 465-471. |
| [56] | LIU C, TANG J, CHEN H M, et al.A fully integrated nanosystem of semiconductor nanowires for direct solar water splitting.Nano Lett., 2013, 13(6): 2989-2992. |
| [57] | PENG Y, GUO Z, YANG J, et al.Enhanced photocatalytic H2 evolution over micro-SiC by coupling with CdS under visible light irradiation.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2014, 2(18): 6296-6300. |
| [58] | LI P, ZHOU Y, LI H, et al.All-solid-state Z-scheme system arrays of Fe2V4O13/RGO/CdS for visible light-driving photocatalytic CO2 reduction into renewable hydrocarbon fuel.Chem. Commun., 2015, 51(4): 800-803. |
| [59] | HE Y, ZHANG L, FAN M, et al.Z-scheme SnO2-x/g-C3N4 composite as an efficient photocatalyst for dye degradation and photocatalytic CO2 reduction.Sol. Energ. Mat. Sol. C, 2015, 137: 175-184. |
| [60] | SEKIZAWA K, MAEDA K, DOMEN K, et al.Artificial Z-scheme constructed with a supramolecular metal complex and semiconductor for the photocatalytic reduction of CO2.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2013, 135(12): 4596-4599. |
| [61] | LIU J, LIU Y, LIU N, et al.Metal-free efficient photocatalyst for stable visible water splitting via a two-electron pathway.Science, 2015, 347(6225): 970-974. |
| [62] | WANG X, MAEDA K, THOMAS A, et al.A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light.Nat. Mater., 2009, 8(1): 76-79. |
| [63] | GONG Y, LI M, WANG Y.Carbon nitride in energy conversion and storage: recent advances and future prospects.ChemSusChem, 2015, 8(6): 931-946. |
| [64] | CAO S, LOW J, YU J, et al.Polymeric photocatalysts based on graphitic carbon nitride.Adv. Mater., 2015, 27(13): 2150-2176. |
| [65] | SUNG S K, Sang S K, PARK H.Photocatalytic comparison of TiO2 nanoparticles and electrospun TiO2 nanofibers: effects of mesoporosity and interparticle charge transfer.J. Phys. Chem. C, 2010, 114(39): 16475-16480. |
| [66] | XIE Y, ZHANG X, MA P, et al.Hierarchical TiO2 photocatalysts with one-dimensional heterojunction for improved photocatalytic activities.Nano Res., 2015, DOI: 10.1007/s12274-015-0720-3. |
| [67] | RAN J, ZHANG J, YU J, et al.Earth-abundant cocatalysts for semiconductor-based photocatalytic water splitting.Chem. Sov. Rev., 2014, 43(22): 7787-7812. |
| [68] | BAIS, WANG L, CHEN X, et al.Chemically exfoliated metallic MoS2 nanosheets: A promising supporting co-catalyst for enhancing the photocatalytic performance of TiO2 nanocrystals.Nano Res., 2015, 8(1): 175-183. |
| [69] | ZHAO H, DONG Y, JIANG P, et al.In situ light-assisted preparation of MoS2 on graphitic-C3N4 nanosheets for enhanced photocatalytic H2 production from water.J. Mater. Chem. A, 2015, 3(14): 7375-7381. |
| [70] | YIN L, YUAN Y P, CAO S W, et al.Enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalytic hydrogen generation over g-C3N4 through loading the noble metal-free NiS2 cocatalyst.RSC Adv., 2014, 4(12): 6127-6132. |
| [71] | HONG J, WANG Y, WANG Y, et al.Noble-metal-free NiS/C3N4 for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen evolution from water.ChemSusChem, 2013, 6(12): 2263-2268. |
| [72] | LI X, WEN J, LOW J, et al.Design and fabrication of semiconductor photocatalyst for photocatalytic reduction of CO2 to solar fuel.Sci. China Mater., 2014, 57(1): 70-100. |
| [73] | MARSZEWSKI M, CAO S, YU J, et al.Semiconductor-based photocatalytic CO2 conversion.Mater. Horiz., 2015, 2(3): 261-278. |
| [74] | LI R, ZHANG F, WANG D, et al.Spatial separation of photogenerated electrons and holes among {010} and {110} crystal facets of BiVO4.Nat. Commun., 2013, 4: 1432. |
| [75] | MAO J, PENG T, ZHANG X, et al.Effect of graphitic carbon nitride microstructures on the activity and selectivity of photocatalytic CO2 reduction under visible light.Catal. Sci. Technol., 2013, 3(5): 1253-1260. |
| [76] | MATSUBU J C, YANG V N, CHRISTOPHER P.Isolated metal active site concentration and stability control catalytic CO2 reduction selectivity.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2015, 137(8): 3076-3084. |
| [77] | NEATU S, MACIA-AGULLO J A, CONCEPCION P, et al. Gold-copper nanoalloys supported on TiO2 as photocatalysts for CO2 reduction by water.J. Am. Chem. Soc., 2014, 136(45): 15969-15976. |
| [1] | ZHU Wenjie, TANG Lu, LU Jichang, LIU Jiangping, LUO Yongming. Research Progress on Catalytic Oxidation of Volatile Organic Compounds by Perovskite Oxides [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(7): 735-746. |
| [2] | HU Zhichao, YANG Hongyu, YANG Hongcheng, SUN Chengli, YANG Jun, LI Enzhu. Usage of the P-V-L Bond Theory in Regulating Properties of Microwave Dielectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 609-626. |
| [3] | WU Qiong, SHEN Binglin, ZHANG Maohua, YAO Fangzhou, XING Zhipeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Lead-based Textured Piezoelectric Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 563-574. |
| [4] | ZHANG Bihui, LIU Xiaoqiang, CHEN Xiangming. Recent Progress of Hybrid Improper Ferroelectrics with Ruddlesden-Popper Structure [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 587-608. |
| [5] | WU Jie, YANG Shuai, WANG Mingwen, LI Jinglei, LI Chunchun, LI Fei. Textured PT-based Piezoelectric Ceramics: Development, Status and Challenge [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 575-586. |
| [6] | JIANG Kun, LI Letian, ZHENG Mupeng, HU Yongming, PAN Qinxue, WU Chaofeng, WANG Ke. Research Progress on Low-temperature Sintering of PZT Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(6): 627-638. |
| [7] | TIAN Ruizhi, LAN Zhengyi, YIN Jie, HAO Nanjing, CHEN Hangrong, MA Ming. Microfluidic Technology Based Synthesis of Inorganic Nano-biomaterials: Principles and Progress [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 337-347. |
| [8] | ZHANG Jiguo, WU Tian, ZHAO Xu, YANG Fan, XIA Tian, SUN Shien. Improvement of Cycling Stability of Cathode Materials and Industrialization Process for Sodium-ion Batteries [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(4): 348-362. |
| [9] | YIN Jie, GENG Jiayi, WANG Kanglong, CHEN Zhongming, LIU Xuejian, HUANG Zhengren. Recent Advances in 3D Printing and Densification of SiC Ceramics [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 245-255. |
| [10] | CHEN Guangchang, DUAN Xiaoming, ZHU Jinrong, GONG Qing, CAI Delong, LI Yuhang, YANG Donglei, CHEN Biao, LI Xinmin, DENG Xudong, YU Jin, LIU Boya, HE Peigang, JIA Dechang, ZHOU Yu. Advanced Ceramic Materials in Helicopter Special Structures: Research Progress and Application Prospect [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 225-244. |
| [11] | FAN Xiaobo, ZU Mei, YANG Xiangfei, SONG Ce, CHEN Chen, WANG Zi, LUO Wenhua, CHENG Haifeng. Research Progress on Proton-regulated Electrochemical Ionic Synapses [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(3): 256-270. |
| [12] | HAIREGU Tuxun, GUO Le, DING Jiayi, ZHOU Jiaqi, ZHANG Xueliang, NUERNISHA Alifu. Research Progress of Optical Bioimaging Technology Assisted by Upconversion Fluorescence Probes in Tumor Imaging [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 145-158. |
| [13] | SUN Shujuan, ZHENG Nannan, PAN Haokun, MA Meng, CHEN Jun, HUANG Xiubing. Research Progress on Preparation Methods of Single-atom Catalysts [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 113-127. |
| [14] | TAO Guilong, ZHI Guowei, LUO Tianyou, OUYANG Peidong, YI Xinyan, LI Guoqiang. Progress on Key Technologies of Cavity-structured Thin Film Bulk Acoustic Wave Filter [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(2): 128-144. |
| [15] | ZHOU Fan, TIAN Zhilin, LI Bin. Research Progress on Carbide Ultra-high Temperature Ceramic Anti-ablation Coatings for Thermal Protection System [J]. Journal of Inorganic Materials, 2025, 40(1): 1-16. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||